| 1143297163 | CHAPTER 1 | ... | | 1 |
| 1143297164 | Biology | The scientific study of life. | | 2 |
| 1143297165 | Characteristics of living organisms | Order (structure), evolutionary adaptation, response to the environment, regulation (ie, blood pressure, internal temperature), energy processing (ie digestion to use food for energy), growth and development, and reproduction. | | 3 |
| 1143297166 | Levels of biological organization | >The biosphere
>Ecosystems
>Communities
>Populations
>Organisms
>Organs and organ systems
>Tissues
>Cells
>Organelles
>Molecules | | 4 |
| 1143297167 | The biosphere | Earth | | 5 |
| 1143297168 | Ecosystems | All the living things in a particular area, plus all the nonliving components of the environment with which life interacts (eg soil, water, atmospheric gases, and light). | | 6 |
| 1143297169 | Communities | The entire array of organisms inhabiting a particular ecosystem. | | 7 |
| 1143297170 | Populations | All the individuals of a species living within the bounds of a specified area. | | 8 |
| 1143297171 | Organisms | Individual living things. | | 9 |
| 1143297172 | Organs and organ systems. | A body part consisting of two or more tissues is an organ; two or more organs make up an organ system. | | 10 |
| 1143297173 | Tissues | A group of similar cells that perform a specific function. | | 11 |
| 1143297174 | Cells | Life's fundamental unit of structure and function. Some organisms, like many bacteria, are single cells. | | 12 |
| 1143297175 | Organelles | The small, various components of a cell, such as the nucleus and mitochondria. | | 13 |
| 1143297176 | Molecules | A chemical structure consisting of two or more atoms. | | 14 |
| 1143297177 | The two major processes of any ecosystem | 1. The cycling of nutrients (eg, plants who acquire minerals will eventually decompose into the environment again).
2. The flow of energy from sunlight to producers to consumers. | | 15 |
| 1143297178 | Producers | Plants and other photosynthetic organisms that convert light energy into chemical energy. | | 16 |
| 1143297179 | Consumers | Organisms that feed on producers and other consumers. | | 17 |
| 1143297180 | Almost all cellular activities involve the action of one or more _________. | Proteins | | 18 |
| 1143297181 | A particular sequence of __________ says the same thing to one organism as it does to another. | Nucleotides | | 19 |
| 1143297182 | Genome | The entire "library" of genetic instructions that an organism inherits. (Each human cell's chromosomes have a genome about 3 billion nucleotides long). | | 20 |
| 1143297183 | Eukaryotic cells | Cells subdivided by internal membranes into various membrane-enclosed organelles, most notably the nucleus, typically the largest organelle, which holds the cell's DNA. | | 21 |
| 1143297184 | Prokaryotic cells | Cells in which the DNA is not separated from the rest of the cell by enclosure in a membrane-bound nucleus. They also lack other kinds of membrane-enclosed organelles like eukaryotic cells, and are usually smaller than eukaryotic cells. | | 22 |
| 1143774508 | Emergent properties | Novel (unique) properties that emerge with each step upward in the hierarchy of biological order, due to the arrangement and interactions of parts as complexity increases. | | 23 |
| 1143774509 | Reductionism | Reducing complex systems to simpler components that are more manageable to study. | | 24 |
| 1143774510 | The Human Genome Project | The project where an international team of scientists sequenced the entire human genome (about 3 billion chemical letters). | | 25 |
| 1143774511 | Systems biology | Biology in which the goal is to model the dynamic behavior of whole biological systems. | | 26 |
| 1143774512 | High-throughput | Mega-data-collection methods for analyzing biological materials very rapidly and producing enormous volumes of data. | | 27 |
| 1143774513 | Bioinformatics | The computing power, software, and mathematical models to process and integrate all this biological information. | | 28 |
| 1143774514 | Negative feedback | The most common form of biological regulation in which accumulation of an end product of a process slows that process. | | 29 |
| 1143774515 | Positive feedback | The less common form of biological regulation in which an end product speeds up its production. | | 30 |
| 1143774516 | Biology's "vertical" dimension | The size scale of biology from molecules to the biosphere. | | 31 |
| 1143774517 | Biology's "horizontal" dimension | The stretch of biology across the great diversity of species. | | 32 |
| 1143774518 | Domain Bacteria | One of the three main domains, consists of bacteria (prokaryotes). | | 33 |
| 1143774519 | Domain Archaea | One of the three main domains, consists of prokaryotes which are typically found in extreme conditions (ie, hot springs). | | 34 |
