Biochemistry Flashcards
Terms : Hide Images [1]
| 7259575443 | Bio | life | 0 | |
| 7259577068 | chemistry | chemicals | 1 | |
| 7259578127 | Neutral | PH7 | 2 | |
| 7259579121 | Polar | water molecules are attracted to other water molecules due to opposite changes | 3 | |
| 7259583055 | Cohesion | Same substances are attracted to water | 4 | |
| 7259583996 | Adhesion | different substances are attracted to water | 5 | |
| 7259585700 | mixture | water that is not pure | 6 | |
| 7259587036 | solutions | all parts evenly disturbed ex; sweet tea | 7 | |
| 7259588068 | solute | what is being dissolved ex; sugar and tea | 8 | |
| 7259591167 | solvent | what is doing the dissolving, water is a universal solvent | 9 | |
| 7259593659 | cation/ anion | +/- H2O H+ OH- | 10 | |
| 7259596154 | ion | molecule that takes positive or negative charge | 11 | |
| 7259599706 | Ph scale | 1-6 acid, 7 neutral 8-14 base | 12 | |
| 7259602061 | Buffers | weak acids or bases that react with strong acids or bases to prevent sudden Ph changes | 13 | |
| 7259604722 | Reactant | what is used to complete the reaction | 14 | |
| 7259605216 | product | what is made after the reaction | 15 | |
| 7259606879 | structural formula | picture of the molecule | 16 | |
| 7259608728 | Empirical formula | numbers of the reaction | 17 | |
| 7259628537 | carbon compounds | organic compounds | 18 | |
| 7259629129 | large molecules | polymers are formed by small molecules, monomers | 19 | |
| 7259632633 | dehydration synthesis | water is removed from monomers to make polymers | 20 | |
| 7259637066 | carbohydrates | Source of energy; contains carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen; sugars and starches | 21 | |
| 7259642781 | monosaccharide | A simple sugar that is the basic subunit of a carbohydrate One sugar C6 H12 O6 | 22 | |
| 7259646289 | disaccharide | A double sugar, consisting of two monosaccharides joined by dehydration synthesis. C6 H22 O11 | 23 | |
| 7259652975 | formula | C6 H12 O6 + C6 H12 O6 = C12 H24 O12 - H2 O1 = C6 H22 O11 | 24 | |
| 7259660792 | isomer | have the same empirical formula but different structural formula | 25 | |
| 7259664240 | Polysaccharides | complex sugars Carbohydrates that are made up of more than two monosaccharides | 26 | |
| 7259669656 | Lactose, Sucrose and Maltose | Disaccharide | 27 | |
| 7259671739 | Starches, Glycogen, Cellulose | polysaccharides | 28 | |
| 7259674040 | lipids | A fatty substance that does not dissolve in water store energy fats, oils, and waxes glycerol and 3 fatty acids 2 times as much energy stored than carbohydrates greater than a 2:1 ratio | 29 | |
| 7259680121 | saturated fats | All single bonds between carbons | 30 | |
| 7259681892 | unsaturated fats | double bonds liquid at room temperature | 31 | |
| 7259684236 | Proteins | amino acids nutrients that help build and maintain body cells and tissues 20 different amino acids | 32 | |
| 7259688932 | amino acid bonds | AA + AA+AA=Protein + water | 33 | |
| 7259691609 | peptide | short chain of amino acids linked by peptide bonds that make protein | 34 | |
| 7259693672 | dipetide | 2 amino acids linked together | 35 | |
| 7259695299 | polypeptide | long chain of amino acids that makes proteins | 36 | |
| 7284588925 | enzymes | proteins that act as biological catalysts Proteins that speed up chemical reactions or slow down chemical reactions in cells | 37 | |
| 7284598536 | lower activation energy | Faster reaction the amount of energy needed to start the reaction | 38 | |
| 7284631699 | lock and key hypothesis | Substrates fit into enzymes like a key fits into a lock There is ONE ENZYME for ONE SUBSTRATE | 39 | |
| 7284636025 | substrate | The reactant on which an enzyme works. | 40 | |
| 7284643574 | enzyme and substrate | they fit together until the reaction is over, when it is over a product is released and the product starts over again | 41 | |
| 7284656762 | nucleic acids | DNA and RNA nucleotide is what they are built with macromolecules containing hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, carbon, and phosphorus Complex macromolecules that store and transmit genetic information helps makes proteins | 42 | |
| 7284671193 | enzyme concentration | The more enzymes, the greater the rate of chemical reactions more enzymes = more they will collide | 43 | |
| 7284679608 | substrate concentration | "Enzyme activity increases as substrate concentration increases" More substrate means more chance encounters between substrate molecules and the enzyme | 44 | |
| 7284793081 | optimum temperature | temperature at which organisms grow best. the temperature at which the enzyme has the highest rate of catalysis. human enzymes = 35* - 40* c body temp 37*c | 45 | |
| 7284809851 | raise temperature | denature protein, unfold= lose shape | 46 | |
| 7284816290 | lower temp. | molecules move slower and decrease collisions | 47 | |
| 7284824278 | pH changes | protein shape | 48 | |
| 7284829729 | pH 6-8 | most human enzymes | 49 | |
| 7284833087 | pH 3 | stomach | 50 | |
| 7284835850 | pH 8 | small intestines | 51 | |
| 7301515422 | monosaccaride molecule |  | 52 | |
| 7301516164 | lipid molecule |  | 53 | |
| 7301517230 | amino acid molecule |  | 54 | |
| 7301518216 | glycerol molecule | 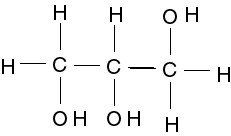 | 55 | |
| 7301519544 | water molecule |  | 56 | |
| 7308543736 | starch | iodine, positive- blue, black color | 57 | |
| 7308546809 | simple sugar | Benedict, positive- orange, blue | 58 | |
| 7308551105 | protein lab | Biuret, positive - light purple | 59 | |
| 7308554964 | lipids lab | brown paper, positive- translucent | 60 |
