AP Psychology: Unit 9 Flashcards
Terms : Hide Images [1]
| 5552349444 | Developmental Psychology | 1) a branch of psychology that studies physical, cognitive, and social change throughout the life span. 2) human form conception until death | 0 | |
| 5552351615 | Zygote | 1) the fertilized egg, it enters a 2-week period of rapid cell division and develops into an embryo. 2) 0-2 weeks old, egg + sperm |  | 1 |
| 5552353370 | Embryo | 1) the developing human organism from about 2 weeks after fertilization through the second month. 2) 2-8 weeks old, major organs are made |  | 2 |
| 5552353371 | Fetus | 1) the developing human organism from 9 weeks after conception to birth. 2) 9+ weeks old | 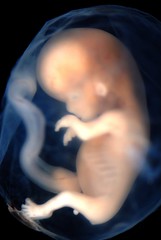 | 3 |
| 5552355745 | Teratogens | 1) agents, such as chemicals and viruses, that can reach the embryo or fetus during prenatal development and cause harm. 2) agents that can reach an unborn baby | 4 | |
| 5552360841 | Fetal Alcohol Syndrome (FAS) | 1) physical and cognitive abnormalities in children caused by a pregnant woman's heavy drinking. In severe cases, symptoms include noticeable facial misproportions. 2) when a mother drinks during pregnancy, causes birth defects |  | 5 |
| 5552363373 | Habituation | 1) decreasing responsiveness with repeated stimulation. As infants gain familiarity with repeated exposure to a visual stimulus, their interest wanes and they look away sooner. 2) adapt to a repeated stimuli | 6 | |
| 5552363398 | Maturation | 1) biological growth processes that enable orderly changes in behavior, relatively uninfluenced by experience. 2) starts of the same but end at different times | 7 | |
| 5552365620 | Cognition | 1) all mental activities associated with thinking, knowing, remembering, and communicating. 2) mental activities | 8 | |
| 5552367130 | Schema | 1) a concept or framework that organizes and interprets information. 2) concepts/ideas | 9 | |
| 5552369031 | Assimilation | 1) interpreting our new experiences in terms of our existing schemas. 2) learn something by comparing to something similar | 10 | |
| 5552370891 | Accommodation | 1) adapting our current understandings (schemas) to incorporate new information. 2) learn something that is not compared to other things | 11 | |
| 5552372574 | Sensorimotor Stage | 1) in Piaget's theory, the stage (from birth to about 2 years of age) during which infants know the world mostly in terms of their sensory impressions and motor activities. 2) learns about the world trough sensory and motor function | 12 | |
| 5552374899 | Object Permanence | 1) the awareness that things continue to exist when not perceived. 2) knows things are still existing even though you cannot see it | 13 | |
| 5552376740 | Preoperational Stage | 1) in Piaget's theory, the stage (from 2 to about 6 or 7 years of age) during which a child learns to use language but does not yet comprehend the mental operations of concrete logic. 2) child understands language, not logic | 14 | |
| 5552382825 | Conservation | 1) the principle (which Piaget believed to be a part of concrete operational reasoning) that properties such as mass, volume, and number remain the same despite changes in the forms of objects. 2) when you know that properties remain the same even with changes in the form | 15 | |
| 5552385284 | Egocentrism | 1) in Piaget's theory, the preoperational child's difficulty taking another's point of view. 2) only their point of view (me, me, me) | 16 | |
| 5552385285 | Theory of Mind | 1) people's ideas about their own and other's mental states - about their feelings, perceptions, and thoughts, and the behaviors these might predict 2) idea about their own mental states | 17 | |
| 5552387228 | Concrete Operational Stage | 1) in Piaget's theory, the stage of cognitive development (from about 6 or 7 to 11 years of age) during which children gain the mental operations that enable them to think logically about concrete events. 2) Children starts understanding logic | 18 | |
| 5552391800 | Formal Operational Stage | 1) in Piaget's theory, the stage of cognitive development (normally beginning about age 12) during which people begin to think logically about abstract concepts. 2) child can think abstractly and like an adult | 19 | |
| 5552393938 | Autism | 1) a disorder that appears in childhood and is marked by deficient communication, social interaction, and understanding of other's states of mind. 2) disorder marked by deficient communication, not social, and don't understand other people's state of mind | 20 | |
| 5552395961 | Stranger Anxiety | 1) the fear of strangers that infants commonly display, beginning by about 8 months of age. 2) fear of strangers | 21 | |
| 5552395962 | Attachment | 1) an emotional tie with another person; shown in young children by their seeking closeness to the caregiver and showing distress on separation. 2) emotional bond | 22 | |
| 5552397797 | Critical Period | 1) an optimal period shortly after birth when an organism's exposure to certain stimuli or experiences produces proper development. 2) important period that produces proper development | 23 | |
| 5552402347 | Imprinting | 1) the process by which certain animals form attachments during a critical period very early in life. 2) following of the first large moving object |  | 24 |
