10 Cell Division (AP Biology) Flashcards
Terms : Hide Images [1]
| 8546474455 | cell division | The process in reproduction and growth by which a cell divides to form daughter cells. |  | 0 |
| 8546475781 | genome | all the DNA in one cell of an organism |  | 1 |
| 8546477512 | binary fission | A form of asexual reproduction in single-celled organisms by which one cell divides into two cells of the same size. |  | 2 |
| 8546478469 | somatic cell | Any cell in a multicellular organism except a sperm or egg or their precursors. |  | 3 |
| 8546480209 | germ cell | Reproductive cell that gives rise to sperm and egg | 4 | |
| 8546481907 | chromosome | one long continuous molecule of DNA (consists of numerous genes and regulatory information) |  | 5 |
| 8546485073 | chromatin | The complex of DNA and proteins that makes up eukaryotic chromosomes. |  | 6 |
| 8546490984 | sister chromatids | One half of a duplicated chromosome (identical); full sets of these are created during the S subphase of interphase. |  | 7 |
| 8546493337 | centromere | The region of the chromosome that holds the two sister chromatids together during mitosis. |  | 8 |
| 8546494041 | centriole | In animal cells, a cytoplasmic organelle that organizes the mitotic spindle fibers during cell reproductions. |  | 9 |
| 8546494961 | centrosome | A structure in animal cells containing centrioles from which the spindle fibers develop. |  | 10 |
| 8546495844 | cell cycle | Series of events that cells go through as they grow and divide. |  | 11 |
| 8546496570 | mitosis | Cell division in which the nucleus divides into nuclei containing the same number of chromosomes. |  | 12 |
| 8546497470 | cytokinesis | Division of the cytoplasm to form two separate daughter cells. |  | 13 |
| 8546499140 | S phase | The synthesis phase of the cell cycle; the portion of interphase during which DNA is replicated. |  | 14 |
| 8546499904 | G1 phase | The first gap, or growth phase, of the cell cycle, consisting of the portion of interphase before DNA synthesis begins. |  | 15 |
| 8546500348 | G2 phase | The second growth phase of the cell cycle, consisting of the portion of interphase after DNA synthesis occurs. |  | 16 |
| 8546500883 | interphase | Cell grows, performs its normal functions, and prepares for division; consists of G1, S, and G2 phases. | 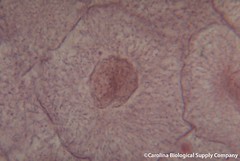 | 17 |
| 8546501485 | mitotic spindle | An assemblage of microtubules and associated proteins that is involved in the movements of chromosomes during mitosis. |  | 18 |
| 8546502682 | kinetochore microtubules | Connects the centrosome with the kinetochore in the centromere region of the chromosome. |  | 19 |
| 8546503213 | kinetochore | proteins that attach to the centromere of a chromosome during mitosis |  | 20 |
| 8546506904 | asters | Microtubules and fibers that radiate out from the centrioles. |  | 21 |
| 8546507348 | metaphase plate | Plane midway between the two poles of the cell where chromosomes line up during metaphase. (aka equator) |  | 22 |
| 8546508042 | cleavage furrow | The first sign of cleavage in an animal cell; a shallow groove in the cell surface near the old metaphase plate. |  | 23 |
| 8546508700 | cell plate | A double membrane across the midline of a dividing plant cell, between which the new cell wall forms during cytokinesis. |  | 24 |
| 8546512092 | density dependent inhibition | dependent inhibition The arrest of cell division that occurs when cells grown in a laboratory dish touch one another. |  | 25 |
| 8546512442 | growth factors | Regulatory proteins that ensure that the events of cell division occur in the proper sequence and at the correct rate. |  | 26 |
| 8546513974 | restriction point | G1 checkpoint; most important checkpoint; a go-ahead here usually leads to completing the cell cycle (through mitosis); a stop leads to the G0 phase |  | 27 |
| 8546514333 | Cdk (cyclin dependent kinases) | an enzyme that activates or inactivates other proteins by phosphorylating them (important at G1 and G2 checkpoints); to be active, these kinases must be joined to cyclin (cyclin fluctuates throughout the cell cycle) |  | 28 |
| 8546514797 | MPF | A cyclin-Cdk complex that causes the cell to move from interphase into mitosis. (think of it as 'mitosis promoting factor') |  | 29 |
| 8546830526 | tumor | a mass of abnormal cells within otherwise normal tissue (may be benign or malignant) |  | 30 |
