Biochemistry Flashcards
Terms : Hide Images [1]
| 5047573248 | disaccharide | A double sugar, consisting of two monosaccharides joined by dehydration synthesis. |  | 0 |
| 5047573249 | alpha-helix | the coiled structural arrangement of many proteins consisting of a single chain of amino acids stabilized by hydrogen bonds. |  | 1 |
| 5047573250 | biurets | used to test solutions for protein; if it is a positive, the color changes from blue to purple; (stays the same for a negative test) | 2 | |
| 5047573251 | glucose | A sugar that's the major source of energy for the body's cells. It is produced during photosynthesis and can be used to make carbohydrates. |  | 3 |
| 5047573252 | nucleotide | A building block of DNA, consisting of a five-carbon sugar covalently bonded to a nitrogenous base and a phosphate group. |  | 4 |
| 5047573253 | cellulose | A large polysaccharide -provides structural support in plant cell walls. | 5 | |
| 5047573254 | glycogen | An extensively branched glucose storage polysaccharide found in the liver and muscle of animals; the animal equivalent of starch. | 6 | |
| 5047573255 | keratin | A fiber protein that is the principal component of hair, skin, and nails | 7 | |
| 5047573256 | structural | The physical shape of a molecule as a result of atoms bonding. | 8 | |
| 5047573257 | 1-2-1 ratio | Carbohydrates are composed of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen in a consistent ratio. | 9 | |
| 5047573258 | central carbon | the carbon atom of an amino acid that the other amino acid groups (corboxyl group, amino group, etc.) all connect to |  | 10 |
| 5047573259 | inhibition | something that interferes with enzymatic activity | 11 | |
| 5047573260 | benedicts | Indicator used to test for simple sugars and most disaccharides (not sucrose), changes from blue to orange in the presence of sugars, when heated | 12 | |
| 5047573261 | phospholipid | A lipid made up of a glyerol joined to two fatty acids and a phosphate group; has two hydrophobic tails and a polar, hydrophilic head | 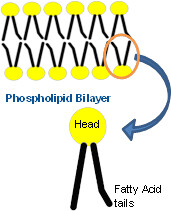 | 13 |
| 5047573262 | R-group | used to represent one of 20 possible side chains found in amino acids of living systems |  | 14 |
| 5047573263 | glycerol backbone | it is the molecule that the fatty acids connect to to form a lipid such as a triglyceride (as well as the phosphate group in a phospholipid) |  | 15 |
| 5047573264 | unsaturated | is a fat or fatty acid in which there is at least one double bond |  | 16 |
| 5047573265 | phosphate group | -this molecule forms the hydrophilic head on a phospholipid - also one of the 3 parts of a nucleotide |  | 17 |
| 5047573266 | sucrose | A disaccharide made of glucose + fructose; Table sugar | 18 | |
| 5047573267 | transparency test | the "paper bag" test used in the lab to test for lipids | 19 | |
| 5047573268 | starch | A storage polysaccharide in plants consisting entirely of glucose. | 20 | |
| 5047573269 | monosaccharide | A single sugar molecule such as glucose or fructose, All monosaccharides have the same chemical formula |  | 21 |
| 5047573270 | iodine | used to test for polysaccharides in the lab. It turns purplish black when positive | 22 | |
| 5047573271 | cholesterol | a type of lipid. | 23 | |
| 5047573272 | enzymes | Functional proteins; their names usually end in - ase Catalyze Reactions (speed it up) | 24 | |
| 5047573273 | nitrogen base | one of the 3 parts of a nucleotide |  | 25 |
| 5047573274 | polysaccharide | Carbohydrates that are made up of more than two monosaccharides | 26 | |
| 5047573275 | dehydration synthesis | A chemical reaction in which two molecules covalently bond to each other with the removal of a water molecule. | 27 | |
| 5047573276 | fatty acids | A building block of lipids, it is a long carbon skeleton, with usually 16-18 carbons, at the end has a carboxyl group attached to a hydrocarbon. |  | 28 |
| 5047573277 | saturated | Fats with the maximum number of hydrogens. Usually animal fats and solid at room temperature |  | 29 |
| 5047573278 | amylase | An enzyme that digests starch into disaccharides. It is secreted by salivary glands and by the pancreas. | 30 | |
| 5047573279 | carboxyl group | A functional group present in organic acids and consisting of a single carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom and also bonded to a hydroxyl group. |  | 31 |
| 5047573280 | peptide bond | The covalent bond between two amino acids, joining them into a peptide or protein. | 32 | |
| 5047573281 | dipeptide | Two amino acids bonded together | 33 | |
| 5047573282 | polypeptide | A polymer (chain) of many amino acids linked together by peptide bonds. | 34 | |
| 5047573283 | primary (protein) | -first level of protein structure - linear sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide chain. -held together by covalent bonds such as peptide bonds |  | 35 |
| 5047573284 | secondary (protein) | Level of protein structure that is formed by the hydrogen bonds between the polar side groups of the main chain. Can be alpha helix or beta pleat sheet |  | 36 |
| 5047573285 | tertiary (protein) | third level of protein structure; the 3-D shape the molecule assumes, as a result of twisting, bending, and folding caused by various types of bonding between R groups (H bonds, ionic bonds, covalent bonds) in large proteins |  | 37 |
| 5047573286 | quaternary (protein) | Relationship among multiple polypeptides of a protein. |  | 38 |
| 5047573287 | maltose | A disaccharide made of glucose + glucose. | 39 | |
| 5047573288 | beta-pleated sheet | polypeptide chain folds back and forth; stabilized by hydrogen bonding |  | 40 |
| 5047573289 | fructose | A 6-carbon monosaccharide in the form of a ring structure. The sweetest of all natural sugars. | 41 | |
| 5047573290 | functional protein | -Proteins that cause chemical changes in the molecules, -control cell activities | 42 | |
| 5047573291 | triglyceride | A molecule made up of three fatty acids covalently bonded to glycerol; Does energy storage, thermal insulation, binds and cushions organs, fills space |  | 43 |
| 5047573292 | amino group | A functional group that consists of a nitrogen atom bonded to two hydrogen atoms |  | 44 |
| 5047573293 | collagen | Fibrous protein that gives the skin form and strength | 45 | |
| 5047573294 | photosynthesis | Plants use the sun's energy to convert water and carbon dioxide into sugars | 46 | |
| 5047573295 | insulation | a material that reduces or prevents the transmission of heat | 47 | |
| 5047573296 | enzyme-substrate complex | A temporary complex formed when an enzyme binds to its substrate molecule(s). |  | 48 |
| 5047573297 | hydrolysis | A chemical reaction that breaks bonds between two molecules by the addition of water; functions in disassembly of polymers to monomers. | 49 | |
| 5047573298 | activation energy | Energy needed to get a reaction started | 50 | |
| 5047573299 | lactase | A digestive enzyme that breaks lactose into glucose and galactose. | 51 | |
| 5047573300 | reusable | able to be used again | 52 | |
| 5047573301 | denature | A change in the shape of a protein (such as an enzyme) that can be caused by changes in temperature or pH (among other things). | 53 | |
| 5047573302 | catalyst | A substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction. | 54 |
