Campbell Biology Chapter 42 Flashcards
Terms : Hide Images [1]
| 15376791392 | Gastrovascular Cavity | Functions in both digestion and distribution of substances throughout the body | 0 | |
| 15376791393 | Rate of diffusion | Proportional to the square of the distance | 1 | |
| 15376791394 | Heart | Muscular pump | 2 | |
| 15376791395 | Open and Closed Circulatory Systems | Both systems have three basic components: A circulatory fluid (blood or hemolymph) A set of tubes (blood vessels) A muscular pump (the heart) | 3 | |
| 15376791396 | Open Circulatory System | Hemolymph bathes the organs directly. No distinction between blood and interstitial fluid. | 4 | |
| 15376791397 | Closed Circulatory System | Blood is confined to vessels and is distinct from the interstitial fluid. Closed systems are more efficient at transporting circulatory fluids to tissues and cells. | 5 | |
| 15376791398 | Cardiovascular System | 3 main types of blood vessels: arteries, veins, and capillaries. | 6 | |
| 15376791399 | Arteries | Blood from heart to organs | 7 | |
| 15376791400 | Arterioles | Small arteries that connect capillaries to arteries. | 8 | |
| 15376791401 | Venules | Small veins that connect capillaries to veins ( blood back to heart). | 9 | |
| 15376791402 | Capillary beds | Network of capillaries | 10 | |
| 15376791403 | Vertebrate Hearts | Contain 2 or more chambers: Atrium and Ventricle | 11 | |
| 15376791404 | Atrium | Blood enters through the atrium. | 12 | |
| 15376791405 | Ventricle | Blood is pumped out through the ventricle. | 13 | |
| 15376791406 | Single Circulation | Blood leaving the heart passes through two capillary beds before returning. Found in bony fishes, rays and sharks. |  | 14 |
| 15376791407 | Double Circulation | Oxygen-poor and oxygen-rich blood are pumped separately from the right and left sides of the heart. Found in reptiles, amphibians and mammals. |  | 15 |
| 15376791408 | Pulmonary Circuit | Deoxygenated blood leaves the heart, goes to the lungs, and then re-enters the heart. |  | 16 |
| 15376791409 | Pulmocutaneous Circuit | Deoxygenated blood leaves the heart, goes to the lungs and skin and then re-enters the heart. ( pulmonary circuit if only lungs) |  | 17 |
| 15376791410 | Systemic Circuit | Part of the cardiovascular system which carries oxygenated blood away from the heart to the body, and returns deoxygenated blood back to the heart. | 18 | |
| 15376791411 | Amphibian Hearts | 3 Chambered Heart: 2 atria, 1 ventricle | 19 | |
| 15376791412 | Reptile Hearts | Turtles, snakes, and lizards have a 3-chambered heart: 2 atria and 1 ventricle. Crocodilians have an additional septum which divides the ventricle. | 20 | |
| 15376791413 | Mammal and Bird Hearts | Endotherms have a 4-chambered heart with 2 atria and 2 ventricles. | 21 | |
| 15376791483 | Mammalian Circulation |  | 22 | |
| 15376791484 | Mammalian Heart |  | 23 | |
| 15376791414 | Cardiac Cycle | The rhythmic cycle in which the heart contracts and relaxes. |  | 24 |
| 15376791415 | Systole | Phase of the cardiac cycle for contraction or pumping of the heart. |  | 25 |
| 15376791416 | Diastole | Phase of the cardiac cycle for relaxation, or filling of the heart. |  | 26 |
| 15376791417 | Cardiac output | Volume of blood each ventricle pumps per minute | 27 | |
| 15376791418 | Heart rate | Rate of contraction | 28 | |
| 15376791419 | Stroke volume | The volume of blood pumped from a ventricle of the heart in one beat | 29 | |
| 15376791420 | Atrioventricular Valves | Separate each atrium and ventricle to prevent back flow of blood into the heart. | 30 | |