| 1143774520 | Domain Eukarya | The last of the three domains, includes all the eukaryotes. | | 35 |
| 1143774521 | Inquiry | A search for information and explanation, often focusing on specific questions. | | 36 |
| 1143774522 | Discovery science | Science based on describing natural structures and processes as accurately as possible through careful observation and analysis of data. | | 37 |
| 1143774523 | Hypothesis-based science | Sciences based on EXPLAINING nature. | | 38 |
| 1143774524 | Data | Recorded observations | | 39 |
| 1143774525 | Qualitative data | Recorded descriptions rather than numerical measurements. | | 40 |
| 1143774526 | Quantitative data | Data which is generally recorded as measurements (numbers). | | 41 |
| 1143774527 | Inductive reasoning | Deriving generalizations based on a large number of specific observations. | | 42 |
| 1143774528 | Hypothesis | A tentative answer to a well-framed question, usually an educated postulate, based on past experience and the available data of discovery science. It makes predictions that can be tested by recording additional observations or by designing experiments. | | 43 |
| 1143774529 | Deductive reasoning | Reasoning in which, from generalizations, one draws specific ideas. | | 44 |
| 1143774530 | Testable hypothesis | A hypothesis that can in some way be checked for validity. | | 45 |
| 1143774531 | Falsifiable hypothesis | A hypothesis that could, by some observation or experiment, be revealed as untrue. | | 46 |
| 1143774532 | Henry Bates | British scientist who, in 1862, proposed that species that 'mimic' the look of other harmful species do so to benefit from predators confusing them with the harmful species and thus not attacking them. | | 47 |
| 1143774533 | Controlled experiment | An experiment where an experimental group is compared with a control group. Ideally, the experimental and control groups should differ in only one factor of the experiment. | | 48 |
| 1143774534 | Theory | Much broader than a hypothesis, an idea general enough to spin off many new, specific hypotheses that can be tested, and is generally supported by a much more massive body of evidence and explains a great diversity of observations and are supported by an accumulation of evidence. | | 49 |
| 1143774535 | Models | A representation of a theory, natural phenomena, or biological process, in the form of diagrams, graphs, three-dimensional objects, computer programs, or mathematical equations. | | 50 |
| 1143774894 | Science and __________ are interdependent. | Technology. | | 51 |
| 1144537203 | CHAPTER 2 | ... | | 52 |
| 1147244765 | Matter | Anything that takes up space and has mass. | | 53 |
| 1147244766 | Element | A substance that cannot be broken down to other substances by chemical reactions. | | 54 |
| 1147244767 | Compound | A substance consisting of two or more different elements combined in a fixed ratio. | | 55 |
| 1147244768 | Trace elements | Elements required by an organism in only minute qualities. | | 56 |
| 1147244769 | Atom | The smallest unit of matter that still retains the properties of an element. | | 57 |
| 1147244770 | Neutrons | Subatomic particles with no electrical charge that is packed tightly with protons in the nucleus. | | 58 |
| 1147244771 | Protons | Subatomic particles with positive electrical charge that is packed tightly with neutrons in the nucleus. | | 59 |
| 1147244772 | Electrons | Subatomic particles with negative electrical charge that move at nearly the speed of light in a cloud around the nucleus. | | 60 |
| 1147244773 | Atomic nucleus | The dense core of an atom, making up nearly all of its mass, comprised of protons and neutrons. | | 61 |
| 1147244774 | Dalton (amu) | A unit of measurement for atoms and subatomic particles. It is also called the atomic mass unit, or amu. | | 62 |
| 1147244775 | John Dalton | A British scientist who helped develop atomic theory around 1800 and who the unit dalton is named after. | | 63 |
| 1147244776 | Mass number | The sum of protons plus neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. | | 64 |
| 1147244777 | Atomic mass | The total mass of an atom. | | 65 |
| 1147244778 | Isotopes | Atoms of an element that have more neutrons than other atoms of the same element and therefore have greater mass. | | 66 |
| 1147244779 | Radioactive isotope | An isotope in which the nucleus decays spontaneously, giving off particles and energy. | | 67 |
| 1147244780 | Energy | The capacity to cause change. | | 68 |
| 1147244781 | Potential energy | The energy that matter possesses because of its location or structure. | | 69 |
| 1147244782 | Energy levels | The different states of potential energy that electrons have in an atom. | | 70 |
| 1147244783 | Electron shells | The discrete average distances that an electron can be from the nucleus in an atom. | | 71 |