| 8546515303 | cancer | Any malignant growth or tumor caused by abnormal and uncontrolled cell division. |  | 31 |
| 8546515784 | malignant tumor | mass of cells that is not self-limited in its growth, is capable of invading into adjacent tissues, and may be capable of spreading to distant tissues |  | 32 |
| 8546519129 | benign tumor | mass of cells that does not invade nearby tissue or spread to other parts of the body the way cancer can |  | 33 |
| 8546521904 | cleavage | The process of cytokinesis in animal cells, characterized by pinching of the plasma membrane |  | 34 |
| 8546523374 | allele | One of the alternative forms of a gene that governs a characteristic, such as hair color. |  | 35 |
| 8546523799 | alteration of generations | The alteration of two or more different forms in the life cycle of a plant or animal (e.g. gametophyte and sporophyte) |  | 36 |
| 8546528877 | gametophyte | Haploid, or gamete-producing, phase of an organism; makes haploid gametes by mitosis |  | 37 |
| 8546529601 | sporophyte | Diploid, or spore-producing, phase of an organism; Makes haploid spores by meiosis. |  | 38 |
| 8546532542 | haploid | an organism or cell having only one complete set of chromosomes (1n) |  | 39 |
| 8546533235 | diploid | an organism or cell having two sets of chromosomes or twice the haploid number (2n) |  | 40 |
| 8546533824 | triploid | A chromosomal mutation where an organism has three sets of chromosomes (3n) instead of two (2n) |  | 41 |
| 8546534244 | trisomy | 3 copies of a chromosome |  | 42 |
| 8546535488 | asexual reproduction | One parent produces a genetically identical offspring by mitosis or binary fission |  | 43 |
| 8546535968 | sexual reproduction | process by which cells from two different parents unite to produce the first cell of a new organism (offspring are diverse) |  | 44 |
| 8546537286 | autosomes | Chromosomes that are not directly involved in determining the sex of an individual. |  | 45 |
| 8546537926 | sex chromosomes | X and Y chromosomes (for people) | 46 | |
| 8546538421 | chiasmata | X-shaped regions where crossing over occurred. |  | 47 |
| 8546538714 | clone | An organism that is genetically identical to the organism from which it was produced |  | 48 |
| 8546541309 | crossing over | Nonsister chromatids exchanging DNA segments. (increases genetic variation) |  | 49 |
| 8546542412 | independent assortment | random distribution of homologous chromosomes during meiosis |  | 50 |
| 8546543272 | fertilization | Union of gametes. |  | 51 |
| 8546543273 | zygote | fertilized egg |  | 52 |
| 8546545166 | gamete | A haploid cell such as an egg or sperm that unite during sexual reproduction to produce a diploid zygote. |  | 53 |
| 8546546973 | gene | A segment of DNA on a chromosome that codes for a specific trait |  | 54 |
| 8546548115 | homologous chromosomes | Pair of chromosomes that are the same size/appearance and have the same genes (but have different variations or alleles for many genes); you get one of each from mom, the other from dad. |  | 55 |
| 8546552811 | karyotype | Photograph of chromosomes grouped in order and in pairs. |  | 56 |
| 8546552812 | life cycle | the sequence of stages leading from the adults of one generation to the adults of the next |  | 57 |
| 8546554831 | locus | The specific site of a particular gene on its chromosome. |  | 58 |
| 8546555590 | nonsister chromatids | the chromatids of the homologous chromosome (they may contain different alleles). |  | 59 |
| 8546568622 | recombinant chromosome | A chromosome that carries genes from each parent (crossing over has occurred). |  | 60 |
| 8546573451 | spore | in plants/algae - a haploid cell that can grow into a multi-cellular haploid individual (gametophyte); in fungi - a haploid cell that produces a mycelium |  | 61 |
| 8546595041 | synapsis | Homologous chromosomes pair up, aligned gene by gene; allows matching-up of homologous pairs prior to their segregation, and possible chromosomal crossover between them. |  | 62 |
| 8546596961 | tetrad | structure containing 4 chromatids (homologous chromosome pair) that forms during meiosis |  | 63 |
| 8546600290 | variation | Any difference between individuals of the same species. |  | 64 |
| 8546674568 | G0 phase (the '0' should be a subscript) | a nondividing state (not really in the cell cycle anymore) | 65 | |
| 8546793786 | metastasis | the spread of cancer cells to locations distant from their original site |  | 66 |
