CHAPTER 5: Histology Flashcards
Terms : Hide Images [1]
| 6194538334 | Histology or Microscopic Anatomy | -the study of tissues and how they are arranged into organs | 0 | |
| 6194538335 | Tissue | -similar cells and cell products (matrix) | 1 | |
| 6194538336 | Matrix | -ground substance and fibers | 2 | |
| 6194538337 | Primary germ layers | -the three layers (ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm) of the late gastrulation, which develop into all parts of an animal. | 3 | |
| 6194538338 | Ectoderm | -outermost germ layer -the germ layer that gives rise to the skin and nervous system | 4 | |
| 6194538339 | Endoderm | -innermost germ layer -develops into the linings (mucous membrane) of the digestive tract and much of the respiratory system | 5 | |
| 6194538340 | Mesoderm | -middle germ layer -the germ layer that gives rise to the blood, bones and muscles | 6 | |
| 6194538341 | Mesenchyme | -embryonic connective tissue that arises from mesoderm and produces all types of connective tissues | 7 | |
| 6194538342 | Histological sections | -tissue preparations mounted on microscope slides. -artificially colored to bring out detail | 8 | |
| 6194538343 | Fixative | -preservative for cells | 9 | |
| 6194538344 | Stains | -artificial color that enhances details | 10 | |
| 6194538345 | Longitudinal Section | | | 11 | |
| 6194538346 | Cross Section | _ | 12 | |
| 6194538347 | Transverse Section | _ | 13 | |
| 6194538348 | Oblique Section | / | 14 | |
| 6194538349 | Smears | -tissue is rubbed or spread across the slide rather than sliced | 15 | |
| 6194538350 | Spreads | -tissue is laid out on the slide | 16 | |
| 6194538351 | Sections | -tissue is sliced | 17 | |
| 6194538352 | Epithelial Tissue | -a body tissue that covers the interior and exterior surfaces of the body | 18 | |
| 6194538353 | 6 Functions of Epithelial Tissue | Functions: Protection, Secretion, Excretion, Absorption, Filtration, Sensation | 19 | |
| 6194538354 | Basement Membrane | -cells at the base (basal cells) of an epithelial layer are attached to this -regulates the exchange of materials between the epithelium and the underlying tissues | 20 | |
| 6194538355 | Simple Epithelium | -has only one layer of cells | 21 | |
| 6194538356 | Simple Squamous | -has only one layer of cells, with a scale like shape | 22 | |
| 6194538357 | Simple Cuboidal | -has only one layer of cells, with a cube like shape | 23 | |
| 6194538358 | Simple Columnar | -has only one layer of cells, with a colum like shape | 24 | |
| 6194538359 | Pseudostratified Columnar | -has only one layer of cells, but appears to be stratified columnar | 25 | |
| 6194538360 | Goblet Cells | -secrete a glycoprotein called mucin | 26 | |
| 6194538361 | Stratified Epithelia | -has more than one layer of cells | 27 | |
| 6194538362 | Stratified Squamous | -has more than one layer of cells, with a scale like shape | 28 | |
| 6194538363 | Stratified Cuboidal | -has more than one layer of cells, with a cube like shape | 29 | |
| 6194538364 | Stratified Columnar | -has more than one layer of cells, with a colum like shape | 30 | |
| 6194538365 | Transitional Epithelium | -somewhat resembles stratified squamous epithelium, but surface cells are rounded, not flattened, and often bulge at surface | 31 | |
| 6194538366 | Exfoliation or Desquamation | -epithelium dies and flakes off of the surface | 32 | |
| 6194538367 | Nonkeratinized | -lacks the surface layer of dead cells -moist and slippery | 33 | |
| 6194538368 | Keratinized | -epithelium, found in the epidermis, is covered with a layer of compact, dead squamous cells -packed with the durable protein keratin -dry and water resistant | 34 | |
| 6194538369 | Connective Tissues | -cells that occupy less space than the extracellular matrix | 35 | |
| 6194538370 | 8 Functions of Connective Tissue | Functions: Binding of organs, Support, Physical protection, Immune protection, Movement, Storage, Heat production, Transport | 36 | |
| 6194538371 | The cells of fibrous connective tissue | Common Cells: Fibroblasts, Macrophages, Leukocytes, Plasma cells, Mast cells, Adipocytes | 37 | |
| 6194538372 | Fibroblasts | -produce fibers and ground substance | 38 | |
| 6194538373 | Macrophages | -cells that wander through the connective tissues, where they engulf and destroy bacteria, other foreign particles, and dead or dying cells of our own body. | 39 | |
| 6194538374 | Leukocytes | -react against bacteria, toxins and other foreign substances | 40 | |
| 6194538375 | Plasma cells | -synthesize disease-fighting proteins called antibodies | 41 | |