| 1147244784 | Electron configuration | The distribution of electrons in the atom's electron shells. | | 72 |
| 1147244785 | Valence electrons | The outer electrons of an atom that participate in chemical reactions. | | 73 |
| 1147244786 | Valence shell | The outermost electron shell that holds the valence electrons. | | 74 |
| 1147244787 | Orbital | The three-dimensional space where an electron is found 90% of the time. | | 75 |
| 1147244788 | Chemical bonds | Attractions that hold atoms close together. | | 76 |
| 1147244789 | Covalent bond | The sharing of a pair of valence electrons by two atoms. | | 77 |
| 1147244790 | Molecule | Two or more atoms held together by covalent bonds. | | 78 |
| 1147244791 | Single bond | A pair of shared valence electrons. | | 79 |
| 1147244792 | Double bond | Two pairs of shared valence electrons. | | 80 |
| 1147244793 | Methane | The main component of natural gas (CH_4). | | 81 |
| 1147244794 | Electronegativity | How strongly an atom pulls its electrons (and its shared electrons) towards itself. | | 82 |
| 1147244795 | Nonpolar covalent bond | A bond in which electrons are shared equally. | | 83 |
| 1147244796 | Polar covalent bond | A bond in which the electrons are NOT shared equally. | | 84 |
| 1147244797 | Ion | A charged atom or molecule. | | 85 |
| 1147244798 | Cation | A positively charged ion. | | 86 |
| 1147244799 | Anion | A negatively charged ion. | | 87 |
| 1147244800 | Ionic bond | The attraction between cations and anions. | | 88 |
| 1147244801 | Ionic compounds | Compounds formed by ionic bonds. | | 89 |
| 1147244802 | Salts | Ionic compounds. | | 90 |
| 1147244803 | Hydrogen bond | A bond that forms between a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to one electronegative atom. | | 91 |
| 1147244804 | van der Waals interactions | Weak bonds that occur frequently between atoms and molecules that are close together. They occur often between cells in the body. | | 92 |
| 1147244805 | Chemical reactions | The making and breaking of chemical bonds, leading to changes in the composition of matter. | | 93 |
| 1147244806 | Reactants | The starting materials in a chemical reaction. | | 94 |
| 1147244807 | Products | The final [produced] reactants in a chemical reaction. | | 95 |
| 1147244808 | "Go to completion" | When all the reactants in a chemical reaction are converted to products. | | 96 |
| 1147244809 | Chemical equilibrium | The point in a chemical reaction at which the reactions offset one another exactly. | | 97 |
| 1147244810 | Dynamic equilibrium | An equilibrium when reactions are still going on but with no net effect on the concentrations of reactants and products (the concentrations are NOT equal; rather, they are in fixed RATIOS). | | 98 |
| 1147244811 | CHAPTER 3 | ... | | 99 |
| 1147244812 | Polar molecule | A molecule that has opposite charges on its opposite ends. | | 100 |
| 1147244813 | Cohesion | A phenomenon in which hydrogen bonds hold the substances together. | | 101 |
| 1147244814 | Adhesion | The clinging of one substance to another. | | 102 |
| 1147244815 | Surface tension | A measure of how difficult it is to stretch or break the surface of a liquid. | | 103 |
| 1147244816 | Kinetic energy | The energy of motion. | | 104 |
| 1147244817 | Heat | A measure of the TOTAL amount of kinetic energy due to molecular motion in a body of matter. | | 105 |
| 1147244818 | Temperature | A measure of the intensity of heat due to the AVERAGE kinetic energy of the molecules. | | 106 |
| 1147244819 | Calorie (cal) | The amount of heat it takes to raise the temperature of 1 g of water by 1˚C. | | 107 |
| 1147244820 | Kilocalorie (kcal) | 1,000 calories; the quantity of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 kilogram (kg) of water by 1˚C. | | 108 |
| 1147244821 | Joule (J) | A unit of energy; 1 calorie = 4.184 joule. | | 109 |
| 1147244822 | Specific heat | The amount of heat that must be absorbed or lost for 1 g of a substance to change its temperature by 1˚C. | | 110 |
| 1147244823 | Heat of vaporization | The quantity of heat a liquid must absorb for 1 g of it to be converted from the liquid to the gaseous state. | | 111 |
| 1147244824 | Evaporative cooling | The phenomenon of when the surface of a liquid that remains behind during evaporation becomes cooler, because the "hottest" molecules, those with the greatest kinetic energy, are most likely to leave as a gas. This means the molecules left behind will be significantly cooler. | | 112 |
| 1147244825 | Solution | A liquid that is a completely homogeneous mixture of two or more substances. | | 113 |
| 1147244826 | Solvent | The dissolving agent of a solution | | 114 |
| 1147244827 | Solute | The substance that is dissolved in a solution. | | 115 |
