| 2987171436 | The 4 fundamental units of life are: | All organisms are made of cells, The cell is the simplest collection of matter that can be alive, all sales are related by their descent from earlier cells, and cells can differ substantially from one another but share common features | 0 | |
| 2987171437 | Biologists use __________ and the tools of ___________ to study cells | microscopes; biochemistry | 1 | |
| 2987171438 | _______ are usually too small to be seen by the naked eye | Cells | 2 | |
| 2987171439 | In a _______________, visible light is passed through a specimen and then through glass lenses | light microscope | 3 | |
| 2987176952 | _________ refract or bend the light, so that the image is magnified | Lenses | 4 | |
| 2987180717 | The three important parameters of microscopy is: | Magnification, resolution, contrast | 5 | |
| 2987189601 | _____________ is the ratio of an object's image size compared to its real size | Magnification | 6 | |
| 2987193782 | ____________ is the measure of the clarity of the image, or the minimum distance of two distinguishable point | Resolution | 7 | |
| 2987196522 | __________ is the visible differences in brightness between parts of the sample | Contrast | 8 | |
| 2987205116 | _________________ can magnify effectively to about 1000 times the size of the actual specimen | Light microscopes | 9 | |
| 2987213591 | The ____________ of standard light microscopy is too low to study organelles | resolution | 10 | |
| 2987219317 | ____________ are the membrane-enclosed structures in eukaryotic cells | organelles | 11 | |
| 2987223096 | Two basic types of electron microscope's are used to study ____________ ___________ | subcellular structures | 12 | |
| 2987228843 | __________ __________ ___________ focus a beam of electrons onto the surface of the specimen, providing images that look 3-D | Scanning electron microscopes | 13 | |
| 2987233884 | _______________________ _____________ focus a beam of electrons through a specimen | Transmission electron microscopes | 14 | |
| 2987236557 | _______________________ are used mainly to study the internal structure of cells | Transmission electron microscopes | 15 | |
| 2987244852 | _____________________ and __________________________ provide sharper images of three-dimensional tissues and cells | Confocal microscopy, deconvolution microscopy | 16 | |
| 2987250642 | _____________________ is the fluorescent lighting and lasers | Confocal microscopy | 17 | |
| 2987258357 | _______________________ is fluorescent lighting and digital removal of out-of-focus light | Deconvolution microscopy | 18 | |
| 2987282172 | _________________ takes cells apart and separates the major organelles from one another | Cell refraction | 19 | |
| 2987295637 | _____________________ cells into their component parts | Centrifuges fractionate | 20 | |
| 2987299259 | _______________________ enable scientists to determine the functions of organelles | Cell refractionation | 21 | |
| 2987317024 | Homogenization |  | 22 | |
| 2987324473 | Eukaryotic cells have __________________ that compartmentalize their functions | internal membranes | 23 | |
| 2987329578 | The only organisms of the domains Bacteria and Archaea consist of ___________________ | prokaryotic cells | 24 | |
| 2987333633 | Protists, fungi, animals, and plants all consist of ___________________ | Eukaryotic cells | 25 | |
| 2987338944 | Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have what 4 features? | Plasma membrane, cytosol, chromosomes, ribosomes | 26 | |
| 2987348698 | __________ is a semi fluid substance | Cytosol | 27 | |
| 2987351858 | Prokaryotic cells differ from eukaryotic cells by having what 4 things? | No nucleus, DNA in an unbound region called the nucleoid, no membrane-bound organelles, cytoplasm bound by the plasma membrane | 28 | |
| 2987377918 | Prokaryotic cell parts |  | 29 | |
| 2987398540 | Eukaryotic cells differ from prokaryotic cells by having what 3 things | DNA in the nucleus that is bounded, membrane bound organelles, cytoplasm in the region between the plasma membrane and the nucleus | 30 | |
| 2987402803 | _____________ cells are usually much larger than _____________ cells | Eukaryotic, prokaryotic | 31 | |
| 2987407411 | The ________________ is a selective barrier that allows sufficient passage of oxygen, nutrients, and waste | plasma membrane | 32 | |
| 2987393828 | Plasma membrane structure and details |  | 33 | |
| 2987458364 | The ____________ to ___________ ratio of a cell is critical | surface area, volume | 34 | |
