Biology Unit-4: Genetics Flashcards
Terms : Hide Images [1]
| 3867008485 | deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) | A nucleic acid molecule consisting of the nucleotides adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine arranged in a double-helix; the genetic material of all organisms | 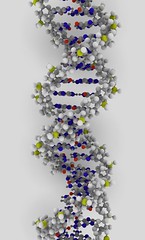 | 0 |
| 3867035859 | DNA replication | The process by which a DNA molecule is copied; also called DNA synthesis; the double-helix opens, the two strands separate, and each is used as a template for producing a new opposing strand |  | 1 |
| 3867061464 | ribonucleic acid (RNA) | A nucleic acid consisting of the nucleotides adenine, guanine, cytosine, and uracil; usually single-stranded; functions in protein synthesis, gene regulation, and as the genome of some viruses |  | 2 |
| 3867097747 | messenger RNA (mRNA) | A type of RNA synthesized using a DNA template that attaches to ribosomes in the cytoplasm and specifies the primary structure of a protein |  | 3 |
| 3867117638 | transfer RNA (tRNA) | An RNA molecule that functions as a translator between nucleic acid and protein languages by carrying specific amino acids to the ribosome, where they recognize the appropriate codons in the mRNA |  | 4 |
| 3867132228 | codon | A three-nucleotide sequence of DNA or mRNA that specifies a particular amino acid or termination signal; the basic unit of the genetic code |  | 5 |
| 3867146085 | anticodon | A nucleotide triplet at one end of a tRNA molecule that base pairs with a particular complementary codon on an mRNA molecule |  | 6 |
| 3867171666 | protein synthesis (gene expression) | The process by which information encoded in DNA directs the synthesis of proteins |  | 7 |
| 3867189846 | transcription | The synthesis of RNA using a DNA template |  | 8 |
| 3867206053 | RNA processing | Modification of RNA primary transcripts, including splicing out of introns, joining together of exons, and alteration of the 5' and 3' ends |  | 9 |
| 3867256705 | translation | The synthesis of a polypeptide (a protein) using the genetic information encoded in an mRNA molecule; there is a change of "language" from nucleotides to amino acids |  | 10 |
| 3867275034 | mutation | A change in the nucleotide sequence of an organism's DNA or in the DNA or RNA of a virus |  | 11 |
| 3867292625 | intron | A region of DNA separating two parts of a gene; transcribed but later removed from mRNA during RNA processing |  | 12 |
| 3867318137 | exon | A sequence transcribed from DNA that remains in the RNA after RNA processing; also refers to the segments of DNA from which this sequence was transcribed |  | 13 |
| 3867345179 | virus | An infectious particle incapable of replicating outside of a cell, consisting of an RNA or DNA genome surrounded by a protein coat (capsid) and in some cases a membranous envelope |  | 14 |
| 3867359482 | bacteriophage | A virus that infects bacteria; also called a phage |  | 15 |
| 3867403778 | allele | A particular form of a gene that may produce distinguishable phenotypic effects |  | 16 |
| 3867437918 | trait | One of two or more detectable variants in a genetic character; a feature of an organism |  | 17 |
| 3867455111 | dominant allele | An allele that is fully expressed in the phenotype of a heterozygote |  | 18 |
| 3867479919 | recessive allele | An allele whose phenotypic effect is not observed in a heterozygote |  | 19 |
| 3867506423 | homozygous | Having two identical alleles for a given gene |  | 20 |
| 3867514026 | heterozygous | Having two different alleles for a given gene |  | 21 |
| 3867530199 | genotype | The genetic makeup or set of alleles of an organism |  | 22 |
| 3867538434 | phenotype | The observable physical and physiological traits of an organism which are determined by its genotype |  | 23 |
| 3867549194 | incomplete dominance | The situation in which the phenotype of heterozygotes is intermediate between the phenotypes of individuals homozygous for either allele |  | 24 |
| 3867580612 | codominance | The situation in which the phenotypes of both alleles are exhibited in the heterozygote because both alleles affect the phenotype in separate, distinguishable ways |  | 25 |
| 3867599733 | monohybrid cross | A cross involving parents that differ only by a single trait, or a cross in which only a single trait is followed |  | 26 |
| 3867632234 | dihybrid cross | A cross between two genotypically identical dihybrids |  | 27 |
| 3867651976 | multiple alleles | The alleles of a gene locus when there are are more than two alternatives in a population |  | 28 |
| 3867664416 | sex-linked gene (sex linked trait) | A gene located on either sex chromosome; most sex-linked genes are on the X-chromosome and show distinctive patterns of inheritance; there are very few genes on the Y-chromosome |  | 29 |
| 3867686470 | sex chromosome | A chromosome responsible for determining the sex of an individual |  | 30 |
| 3867702136 | pedigree | A diagram of a family tree with conventional symbols, showing the occurrence of heritable characters in parents and offspring over multiple generations |  | 31 |
| 3867711100 | karyotype | The display of the chromosome pairs of a cell arranged by size and shape (researchers do this; it does not occur naturally) |  | 32 |
| 3867387358 | biotechnology | The exploitation of biological processes for industrial and other purposes, especially the genetic manipulation of microorganisms for the production of antibiotics, hormones, etc. |  | 33 |
| 3867368105 | restriction enzyme | A type of enzyme that recognizes and cuts DNA molecules at specific nucleotide sequences (restriction sites) |  | 34 |