| 1147244828 | Aqueous solution | A solution in which water is the solvent. | | 116 |
| 1147244829 | Hydration shell | The sphere of water molecules around each dissolved ion. | | 117 |
| 1147244830 | Hydrophilic | Any substance that has an affinity for water. | | 118 |
| 1147244831 | Colloid | A stable suspension of fine particles in a liquid. | | 119 |
| 1147244832 | Hydrophobic | Substances that are nonionic, nonpolar, and seem to repel water. | | 120 |
| 1147244833 | Molecular mass | The sum of the masses of all the atoms in a molecule. | | 121 |
| 1147244834 | Mole (mol) | An exact, discrete number of objects (6.02 x 10^23 atoms) that is used as a unit of measurement for molecules. | | 122 |
| 1147244835 | Avogadro's number | 6.02 x 10^23 atoms. | | 123 |
| 1147244836 | Molarity | The number of moles of solute per liter solution. It is the unit of concentration most often used by biologists for aqueous solutions. | | 124 |
| 1147244837 | pH scale | A scale used to describe how acidic or basic a solution is. The pH of a solution is the negative logarithm of the hydrogen ion concentration. | | 125 |
| 1147244838 | Acid | A substance that increases the hydrogen ion concentration of a solution. | | 126 |
| 1147244839 | Base | A substance that reduces the hydrogen ion concentration of a solution that it is added to. | | 127 |
| 1147244840 | Strong acid/base | Acids and bases that dissociate completely in water. | | 128 |
| 1147244841 | Buffers | Substances that minimize changes in the concentrations of H+ (acidity) and OH- (basicness) in a solution. | | 129 |
| 1147244842 | Acid precipitation | Rain, snow, or fog with a pH lower or more acidic than pH 5.6. It is caused by the presence in the atmosphere of sulfur oxides and nitrogen oxides, gaseous compounds that react with water in the air to form strong acids. When it falls on land it washes away certain mineral ions which ordinarily help buffer soil and are essential to plant growth. We have made progress in reducing acid precipitation. | | 130 |
| 1147244843 | CHAPTER 4 | ... | | 131 |
| 1147244844 | Organic chemistry | The branch of chemistry that specializes in the study of carbon compounds. | | 132 |
| 1147244845 | Mechanism | The view that all natural phenomena, including the processes of life, are governed by physical and chemical laws. | | 133 |
| 1147244846 | Hydrocarbons | Organic molecules consisting only of carbon and hydrogen. | | 134 |
| 1147244847 | Fossil fuel | A fuel that consists of a partially decomposed remains of organisms that lived millions of years ago. | | 135 |
| 1147244848 | Structural isomers | Isomers that differ in the covalent ARRANGEMENTS of their atoms. | | 136 |
| 1147244849 | Geometric isomers | Isomers that have the same covalent partnerships as their elements, but differ in their SPATIAL arrangements. | | 137 |
| 1147244850 | "Cis" arrangements | Arrangements where two molecules are on the same side relative to a double bond. | | 138 |
| 1147244851 | "Trans" arrangements | Arrangements where two molecules are opposite each other relative to a double bond. | | 139 |
| 1147244852 | Enantiomers | Molecules that are mirror images of each other. | | 140 |
| 1147244853 | Functional groups | The components of organic molecules that are most commonly involved in chemical reactions. | | 141 |
| 1147244854 | The six functional groups most important in the chemistry of life are: | The hydroxyl, carbonyl, carboxyl, amino, sulfhydryl, and phosphate groups. | | 142 |
| 1147244855 | Hydroxyl group | 1. A functional group in which a hydrogen atom is bonded to an oxygen atom, which in turn is bonded to the carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
2. (-OH).
3. Are alcohols, ending in -ol.
4. Polar as a result of the electronegative oxygen atom drawing electrons toward itself.
5. Attracts water molecules, helping dissolve organic compounds (ie sugars). | | 143 |
| 1147244856 | Carbonyl | 1. A function group that consists of a carbon atom joined to an oxygen atom by a double bond.
2. (>CO).
3. Are either ketones, if the carbonyl group is within a carbon skeleton, or aldehydes, if the carbonyl group is at the end of the carbon skeleton.
4. A ketone and an aldehyde may be structural isomers with different properties (ie, acetone). | | 144 |
| 1147244857 | Carboxyl | 1. A functional group in which an oxygen atom is double-bonded to a carbon atom that is also bonded to a hydroxyl group.
2. (-COOH).
3. Are carboxylic acids.
4. Has acidic properties because it is a source of hydrogen ions.
5. The covalent bond between oxygen and hydrogen is so polar that hydrogen ions (H+) tend to dissociate reversibly.
6. In cells, it is found in the ionic form (called the carboxylate group). | | 145 |
| 1147244858 | Amino | 1. A function group consisting of a nitrogen atom bonded to two hydrogen atoms and to the carbon skeleton.
