Mitosis - AP Biology Flashcards
Terms : Hide Images [1]
| 6086797002 | G1 Phase | First stage of interphase in which cell grows and performs its normal functions. Cell is diploid. | 0 | |
| 6086797003 | G0 Phase | Cell is performing its normal functions, but has left the cell cycle and is not dividing. | 1 | |
| 6086797004 | S Phase | The synthesis phase of the cell cycle; the portion of interphase during which DNA is replicated. | 2 | |
| 6086797005 | G2 Phase | Last stage of interphase in which cell grows and performs its normal functions. Cell is tetraploid. | 3 | |
| 6086797006 | Interphase | Cell grows, performs its normal functions, and prepares for division; consists of G1, S, and G2 phases |  | 4 |
| 6086797008 | Align - Metaphase | Phase of mitosis in which spindle fibers help chromosomes line up on the midline of the cell. | 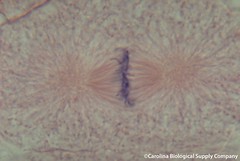 | 5 |
| 6086797009 | Separate - Anaphase | Phase of mitosis in which the chromosomes separate and move to opposite ends of the cell. |  | 6 |
| 6086797010 | Telophase | Phase of mitosis during which chromosomes uncoil, a nuclear envelope returns around the chromatin, and a nucleolus becomes visible in each daughter cell" |  | 7 |
| 6086797011 | Cytokinesis | At the end of telophase, actin fibers form an equator around the cell and contract, separating the cytoplasm into two daughter cells. |  | 8 |
| 6086797012 | Centriole | A paired cluster of microtubules near the nucleus in animal cells. This organelle organizes spindle fibers during mitosis. | 9 | |
| 6086797013 | Centromere | Region of a chromosome where the two sister chromatids attach to one another. Contains the kinetochore. | 10 | |
| 6086797014 | Kinetochore | A specialized region on the centromere that links each sister chromatid to the mitotic spindle. | 11 | |
| 6086797015 | Spindle Fibers | Made of microtubules that connect centrioles to kinetochores of chromosomes and that separate sister (mitosis) or homologous (meiosis) chromosomes during cell division | 12 | |
| 6086797016 | Chromosome | A threadlike, gene-carrying structure found in the nucleus. Each chromosome consists of one very long DNA molecule and associated proteins. | 13 | |
| 6086797017 | Chromatid | One of two identical "sister" parts of a duplicated chromosome. | 14 | |
| 6086797018 | Haploid | A cell with only one copy of each chromosome. | 15 | |
| 6086797019 | Diploid | A cell with two copies of each chromosome. | 16 | |
| 6086797022 | Cyclin-Dependent Kinase (CDK) | A group of protein kinases that are activated by the formation of a complex with a cyclin and are involved in the regulation of the cell cycle. Only active when bound to a cyclin. | 17 | |
| 6086797023 | Cyclin | A cellular protein that occurs in a cyclically fluctuating concentration and that plays an important role in regulating the cell cycle. | 18 | |
| 6086797026 | p53 | This tumor suppressor gene causes cell cycle arrest in G1, providing time for DNA repair. If repair is successful, cells re-enter the cycle. If unsuccessful, apoptosis. Damage to this protein can cause cancer. | 19 | |
| 6086797027 | Proto-oncogene | A normal cellular gene corresponding to an oncogene; a gene with a potential to cause cancer but that requires some alteration to become an oncogene. | 20 | |
| 6086797028 | Tumor Suppressor Gene | A gene whose protein products inhibit cell division, thereby preventing uncontrolled cell growth. Mutations in this gene can cause cancer. | 21 | |
| 6086797029 | Kinase | An enzyme that adds a phosphate group to a protein. Phosphorylation usually activates protein activity. | 22 | |
| 6086797030 | Phosphatase | An enzyme that removes a phosphate group from a protein. Phosphorylation usually activates protein activity. | 23 | |
| 6086840324 | G2 checkpoint | mistakes in DNA, proteins check that cell is large enough to divide | 24 | |
| 6086842997 | M checkpoint | (spindle assembly checkpoint) mitosis will not continue if chromosomes are not aligned properly | 25 |