| 2987469275 | As a cell increases in size, its __________ grows proportionately more than its ___________ | volume, surface area | 35 | |
| 2987482209 | There are more cells which is better than less cells because of the amount of cell membranes between |  | 36 | |
| 2987488107 | A ________________ has internal membranes that break the cell into organelles | Eukaryotic cell | 37 | |
| 2987495070 | The basic fabric of biological membranes is a _________________________ and other __________. | double layer of phospholipids, lipids | 38 | |
| 2987502917 | Plant and animal cells have most of the same _____________ | Organelles | 39 | |
| 2987504612 | Endoplasmic reticulum |  | 40 | |
| 2987508510 | Plant cell |  | 41 | |
| 2990949780 | The eukaryotic cell's genetic instructions are housed in the ___________ and carried out by the ___________ | nucleus, ribosomes | 42 | |
| 2990951701 | The nucleus contains most of the __________ in a eukaryotic cell | DNA | 43 | |
| 2990954089 | ___________ use information from the DNA to make proteins | Ribosomes | 44 | |
| 2990978129 | The _________ contains most of the cell's genes and is usually the most obvious organelle | Nucleus | 45 | |
| 2990982443 | The ______________ encloses the nucleus, separating it from the cytoplasm | nuclear envelope | 46 | |
| 2990987545 | In the nuclear membrane, each membrane consists of a ____________ | lipid bilayer | 47 | |
| 2990992268 | Nuclear envelope |  | 48 | |
| 2990996759 | _________ regulates the entry and exit of molecules from the nucleus | Pores | 49 | |
| 2990999565 | The nuclear size of the envelope is lined by the _______________ | nuclear lamina | 50 | |
| 2991001111 | The nuclear lamina is composed of _________ and maintains the shape of the _________ | proteins, nucleus | 51 | |
| 2991037546 | In the nucleus, DNA is organized into discrete units called _____________ | chromosomes | 52 | |
| 2991042734 | The DNA and proteins of chromosomes are together called __________ | chromatin | 53 | |
| 2991046935 | __________ condenses to form discrete ____________ as a cell prepares to divide | Chromatin, chromosomes | 54 | |
| 2991051991 | The ___________ is located within the nucleus and is the site of ribosomal RNA a synthesis | nucleolus | 55 | |
| 2991053955 | Ribosomes carry out __________ synthesis in the cytosol and outside the ER | Protein | 56 | |
| 2991063512 | The ______________ system regulates protein traffic and performs metabolic functions in the cell | endomembrane | 57 | |
| 2991068571 | The Endomembrane system consist of the _______________, _____________________, ______________, ___________, __________, and _________________ | nuclear envelope, the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, vacuoles, and plasma membrane | 58 | |
| 2991080135 | The Endomembrane system components are either continuous or connected via transfer by _________ | vesicles | 59 | |
| 2991083174 | The _____ accounts for more than half of the total membrane in many eukaryotic cells | ER | 60 | |
| 2991085438 | The ER membrane is continuous with the _______________ | nuclear envelope | 61 | |
| 2991087208 | The ________ ER lacks ribosomes and the ________ ER is studded with ribosomes | smooth, rough | 62 | |
| 2991092224 | Endoplasmic reticulum and nuclear envelope model |  | 63 | |
| 2991096780 | The _____________ functions to synthesize lipids, medibolize carbohydrates, detoxify drugs and poisons, store calcium ions | Smooth ER | 64 | |
| 2991103397 | The __________ functions to secrete glycoproteins, distribute transport vesicles, to be a membrane factory for the cell | rough ER | 65 | |
| 2991104409 | _________________ are secretory proteins surrounded by membranes | Transport vesicles | 66 | |
| 2991107017 | _______________ are proteins covalently bonded to carbohydrates | Glycoproteins | 67 | |
| 2991114867 | The Golgi apparatus consist of flattened membranous sacs called ___________ | cisternae | 68 | |
| 2991118844 | The _________________ functions to modify products of the ER, manufacture certain macromolecules, sort and package materials into transport vesicles | Golgi apparatus | 69 | |
| 2991123441 | The Golgi apparatus |  | 70 | |
| 2991176499 | A lysosome is a membranous sac of ___________ enzymes that can digest _______________ | hydrolytic, macromolecules | 71 | |
| 2991181084 | Lysosomal enzymes work best in the ________ environment inside the lysosome | acidic | 72 | |