2. (-NH_2).
3. Are amines.
4. Acts as a base; can pick up a proton from the surrounding solution.
5. Ionized, with a charge of 1+, under cellular conditions. | | 146 |
| 1147244859 | Sulfhydryl group | 1. A functional group consisting of a sulfur atom bonded to an atom of hydrogen.
2. (-SH).
3. Are thiols.
4. Two sulfhydryl groups can interact to help stabilize protein structure. | | 147 |
| 1147244860 | Phosphate | 1. A functional group in which a phosphorus atom bonded to four oxygen atoms; one oxygen atom is bonded to the carbon skeleton; two oxygens carry negative chargers.
2. The phosphate group (-OPO_3^2-) is an ionized form of a phosphoric acid group (-OPO_3H_2).
3. Are organic phosphates.
4. Makes the molecule of which it is a part an anion.
5. Can transfer energy between organic molecules. | | 148 |
| 1147244861 | Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) | A complicated organic phosphate which acts as the primary energy-transferring molecule in the cell, consisting of an organic molecule called adenosine attached to a string of three phosphate groups. | | 149 |
| 1147244862 | CHAPTER 5 | ... | | 150 |
| 1147249971 | The four main classes of large biological molecules are: | Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. | | 151 |
| 1147249972 | Macromolecule | Giant molecules. | | 152 |
| 1147249973 | Polymer | A long molecule consisting of many similar or identical building blocks linked by covalent bonds. | | 153 |
| 1147249974 | Monomers | Small molecules that serve as the repeating units that serve as the building blocks of a polymer. | | 154 |
| 1147249975 | Condensation reaction | A reaction in which two monomers are bonded covalently through loss of a water molecule. Also called a DEHYDRATION molecule. | | 155 |
| 1147249976 | Hydrolysis | The process in which polymers are disassembled into monomers through essentially the reverse of the dehydration reaction. The bonds between monomers are broken by the addition of water molecules. | | 156 |
| 1147249977 | Carbohydrates | Sugars and polymers of sugar. | | 157 |
| 1147249978 | Monosaccharides | The simplest carbohydrates, also known as single sugars. Generally have molecular formulas that are some multiple of the unit CH_2O. | | 158 |
| 1147249979 | Disaccharides | Double sugars, consisting of two monosaccharides joined by a glycosidic linkage. | | 159 |
| 1147625148 | Glycosidic linkage | A covalent bond formed between two monosaccharides by a dehydration reaction. | | 160 |
| 1147249980 | Polysaccharides | Macromolecules of carbohydrates. Polymers composed of a few hundred to a few thousand monosaccharides joined by glycosidic linkages. | | 161 |
| 1147625149 | Glucose is an ______. | Aldose. | | 162 |
| 1147625150 | Fructose, a structural isomer of _________, is a ___________. | Glucose, ketose. | | 163 |
| 1147625151 | The size of the carbon skeleton ranges from _______ to ________ carbons long. | Three to seven. | | 164 |
| 1147625152 | Asymmetric carbon | A carbon attached to four different kinds of partners. | | 165 |
| 1147625153 | In aqueous solutions, most sugars form _______. | Rings. | | 166 |
| 1147625154 | Starch | A storage polysaccharide of plants. It is a polymer consisting entirely of glucose monomers. | | 167 |
| 1147625155 | Glycogen | A polymer of glucose that is like a more complex form of starch that is extensively branched. Humans and other vertebrates store it in liver and muscle cells, where it is used as fuel, but only if it is replenished often (ie by eating food). | | 168 |
| 1147625156 | Cellulose | A polysaccharide that is a major component of the tough walls that enclose plant cells. It is the most abundant organic compound on Earth. | | 169 |
| 1147625157 | Chitin | A carbohydrate (polysaccharide) used by arthropods (insects, spiders, crustaceans, etc) to build their exoskeletons. It is also found in fungi, which use it to make their cell walls instead of using cellulose, because the two carbohydrates are similar. It is also used to make surgical thread. | | 170 |
| 1148389665 | Lipids | Compounds that are uniquely hydrophobic. They are one class of large biological molecules, but are NOT polymers. | | 171 |
| 1148389666 | Fats | Large molecules (NOT polymers) that are constructed from two kinds of smaller molecules through dehydration reactions: glycerol and fatty acids. | | 172 |
| 1148389667 | Glycerol | An alcohol with three carbons, each bearing a hydroxyl group. | | 173 |
