| 15053233446 | Anterior | toward the front of the body; in front of | 0 | |
| 15053233447 | Posterior | toward the back of the body | 1 | |
| 15053233448 | Distal | farther from the origin of a body part or the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk | 2 | |
| 15053233449 | Lateral | Away from the midline of the body | 3 | |
| 15053233450 | Medial | Toward the midline of the body | 4 | |
| 15053233451 | Frontal | pertaining to the forehead | 5 | |
| 15053233452 | Proximal | Closer to the origin of the body part or the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk | 6 | |
| 15053233453 | sagittal plane | a vertical plane that divides the body into right and left parts | 7 | |
| 15053233454 | Superior | Higher on the body, nearer to the head | 8 | |
| 15053233455 | Transverse plane | line that divides the body into upper and lower sections | 9 | |
| 15053233456 | oblique plane | passes through the body at an angle | 10 | |
| 15053233457 | inferior plane | everything below the transverse line (below the waist). Opposite of superior plane. | 11 | |
| 15053233458 | Abdominal pelvic cavity | Inferior subdivision below diaphragm | 12 | |
| 15053233459 | anatomical position | To stand erect with arms at the sides and palms of the hands turned forward | 13 | |
| 15053233460 | Hiatil hernia | upper part of stomach bulges through opening in diaphragm. (obesity, smoking) | 14 | |
| 15053233461 | situs inversus | reversed position of organs | 15 | |
| 15053233462 | integumentary system consists of? | skin, hair, nails, cutaneous sense organs (smell,touch,see,hear) | 16 | |
| 15053233463 | skeletal system consists of? | bones, cartilage, ligaments, joints, tendons | 17 | |
| 15053233464 | Muscular System consists of? | Muscles attached to the skeleton | 18 | |
| 15053233465 | Nervous system consists of? | brain, spinal cord, nerves, and sensory receptors | 19 | |
| 15053233466 | Endocrine system consists of? | pituitary, thyroid, parathyroids, adrenals, thymus, pancreas, pineal, ovaries (female), and testes (male) | 20 | |
| 15053233467 | cardiovascular system consists of? | heart and blood vessels | 21 | |
| 15053233468 | Lymphatic system consists of? | lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, spleen, and thymus | 22 | |
| 15053233469 | Respiratory system consists of? | nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and lungs | 23 | |
| 15053233470 | Digestive system consists of? | oral cavity, esophagus, stomach small and large intestines, rectum, and accessory organs (liver, salivary glands, pancreas, etc.) | 24 | |
| 15053233471 | Urinary system consists of? | kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, urethra | 25 | |
| 15053233472 | Reproductive system consists of? | Testes, penis, ovaries, vagina, and breasts | 26 | |
| 15053233473 | function of integumentary system | excretes salts and urea, produces vitamin D, aids in body regulation, protects internal organs | 27 | |
| 15053233474 | Function of skeletal system | -body support and protection of internal organs -provides levers for muscular action -cavities provide a site for blood cell formation | 28 | |
| 15053233475 | function of muscular system | Allows manipulation of the environment, locomotion, and facial expression. Maintains posture, and produces heat. | 29 | |
| 15053233476 | function of nervous system | -allows body to detect changes in its internal and external environment and to respond to such information by activating appropriate muscles or glands -helps maintain homeostasis of the body via rapid transmission of electrical signals | 30 | |
| 15053233477 | function of cardiovascular system | transport system that carries blood containing oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients, waste,ions,and hormones. antibodies and other protein molecules in the blood protect the body. | 31 | |
| 15053233478 | function of lymphatic system | Defense against infection and disease houses lymphocytes that act via the immune response to protect body from foreign substances | 32 | |
| 15053233479 | function of respiratory system | supply the body and blood with oxygen and dispose of carbon dioxide contributes to acid-base balance of blood | 33 | |