| 15376791421 | Semilunar Valves | Control blood flow to the aorta and the pulmonary artery | 31 | |
| 15376791422 | "lup dup" | "Lup" sound of blood recoiling against AV valves. "Dup" sound of blood recoiling against Semilunar valves. | 32 | |
| 15376791423 | Heart Murmur | Caused by back flow of blood through a defective valve. | 33 | |
| 15376791424 | Sinoatrial Node | Pacemaker; sets the rate and timing at which cardiac muscle cells contract. |  | 34 |
| 15376791425 | Atrioventricular Node | Impulses are delayed and then travel to the Purkinje fibers that make the ventricles contract. |  | 35 |
| 15376791426 | Electrocardiogram | Records impulses that travel during the cardiac cycle. (ECG or EKG) |  | 36 |
| 15376791427 | Endothelium | The epithelial layer that lines blood vessels. Capillaries have endothelium and a basement membrane. Arteries and veins have an endothelium, smooth muscle, and connective tissue | 37 | |
| 15376791428 | Basal lamina | Extra cellular layer surrounding capillaries | 38 | |
| 15376791485 | Arteries and Veins |  | 39 | |
| 15376791429 | Systolic Pressure | The pressure in the arteries during ventricular systole. | 40 | |
| 15376791430 | Diastolic Pressure | The pressure in the arteries during diastole. | 41 | |
| 15376791431 | Pulse | The rhythmic bulging of artery walls with each heartbeat. | 42 | |
| 15376791432 | Vasoconstriction | The contraction of smooth muscle in arteriole walls. | 43 | |
| 15376791433 | Vasodilation | The relaxation of smooth muscles in the arterioles. | 44 | |
| 15376791434 | Blood Pressure | Generally measured using an artery in the arm at the same height as the heart. (120/80). Systole/ diastole | 45 | |
| 15376791435 | precapillary sphincters | smooth muscle cells that guard the entrance to capillaries | 46 | |
| 15376791436 | Lymphatic System | Returns fluid that leaks out in the capillary beds. The lymphatic system drains into veins in the neck | 47 | |
| 15376791437 | Lymph | Fluid lost by capillaries, similar to interstitial fluid | 48 | |
| 15376791438 | Lymph Nodes | Organs that filter lymph and play an important role in the body's defense. | 49 | |
| 15376791439 | Plasma | Liquid matrix of blood. 45% of the blood volume. Blood plasma is 90% water. | 50 | |
| 15376791440 | Erythrocytes | Red blood cells. Erythrocytes transport oxygen. Contains hemoglobin. | 51 | |
| 15376791441 | Leukocytes | White blood cells. Monocytes, neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils, and lymphocytes. | 52 | |
| 15376791442 | Leukocytes in Defense | Phagocytizing bacteria and debris or by producing antibodies. | 53 | |
| 15376791443 | Platelets | Fragments of cells that are involved in clotting. | 54 | |
| 15376791444 | Hemoglobin | An iron-containing protein in red blood cells that reversibly binds oxygen. | 55 | |
| 15376791445 | Sickle cell disease | Abnormal form of hemoglobin polymerizes into aggregates | 56 | |
| 15376791446 | Blood Clotting | Fibrinogen converts into fibrin forming the clot. | 57 | |
| 15376791447 | Erythropoietin | stimulates generation of more erythrocytes | 58 | |
| 15376791448 | Anemia | a lower than normal number of erythrocytes in the blood | 59 | |
| 15376791449 | Thrombus | Blood clot formed within a blood vessel. | 60 | |
| 15376791450 | Cardiovascular Disease | Accounts for more than half the deaths in the United States. | 61 | |
| 15376791451 | Atherosclerosis | The buildup of plaque deposits within arteries. |  | 62 |
| 15376791452 | Heart Attack | The death of cardiac muscle tissue resulting from blockage of one or more coronary arteries. Myocardial infarction |  | 63 |