| 6194538376 | Mast cells | -secrete heparin (inhibits blood clotting) and histamine (dilates blood vessels) | 42 | |
| 6194538377 | Adipocytes | -specialized fat cells whose cytoplasm contains nothing but triglycerides | 43 | |
| 6194538378 | 3 types of fibers | -Collagenous Fibers, Reticular fibers, Elastic fibers | 44 | |
| 6194538379 | Collagenous Fibers | -fibers made of collagen, that are tough, flexible and resist stretching | 45 | |
| 6194538380 | Reticular fibers | -thin collagen fibers coated with glycoprotein that form a spongelike framework | 46 | |
| 6194538381 | Elastic fibers | -fibers made of a protein called elastin | 47 | |
| 6194538382 | Elastin | -a protein whose coiled structure allows it to stretch and recoil like a rubber band. | 48 | |
| 6194538383 | Ground Substance | -a gelatinous substance that is made of 3 large molecules glycosaminoglycans, proteoglycans, and adhesive glycoproteins | 49 | |
| 6194538384 | Glycosaminoglycan | -long polysaccharide composed of unusual disaccharides called amino sugars -it includes chondroitin sulfate, heparin (an anticoagulant) and hyaluronic (lubricant in the joints) -good at attracting and holding water. | 50 | |
| 6194538385 | Chondroitin Sulfate | -the most abundant type of glycosaminoglycan that makes cartilage stiff | 51 | |
| 6194538386 | Proteoglycan | -gigantic molecule that forms thick colloids which slows the spread of pathogenic organisms through the tissues -also bind the cell to the matrix | 52 | |
| 6194538387 | Adhesive Glycoproteins | -bind plasma membrane proteins to collagen and proteoglycans outside the cell | 53 | |
| 6194538388 | Loose Connective Tissue | -ground substane occupies more space than the cells and fibers | 54 | |
| 6194538389 | Dense Connective Tissue | -fiber occupies more space than the cells and ground substance | 55 | |
| 6194538390 | Areolar Tissue | -Fibers: mostly collagenous fibers -Cells: all of the 6 cells found in connective tissues -found in almost every part of the body -has an abundance of blood vessels | 56 | |
| 6194538391 | Reticular Tissue | -Fibers: reticular fibers -Cells: fibroblasts -forms the structural framework (spongy) for some viscera | 57 | |
| 6194538392 | Dense Regular Connective Tissue | -very little space between parallel collagen fibers | 58 | |
| 6194538393 | Elastic Tissue | -a type of dense regular tissue with added elastic fibers -has more fibroblasts (larger nuclei) than normal dense regular tissue | 59 | |
| 6194538394 | Dense Irregular Connective Tissue | -very little space between collagen fibers that run in random directions | 60 | |
| 6194538395 | Adipose tissue | -Fibers: areolar tissue and reticular tissue -Cells: adipocytes | 61 | |
| 6194538396 | White Fat | -is the only significant adipose tissue of the adult body | 62 | |
| 6194538397 | Brown fat | -abundance of blood vessels and mitochondria -mitochondria don't produce ATP only energy as heat only in children and under. | 63 | |
| 6194538398 | Cartilage | -a strong connective tissue that is more flexible than bone | 64 | |
| 6194538399 | Chondroblasts | -cartilage producing cell that secrete matrix until surrounded | 65 | |
| 6194538400 | Chondrocytes | -cartilage producing cell enclosed in a lacunae | 66 | |
| 6194538401 | Lacunae | -a little cavity that a cell becomes enclosed in | 67 | |
| 6194538402 | Hyaline Cartilage | -fine collagen fibers that appear glassy | 68 | |
| 6194538403 | Elastic Cartilage | -cartilage with abundant elastic fibers; more flexible than hyaline cartilage. | 69 | |
| 6194538404 | Fibrocartilage | -tough form of cartilage, made of thick bundles of collagen fibers embedded in chondroitin sulfate ground substance | 70 | |
| 6194538405 | Perichondrium | -a sheath of dense irregular connective tissue surrounding most hyaline and elastic cartilage | 71 | |
| 6194538406 | Osseous Tissue | -is a hard, calcified connective tissue that composes the skeleton | 72 | |
| 6194538407 | Spongy Bone | -fills the heads of the long bones and forms the middle layer of flat bones -always covered by a shell of compact bone | 73 | |
| 6194538408 | Compact Bone | -is a denser calcified tissue with no spaces visible to the naked eye | 74 | |
| 6194538409 | Central Canals | 1 |  | 75 |
| 6194538410 | Concentric Lamellae | 3 |  | 76 |
| 6194538411 | Osteon |  | 77 | |
| 6194538412 | Lacunae of Osseous Tissue | 4 |  | 78 |
| 6194538413 | Canaliculi | 2 |  | 79 |
| 6194538414 | Periosteum | -a sheath of dense irregular connective tissue covering the bone | 80 | |