| 15053233480 | function of digestive system | break down and absorbs nutrients from food; removes waste; maintains water balance | 34 | |
| 15053233481 | function of urinary system | elimination of excess water, salts, and waste products; control of pH | 35 | |
| 15053233482 | function of reproductive system | Males: produce and maintain sperm cells, transfer sperm cells into female reproductive tract. Females: produce and maintain egg cells, receive sperm cells, support development of embryo, and function in birth process. | 36 | |
| 15053233483 | serous membrane function | Secretes a watery fluid that allows organs to glide over nearby structures and reduces friction | 37 | |
| 15053233484 | thyroid cartilage | A firm prominence of cartilage that forms the upper part of the larynx; the Adam's apple. |  | 38 |
| 15053233485 | thyroid gland | endocrine gland that surrounds the trachea in the neck |  | 39 |
| 15053233486 | function of brain | control center for the entire nervous system | 40 | |
| 15053233487 | function of diaphragm | separates the digestive cavity from the respiratory cavity, contracts and relaxes to help the lungs inflate and deflate | 41 | |
| 15053233488 | function of spleen | Immune surveillance and response in BLOOD. Collects antigens in blood and also degrades old Red Blood Cells and damaged Red Blood Cells. | 42 | |
| 15053233489 | function of large intestine | absorption of water | 43 | |
| 15053233490 | function of small intestine | digestion and absorption of nutrients | 44 | |
| 15053233491 | Function of visceral mass | holds internal organs | 45 | |
| 15053233492 | Trachea (windpipe) | transports air to and from lungs |  | 46 |
| 15053233493 | Cell System | The cell is the basic unit of living organisms & the simplest living unit of life. Living organisms are composed of cells that have the following common characteristics: - Have a membrane that regulates the flow of nutrients & water that enter & exit the cell -contain the genetic material (DNA) that allows for reproduction -Require a supply of energy -Contain basic chemicals to make metabolic decisions for survival -Reproduce & are the result of reproduction | 47 | |
| 15053233494 | tissue system | One or more tissues organized into a functional unit connecting the organs of a plant. | 48 | |
| 15053233495 | tissue | A group of similar cells that perform the same function. | 49 | |
| 15053233496 | Organ | group of tissues that work together to perform closely related functions | 50 | |
| 15053233497 | organ system | A group of organs that work together in performing vital body functions. | 51 | |
| 15053233498 | Ventral | Toward the belly | 52 | |
| 15053233499 | Contralateral | on the opposite side of the body | 53 | |
| 15053233500 | Ipsilateral | on the same side of the body | 54 | |
| 15053233501 | superficial | near the surface of the body | 55 | |
| 15053233502 | deep | Away from the body surface; more internal | 56 | |
| 15053233503 | Dorsal cavity contains | includes the cranial and spinal cavities. | 57 | |
| 15053233504 | cranial cavity contains | the brain | 58 | |
| 15053233505 | vertebral cavity contains | vertebrae, spinal cord | 59 | |
| 15053233506 | ventral cavity contains | thoracic cavity and abdominopelvic cavity | 60 | |
| 15053233507 | thoracic cavity contains | contains heart and lungs | 61 | |
| 15053233508 | mediastinum cavity contains | area between the lungs containing the heart, aorta, venae cavae, esophagus, and trachea | 62 | |
| 15053233509 | plueral cavity contains | the lungs | 63 | |
| 15053233510 | Pericardial cavity contains | the heart | 64 | |
| 15053233511 | abdominal cavity contains | digestive organs | 65 | |
| 15053233512 | pelvic cavity contains | urinary bladder, reproductive organs, rectum | 66 | |
| 15053233513 | peritoneum serous membrane | Membrane surrounding the organs in the abdomen. (Abdominal cavity) | 67 | |
| 15053233514 | parietal peritoneum | portion that lines the abdominal and pelvic cavities | 68 | |
| 15053233515 | visceral peritoneum | covers the external surfaces of most abdominal organs, including the intestinal tract. | 69 | |
| 15053233516 | plueral membrane | Serous membrane that surrounds the lungs and lines the thoracic cavity | 70 | |