| 1148389668 | Fatty acid | A long carbon skeleton (usually 16 to 18 carbons in length) At one end is a carboxyl group, giving it the name fatty ACID. Attached to the carboxyl group is a long hydrocarbon chain. The nonpolarity of the hydrocarbons are why fats are hydrophobic. | | 174 |
| 1148389669 | In making a fat, three _____ molecules each join to ______ by an ester linkage, creating a __________. | Fatty acid, glycerol, triacylglycerol. | | 175 |
| 1148389670 | Ester linkage | A bond between a hydroxyl group and a carboxyl group. | | 176 |
| 1148389671 | Saturated fatty acid | A fatty acid where there are no double bonds between the carbon acids of the hydrocarbon chain (thus, the acid is said to be 'saturated' with hydrogen). | | 177 |
| 1148389672 | Unsaturated fatty acid | A fatty acid that has one or more double bonds, formed by the removal of hydrogen atoms from the carbon skeleton. The chains will have a kink wherever a cis double bond occurs. | | 178 |
| 1148389673 | The major function of fats is ____________. | Energy storage. | | 179 |
| 1148395487 | Phospholipid | Similar to a fat, but it only has two fatty acids attached to the glycerol; the third hydroxyl group of glycerol is joined to a phosphate group, which has a negative electrical charge. They self-assemble into bilayers when exposed to water. | | 180 |
| 1148395488 | Bilayers | Double layers that are the main fabric of biological membranes, composed out of phospholipids, where the phospholipid's hydrophobic hydrocarbon tails are arranged on the inside, away from water, and their hydrophilic phosphate heads are on the outside. | | 181 |
| 1148395489 | Steroid | Lipids characterized by a carbon skeleton consisting of four fused rings. Different steroids vary in the functional groups attached to these rings. | | 182 |
| 1148395490 | Cholesterol | A steroid and a common component of animal cell membranes and is also the precursor from which other steroids are synthesized. | | 183 |
| 1182018725 | Enzymes | Proteins that speed up chemical reactions without being consumed by the reaction. | | 184 |
| 1182018726 | Catalysts | Enzymatic proteins that regulate metabolism. | | 185 |
| 1182018727 | Proteins | Polymers constructed from the same set of 20 amino acids, consisting of one or more polypeptides folded and coiled into specific formations. | | 186 |
| 1182018728 | Polypeptides | Polymers of amino acids. | | 187 |
| 1182018729 | Amino acids | Organic molecules possessing both carboxyl and amino groups. | | 188 |
| 1182018730 | R-group | A variable group, also called the side chain, that differs with each amino acid-causes the variation between proteins. | | 189 |
| 1182018731 | Peptide bonds | The covalent bond between two amino acids that's formed when a carboxyl group of one is adjacent to the other, and an enzyme joins them by a dehydration reaction. | | 190 |
| 1182018732 | N-terminus | The free amino end of a polypeptide chain. | | 191 |
| 1182018733 | C-terminus | The free carboxyl end of a polypeptide chain. | | 192 |
| 1182018734 | Polypeptide backbone | The repeating sequence of atoms of a polypeptide. Attached to this backbone are different side chains of the amino acids. | | 193 |
| 1182018735 | Frederick Sanger | The pioneer in determining the amino acid sequence of proteins from Cambridge University in 1940-1950, figured out the primary structure of insulin. | | 194 |
| 1182018736 | Lock and key model | The type of fit between an enzyme and a protein receptor. | | 195 |
| 1182018737 | Denaturation | When a protein unravels and loses its native conformation, rendering it biologically inactive. | | 196 |
| 1182018738 | Chaperonins | Protein molecules that assist the proper folding of other proteins. | | 197 |
| 1182018739 | X-raycrystallography | An important method used to determine a protein's three-dimensional structure. | | 198 |
| 1182018740 | DNA | A polymer belonging to the class of compounds known as nucleic acids; makes up genes. | | 199 |
| 1182018741 | Polynucleotides | Polymers of nucleic acids. | | 200 |
| 1182018742 | Nucleotide | A monomer composed of a nitrogenous base, a pentose (five-carbon sugar, and a phosphate group. | | 201 |
| 1182018743 | Nucleoside | A nucleotide without a phosphate group. | | 202 |
| 1190390579 | CHAPTER 6 | ... | | 203 |
| 1190390580 | Light microscopes (LMs) | More basic microscopes that can see most plant and animal cells, nuclei, bacteria, and mitochondria. | | 204 |
| 1190390581 | Magnification | In microscopy, it is the ratio of an object's image size to its real size. | | 205 |
| 1190390582 | Resolution | In microscopy, a measure of the clarity of the image. | | 206 |
