9th Biology: Cell Division/Cell Cycle (Mitosis & Meiosis) Quiz Flashcards
Terms : Hide Images [1]
| 564901815 | meiosis | Purpose of this is to create sex cells | |
| 564901816 | gametes | Another name for sex cells | |
| 564901817 | 0 | When a cell with a diploid number of 12 chromosomes goes through meiosis, how many chromosomes are visible before Interphase? | |
| 564901818 | 12 | When a cell with a diploid number of 12 chromosomes goes through meiosis, how many chromosomes are visible at the beginning of Metaphase I? | |
| 564901819 | 6 | When a cell with a diploid number of 12 chromosomes goes through meiosis, how many chromosomes are visible at the end of Telophase I? | |
| 564901820 | 6 | When a cell with a diploid number of 12 chromosomes goes through meiosis, how many chromosomes are visible at the beginning of Prophase II? | |
| 564901821 | 6 | When a cell with a diploid number of 12 chromosomes goes through meiosis, how many chromosomes are visible at the end of end of Meiosis? | |
| 564901822 | tetrad | A paired set of homologous chromosomes, each composed of two sister chromatids | |
| 564901823 | Prophase I | Stage when tetrads form | |
| 564901824 | Prophase I | Stage when crossing-over occurs | |
| 564901825 | Interphase I | Stage when chromosomes are duplicated in Meiosis | |
| 564901826 | Telophase II | Stage when the sex cells are produced | |
| 564901827 | Meiosis | The type of cell division in where chromosomes line up in pairs | |
| 564901828 | F | T/F: Some of the sex cells are genetically alike after Meiosis | |
| 564901829 | F | T/F: If a cell with a diploid # of 2 chromosomes goes through Meiosis, after the end of Telophase I there would be 2 chromosomes visible. | |
| 564901830 | F | T/F: Each chromatid in a chromosome is from either the father or mother | |
| 564901831 | 0 | At the end of anaphase, how many chromatids would still be visible? | |
| 564901832 | 2 | If a cell with 2 visible chromosomes is about to enter Metaphase II, what is its haploid #? | |
| 564901833 | half, chromosomes | Meiosis creates gametes with ___________ the # of ______________ that body cells have | |
| 564901834 | F | T/F: Meiosis is mitosis, but it happens twice | |
| 564901835 | Somatic cells | Another name for body cells | |
| 564901836 | Sperm, egg | What are examples of gametes? | |
| 564901837 | ovaries, testes | Gametes are made in the ______________ for females, and _____________ for males | |
| 564901838 | male | XY determines what gender? | |
| 564901839 | female | XX determines what gender? | |
| 564901840 | T | T/F: Body cells are diploid, gametes are haploid | |
| 564901841 | 22 | How many autosomes do humans have? | |
| 564901842 | 1 | How many sex chromosomes do humans have? | |
| 564901843 | Genetic diversity | Crossing over helps create what? (2 words) | |
| 564901844 | F | T/F: DNA replication occurs while chromosomes are visible | |
| 564901845 | 23 | How many chromosomes would be expected in each daughter cell of a human during late Anaphase II? | |
| 564901846 | F | T/F: Chromosomes are pulled apart in Anaphase | |
| 564901847 | F | T/F: In Interphase II, chromosomes are duplicated again. | |
| 564901848 | Determine gender | What do sex chromosomes do? | |
| 564901849 | Crossing-over creates genetically different sex cells | Why is meiosis important for diversity? | |
| 564901850 | Crossing-over | process in which homologous chromosomes exchange portions of their chromatids during meiosis | |
| 564901851 | homologous pairs | a pair of chromosomes, one from each parent | |
| 564901852 | diploid | an organism or cell having two sets of chromosomes | |
| 564901853 | sister chromatids | Two identical copies of a single chromosome that are connected by a centromere are called this | |
| 564901854 | polar fibers | Spindle microtubules that extend from the two poles of a dividing cell are called this | |
| 564901855 | metaphase | What stage of mitosis is this? | 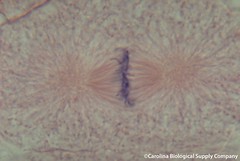 |
| 564901856 | anaphase | What stage of mitosis is this? | 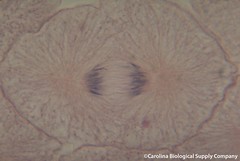 |
| 564901857 | telophase | What stage of mitosis is this? | 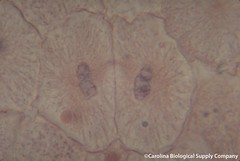 |
| 564901858 | Cell plate | If the picture above was a plant cell in mitosis, what would the middle line be called? |  |
| 564901859 | prophase | What stage of mitosis is this? |  |
| 564901860 | Metaphase plate | In the stage where chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell, what is the line called? | |
| 564901861 | F | T/F: The chromosomes in metaphase always line up straight. | |
| 564901862 | mitosis | cell division (phase of cell cycle) | |
| 564901863 | G1 | cell grows in size, proteins and organelles made (phase of cell cycle) | |
| 564901864 | G2 | cell grows in size, proteins and organelles made phase (phase of cell cycle) | |
| 564901865 | S | DNA synthesis phase (phase of cell cycle) | |
| 564901866 | F | T/F: The stages of Mitosis are G1, S, G2 | |
| 564901867 | G1, S, G2, Mitosis | What are the stages of the cell cycle? In order | |
| 564901868 | F | T/F: The largest stage of the cell cycle is mitosis. | |
| 564901869 | T | T/F: Interphase is the largest stage of mitosis. | |
| 564901870 | Material exchange efficiency | A factor that limits cell size | |
| 564901871 | Overworked DNA | A factor that limits cell size | |
| 564901872 | interphase | phase where cells grow, copy DNA, and grow more | |
| 564901873 | interphase | phase where centrioles are duplicated | |
| 564901874 | becomes visible as chromosomes | what happens to DNA in prophase? | |
| 564901875 | prophase | nuclear membrane breaks down, centrioles separate, and become chromosomes, and spindle fibers become attached to them in this phase | |
| 564901876 | F | T/F: The cell plate exists when animal cells divide | |
| 564901877 | cyclin | A regulator of the cell cycle | |
| 564901878 | cancer | when cells divide uncontrollably | |
| 564901879 | tumors | masses of cells formed by uncontrollable division of cells | |
| 564901880 | chromatid | one of two identical strands into which a chromosome splits during mitosis | |
| 564901882 | centrome | The point where 2 chromatids meet in a chromosome | |
| 564901884 | interphase | What phase of mitosis is this? | 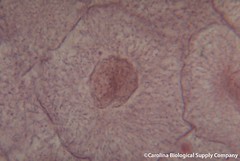 |
