AP Economics Flashcards
Terms : Hide Images [1]
| 14176023689 | Economics | The study of production, consumption, and transfer of wealth Ex: The study of the stock market | 0 | |
| 14176023690 | Opportunity Cost | The loss of potential gain from an alternative decision Ex: If you spend your time watching a movie instead of studying, the opportunity cost is the good grade that you could've got from studying | 1 | |
| 14176023691 | Marginal Analysis | The identification of both benefits and costs of everyday decisions to maximize profit Ex: A farm might use marginal analysis to determine the potential benefits of an increase in crop production | 2 | |
| 14176023692 | Macroeconomics | Larger-scale economics concerned with the nation as a whole Ex: Unemployment | 3 | |
| 14176023693 | Microeconomics | Smaller-scale economics concerned with individuals, groups, and companies Ex: Supply and Demand | 4 | |
| 14176023694 | Positive Economics | Part of economics that is objective and fact-based Ex: "The debt has increased in the United States" | 5 | |
| 14176023695 | Normative Economics | Part of economics that is subjective and value-based Ex: "The price of eggs should be $5 a dozen to help farmers with their living needs and to maintain their farms" | 6 | |
| 14176023696 | Scarcity | Unlimited human wants with limited resources available Ex: Overhunting of a species can lead to the scarcity of those animals | 7 | |
| 14176023697 | Economic Resources | Goods/Services available to individuals to produce the products they desire Ex: Labor (Human Resources) | 8 | |
| 14176023698 | Land | Natural Resources Ex: Oil | 9 | |
| 14176023699 | Labor | Human Resources Ex: Factory Worker | 10 | |
| 14176023700 | Capital | Goods used to produce products or services Ex: Machines | 11 | |
| 14176023701 | Entrepreneurial Ability | The human resource that combines the other resources to produce a product, innovates, and bear risks Ex: Mark Zuckerberg had the entrepreneurial ability to create Facebook | 12 | |
| 14176023702 | Consumer Goods | Products produced for the consumption by the consumer Ex: Clothing | 13 | |
| 14176023703 | Capital Goods | Goods that are utilized for the production of other goods Ex: Machines | 14 | |
| 14176023704 | Production Possibilities Curve | Curve that showcases the maximum possible output of two goods or services Ex: A farmer needs to reduce the amount of crops and they may use the product possibilities curve to determine the best possible combination of crops to grow |  | 15 |
| 14176023705 | Law of Increasing Opportunity Cost | Law that states that if production increases the opportunity cost of additional units also increases Ex: More pizzas means fewer industrial robots. The number of units of industrial robots that must be given up to obtain another unit of pizzas is the opportunity cost of that unit of pizzas | 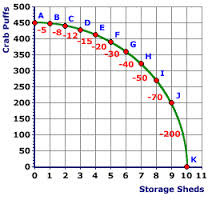 | 16 |
| 14176023706 | Costs | The combination of gains and losses that come from a course of action Ex: Cost of Attending College | 17 | |
| 14176023707 | Economic Growth | The increase in the production of goods and services per head of the population over time Ex: The increase in resources, improvements, and advancements move the PPC outward and to the right, allowing the economy to have larger quantities of both types of goods |  | 18 |
| 14176023708 | Command Economy | Economic system in which the government has control over economic decisions Ex: Cuban Economy | 19 | |
| 14176023709 | Market Economy | Economic system in which individuals and businesses guide economic decisions and pricing of goods Ex: United States Economy | 20 | |
| 14176023710 | Market | Location where buyers and sellers exchange goods/services Ex: The Internet |  | 21 |
| 14176023711 | Specialization | Nation/Individual that focuses their productive efforts on a limited variety of goods Ex: Assembly Line | 22 | |
| 14176023712 | Consumer Sovereignty | The system where the consumer's preference guides the output of products based on the goods/services that are purchased Ex: If consumers purchase diet soda, then companies will produce diet soda to go along with the consumer's preference | 23 | |
| 14176023713 | Invisible Hand | Metaphorical market force in which individual self-interested actions benefit the economic society Ex: When an individual buys a latte and a muffin it benefits both the seller and the production market, and therefore the economic society | 24 | |
