AP World History Chapter 8 Vocabulary Flashcards
Terms : Hide Images [1]
| 6245971615 | bushido | The "way of the warrior," referring to the military virtues of the Japanese samurai, including bravery, loyalty, and an emphasis on death over surrender. (pron. boo-SHEE-doh) |  | 0 |
| 6245971616 | Chinese Buddhism | Buddhism was China's only large-scale cultural borrowing before the twentieth century; Buddhism entered China from India in the first and second centuries C.E. but only became popular in 300-800 C.E. through a series of cultural accommodations. At first supported by the state, Buddhism suffered persecution during the ninth century but continued to play a role in Chinese society. |  | 1 |
| 6245971617 | chu nom | A variation of Chinese writing developed in Vietnam that became the basis for an independent national literature; "southern script." (pron. choo nom) |  | 2 |
| 6245971618 | Song economic revolution | A major economic quickening that took place in China under the Song dynasty (960-1279); marked by rapid population growth, urbanization, economic specialization, the development of an immense network of internal waterways, and a great increase in industrial production and innovation. (pron. soong) |  | 3 |
| 6245971619 | Emperor Wendi | Sui emperor (r. 581-604) who particularly patronized Buddhism. (pron. WEN-dee) |  | 4 |
| 6245971620 | foot binding | Chinese practice of tightly wrapping girls' feet to keep them small, begun in the Tang dynasty; an emphasis on small size and delicacy was central to views of female beauty. | 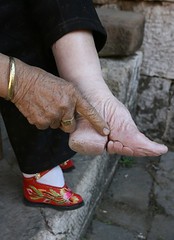 | 5 |
| 6245971621 | hangul | A phonetic alphabet developed in Korea in the fifteenth century (pron. HAHN-gool) | 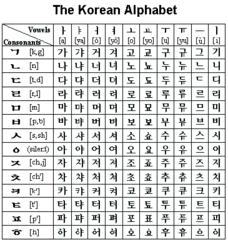 | 6 |
| 6245971622 | Hangzhou | China's capital during the Song dynasty, with a population of more than a million people. (pron. hong-joe) |  | 7 |
| 6245971623 | Khitan/ Jurchen people | A nomadic people who established a state that included parts of northern China (907-1125). (pron. kee-tahn); A nomadic people who established a state that included parts of northern China (1115-1234). |  | 8 |
| 6245971624 | Shotoku Taishi | Japanese statesman (572-622) who launched the drive to make Japan into a centralized bureaucratic state modeled on China; he is best known for the Seventeen Article Constitution, which lays out the principles of this reform. (pron. show-TOE-koo tie-EESH-ah) |  | 9 |
| 6245971625 | Silla dynasty | The first ruling dynasty to bring a measure of political unity to the Korean peninsula (688-900). (pron. SILL-ah or SHILL-ah) |  | 10 |
| 6245971626 | Sui dynasty | Ruling dynasty of China (581-618) that effectively reunited the country after several centuries of political fragmentation. (pron. sway) |  | 11 |
| 6245971627 | Tang dynasty | Ruling dynasty of China from 618 to 907; noted for its openness to foreign cultural influences. (pron. tahng) |  | 12 |
| 6245971628 | tribute system | Chinese method of dealing with foreign lands and peoples that assumed the subordination of all non-Chinese authorities and required the payment of tribute—produce of value from their countries—to the Chinese emperor (although the Chinese gifts given in return were often much more valuable). |  | 13 |
| 6245971629 | Xiongnu | Major nomadic confederacy that was established ca. 200 B.C.E. and eventually reached from Manchuria to Central Asia. (pron. SHE-OONG-noo) |  | 14 |
