APES Ch. 16 & 17 Flashcards
Terms : Hide Images [1]
| 9814703749 | Waste | Material outputs from a system that are not useful or consumed. |  | 0 |
| 9814703750 | Municipal solid waste (MSW) | Refuse collected by municipalities from households, small businesses, and institutions. |  | 1 |
| 9814703751 | Waste stream | The flow of solid waste that is recycled, incinerated, placed in a solid waste landfill, or disposed of in another way. | 2 | |
| 9814703752 | Reduce, reuse, recycle | A popular phrase promoting the idea of diverting materials from the waste stream. Also known as The three Rs. |  | 3 |
| 9814703753 | The three Rs | A popular phrase promoting the idea of diverting materials from the waste stream. Also known as Reduce, reuse, recycle. |  | 4 |
| 9814703754 | Source reduction | An approach to waste management that seeks to cut waste by reducing the use of potential waste materials in the early stages of design and manufacture. | 5 | |
| 9814703755 | Reuse | Using a product or material that was intended to be discarded. |  | 6 |
| 9814703756 | Recycling | The process by which materials destined to become municipal solid waste (MSW) are collected and converted into raw material that is then used to produce new objects. |  | 7 |
| 9814703757 | Closed-loop recycling | Recycling a product into the same product. |  | 8 |
| 9814703758 | Open-loop recycling | Recycling a product into a different product. |  | 9 |
| 9814703759 | Composting | Creation of organic matter (humus) by decomposition under controlled conditions to produce an organic-rich material that enhances soil structure, cation exchange capacity, and fertility. |  | 10 |
| 9814703760 | Leachate | Liquid that contains elevated levels of pollution as a result of having passed through municipal solid waste (MSW) or contaminated soil. | 11 | |
| 9814703761 | Sanitary landfill | An engineered ground facility designed to hold municipal solid waste (MSW) with little contamination of the surrounding environment as possible. |  | 12 |
| 9814703762 | Tipping fee | A fee charged for the disposing of material in a landfill or incinerator. | 13 | |
| 9814703763 | Siting | The designation of a landfill location, typically through a regulatory process involving studies, written reports, and public hearings. | 14 | |
| 9814703764 | Incineration | The process of burning waste material to reduce the volume and mass, sometimes to generate electricity and heat. |  | 15 |
| 9814703765 | Ash | The residual nonorganic material that does not combust during incineration. |  | 16 |
| 9814703766 | Bottom ash | Residue collected at the bottom of the combustion chamber in a furnace. | 17 | |
| 9814703767 | Fly ash | The residue collected from the chimney or exhaust pipe of a furnace. |  | 18 |
| 9814703768 | Waste-to-energy | A system in which heat generated by incineration is used as an energy source rather than released into the atmosphere. | 19 | |
| 9814703769 | Hazardous waste | Liquid, solid, gaseous, or sludge waste material that is harmful to humans or ecosystems. |  | 20 |
| 9814703770 | Superfund Act | The common name for the Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act (CERCLA); a 1980 U.S. federal act that imposes a tax on the chemical and petroleum industries, funds the cleanup of abandoned and nonoperating hazardous waste sites, and authorizes the federal government to respond directly to the release or threatened release of substances that may pose a threat to human health or the environment. | 21 | |
| 9814703771 | Brownfields | Contaminated industrial or commercial sites that may require environmental cleanup before they can be redeveloped or expanded. | 22 | |
| 9814703772 | Life-cycle analysis | A systems tool that looks at the materials used and released throughout the lifetime of a product-from the procurement of new materials through their manufacture, use, and disposal. Also known as Cradle-to-grave analysis. | 23 | |
| 9814703773 | Cradle-to-grave analysis | A systems tool that looks at the materials used and released throughout the lifetime of a product-from the procurement of new materials through their manufacture, use, and disposal. Also known as Life-cycle analysis. | 24 | |
| 9814703774 | Integrated waste management | An approach to waste disposal that employs several waste reduction, management, and disposal strategies in order to reduce the environmental impact of municipal solid waste (MSW). |  | 25 |
| 9814703775 | Disease | Any impaired function of the body with a characteristic set of symptoms. | 26 | |
| 9814703776 | Infectious disease | A disease caused by a pathogen. | 27 | |
| 9814703777 | Acute disease | A disease that rapidly impairs the functioning of an organism. | 28 | |
| 9814703778 | Chronic disease | A disease that slowly impairs the functioning of an organism. | 29 | |
| 9814703779 | Epidemic | A situation in which a pathogen causes a rapid increase in a disease. | 30 | |
| 9814703780 | Pandemic | An epidemic that occurs over a large geographic region. | 31 | |