| 2991185858 | Hydrolytic enzymes and lysosomal membranes are made by ___________ and then transferred to the ________________ for further processing | rough ER, Golgi apparatus | 73 | |
| 2991192518 | Some cell types can engulf another cell by a process called ______________ | Phagocytosis | 74 | |
| 2991196125 | In order to digest the molecules, a __________ has to fuse with the food vacuole | lysosome | 75 | |
| 2991202849 | ____________ is a process where lysosomes use enzymes to recycle the cell's own organelles and macromolecules | Autophagy | 76 | |
| 2991204636 | Phagocytosis and autophagy model |  | 77 | |
| 2991230364 | Vacuoles are large vesicles derived from the ________________ and __________________ | ER ,Golgi apparatus | 78 | |
| 2991236765 | Food vacuoles are formed by ____________ | phagocytosis | 79 | |
| 2991238010 | _________________, which are found in many freshwater protist, pump excess water out of cells | Contractile vacuoles | 80 | |
| 2991243854 | _________________, which are found in mature plant cells, hold organic compounds and water | Central vacuoles | 81 | |
| 2991248895 | _____________ and _____________ change energy from one form to another | Mitochondria, chloroplasts | 82 | |
| 2991252677 | _______________ are the sites of cellular respiration | Mitochondria | 83 | |
| 2991254255 | ______________ are the sites of photosynthesis | Chloroplasts | 84 | |
| 2991256221 | Peroxisomes are ___________ organelles | oxidative | 85 | |
| 2991322188 | ____________ and __________ are similar to bacteria because they are enveloped by double membrane, contain free ribosomes and circular DNA, grow and reproduced somewhat independently in cells | Mitochondria and chloroplasts | 86 | |
| 2991332561 | The similarities between mitochondria and chloroplasts, and bacteria has led to _______________________ | the endosymbiont theory | 87 | |
| 2991339362 | The ___________________ suggests that an early ancestor of eukaryotes engulfed an oxygen-using nonphotosynthetic prokaryotic cell | endosymbiont theory | 88 | |
| 2997503056 | Mitochondria are in nearly all _____________ cells | eukaryotic | 89 | |
| 2997512903 | Mitochondria have a smooth outer membrane and an inner membrane folded into ________ | cristae | 90 | |
| 2997521982 | The inner membrane in a mitochondrion create two compartments: _________________ and _________________ | Intermembrane space, mitochondrial matrix | 91 | |
| 2997535067 | Diagram of mitochondrion |  | 92 | |
| 2997541023 | Chloroplasts contain the green pigment called ______________ | chlorophyll | 93 | |
| 2997545040 | _____________ are found in leaves and other green organs of plants and in algae | Chloroplasts | 94 | |
| 2997555660 | Diagram of chloroplast |  | 95 | |
| 2997562637 | The chloroplast structure includes ___________ and the _________ | thylakoids, stroma | 96 | |
| 2997568031 | _____________ are membranous sacs in chloroplasts | Thylakoids | 97 | |
| 2997573396 | The ________ is the internal fluid in a chloroplast | Stroma | 98 | |
| 2997581434 | Granum are stacks of ____________ in a chloroplast | Thylakoids | 99 | |
| 2997588199 | The chloroplast is one of a group of plant organelles called ________ | plastids | 100 | |
| 2997594574 | ______________ are specialized metabolic compartments bounded by single membrane | Peroxisomes | 101 | |
| 2997599486 | Peroxisomes produce __________________ and convert it to water | hydrogen peroxide | 102 | |
| 2997606052 | The _______________ is a network of fibers extending throughout the cytoplasm | cytoskeleton | 103 | |
| 2997609390 | The cytoskeleton organizes the cell's ___________ and __________, anchoring many organelles | structures, activities | 104 | |
| 2997621048 | ______________, ________________, _____________________ make up the cytoskeleton | Microtubules, microfilaments, and intermediate filaments | 105 | |
| 2997636030 | Microtubules, microfilaments model | Intermediate filaments not shown |  | 106 |
| 2997648359 | The cytoskeleton help to __________ the cell and maintain its _______ | support, shape | 107 | |
| 2997659381 | Motor protein diagram |  | 108 | |
| 2997669099 | The three main types of fibers that make up the cytoskeleton in order from thickest to thinnest: | Microtubules, intermediate filaments, microfilaments | 109 | |
| 2997684312 | The main function of microtubules, also called ________ _________, maintain the cell _________________ | tubulin polymers, shape and motility | 110 | |
| 2997698945 | The main function of microfilaments, also called _______ __________, is __________________ | actin filaments, muscle contraction | 111 | |