| 15053233517 | parietal pluera | lines the walls of the thoracic cavity; fluids are made that adhere the lung pleura to this for a very tight fit | 71 | |
| 15053233518 | visceral pluera | inner layer which covers the external surface of the lungs | 72 | |
| 15053233519 | pericardium membrane | surrounds the heart | 73 | |
| 15053233520 | parietal pericadrium | The outer layer of the pericardium which is a conical sac of fibrous tissue that surrounds the heart and the roots of the great blood vessels. | 74 | |
| 15053233521 | plane | A flat surface on which a straight line joining any two points would wholly lie. | 75 | |
| 15053233522 | visceral pericardium | layer closest to the heart | 76 | |
| 15053233523 | adominopelvic quadrants | right upper, left upper, right lower, left lower |  | 77 |
| 15053233524 | abdominopelvic regions | nine specific anatomic areas of the abdominopelvic cavity | 78 | |
| 15053233525 | left hypochondriac region contains | stomach, liver (tip), left kidney, spleen |  | 79 |
| 15053233526 | right hypochondriac contains | Liver, gall bladder, small intestine, ascending colon, transverse colon, right kidney | 80 | |
| 15053233527 | epigastric region contains | Parts of the right and left lobes of the liver, a large portion of the stomach. | 81 | |
| 15053233528 | right lumbar region contains | liver (tip), small intestines, ascending colon, right kidney | 82 | |
| 15053233529 | left lumbar region contains | descending colon of large intestine | 83 | |
| 15053233530 | umbilical region contains | A portion of the transverse colon and loops of the small intestine | 84 | |
| 15053233531 | right lilac region contains | appendix, cecum, and the right iliac fossa | 85 | |
| 15053233532 | left lilac region contains | descending colon, the sigmoid colon, and the right illiac fossa | 86 | |
| 15053233533 | HYPOGASTRIC REGION | contains the organs around the pubic bone. These include bladder, part of the sigmoid colon, the anus, and many organs of the reproductive system, such as the uterus and ovaries in females and the prostate in males. | 87 | |
| 15053233534 | Cephalic | pertaining to the head | 88 | |
| 15053233535 | Orbital | eye cavity | 89 | |
| 15053233536 | Nasal | nose area | 90 | |
| 15053233537 | Buccal | cheek area | 91 | |
| 15053233538 | oral | pertaining to the mouth | 92 | |
| 15053233539 | mental | chin | 93 | |
| 15053233540 | Cervical | neck region | 94 | |
| 15053233541 | thoracic | chest region | 95 | |
| 15053233542 | sternal | sternum | 96 | |
| 15053233543 | axillary | armpit area | 97 | |
| 15053233544 | Axial | Relating to head, neck, and trunk | 98 | |
| 15053233545 | appendicular | Relating to limbs and their attachments to the axis | 99 | |
| 15053233546 | axis of the body | head, neck, trunk | 100 | |
| 15053233547 | Mammary | breast region | 101 | |
| 15053233548 | pelvic | pelvis region | 102 | |
| 15053233549 | Pubic | genital region | 103 | |
| 15053233550 | upper limb | humerus, radius, ulna, carpals, metacarpals, phalanges | 104 | |
| 15053233551 | Acromial | top of shoulder | 105 | |
| 15053233552 | brachial | upper arm | 106 | |
| 15053233553 | Antecubital | anterior surface of elbow | 107 | |
| 15053233554 | olecranal | posterior of elbow | 108 | |
| 15053233555 | carpal | wrist | 109 | |
| 15053233556 | manus | pertaining to the hand | 110 | |
| 15053233557 | cephalic | pertaining to the head | 111 | |
| 15053233558 | patellar | front of knee | 112 | |
| 15053233559 | Brachial | upper arm | 113 | |
| 15053233560 | Olecranal | back of elbow | 114 | |
| 15053233561 | Antebrachial | pertaining to the forearm | 115 | |
| 15053233562 | palmar | palm of hand | 116 | |
| 15053233563 | Pollex | thumb | 117 | |
| 15053233564 | digital | fingers, toes | 118 | |
| 15053233565 | lower limb | leg | 119 | |
| 15053233566 | Coxal | hip | 120 | |
| 15053233567 | Femoral | thigh | 121 | |
| 15053233568 | Popiteal | back of knee | 122 | |
| 15053233569 | Crural | shin | 123 | |
| 15053233570 | Sural | calf | 124 | |
| 15053233571 | peroneal | pertaining to the fibula | 125 | |
| 15053233572 | Fibular | lateral part of leg | 126 | |
| 15053233573 | pedal | foot | 127 | |
| 15053233574 | Torsal | ankle region | 128 | |
| 15053233575 | Calcaneal | heel | 129 | |
| 15053233576 | plantar | sole of foot | 130 | |
