Key Concepts:
• External signals are converted to responses within the cell.
• Reception: A signaling molecule binds to a receptor protein, causing it to change shape.
• Transduction: Cascades of molecular interactions relay signals from receptors to target molecules in the cell.
• Response: Cells signaling leads to regulation of transportation or cytoplasmic activities.
• Apoptosis integrates multiple cell-signaling pathways.
| 8090404568 | Adenylyl Cyclase | an enzyme that converts ATP to cyclic AMP in response to an extracellular signal |  | 0 |
| 8090404569 | Apoptosis | a type of programmed cell death, which is brought about by activation of enzymes that break down many chemical components in the cell |  | 1 |
| 8090404570 | Aster | a radial array of short microtubules that extends from each centrosome toward the plasma membrane in an animal cell undergoing mitosis |  | 2 |
| 8090404571 | Autosome | a chromosome that is not directly involved in determining sex; not a sex chromosome |  | 3 |
| 8090404572 | Cyclic AMP (cAMP) | cyclic adenosine monophosphate, a ring-shaped molecule made from ATP that is a common intracellular signaling molecule (second messenger) in eukaryotic cells; it is also a regulator of some bacterial operons |  | 4 |
| 8090404573 | Diacylglycerol (DAG) | second messenger produced by the cleavage of the phospholipid PIP2 in the plasma membrane | 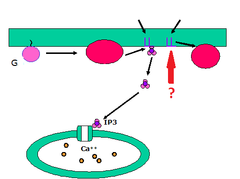 | 5 |
| 8090404574 | Diploid Cell | a cell containing two sets of chromosomes (2n), one set inherited from each parent |  | 6 |
| 8090404575 | G Protein | a GTP-binding protein that relays signals from a plasma membrane signal receptor, known as a G protein-coupled receptor, to other signal transduction proteins inside the cell |  | 7 |
| 8090404576 | G Protein-Coupled Receptor (GPCR) | a signal receptor protein in the plasma membrane that responds to the binding of a signaling molecule by activating a G protein; also called a G protein-linked receptor |  | 8 |
| 8090404577 | Hormone | in multicellular organisms, one of many types of secreted chemicals that are formed in specialized cells, travel in body fluids, and act on specific target cells in other parts of the organism, changing the target cells' functioning |  | 9 |
| 8090404578 | Inositol Trisphosphate (IP3) | a second messenger that functions as an intermediate between certain signaling molecules and a subsequent second messenger, Ca2+, by causing a rise in cytoplasmic Ca2+ concentration |  | 10 |
| 8090404579 | Ligand | a molecule that binds specifically to another molecule, usually a larger one |  | 11 |
| 8090404580 | Ligand-Gated Ion Channel | a transmembrane protein containing a pore that opens or closes as it changes shape in response to a signaling molecule (ligand), allowing or blocking the flow of specific ions; also called an ionotropic receptor |  | 12 |
| 8090404581 | Protein Kinase | an enzyme that transfers phosphate groups from ATP to a protein, thus phosphorylating the protein |  | 13 |
| 8090404582 | Protein Phosphatase | an enzyme that removes phosphate groups from (dephosphorylates) proteins, often functioning to reverse the effect of a protein kinase |  | 14 |
| 8090404583 | Reception | in cellular communication, the first step of a signaling pathway in which a signaling molecule is detected by a receptor molecule on or in the cell | 15 | |
| 8090404584 | Receptor Tyrosine Kinase (RTK) | a receptor protein spanning the plasma membrane, the cytoplasmic (intracellular) part of which can catalyze the transfer of a phosphate group from ATP to a tyrosine on another protein; receptor tyrosine kinases often respond to the binding of a signaling molecule by dimerizing and then phosphorylating a tyrosine on the cytoplasmic portion of the other receptor in the dimer |  | 16 |
| 8090404585 | Response | (1) in cellular communication, the change in a specific cellular activity brought about by a transduced signal from outside the cell; (2) in feedback regulation, a physiological activity triggered by a change in a variable |  | 17 |
| 8090404586 | Scaffolding Protein | a type of large relay protein to which several other relay proteins are simultaneously attached, increasing the efficiency of signal transduction |  | 18 |
| 8090404587 | Second Messenger | a small, nonprotein, water-soluble molecule or ion, such as a calcium ion (Ca2+) or cyclic AMP, that relays a signal to a cell's interior in response to a signaling molecule bound by a signal receptor protein |  | 19 |
| 8090404588 | Signal Transduction Pathway | a series of steps linking a mechanical, chemical, or electrical stimulus to a specific cellular response |  | 20 |