| 15376791453 | Stroke | The death of nervous tissue in the brain, usually resulting from rupture or blockage of arteries in the head. | 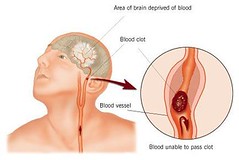 | 64 |
| 15376791454 | Low-density Lipoproteins | Associated with plaque formation; "bad cholesterol". | 65 | |
| 15376791455 | High-density Lipoproteins | Reduce the deposition of cholesterol; "good cholesterol". | 66 | |
| 15376791456 | Hypertension | High blood pressure, promotes atherosclerosis and increases the risk of heart attack and stroke. | 67 | |
| 15376791457 | Gas Exchange | Supplies oxygen for cellular respiration and disposes of carbon dioxide. | 68 | |
| 15376791458 | Partial Pressure | Pressure exerted by a particular gas in a mixture of gases. | 69 | |
| 15376791459 | Respiratory Media | In a given volume, there is less oxygen available in water than in air. | 70 | |
| 15376791460 | Respiratory Surfaces | Gas exchange across respiratory surfaces takes place by diffusion. Respiratory surfaces may include: the outer surface, skin, gills, trachea, and lungs. | 71 | |
| 15376791461 | Ventilation | Moves the respiratory medium over the respiratory surface. | 72 | |
| 15376791462 | Countercurrent Exchange | Used by fish; blood flows in the opposite direction to water passing over the gills |  | 73 |
| 15376791463 | Tracheal System | Used by insects; consists of tiny branching tubes that penetrate the body. Tracheal tubes supply oxygen directly to the cells. |  | 74 |
| 15376791464 | Lungs | respiratory organs | 75 | |
| 15376791465 | Larynx | upper part of the respiratory tract | 76 | |
| 15376791466 | Trachea | windpipe | 77 | |
| 15376791467 | Bronchi | two short branches located at the lower end of the trachea that carry air into the lungs. | 78 | |
| 15376791468 | Bronchioles | smallest branches of the bronchi | 79 | |
| 15376791469 | Alveoli | Terminal air sacs that constitute the gas exchange surface of the lungs. | 80 | |
| 15376791470 | Surfacants | Secretions that cover alveoli. Keeps alveoli from collapsing in on themselves. | 81 | |
| 15376791471 | Positive Pressure Breathing | Used by amphibians; Gulping of air forces air down the trachea. | 82 | |
| 15376791472 | Negative Pressure Breathing | Used by mammals; pulls air into the lungs via diaphragm | 83 | |
| 15376791473 | Tidal Volume | The volume of air inhaled with each breath. | 84 | |
| 15376791474 | vital capacity | tidal volume during maximal inhalation and exhalation | 85 | |
| 15376791475 | residual volume | Amount of air remaining in the lungs after a forced exhalation | 86 | |
| 15376791476 | Respiration in Birds | Air passes through the lungs in one direction only. Every exhalation completely renews the air in the lungs. | 87 | |
| 15376791477 | Respiratory Pigments | Proteins that transport oxygen, greatly increase the amount of oxygen that blood can carry. | 88 | |
| 15376791478 | Hemocyanin | Used by arthropods and some mollusks; respiratory pigments utilizing copper as the oxygen-binding component. | 89 | |
| 15376791479 | Hemoglobin | Respiratory pigment utilizing iron as the oxygen-binding component. A single hemoglobin molecule can carry four molecules of O2. Hemoglobin also helps transport CO2 and assists in buffering |  | 90 |
| 15376791480 | Bohr shift | CO2 produced during cellular respiration lowers blood pH and decreases the affinity of hemoglobin for O2. |  | 91 |
| 15376791481 | breathing control centers | Medulla oblongata | 92 | |
| 15376791482 | Myglobin | Oxygen storing protein | 93 |