| 15053233577 | hallux | big toe | 131 | |
| 15053233578 | otic | ear | 132 | |
| 15053233579 | occipital | base of skull | 133 | |
| 15053233580 | Scapular | shoulder blade region | 134 | |
| 15053233581 | veterbral | spine | 135 | |
| 15053233582 | Lumbar | area of back between ribs and hips | 136 | |
| 15053233583 | Sacral | area between hips | 137 | |
| 15053233584 | Gluteal | buttock | 138 | |
| 15053233585 | Perineal | region between the anus and the external reproductive organs | 139 | |
| 15053233586 | base | The bottom of the microscope, used for support |  | 140 |
| 15053233587 | substage light | Located in the base. The light from the lamp passes directly upward through the microscope. |  | 141 |
| 15053233588 | light control | adjusts the brightness of the light source |  | 142 |
| 15053233589 | stage | Supports the slide being viewed |  | 143 |
| 15053233590 | mechanical stage | holds the slide in position for viewing and has two adjustable knobs that control the precise movement of the slide |  | 144 |
| 15053233591 | condenser | focuses light through the specimen |  | 145 |
| 15053233592 | iris diaphragm lever | arm attached to the base of the condenser that regulates the amount of light passing through the condenser |  | 146 |
| 15053233593 | coarse adjustment knob | Moves the stage up and down for focusing |  | 147 |
| 15053233594 | fine adjustment knob | Moves the stage slightly to sharpen the image |  | 148 |
| 15053233595 | head | vertical portion of microscope that connects the base and the head |  | 149 |
| 15053233596 | arm | vertical portion of the microscope that connects the base and the head | 150 | |
| 15053233597 | nosepiece | Rotating mechanism connected to the head. Generally, it carries three or four objective lenses and permits positioning of these lenses over the hole in the stage. |  | 151 |
| 15053233598 | objective lense | are attached to the nose piece, usually a compound microscope has four objective lenses, scanning 4x, 10x,40x, and 100x |  | 152 |
| 15053233599 | ocular lense | eyepiece | 153 | |
| 15053233600 | Cell | The basic unit of structure and function in living things | 154 | |
| 15053233601 | Organelle | specialized structure that performs important cellular functions within a eukaryotic cell | 155 | |
| 15053233602 | Inclusion | Cell inclusions are considered various nutrients or pigments that can be found within the cell | 156 | |
| 15053233603 | tight junctions | A series of integra protein molecules in the plasma membrane of adjacent cells fuse together, forming an IMPERMEABLE junction that encircles the cell. -----help to prevent molecules from passing through the extracellular space between adjacent cells. | 157 | |
| 15053233604 | plasma membrane | composed of phospholipids, cholesterol, and proteins, that encloses cell |  | 158 |
| 15053233605 | nucelar envelope | double membrane barrier of a cell nucleus | 159 | |
| 15053233606 | nucelear pores | Each nuclear pore is a large complex of proteins that allows small molecules and ions to freely pass, or diffuse, into or out of the nucleus. | 160 | |
| 15053233607 | cytoplasm | cellular material surrounding the nucleus and enclosed by the plasma membrane |  | 161 |
| 15053233608 | cytosol | viscous, semitransparent fluid substance of cytoplasm in which other elements are suspended |  | 162 |
| 15053233609 | chromatin | strands of dna and associated proteins;forms chromosomes when condensed |  | 163 |
| 15053233610 | chromosomes | a threadlike structure of nucleic acids and protein found in the nucleus of most living cells, carrying genetic information in the form of genes. | 164 | |
| 15053233611 | selectively permeable | Selective permeability is a property of cellular membranes that only allows certain molecules to enter or exit the cell. | 165 | |
| 15053233612 | microvilli | Tiny hair-like projections of the cytoplasmic membrane located only in the small intestine to facilitate absorption by increasing surface area. |  | 166 |
| 15053233613 | Lysosomes | organelles involved in digestion and waste removal | 167 | |
| 15053233614 | ribosomes | site of protein synthesis |  | 168 |
| 15053233615 | rough endoplasmic reticulum | is an organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Its main function is to produce proteins. |  | 169 |
