AP Human Geography Midterms Flashcards
Terms : Hide Images [1]
| 5833133354 | Scale | the relationship (or ratio) between distance on a map and the corresponding distance on the ground. For example, on a 1:100000 scale map, 1cm on the map equals 1km on the ground. | 0 | |
| 5833142788 | Local Diversity v. Globalization | Local diversity allows unique culture and differentiation of people whereas globalization pulls people together through info. technology and communication | 1 | |
| 5833166080 | Maps/Cartography | a diagrammatic representation of an area of land or sea showing physical features, cities, roads, etc. Cartography is the science or practice of making maps | 2 | |
| 5835581798 | Environmental Determinism | how the physical environment predisposes societies and states towards particular development trajectories | 3 | |
| 5835583522 | Absolute Location | Uses latitudes and longitudes to | 4 | |
| 5835721500 | International date line | The line in the pacific that determines when the next day is | 5 | |
| 5835723680 | Prime Meridian | 0 degree meridian on Greenwich | 6 | |
| 5835724709 | Equator | Centermost parallel on earth. Gets most direct sunlight all year. | 7 | |
| 5835724710 | Tropics | Cancer and Capricorn. | 8 | |
| 5835726433 | What is a place? | Where unique things and culture and people are | 9 | |
| 5835728611 | Map Scale/Map projection | The earth projected by some proportion into 2 dimensions | 10 | |
| 5836375601 | Climate/Biomes | Common weather and landscape patterns of a large mass of land | 11 | |
| 5836376047 | Popluation Distribution | the arrangement or spread of people living in a given area; also, how the population of an area is arranged according to variables such as age, race, or sex | 12 | |
| 5836376048 | LDC | Less developed country. High birth rate and high death rate. Low living conditions. | 13 | |
| 5836376049 | MDC | More developed country. Low to moderate birth rate to low death rate. Better medicine and technology | 14 | |
| 5836376502 | Demography | the study of statistics such as births, deaths, income, or the incidence of disease, which illustrate the changing structure of human populations. | 15 | |
| 5836376503 | Cartogram | a map on which statistical information is shown in diagrammatic form. | 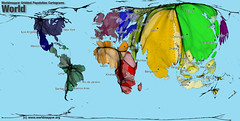 | 16 |
| 5836376944 | Ecumene | inhabited land | 17 | |
| 5836377249 | Arithmetic Density | People per measure of land | 18 | |
| 5836377250 | Agricultural Density | number of farmers per unit area of arable land | 19 | |
| 5836381368 | Earth's Population Clusters | East Asia, South Asia, Europe and Eastern North America | 20 | |
| 5836381783 | CBR | Crude birth rate. | 21 | |
| 5836381784 | CDR | Crude death rate | 22 | |
| 5836383051 | Natural Increase NIR | CBR minus CDR plus immigration and emigration | 23 | |
| 5836383052 | ZPG | Zero population growth | 24 | |
| 5836383053 | Echo Boom (population pyramid) | A small baby boom after the generation of a previous, more major baby boom | 25 | |
| 5836385755 | Doubling Time | the period of time required for a quantity to double in size or value. | 26 | |
| 5836387499 | Areas where there are population issues either overpopulation or negative growth | Ex. Russia has negative population growth at the moment | 27 | |
| 5836388480 | TFR | Total fertility rate- the average number of children born | 28 | |
| 5836388481 | IMR | Infant mortality rate- the average number of infant deaths usually at birth | 29 | |
| 5836388873 | Age-Sex Ratio | The ratio of men to women as well as different ages | 30 | |
| 5836389591 | Analyze the population pyramids | (Rapid, Slow, Negative Growth) why? |  | 31 |
| 5836397182 | Demographic Transition Model | Shows population trends of countries and their correlation with the country's development |  | 32 |
| 5836398215 | Malthus Theory | human populations grow exponentially (i.e., doubling with each cycle) while food production grows at an arithmetic rate | 33 | |
| 5836398216 | Carrying Capacity | Capacity at which a population can be supported | 34 | |