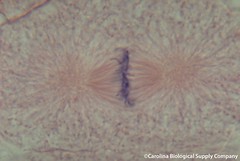
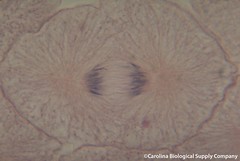
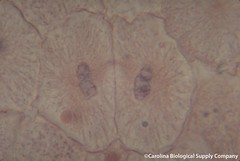
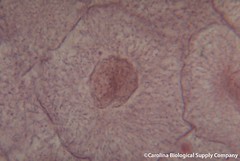
| 1190390583 | Robert Hooke | Discovered cells in 1665. | | 207 |
| 1190390584 | Electron microscope (EM) | A microscope which utilizes beams of electrons, so that it can see viruses, ribosomes, proteins, lipids, atoms, and the smallest bacteria and molecules. | | 208 |
| 1190390585 | Cell ultrastructure | A cell's anatomy as revealed by an electron microscope. | | 209 |
| 1190390586 | Scanning electron microscope (SEM) | An electron microscope used to study the fine details of cell surfaces. | | 210 |
| 1190390587 | Transmission electron microscope (TEM) | An electron microscope used to study the internal structure of thin sections of cells. | | 211 |
| 1190390588 | Cell fractionation | A method that takes cells apart and separates the major organelles from one another. | | 212 |
| 1190390589 | Ultracentrifuges | Centrifuges that are extremely powerful. | | 213 |
| 1190390590 | Cytosol | A semifluid substance within the cell's membrane. | | 214 |
| 1190390591 | Prokaryotic cell | A type of cell where the DNA is not bound by a membrane by rather concentrated in the region called the nucleoid. | | 215 |
| 1190390592 | Cytoplasm | The entire region between the nucleus and the plasma membrane. | | 216 |
| 1190390593 | The smaller the object, the ________ its ratio of surface to volume. | Greater. | | 217 |
| 1190390594 | Plasma membrane | The selective barrier of every cell that allows sufficient passage of oxygen, nutrients, and wastes to service the entire volume of the cell. | | 218 |
| 1190390595 | Nucleus | Contains most of the genes in the eukaroytic cell. | | 219 |
| 1190390596 | Nuclear envelope` | Encloses the nucleus, separating its contents from the cytoplasm. | | 220 |
| 1190390597 | Some genes are located not in the nucleus but in the ______ and ______. | Mitochondria and chloroplasts. | | 221 |
| 1190390598 | Nuclear lamina | The netlike array of protein filaments that maintains the shape of the nucleus by mechanically supporting the nuclear envelope. | | 222 |
| 1190390599 | The nuclear envelope has a ______ membrane. | Double. | | 223 |
| 1190390600 | Nucleolus | A mass of densely stained granules and fibers adjoining part of the chromatin. | | 224 |
| 1190390601 | Ribosomes | Organelles made of ribosomal RNA and protein that carry out protein synthesis. | | 225 |
| 1190390602 | Endomembrane system | The collection of membranes inside and around a eukaryotic cell, related either through direct physical contact or by the transfer of membranous vesicles. | | 226 |
| 1190390603 | Vesicles | Sacs made of membrane. | | 227 |
| 1190390604 | Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) | The extensive network of membranes that works with the creation and shipment of proteins and other cellular substances. | | 228 |
| 1190390605 | ER lumen | The space inside the ER where proteins are folded, modified and prepared for transport to other locations in the cell or are tagged for export from the cell. | | 229 |
| 1190390606 | Cisternal space | The space between the folds of ER, increases surface area. | | 230 |
| 1190390607 | Smooth ER | ER without ribosomes on its surface. | | 231 |
| 1190390608 | Rough ER | "Rough" because its surface is covered in ribosomes. | | 232 |
| 1190390609 | Glycoproteins | Secretory proteins that have carbohydrates covalently bonded to them. | | 233 |
| 1190390610 | Transport vesicles | Vesicles in transit from one part of the cell to another. | | 234 |
| 1190390611 | Golgi apparatus | An organelle in eukaryotic cells consisting of stacks of flat membranous sacs that modify, store, and route products of the endoplasmic reticulum. | | 235 |
| 1190390612 | Lysosome | A membranous sac of hydrolytic enzymes that an animal cell uses to digest all kinds of macromolecules. | | 236 |
| 1190390613 | The cytosol has a ______ pH. | Neutral. | | 237 |
| 1190390614 | Phagocytosis | Engulfing smaller organisms or other food particles, as done by lysosomes. | | 238 |
| 1190390615 | Autophagy | Eating(/recycling) a cell's own material. | | 239 |
| 1190390616 | Food vacuoles | Hold food. | | 240 |
| 1190390617 | Contractile vacuoles | Pump excess water out of the cell. | | 241 |
| 1190390618 | Central vacuole | Develops by a coalescence of smaller vacuoles, holds most stuff in the cell. | | 242 |
| 1190390619 | Tonoplast | Membrane that encloses a mature plant cell's central vacuole. | | 243 |