| 15053233616 | Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum | creates lipids or fat |  | 170 |
| 15053233617 | Golgi apparatus | Membranous system close to the cell nucleus that packages protein secretion for export |  | 171 |
| 15053233618 | Peroxisomes | Membranous sacs in cytoplasm containing powerful oxidase enzymes that use molecular oxygen to detoxify harmful or toxic substances | 172 | |
| 15053233619 | mitochondria | Cytoplasmic organelles responsible for ATP generation for cellular activities. |  | 173 |
| 15053233620 | centrioles | a minute cylindrical organelle near the nucleus in animal cells, occurring in pairs and involved in the development of spindle fibers in cell division. |  | 174 |
| 15053233621 | Nucleus | A part of the cell containing DNA and RNA and responsible for growth and reproduction |  | 175 |
| 15053233622 | Interphase | Cell grows, performs its normal functions, and prepares for division; consists of G1, S, and G2 phases | 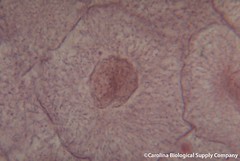 | 176 |
| 15053233623 | Prophase | first phase of mitosis chromosomes become visable, nuclear envelop dissolves, spindle forms |  | 177 |
| 15053233624 | Metaphase | second phase of mitosis, during which the chromosomes line up across the center of the cell | 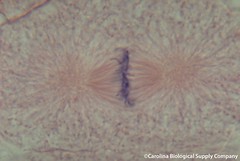 | 178 |
| 15053233625 | Anaphase | the third phase of mitosis, during which the chromosome pairs separate and move toward opposite poles | 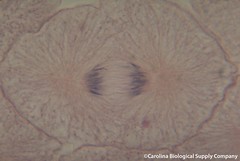 | 179 |
| 15053233626 | Telophase | the final phase of cell division, between anaphase and interphase, in which the chromatids or chromosomes move to opposite ends of the cell and two nuclei are formed. |  | 180 |
| 15053233627 | Cytokenisis (Mitosis) | the division of cytoplasm that occurs after the cell nucleus has divided |  | 181 |
| 15053233628 | importance of cell division | - results in growth - replacement of dead cells - repairs damaged cells | 182 | |
| 15053233629 | Mitosis | part of eukaryotic cell division during which the cell nucleus divides | 183 | |
| 15053233630 | simple squamous epithelium | single layer of flattened cells -Kidney,lining of lungs airsacs, lining of blood vessels |  | 184 |
| 15053233631 | simple cuboidal epithelium | single layer of cube shaped cells -lines small kidney tubes, small glands (sweat glands) |  | 185 |
| 15053233632 | simple columnar epithelium | Made up of a single layer of tall cells that fit closely together -lines most of digestive tract, brochi,uterine tubes |  | 186 |
| 15053233633 | psuedostratified columnar epithelium | single layer of columnar cellsk, often with cilia -lines sperm carrying tubes in males, lines trachea |  | 187 |
| 15053233634 | stratified squamous epithelium | many layers of squamos (flat) cells -lines esophagus, mouth, vagina, skin epidermis |  | 188 |
| 15053233635 | transitional epithelium | Multiple layers of cells which appear cuboidal when not stretched, but squamous when stretched; found in the urinary organs |  | 189 |
| 15053233636 | squamos cells | flattened cells |  | 190 |
| 15053233637 | cuboidal cells | cube shaped cells |  | 191 |
| 15053233638 | columnar cells | tall and column shaped |  | 192 |
| 15053233639 | simple cells | one layer of cells | 193 | |
| 15053233640 | stratified cells | multiple layers of cells | 194 | |
| 15053233641 | connective tissue | A body tissue that provides support for the body and connects all of its parts | 195 | |
| 15053233642 | muscle tissue | A body tissue that contracts or shortens, making body parts move. | 196 | |
| 15053233643 | nervous tissue | A body tissue that carries electrical messages back and forth between the brain and every other part of the body. | 197 | |
| 15053233644 | epithelial tissue | A body tissue that covers the surfaces of the body, inside and out | 198 | |
| 15053233645 | areolar connective tissue | transparent matrix with all three fivers (elastin,collagen,reticular) -pakages organs |  | 199 |
| 15053233646 | adipose tissue | very little matrix and large adipocytes or fat cells -deep to skin,around kidney, eye, breasts, and abdomen |  | 200 |
| 15053233647 | reticular connective tissue | thick reticular fibers around many small cells -lymph nodes,spleen,bone marrow |  | 201 |