| 9814703781 | Plague | An infectious disease caused by a bacterium (Yersinia pestis) that is carried by fleas. |  | 32 |
| 9814703782 | Malaria | An infectious disease caused by one of several species of protists in the genus Plasmodium. | 33 | |
| 9814703783 | Tuberculosis | A highly contagious disease caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis that primarily infects the lungs. | 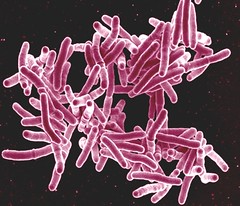 | 34 |
| 9814703784 | Emergent infectious disease | An infectious disease that has not been previously described or has not been common for at least 20 years. |  | 35 |
| 9814703785 | Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS) | An infectious disease caused by the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). |  | 36 |
| 9814703786 | Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) | A type of virus that causes Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS). |  | 37 |
| 9814703787 | Ebola hemorrhagic fever | An infectious disease with high death rates, caused by the Ebola virus. |  | 38 |
| 9814703788 | Mad cow disease | A disease in which prions mutate into deadly pathogens and slowly damage a cow's nervous system. | 39 | |
| 9814703789 | Prion | A small, beneficial protein that occasionally mutates into a pathogen. | 40 | |
| 9814703790 | Swine flu | A type of flu caused by the H1N1 virus. |  | 41 |
| 9814703791 | Bird flu | A type of flu caused by the H5N1 virus. |  | 42 |
| 9814703792 | Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) | A type of flu caused by a coronavirus. | 43 | |
| 9814703793 | West Nile virus | A virus that lives in hundreds of species of birds and is transmitted among birds by mosquitoes. |  | 44 |
| 9814703794 | Neurotoxin | A chemical that disrupts the nervous system of animals. | 45 | |
| 9814703795 | Carcinogen | A chemical that causes cancer. | 46 | |
| 9814703796 | Mutagen | A type of carcinogen that causes damage to the genetic material of a cell. | 47 | |
| 9814703797 | Teratogen | A chemical that interferes with the normal development of embryos or fetuses. | 48 | |
| 9814703798 | Allergen | A chemical that causes allergic reactions. | 49 | |
| 9814703799 | Endocrine disruptor | A chemical that interferes with the normal functioning of hormones in an animal's body. | 50 | |
| 9814703800 | Dose-response study | A study that exposes organisms to different amounts of a chemical and then observes a variety of possible responses, including mortality or changes in behavior or reproduction. | 51 | |
| 9814703801 | Acute study | An experiment that exposes organisms to an environmental hazard for a short duration. | 52 | |
| 9814703802 | Chronic study | An experiment that exposes organisms to an environmental hazard for a long duration. | 53 | |
| 9814703803 | LD50 | The lethal dose of a chemical that kills 50 percent of the individuals in a dose-response-study. |  | 54 |
| 9814703804 | Sublethal effect | The effect of an environmental hazard that is not lethal, but which may impair an organism's behavior, physiology, or reproduction. | 55 | |
| 9814703805 | ED50 | The effective dose of a chemical that causes 50 percent of the individuals in a does-response study to display a harmful, but nonlethal, effect. | 56 | |
| 9814703806 | Retrospective study | A study that monitors people who have been exposed to an environmental hazard at some time in the past. | 57 | |
| 9814703807 | Prospective study | A study that monitors people who might become exposed to harmful chemicals in the future. | 58 | |
| 9814703808 | Synergistic interaction | A situation in which two risks together cause more harm than expected based on the separate effects of each risk alone. | 59 | |
| 9814703809 | Route of exposure | The way in which an individual might come into contact with an environmental hazard. | 60 | |
| 9814703810 | Solubility | How well a chemical dissolves in a liquid. | 61 | |
| 9814703811 | Bioaccumulation | An increased concentration of a chemical within an organism over time. | 62 | |
| 9814703812 | Biomagnification | The increase in chemical concentration in animal tissue as the chemical moves up the food chain. |  | 63 |
| 9814703813 | Persistence | The length of time a chemical remains in the environment. |  | 64 |
| 9814703814 | Environmental hazard | Anything in the environment that can potentially cause harm. | 65 | |
| 9814703815 | Innocent-until-proven-guilty principle | A principle based on the belief that a potential hazard should not be considered an actual hazard until scientific data definitively demonstrates that it actually causes harm. |  | 66 |
| 9814703816 | Precautionary principle | A principle based on the belief that action should be taken against a plausible environmental hazard. |  | 67 |
| 9814703817 | Stockholm Convention | A 2001 agreement among 127 nations concerning 12 chemicals to be banned, phased out, or reduced. | 68 | |
| 9814703818 | REACH | A 2007 agreement among the nations of the European Union about regulation of chemicals; the acronym stands for registration, evaluation, authorization, and restriction of chemicals. | 69 |