| 5836400547 | Epidemiologic Transition | a phase of development witnessed by a sudden and stark increase in population growth rates brought about by medical innovation in disease or sickness therapy and treatment | 35 | |
| 5836402332 | Chain Migration | the social process by which immigrants from a particular town follow others from that town to a particular city or neighborhood | 36 | |
| 5836404289 | Interregional migration | Migration within a country or general region | 37 | |
| 5836405435 | International Migration | Migration across countries | 38 | |
| 5836406984 | Rust Belt | The American Eastern Midwest | 39 | |
| 5836407370 | Cotton Belt | The American "South" | 40 | |
| 5836407371 | Hollow Core | 41 | ||
| 5836407652 | Sun Belt | The American Southwest | 42 | |
| 5836408205 | Counterurbanization | a demographic and social process whereby people move from urban areas to rural areas | 43 | |
| 5836409633 | In a LDC, what direction does migration move and why? | Outward so people can live better lives | 44 | |
| 5836410160 | EG Ravenstein | German English geographer photographer | 45 | |
| 5836410561 | Short Term Migration | When a migrant moves to another country for at least three months but less than a year | 46 | |
| 5836410852 | Emigration vs. Immigration | Emigration is the act of leaving one's own country, whereas immigration is the articulate of migrants | 47 | |
| 5836411150 | Push Factors | Factors that drive a person away from a place | 48 | |
| 5836411151 | Pull Factors | Factors that attract people to a place | 49 | |
| 5836411758 | Economic or Place Utility | A place's "usefulness" that makes it attractive | 50 | |
| 5836411759 | Refugee | A person forced to leave their own country in order to escape conflict | 51 | |
| 5836411987 | Asylum Seeker | A person who has left their home a political refugee and is seeking asylum in another | 52 | |
| 5836412594 | Intervening obstacle/ Intervening opportunity | Obstacles are factors that make it more difficult to migrate/ opportunities are factors that make a closer place seem more attractive than the previous choice | 53 | |
| 5836413101 | Voluntary vs. Forced Migration | Voluntary migration is a choice whereas forced is when a person doesn't have a choice but to leave | 54 | |
| 5836414158 | According to Ravenstein, who are most of the long distance migrants? Why has it changed? | 55 | ||
| 5836417318 | Wilbur Zelinsky migration transition concepts | 56 | ||
| 5836417907 | Undocumented Workers | Workers without legal documentation to live and/or work in another country | 57 | |
| 5836417908 | Cultural Ecology | The study of human adaptations to social and physical environments | 58 | |
| 5836419514 | Core-Domain-Sphere model | The area outside of the core of a culture region is still dominant but less intense | 59 | |
| 5836419835 | Cultural Transition Zone | Area where two different cultures come together | 60 | |
| 5836420652 | Folk Culture v. Popular Culture | Isolated, traditional, unique, and less prevalent v. Placeless, dynamic, and common | 61 | |
| 5836421312 | Different types of diffusion | Hierarchal- VIPs spread innovations and ideas Relocation- people bring ideas and innovations from other places Contagious- an idea or innovation spreads through people-people contact | 62 | |
| 5836421629 | Western culture's impact | Cars, music, fashion, technology, language, military strength, government | 63 | |
| 5836422578 | Values associated with American culture | Constitutional, fundamental human rights, diversity and expressionism | 64 | |
| 5836422921 | Cultural hearth | Place where culture originates | 65 | |
| 5836422922 | Cultural Realm | The general language, religion, economic development, and artistry of general region | 66 | |
| 5836423419 | Cultural Trait | A certain aspect of culture unique to a people or place | 67 | |
| 5836423420 | Cultural Landscape | a geographic area, including both cultural and natural resources and the wildlife or domestic animals therein, associated with a historic event, activity, or person or exhibiting other cultural or aesthetic values | 68 | |