| 15053233648 | elastic cartilage | like hylaine cartilage but dark elastin fibers fill the matrix -external ear, epiglottis |  | 202 |
| 15053233649 | fibrocartilage | similar to hylane has thicker fibers (more visible) -intervertebral discs, discs of knee joint |  | 203 |
| 15053233650 | bone | looks like a tree trunk (rings) \ -in bones |  | 204 |
| 15053233651 | blood | red and white blood cells in fluid (blood plasma) just dots floating does not look like anything is connecting them |  | 205 |
| 15053233652 | skeletal muscle tissue | long, thin cells with striations -attached to bones , and sometimes skin |  | 206 |
| 15053233653 | cardiac muscle tissue | long, thing cells with branches and striations -walls of heart |  | 207 |
| 15053233654 | smooth muscle tissue | long,thin cells with no branches and no striations -walls of hollow organs except heart |  | 208 |
| 15053233655 | nervous tissue cells | branching cells with long,narrow extension -brain,spinal cord, nerves |  | 209 |
| 15053362671 | dense irregular connective tissue | irregularly arranged collagen fibers -dermis of skin, joints |  | 210 |
| 15053363725 | Hylaine cartilage | transparent matrix with imperceptible collagen fibers around cartilage cells -embroyonic skeleton, rib nose,trachea, larynx |  | 211 |
| 15053360871 | dense regular connective tissue | many collagen fibers travelling together in a parallel wave pattern -tendons,ligaments |  | 212 |
| 15053485892 | Epidermis | outermost layer of skin, superficial | 213 | |
| 15055192420 | Dermis | deepest layer of skin, deep | 214 | |
| 15055194860 | stratum basale | single layer of cells, closest to the dermis, dividing keratinacytes, few melanocytes and tactille cells | 215 | |
| 15055268003 | stratum spinosum | Several layers of keratinocytes joined by desmosomes. Cells contain thick bundles of intermediate filaments made of pre-keratin. | 216 | |
| 15055279538 | stratum granulosum | a layer of the epidermis that marks the transition between the deeper, metabolically active strata and the dead cells of the more superficial strata | 217 | |
| 15055286770 | stratum lucidum | Clear, transparent layer of the epidermis under the stratum corneum. lacks blood vessels, few layers of flattened dead cells, only in thick skin. | 218 | |
| 15055288277 | stratum corneum | the most superficial layer of the epidermis consisting of dead cells. thickest layer, protected by keratin | 219 | |
| 15055303246 | Keratinocytes | produce keratin, cells attached by tight junctions | 220 | |
| 15055306810 | Keratin | hard protein material found in the epidermis, hair, and nails | 221 | |
| 15055307721 | Melanocytes | produce melanin, protects skin from sun | 222 | |
| 15055309186 | dendritic cells | specialized white blood cells that patrol the body searching for antigens that produce infections | 223 | |
| 15055311762 | tactile cells | touch receptors | 224 | |
| 15055326041 | papillary layer | outer layer of the dermis, directly beneath the epidermis | 225 | |
| 15055329878 | dermal papillae | Found in the upper layers of the dermis, they create your fingerprint pattern | 226 | |
| 15055332780 | dermal ridges | surface ridges of the epidermis of the palms and soles, where the sweat pores open | 227 | |
| 15055334280 | organization of ridges is | genetically determined | 228 | |
| 15055336742 | reticular layer | Deeper layer of the dermis that supplies the skin with oxygen and nutrients, 80% of dermis, and the thickest layer. | 229 |
AP lab Flashcards
Primary tabs
Need Help?
We hope your visit has been a productive one. If you're having any problems, or would like to give some feedback, we'd love to hear from you.
For general help, questions, and suggestions, try our dedicated support forums.
If you need to contact the Course-Notes.Org web experience team, please use our contact form.
Need Notes?
While we strive to provide the most comprehensive notes for as many high school textbooks as possible, there are certainly going to be some that we miss. Drop us a note and let us know which textbooks you need. Be sure to include which edition of the textbook you are using! If we see enough demand, we'll do whatever we can to get those notes up on the site for you!

