Art Vocabulary
Art vocabulary used for all 2009-2010 art classes at Grayson County Middle School
Terms : Hide Images [1]
| based on real people, places and things but does not look like the real people, places and things. This style shows an object you can name but does not show it clearly. |  | |
| a water based paint that has a (polymer) plastic binder and dries to a permanent covering. |  | |
| colors found side by side on the color wheel which are closely related |  | |
| in visual art, examining the unique features of a work as they relate to the elements of art and the principles of design. | ||
| the art of designing buildings | ||
| the process and the results of critical thinking about art. The parts are: describe, analyze, interpret, and judge. | ||
| a person who creates works of art. |  | |
| not being the same on both sides. |  | |
| the illusion of depth and distance created by using the weather in a landscape and dull, pale colors with hazy details in the background of a painting. |  | |
| those things that seem the most distant, as if at the back of the picture. | ||
| the principle of design that refers to the visual equalization of the elements in a work of art so that one side of the artwork does not appear heavier than the other side. Balance may also be radial, symmetrical, or asymmetrical. | ||
| a tightly stretched cloth surface on which to paint. |  | |
| objects made of fired clay or porcelain. |  | |
| using a combination of light (chiaro) and dark, or shade | ||
| artwork made by pasting pieces of paper or other materials to a flat | ||
| the result of the reflection or absorption of light by a surface. |  | |
| sometimes known as color families or relationships , these are groups of colors used together in the same artwork. | ||
| a tool for organizing color. | 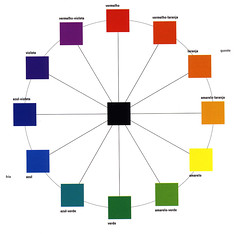 | |
| colors found opposite on the color wheel and have the |  | |
| an arrangement of the elements of art and the principles of | ||
| a principle of art, that places 2 opposites side by side | ||
| colors that make you feel cool - blue, green and violet | ||
| to make or produce. | ||
| shading done by drawing closely set parallel lines that | ||
| an early form of photography that uses chemicals to produce the image. | ||
| the look of space or distance | ||
| this process in responding to art work refers to the subject matter of the artwork. | ||
| Mexican Muralist who created artworks in Mexico and the U.S. focusing on political messages. | ||
| a frame used to support an artist's canvas., an upright tripod for displaying something (usually an artist's canvas) | ||
| the basic components of visual communication. They | ||
| All art and architecture was created for a ceremonial purpose. Greatest Architectural achievement was the pyramids. Sculpture was created using specific rules. Faces are forward, the left foot is slightly ahead of the right. | ||
| focal point - the principle of design that is concerned with | ||
| During the Ming dynasty the Zhougan province created porcelin pottery that influenced the design and quality of our ceramics today. The special firing technique used by the Chinese influences the way pottery is made. Pottery is made using heavy silt (powdered clay), and water whereas ceramics are made using a fine silt (as light as baby powder) and sifted water. | ||
| a natural or synthetic filament, such as cotton or nylon, which can | ||
| that area in a composition at which the emphasis is greatest | ||
| people who create art using styles that have been handed down through generations. Folk Artists are usually untrained. Artists that create using things from nature. | ||
| Part of a picture which appears closest to the viewer and | ||
| An element of art that is three-dimensional and encloses | ||
| utilitarian art - functional objects such as dishes and | ||
| created Native American portraits based on the Plains Indians. He thought that the Native American way of life was going to be extinct. | ||
| the use of post and lintel construction and symmetrical balance. Included 6 main parts of a temple: cornice, pediment, frieze, capitol, shaft, and base. The three columns types were Doric, Ionic, and Corinthian. | ||
| the use of stained glass windows, flying buttresses, thin walls, ribbed vaults, and very high buildings. Use of gargoyles as water spouts. | ||
| the use of elongated human figures, paintings were flat and used gold paint in the background. All paintings were of religious people. | ||
| shading done by drawing tiny, closely set parallel lines. | ||
| a level line where water or land seem to meet the sky. | ||
| a color found on the color wheel. |
