THE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF MACROMOLECULES
| 7276269354 | macromolecule | A giant molecule formed by the joining of smaller molecules, usually by a condensation reaction. Polysaccharides, proteins, and nucleic acids are examples of this type of molecule. | 0 | |
| 7276269355 | polymer | A long molecule consisting of many similar or identical monomers linked together. | 1 | |
| 7276269356 | monomer | The subunit that serves as the building block of a polymer. | 2 | |
| 7276269357 | condensation reaction (dehydration synthesis) | A reaction in which two molecules become covalently bonded to each other through the loss of a small molecule, usually water, in which case it is also called a dehydration reaction. |  | 3 |
| 7276269358 | hydrolysis | A chemical process that lyses, or splits, molecules by the addition of water, functioning in disassembly of polymers to monomers. |  | 4 |
| 7276269359 | carbohydrate | A sugar (monosaccharide) or one of its dimers (disaccharides) or polymers (polysaccharides). | 5 | |
| 7276269360 | monosaccharide | The simplest carbohydrate, active alone or serving as a monomer for disaccharides and polysaccharides. Also known as simple sugars, monosaccharides have molecular formulas that are generally some multiple of CHO. |  | 6 |
| 7276269361 | dissacharide | A double sugar, consisting of two monosaccharides joined by a glycosidic linkage formed during dehydration synthesis. |  | 7 |
| 7276269362 | glycosidic linkage | A covalent bond formed between two monosaccharides by a dehydration reaction. |  | 8 |
| 7276269363 | polysaccharide | A polymer of many monosaccharides, formed by dehydration reactions. |  | 9 |
| 7276269364 | starch | A storage polysaccharide in plants, consisting entirely of glucose monomers joined by glycosidic linkages. |  | 10 |
| 7276269365 | glycogen | An extensively branched glucose storage polysaccharide found in the liver and muscle of animals; the animal equivalent of starch. |  | 11 |
| 7276269366 | cellulose | A structural polysaccharide of plant cell walls, consisting of glucose monomers joined by β glycosidic linkages. |  | 12 |
| 7276269367 | chitin | A structural polysaccharide, consisting of amino sugar monomers, found in many fungal cell walls and in the exoskeletons of all arthropods. |  | 13 |
| 7276269368 | fat | A lipid consisting of three fatty acids linked to one glycerol molecule; also called a triacylglycerol or triglyceride. | 14 | |
| 7276269369 | triaglycerol (Triglyceride) | Three fatty acids linked to one glycerol molecule; also called a fat or a triglyceride. |  | 15 |
| 7276269370 | unsaturated fatty acid | A fatty acid possessing one or more double bonds between the carbons in the hydrocarbon tail. Such bonding reduces the number of hydrogen atoms attached to the carbon skeleton. |  | 16 |
| 7276269371 | saturated fatty acid | A fatty acid in which all carbons in the hydrocarbon tail are connected by single bonds, thus maximizing the number of hydrogen atoms that are attached to the carbon skeleton. |  | 17 |
| 7276269372 | trans fat | An unsaturated fat containing one or more trans double bonds. |  | 18 |
| 7276269373 | phospholipid | A lipid made up of glycerol joined to two fatty acids and a phosphate group. The hydrocarbon chains of the fatty acids act as nonpolar, hydrophobic tails, while the rest of the molecule acts as a polar, hydrophilic head. Phospholipids form bilayers that function as biological membranes. |  | 19 |
| 7276269374 | steroid | A type of lipid characterized by a carbon skeleton consisting of four rings with various chemical groups attached. |  | 20 |
| 7276269375 | cholesterol | A steroid that forms an essential component of animal cell membranes and acts as a precursor molecule for the synthesis of other biologically important steroids, such as hormones. |  | 21 |
| 7276269376 | polypeptide | A polymer (chain) of many amino acids linked together by peptide bonds. |  | 22 |
| 7276269377 | protein | A functional biological molecule consisting of one or more polypeptides folded and coiled into a specific three-dimensional structure. | 23 | |
| 7276269378 | amino acid | An organic molecule possessing both carboxyl and amino groups. Amino acids serve as the monomers of polypeptides. |  | 24 |