| 14176023714 | Circular Flow Diagram | Model that showcases the monetary transactions in an economy Ex: Households may supply resources to firms so that firms can make products that households need and consume |  | 25 |
| 14176023715 | Resource Market | Market in which businesses can go and purchase resources to produce goods and services Ex: Labor needed by businesses to produce goods |  | 26 |
| 14176023716 | Product Market | Market in which the produced goods and services are offered to consumers Ex: Macys |  | 27 |
| 14176023717 | Demand | Consumer's desire for products or services Ex: When the price of a product goes down because of the decreased supply, the demand will then increase |  | 28 |
| 14176023718 | Law of Demand | Law that states that if the price of a good or service increases the demand for that good or service will decrease and vice versa Ex: When the coffee at Starbucks raises from $1.50 to $2, the quantity of coffee demanded by consumers will decrease | 29 | |
| 14176023719 | Diminishing Marginal Utility | Law that states that as a person increases the consumption of a product the marginal utility of each additional unit of that product decreases Ex: Buffets-Style Restaurants | 30 | |
| 14176023720 | Income Effect | Change in consumption based on the change in real income Ex: If an individual's income increases their desire for goods and services, also known as their consumption, increases | 31 | |
| 14176023721 | Determinants of Demand | The factors that determine the quantity that is demanded of the individual Ex: Price of the Commodity | 32 | |
| 14176023722 | Normal Goods | Goods for which demand increases when income increases Ex: Organic Groceries | 33 | |
| 14176023723 | Inferior Goods | Goods for which demand decreases when income increases Ex: Cheaper Cars | 34 | |
| 14176023724 | Substitute Good | Good with a positive cross elasticity of demand Ex: Oranges and Apples | 35 | |
| 14176023725 | Complementary Good | Good with a negative cross elasticity of demand Ex: Peanut Butter and Jelly | 36 | |
| 14176023726 | Supply | The amount of goods or services available to the consumer Ex: When supply of a product goes up, the price goes down and the demand for that product increases |  | 37 |
| 14176023727 | Determinants of Supply | The factors that determine the quantity of a product of service available Ex: Number of Sellers in the Market | 38 | |
| 14176023728 | Equilibrium Price | The market price in which the quantity of goods available is equal to the quantity of goods demanded Ex: Muffins are sold for $3 and 25 were demanded and then supplied, the EP is $3 |  | 39 |
| 14176023729 | Equilibrium Quantity | The quantity in which both the amount demanded and the amount supplied is equal Ex: Muffins are sold for $3 and 25 were demanded and then supplied, the EQ is 25 |  | 40 |
| 14176023730 | Surplus | More supply than demand in the market Ex: Muffins were sold for $6 and only 5 were demanded when 50 were supplied, the surplus is 45 |  | 41 |
| 14176023731 | Shortage | More demand than supply in the market Ex: Muffins were sold for $1 and 50 were demanded when only 5 were supplied, the shortage is 45 |  | 42 |
| 14176023732 | Price Floor | The limit on how low a price can be charged for a product Ex: Minimum Wage Laws |  | 43 |
| 14176023733 | Price Ceiling | The limit on how high a price can be charged for a product Ex: City-imposed limits for landlords on the price of apartment rents |  | 44 |
| 14176023734 | Productive Efficiency | Least costly production methods to produce desired goods and services Ex: Society may produce corn at the lowest achievable per-unit cost with expending the least-valued combination of resources to produce that product | 45 | |
| 14176023735 | Allocative Efficiency | Resources that are utilized for the production of both goods and services Ex: Society may want diamonds to be utilized for jewelry rather than being crushed up and utilized as an additive to give concrete sparkle | 46 | |
| 14176023736 | Total Revenue | The total receipts from sales of a given quantity of goods or services Ex: If a company sells 100 toys for $50 each, the total revenue is $5,000 | 47 | |
| 14176023737 | Expenditures | Payment for goods/services Ex: Property | 48 | |
| 14176023738 | Economic Profit | Economic difference between the output and the input Ex: If economic costs are $96,000 and revenue is $120,000 the economic profit would be $24,000 | 49 |