| 2997714848 | The main function of intermediate filaments is to _______________________ ________________ | anchor the nucleus and other organelles | 112 | |
| 2997726620 | ______________ are hollow rods and function to separate chromosomes during cell division | Microtubules | 113 | |
| 2997735924 | In animal cells, microtubules grow out from a _____________ near the nucleus | centrosome | 114 | |
| 2997744721 | In animal cells, the centrosome has a pair of ___________, each with _____ triplets of microtubules arranged in a ______ | centrioles, nine, ring | 115 | |
| 2997751790 | Centrioles and centrosome |  | 116 | |
| 2997759021 | Microtubules control the _________ of flagella and cilia, which differ in pattern | beating | 117 | |
| 2997771635 | ______ and _________ are microtubule-containing extensions that project from some cells | Cilia, flagella | 118 | |
| 2997789320 | Cilia and flagella share 3 common structures: | A core of microtubules sheathed by the plasma membrane, a basal body, and a motor protein called dynein | 119 | |
| 2997811953 | Structure of cilium |  | 120 | |
| 2997819274 | Cells crawl along a surface by extending _____________ and moving toward them | pseudopodia | 121 | |
| 2997825365 | __________ ____________ is a circular flow of cytoplasm within cells | Cytoplasmic streaming | 122 | |
| 2998086887 | In plant cells, ______-_______ interactions and _____-____ transformations drive cytoplasmic streaming | actin-myosin, sol-gel | 123 | |
| 2998107471 | __________________ are more permanent cytoskeleton fixtures than the other two classes | Intermediate filaments | 124 | |
| 2998120972 | The _________ is an extracellular structure that distinguishes plant cells from animal cells | cell wall | 125 | |
| 2998115325 | Prokaryotes, fungi, and some unicellular eukaryotes have a __________ | Cell wall | 126 | |
| 2998127054 | Plant cell walls are made of __________________ embedded in other polysaccharides and protein | cellulose fibers | 127 | |
| 2998134143 | The multiple layers in a plant cell wall are: | Primary cell wall, middle lamella, secondary cell wall | 128 | |
| 2998148694 | The _________________ layer is relatively thin and flexible | primary cell wall | 129 | |
| 2998158345 | The ______________ is a thin layer between primary walls of adjacent cells | middle lamella | 130 | |
| 2998164750 | The __________________ is added between the plasma membrane and the primary cell wall | secondary cell wall | 131 | |
| 2998170538 | __________________ are channels between adjacent plant cells | Plasmodesmata | 132 | |
| 2998194517 | Plasmodesmata, and plant cell wall diagram | 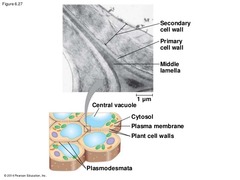 | 133 | |
| 2998204642 | Animal cells lack cell walls but are covered by an elaborate extracellular matrix which is made of certain _______________ | glycoproteins | 134 | |
| 2998214838 | Collagen, proteoglycans, and fibronectin make up the ___________________ | Extracellular matrix (ECM) | 135 | |
| 2998223516 | ECM proteins bind to receptor proteins in the plasma membrane called __________ | integrins | 136 | |
| 2998228467 | Extracellular matrix |  | 137 | |
| 2998237206 | ECM can regulate a cell's behavior by communicating with the cell through __________ | integrins | 138 | |
| 2998269915 | _______________ are membranes of neighboring cells that are pressed together to prevent leakage of extracellular fluid in animal cells | Tight junctions | 139 | |
| 2998278854 | ______________, also called anchoring junctions, fasten cells together into strong sheets | Desmosomes | 140 | |
| 2998287782 | ______________, also called communicating junctions, provide cytoplasmic channels between adjacent cells | Gap junctions | 141 | |
| 2998343894 | Cell junctions |  | 142 |
(AP Biology) Chapter 6: A tour of the cell Flashcards
Primary tabs
Need Help?
We hope your visit has been a productive one. If you're having any problems, or would like to give some feedback, we'd love to hear from you.
For general help, questions, and suggestions, try our dedicated support forums.
If you need to contact the Course-Notes.Org web experience team, please use our contact form.
Need Notes?
While we strive to provide the most comprehensive notes for as many high school textbooks as possible, there are certainly going to be some that we miss. Drop us a note and let us know which textbooks you need. Be sure to include which edition of the textbook you are using! If we see enough demand, we'll do whatever we can to get those notes up on the site for you!