| 7276269379 | peptide bond | The covalent bond between the carboxyl group on one amino acid and the amino group on another, formed by a dehydration reaction. | 25 | |
| 7276269380 | X-ray crystallography | A technique that depends on the diffraction of an X-ray beam by the individual atoms of a crystallized molecule to study the three-dimensional structure of the molecule. |  | 26 |
| 7276269381 | gene | A discrete unit of hereditary information consisting of a specific nucleotide sequence in DNA (or RNA, in some viruses). | 27 | |
| 7276269382 | nucleic acid | A polymer (polynucleotide) consisting of many nucleotide monomers; serves as a blueprint for proteins and, through the actions of proteins, for all cellular activities. The two types are DNA and RNA. | 28 | |
| 7276269383 | deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) | A double-stranded, helical nucleic acid molecule consisting of nucleotide monomers with a deoxyribose sugar and the nitrogenous bases adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and thymine (T); capable of replicating and determining the inherited structure of a cell's proteins. | 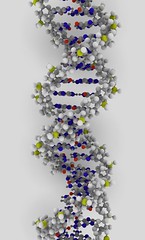 | 29 |
| 7276269384 | ribonucleic acid (RNA) | A type of nucleic acid consisting of nucleotide monomers with a ribose sugar and the nitrogenous bases adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and uracil (U); usually single-stranded; functions in protein synthesis, gene regulation, and as the genome of some viruses. |  | 30 |
| 7276269385 | polynucleotide | A polymer consisting of many nucleotide monomers in a chain; nucleotides can be those of DNA or RNA. |  | 31 |
| 7276269386 | nucleotide | The building block of a nucleic acid, consisting of a five-carbon sugar covalently bonded to a nitrogenous base and a phosphate group. |  | 32 |
| 7276269387 | purine | One of two types of nitrogenous bases found in nucleotides, characterized by a six-membered ring fused to a five-membered ring. |  | 33 |
| 7276269388 | pyrimidine | One of two types of nitrogenous bases found in nucleotides, characterized by a six-membered ring. |  | 34 |
| 7276269389 | ribose | The sugar component of RNA nucleotides. | 35 | |
| 7276269390 | deoxyribose | The sugar component of DNA nucleotides, having one fewer hydroxyl group than ribose, the sugar component of RNA nucleotides. | 36 | |
| 7276269391 | double helix | The form of native DNA, referring to its two adjacent antiparallel polynucleotide strands wound around an imaginary axis into a spiral shape. |  | 37 |
| 7276269392 | 2 purines | Adenine (A) and guanine (G). | 38 | |
| 7276269393 | 3 pyrimidines | Cytosine (C), thymine (T), and uracil (U). | 39 | |
| 7276269394 | endergonic reaction | A reaction requiring a net input of free energy | 40 | |
| 7276269395 | exergonic reaction | Reaction that proceeds with a net release of free energy. | 41 | |
| 7276269396 | alcohol | A substituted hydrocarbon that contains one or more hydroxyl groups |  | 42 |
| 7276269397 | carbonyl/aldehyde | carbon atom with a double bond to an oxygen atom |  | 43 |
| 7276269398 | carboxyl | A functional group present in organic acids and consisting of a single carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom and also bonded to a hydroxyl group. |  | 44 |
| 7276269399 | hydroxyl | A functional group consisting of a hydrogen atom joined to an oxygen atom by a polar covalent bond. Molecules possessing this group are soluble in water and are called alcohols. |  | 45 |
| 7276269400 | reduction | Any process in which electrons are added to an atom or ion (as by removing oxygen or adding hydrogen) | 46 | |
| 7276269401 | oxidation | To attach oxygen, to remove hydrogen, or to remove electrons from a molecule. | 47 | |
| 7276269402 | phosphate |  | 48 | |
| 7276269403 | amino group | A functional group that consists of a nitrogen atom bonded to two hydrogen atoms |  | 49 |
| 7276269404 | sulfhydryl |  | 50 | |
| 7276269405 | greenhouse effect | Natural situation in which heat is retained in Earth's atmosphere by carbon dioxide, methane, water vapor, and other gases |  | 51 |
| 7276269406 | ozone layer | Layer of the stratosphere with a high concentration of ozone; absorbs most of the Sun's harmful ultraviolet radiation |  | 52 |