| 1190390620 | Mitochondria | The organelles that are sites of cellular respiration. | | 244 |
| 1190390621 | Chloroplasts | Plant organelles that are sites of photosynthesis. | | 245 |
| 1190390622 | Peroxisome | An oxidative organelle that is not part of the endomembrane system. It is a specialized metabolic compartment, not bounded by a single membrane, that contains enzymes which transfer hydrogen from various substrates to oxygen, producing hydrogen peroxide. | | 246 |
| 1190390623 | Cristae | The infoldings in the mitochondrial matrix. | | 247 |
| 1190390624 | Mitochondrial matrix | The space inside the mitochondria containing many different enzymes as well as the mitochondrial DNA and ribosomes. | | 248 |
| 1190390625 | Plastids | Closely related plant organelles | | 249 |
| 1190390626 | Amyloplasts | Colorless plastids that store starch | | 250 |
| 1190390627 | Chromoplasts | Have pigments that give fruits and flowers their hues. | | 251 |
| 1190390628 | Cytoskeleton | A network of fibers extending throughout the cytoplasm. | | 252 |
| 1190390629 | Cell motility | Changes in cell location and more limited movements of parts of the cell. | | 253 |
| 1190390630 | Motor proteins | Proteins that interact with the cytoskeleton to create cell motility. | | 254 |
| 1190390631 | Microtubules | A hollow rod composed of tubulin proteins that makes up part of the cytoskeleton in all eukaryotic cells and is found in cilia and flagella. | | 255 |
| 1190390632 | Centrosome | A structure present in the cytoplasm of animal cells that functions as a microtubule-organizing center and is important during cell division. A centrosome has two centrioles. | | 256 |
| 1190390633 | Centriole | Cell organelle that aids in cell division [in animal cells only]. | | 257 |
| 1190390634 | Flagell and cilia | The thingies that make the cell do the wiggly moving thingy. | | 258 |
| 1190390635 | Primary cell wall | A relatively thin and flexible wall secreted by a young plant cell. | | 259 |
| 1190390636 | Middle lamella | A thin layer rich in sticky polysaccharides called pectins, glueing adjacent cells together within a plant. | | 260 |
| 1190390637 | Secondary cell wall | A strong and durable matrix often deposited in several laminated layers for plant cell protection and support. | | 261 |
| 1190390638 | Extracellular matrix (ECM) | The substance in which animal tissue cells are embedded, consisting of protein and polysaccharides. | | 262 |
| 1190390639 | Integrins | They span the membrane and bind on their cytoplasmic side to associated proteins attached to microfilaments of the cytoskeleton. Transmit changes between the ECM and the cytoskeleton and thus integrate changes occurring outside and inside the cell. | | 263 |
| 1190390640 | Plasmodesmata | Channels in plant cell walls that connect plant cells by allowing cytosol to pass through and connect the chemical environments of adjacent cells. | | 264 |
| 1190390641 | Tight junctions | Hold the membranes of neighboring cells very tightly against each other, bound together by specific proteins. These junctions prevent leakage of extracellular fluid across a layer of epithelial cells. | | 265 |
| 1190390642 | Desmosomes | Function like rivets, fastening cells together into strong sheets. | | 266 |
| 1190390643 | Gap junctions | Provide cytoplasmic channels from one cell to an adjacent cell. Consist of special membrane proteins that surround a pore through which ions, sugars, amino acids, and other small molecules may pass. Necessary for communicating between cells in many types of tissues. | | 267 |
| 1190390644 | CHAPTER 7 | ... | | 268 |
| 1190390645 | Selective permeability | Allowing some substances to cross more easily than others, seen in al biological membranes. | | 269 |
| 1190390646 | Amphipathic molecule | A molecule which has both a hydrophilic and a hydrophobic region (ie, a PHOSPHOLIPID). | | 270 |
| 1190390647 | Fluid mosaic model | The currently accepted model of cell membrane structure, which envisions the membrane as a mosaic of individually inserted protein molecules drifting laterally in a fluid bilayer of phospholipids. | | 271 |
| 1190390648 | Integral proteins | Membrane proteins that penetrate the hydrophobic core of a lipid bilayer. | | 272 |
| 1190390649 | Peripheral proteins | Membrane proteins are not embedded in the lipid bilayer at all. | | 273 |
| 1190535283 | Cell-cell recognition | A cell's ability to distinguish one type of neighboring cell from another. | | 274 |
| 1190535285 | Glycolipids | Membrane carbohydrates bonded to lipids. | | 275 |