| 5552407841 | Temperament | 1) a person's characteristic emotional reactivity and intensity. 2) a person's characteristics | 25 | |
| 5552411443 | Basic Trust | 1) according to Erik Erikson, a sense that the world is predictable and trustworthy; said to be formed during infancy by appropriate experiences with responsive caregivers. 2) sense that the world is predictable and trustworthy | 26 | |
| 5552413771 | Self-concept | 1) our understanding and evaluation of who we are. 2) who we think we are | 27 | |
| 5552416584 | Gender | 1) in psychology, the biologically and socially influenced characteristics by which people define male and female. 2) our role as a male or female (bio and Social) | 28 | |
| 5552418716 | Aggression | 1) physical or verbal behavior intended to hurt someone. 2) ability to hurt others on purpose | 29 | |
| 5552418717 | X Chromosome | 1) the sex chromosome found in both men and women. Females have two X chromosomes; males have one. An X chromosome from each parent produces a female child. 2) a female and male chromosome but females have more | 30 | |
| 5552421362 | Y Chromosome | 1) the sex chromosome found only in males. When paired with an X chromosome from the mother, it produces a male child. 2) a male chromosome | 31 | |
| 5552423590 | Testosterone | 1) the most important of the male sex hormones. Both males and females have it, but the additional testosterone in males stimulates the growth of the male sex organs in the fetus and the development of the male sex characteristics during puberty. 2) sex hormone | 32 | |
| 5552425590 | Role | 1) a set of expectations (norms) about a social position, defining how those in the position ought to behave. 2) our norms | 33 | |
| 5552427541 | Gender Role | 1) a set of expected behaviors for males or for females. 2) norms for males and females | 34 | |
| 5552431309 | Gender Identity | 1) our sense of being male or female 2) how we feel about our gender | 35 | |
| 5552433185 | Gender Typing | 1) the acquisition of a traditional masculine or feminine role. 2) learning of male and female roles | 36 | |
| 5552435835 | Social Learning Theory | 1) the theory that we learn social behavior by observing and imitating and by being rewarded or punished. 2) learn by watching (observational learning) | 37 | |
| 5552437643 | Adolescence | 1) the transition period from childhood to adulthood, extending from puberty to independence. 2) teen years | 38 | |
| 5552439303 | Puberty | 1 the period of sexual maturation, during which a person becomes capable of reproducing. 2) time in life when you can start having babies | 39 | |
| 5552439304 | Primary Sexual Characteristics | 1) the body structures (ovaries, testes, and external genitalia) that makes sexual reproduction possible. 2) what is needed for babies | 40 | |
| 5552441348 | Secondary Sex Characteristics | 1) non-reproductive sexual characteristics, such as female breasts and hips, male voice quality, and body hair. 2) the side-effects of puberty (not needed) | 41 | |
| 5552447090 | Menarche | 1) the first menstrual period. 2) women's first period | 42 | |
| 5552447091 | Identity | 1) our sense of self; according to Erikson, the adolescent's task is to solidify a sense of self by testing and integrating various roles. 2) how we see our self | 43 | |
| 5552449121 | Social Identify | 1) the "we" aspect of our self-concept; the part of our answer to "Who am I?" that comes from our group memberships. 2) how we see ourselves as a generation | 44 | |
| 5552451356 | Intimacy | 1) in Erikson's theory, the ability to form close, loving relationships; a primary developmental task in late adolescence and early adulthood. 2) when you start making strong, forever lasting relationships | 45 | |
| 5552453552 | Emerging Adulthood | 1) for some people in modern cultures, a period from the late teens to mid-twenties, bridging the gap between adolescent dependence and full independence and responsible adulthood. 2) starting to be a adult | 46 | |
| 5552456523 | Menopause | 1) the time of natural cessation of menstruation; also refers to the biological changes a woman experiences as her ability to reproduce declines. 2) loss the ability to let go of eggs (don't have any more) | 47 | |
| 5552457977 | Cross-sectional Study | 1) a study in which people of different ages are compared with one another. 2) fast paced learning with different ages | 48 | |
| 5552459920 | Longitudinal Study | 1) research in which the same people are restudied and retested over a long period. 2) expensive experimentation with one group of people | 49 | |
| 5552463003 | Crystallized Intelligence | 1) our accumulated knowledge and verbal skills; tends to increase with age. 2) things we already know that tends to increase with age | 50 | |
| 5552466742 | Fluid Intelligence | 1) our ability to reason speedily and abstractly; tends to decrease during late adulthood. 2) how fast our mind works that tends to decrease with age | 51 | |
| 5552470461 | Social Clock | 1) the culturally preferred timing of social events such as marriage, parenthood, and retirement. 2) how people see when it is necessary to do certain things in life |  | 52 |