| 5836423826 | Functional and nodal region | Functional- consist of a central place and the surrounding areas that are dependent upon that place, such as a metropolitan area. Nodal- an area organized around a node, or focal point, and is defined by interactions or connections | 69 | |
| 5836423827 | Syncretism | The amalgamation of different cultures or schools of thought | 70 | |
| 5836424681 | Acculturation | The adaptation of a more dominant culture to a less dominant one | 71 | |
| 5836424682 | Assimilation | The almost indistinguishable merging of two different cultures into one or the complete domination of a more dominant one | 72 | |
| 5836426459 | Universalizing v. Ethnic Religion | Universalizing try to get people to join whereas ethnic keep to there own people or place | 73 | |
| 5836427873 | Popular Religious Concepts | Afterlife, deity, nature is sacred, certain way of life | 74 | |
| 5836427874 | Diaspora | The the scattering of the Jewish population from the Levant area | 75 | |
| 5836429565 | Which languages have been globally diffused? | English, German, French, Chinese, | 76 | |
| 5836430462 | Latin based languages | Spanish, French, Italian, Portuguese, Romanian | 77 | |
| 5836431183 | French-speaking North American city | Montreal, Quebec | 78 | |
| 5836431829 | Half of world's citizens speak from what language family? | Indo-European | 79 | |
| 5836432404 | Components of a dialect | Grammar, speech, and sound | 80 | |
| 5836432639 | Isogloss | A line in a dialect map marking the boundary between linguistic features | 81 | |
| 5836433580 | Language that uses ideographic writing and why it is a problem to learn | Chinese. There is a different character(s) for every word | 82 | |
| 5836434708 | Language no longer used | Dead language | 83 | |
| 5836435756 | Why would a country have an official language? | To make it easier to organize legal documentation | 84 | |
| 5836437090 | American English has adopted vocab from what other languages? | French, | 85 | |
| 5836438297 | Lingua franca | A language that is adopted as a common language between speakers whose native languages are different | 86 | |
| 5836438841 | Does U.S have official language? | No | 87 | |
| 5836440161 | Why is french the official language in places like Senegal? | They were under French rule during the imperialist era | 88 | |
| 5836440162 | Pidgin language | A grammatically simplified means of communication with elements from multiple languages | 89 | |
| 5836440529 | Creole | A pidgin language with elements of French, Spanish, African, and Native-American roots | 90 | |
| 5836440862 | Why is English used globally | Western culture became highly influential after the Great War | 91 | |
| 5836441979 | Why is Basque unusual? | Its language is not of the Indo-European family yet it is in the middle of two European countries | 92 | |
| 5836442903 | Cultural Diffusion | The spread of ideas and innovation | 93 | |
| 5836443246 | How is culture spread? | Through diffusion and immigration | 94 | |
| 5836443247 | Ethnicity | the fact or state of belonging to a social group that has a common national or cultural tradition | 95 | |
| 5836443618 | Ethnocentrism | The judgement of another ethnicity based on the traits and mindset of one's own | 96 | |
| 5836443949 | Subsistence Agriculture | Farming to only sustain one household | 97 | |
| 5836444971 | Hispanic population focused where in U.S? African-Americans? | Southwest. Midwest and South | 98 | |
| 5836447407 | Ethnic enclaves | A neighborhood with a high density of a certain ethnicity | 99 | |
| 5836447934 | Apartheid | Segregation of government by race or ethnicity. Ex. South Africa in the 20th century | 100 | |
| 5836447940 | Ethnic Conflict | Conflict of interests or morals due to the difference in way of life or territorial claims by two different peoples | 101 | |
| 5836448452 | Cultural hearths | Origins of culture (ideas and innovation) | 102 | |
| 5836449135 | Chain migration and ethnic enclave connection | As certain people move to a neighborhood,it causes a chain of migration to a certain neighborhood, causing that neighborhood to become an ethnic enclave | 103 |