| 6194538415 | Blood | -Fibers: none -Cells: erythrocytes, leukocytes and platelets -GS: blood plasma (more abundant in GS than anything) | 81 | |
| 6194538416 | Blood Plasma | -the ground substance in blood | 82 | |
| 6194538417 | Formed Elements | -collective of cells inside blood (erythrocytes, leukocytes, and platelets) | 83 | |
| 6194538418 | Erythrocytes | -transport O2 and CO2 | 84 | |
| 6194538419 | Platelets | -small cell fragments that are involved in clotting and secreting growth factors that promote blood vessel growth and maintenance | 85 | |
| 6194538420 | Excitable Tissues | -tissues such as neurons or muscles that are capable of producing membrane potential | 86 | |
| 6194538421 | Membrane Potential | -the voltage across a cell's plasma membrane. | 87 | |
| 6194538422 | Nervous tissue | -is specialized for communication by means of electrical and chemical signals -Cells: neurons and glial cells (which are more abundant) | 88 | |
| 6194538423 | Neurons | -detect stimuli, respond quickly, and transmit coded information rapidly to other cells | 89 | |
| 6194538424 | Glial Cell | -protect and assist the neurons | 90 | |
| 6194538425 | Neurosoma | -cell body of a neuron that houses the nucleus and most other organelles | 91 | |
| 6194538426 | Dendrites | -branch out of the neurosoma -receive signals from other cells and conduct messages to the neurosoma | 92 | |
| 6194538427 | Axon (Nerve Fiber) | -sends outgoing signals to other cells | 93 | |
| 6194538428 | Muscular Tissue | -contract moving various parts of the body when stimulated | 94 | |
| 6194538429 | Skeletal Muscle | -striated and voluntary | 95 | |
| 6194538430 | Muscle Fibers | -long, slender cells that make up (skeletal) muscles | 96 | |
| 6194538431 | Sphincter | -muscular rings or cuffs that open and close body passages | 97 | |
| 6194538432 | Striations | -alternating vertical light and dark bands |  | 98 |
| 6194538433 | Cardiac Muscle | -striated and involuntary -only located on the heart | 99 | |
| 6194538434 | Cardiocytes | -short muscle cells of the heart | 100 | |
| 6194538435 | Myocytes | -short muscle cells (smooth or cardiac muscle) | 101 | |
| 6194538436 | Intercalated Discs | -junctions that join cardiocytes together end to end | 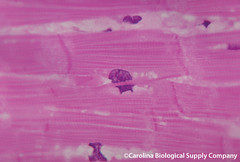 | 102 |
| 6194538437 | Smooth Muscle | -fusiform and involuntary | 103 | |
| 6194538438 | Visceral Muscle | -muscles of the viscera (internal organs) -usually smooth muscle | 104 | |
| 6194538439 | Cell Junctions | -The connections between one cell and another | 105 | |
| 6194538440 | Tight Junction | -completely encircles an epithelial cell near its apical surface creating a seal -linked by transmembrane cell-adhesion proteins | 106 | |
| 6194538441 | Desmosome | -doesn't completely encircles an epithelial cell -enables a tissue to resist mechanical stress | 107 | |
| 6194538442 | Hemidesmosomes | -half desmosomes that attach the basal cells to the basement membrane | 108 | |
| 6194538443 | Gap Junction | -a channel that connects cells together -allows ions, glucose, amino acids, and other small solutes to pass directly from one cell to it's neighbor | 109 | |
| 6194538444 | Gland | -a cell or organ that secretes substances for use elsewhere in the body or for elimination as waste | 110 | |
| 6194538445 | Secretion | -a product useful to the body that is released | 111 | |
| 6194538446 | Excretion | -a waste product that is released | 112 | |
| 6194538447 | Exocrine Glands | -secrete chemical substances into ducts that lead either to other organs or out of the body | 113 | |
| 6194538448 | Duct | -an epithelial tube that moves secretion to the surface | 114 | |
| 6194538449 | Endocrine Glands | -lost contact with the surface and have no ducts -secrete their products directly into the blood | 115 | |
| 6194538450 | Unicellular glands | -secretory cells found in an epithelium that is predominantly nonsecretory -ex: goblet cells | 116 | |
| 6194538451 | Capsule | -encloses gland | 117 | |
| 6194538452 | Septa or Trabeculae | -extensions of the capsule that divide the interior of glands | 118 | |
| 6194538453 | Lobes | -the compartments made by septa | 119 | |
| 6194538454 | Lobules | -created by fine septa further dividing lobes | 120 | |
| 6194538455 | Stroma | -connective tissue framework of the gland i.e. capsule and septa | 121 | |
| 6194538456 | Parenchyma | -cells that perform the tasks of synthesis and secretion | 122 | |
| 6194538457 | Simple | -a single unbranched duct |  | 123 |
| 6194538458 | Compound | -branched ducts |  | 124 |
| 6194538459 | Tubular | -duct and secretory portion are of uniform diameter | 125 | |
| 6194538460 | Acinar | -secretory gland form a dilated sac | 126 | |
| 6194538461 | Acinus or Alveolus | -secretory cells form a dilated sac | 127 | |
| 6194538462 | Tubuloacinar Gland | -secretory cells in both the tubular and acinar portions | 128 | |
| 6194538463 | Serous Glands | -produce relatively thin, watery fluids | 129 | |
| 6194538464 | Mucous Glands | -has cells that secrete a glycoprotein called mucin (mucin absorbs water and forms the sticky product mucus) | 130 | |
| 6194538465 | Mixed Glands | -contain both serous and mucous cells | 131 | |
| 6194538466 | Cytogenic Glands | -release whole cells (testes and ovaries) | 132 | |
| 6194538467 | Eccrine Glands or Merocrine Glands | -have vesicles that release their secretion by exocytosis | 133 | |
| 6194538468 | Holocrine Glands | -cells accumulate a product and then the entire cell disintegrates | 134 | |
| 6194538469 | Apocrine Glands | -same as merocrine with the exception of larger lumen | 135 | |
| 6194538470 | Cutaneous Membrane | -the skin -dry | 136 | |
| 6194538471 | muscularis mucosae | -a layer of smooth muscle in mucous membrane | 137 | |
| 6194538472 | lamina propria | -an areolar connective tissue layer of mucous membrane | 138 | |
| 6194538473 | Mucous Membrane | -lines passages that open to the exterior environment -layers; (1) an epithelium (2) lamina propria (3) muscularis mucosae | 139 | |
| 6194538474 | Serous Membrane | -a simple squamous epithelium resting on a thin layer of areolar connective tissue -produces watery fluid | 140 | |
| 6194538475 | Serous Fluid | -watery product of serous membrane | 141 | |
| 6194538476 | Mesothelium | -the epithelium found in serous membranes lining the ventral body cavity and covering its organs | 142 | |
| 6194538477 | Endothelium | -layer of simple squamous epithelium lining cavities of heart, blood & lymphatic vessels | 143 | |
| 6194538478 | Synovial Membranes | -lines some joints -made only of connective tissue | 144 | |
| 6194538479 | Hyperplasia | -tissue growth through cell multiplication | 145 | |
| 6194538480 | Hypertrophy | -the enlargement of preexisting cells | 146 | |
| 6194538481 | Neoplasia | -the development of a tumor | 147 | |
| 6194538482 | Differentiation | -process in which cells become specialized in structure and function | 148 | |
| 6194538483 | Metaplasia | -a change from one type of mature tissue to another | 149 | |
| 6194538484 | Stem Cells | -undifferentiated cells that are not yet performing any specialized function | 150 | |
| 6194538485 | Developmental Plasticity | -range of mature cell types that a stem cell can become | 151 | |
| 6194538486 | Embryonic Stem Cells | -compose the early human embryo | 152 | |
| 6194538487 | Totipotent | -have the potential to develop into any type of fully differentiated human cell | 153 | |
| 6194538488 | Pluripotent | -cells of the inner cell mass -can still develop into any cell type of the embryo, but not into the accessory organs of pregnancy | 154 | |
| 6194538489 | Adult Stem Cells | -undifferentiated cells found among differentiated cells in a tissue or organ | 155 | |
| 6194538490 | Multipotent | -able to develop into two or more different cell lines, but not just any type of body cell. | 156 | |
| 6194538491 | Unipotent | -able to develop into only one cell type | 157 | |
| 6194538492 | Regeneration | -replacement of dead or damaged cells by the same type of cells as before | 158 | |
| 6194538493 | Fibrosis | -replacement of damaged tissue with scar tissue, composed mainly of collagen produced by fibroblasts | 159 | |
| 6194538494 | Granulation Tissue | -deeper portions of the clot become infiltrated by capillaries and fibroblasts and transform into a soft mass | 160 | |
| 6194538495 | Atrophy | -the shrinkage of a tissue through a loss in cell size or number | 161 | |
| 6194538496 | Necrosis | -premature tissue death | 162 | |
| 6194538497 | Infarction | -the sudden death of tissue, such as cardiac muscle or brain tissue -occurs when its blood supply is cut off | 163 | |
| 6194538498 | Gangrene | -any tissue necrosis resulting from an insufficient blood supply, usually involving infection | 164 | |
| 6194538499 | Decubitus Ulcer | -a form of dry gangrene that occurs when an immobilized person, have continual pressure on the skin cutting off blood flow to the area | 165 | |
| 6194538500 | Apoptosis | -is the normal death of cells that have completed their function and best serve the body by dying | 166 |
