| 8296297583 | Environmental Determinism | proposes that cultures are a direct result of where they exist - warmer climates tend to cause inhabitants to have a more relaxed attitude toward work & progress -Europeans and people from colder climates were more motivated, intelligent, and culturally advanced than those from warmer climates | 0 | |
| 8392169274 | Possiblism | humans are not a product of their environment but posses the skills necessary to modify their environment to fit human needs- people determine their outcomes | 1 | |
| 8392410315 | Cultural ecology | is the study of human adaptations to social and physical environments | 2 | |
| 8392437181 | GIS | uses geographic information and layers into a new map showing specific types of geographic data ----help us get around -highways,population density |  | 3 |
| 8392482974 | GPS | satalite imagery,remote sensing- found in cars, cell phones | 4 | |
| 8392498570 | Map distortion | the further that one goes from the equator, the greater the distortion on the map | 5 | |
| 8392515917 | Cartography | someone who makes maps | 6 | |
| 8392525338 | Small scale map | shows more area but in less detail -small=large | 7 | |
| 8392553087 | large scale map | shows a smaller area but in greater detail | 8 | |
| 8392562670 | Cartogram | assigned data by size | 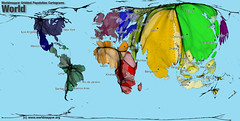 | 9 |
| 8392583716 | Choropleth map | useful for determing demographic data Ex. infant mortality rates, assigning colors or patterns to areas -lightest-lowest concentration -dark heavy/more amount of people per square mile |  | 10 |
| 8392649056 | Flow line map | movement of immigrants/migration by religion- thicker arrow more people |  | 11 |
| 8392681611 | Proportional symbol map | the amount of oil the state is using- larger circle the greater the data |  | 12 |
| 8392711246 | Dot maps | more dots- more libraries- east coast-more detailed |  | 13 |
| 8392726920 | Isoline maps | uses color- characteristics of an area- elevation amount of rainfall temperature |  | 14 |
| 8392747549 | Formal region | Regions were anything and everyhting inside has the same characteristics- political zone, language and other cultural traits-state- regions | 15 | |
| 8392930574 | Functional region | point or range-movement-intensity-cell phone towers- central place | 16 | |
| 8392971535 | Distance decay | sphere of influence is reduced as the distance increases |  | 17 |
| 8395380117 | Perceptual/Vernacular Region | Vernacular- based off of perseptions or feeling boundaries can change Perceptual- middle east- sw asia | 18 | |
| 8395491248 | Relative location | giving their location in reference to another feature on Earth's surface |  | 19 |
| 8395528701 | Absolute location | using latitude and longitude coordinates to find an exact location- specific |  | 20 |
| 8395560989 | Hearth | starting point- place where the characteristics began Ex. hearth of basketball is in Springfield, Mass | 21 | |
| 8395915062 | Relocation diffusion | physical spread of cultures, ideas, and disease through people - must move through one place to another | 22 | |
| 8395869411 | Migration diffusion | physical spread of people and their movement from one place to another - perminate move | 23 | |
| 8395970054 | Expansion diffusion | spread of a characteristic from a central node or a hearth through various means - no physical movement- spread through internet, book | 24 | |
| 8396023747 | Hierarchical diffusion | idea that a phenomenon (thing) spreads as a result of a group, usually the social elite spreading ideas or patterns in a society | 25 | |
| 8396089558 | Contagious diffusion | spread of disease -internet | 26 | |
| 8396191451 | Physiological diffusion | refers to the total number of people divided by the farmable land | 27 | |
| 8396264384 | Arithmetic density | more accurate - calculates the density using all the land in a given area |  | 28 |
| 8396330719 | Concentration | refers to the proximity of a particular phenomenon over the area in which it is spread - in the concentration the objects considered clustered or agglomerated- close togeather dispersed or scattered- spread out | 29 | |
| 8400422908 | Pattern -linear -centralized - random distrubition | relates to how objects are organized in their space - laid out on a singular line -clustered together -lack of pattern on the landscape | 30 | |
| 8400498719 | Crude birth rate | refers to the number of births per 1,000 people in the population |  | 31 |
| 8400526842 | Crude death rate | number of deaths per 1,000 people |  | 32 |
| 8400564346 | Overpopulation | defined as the lack of necessary resources to meet the needs of the population of a defined area Ex. food,water,shelter |  | 33 |
| 8400723119 | Carrying capicity | the ability of the land to sustain a certain number of people |  | 34 |
| 8400789191 | Ecumene | habitable land - area where humans can live | 35 | |
| 8400849908 | Underpopulated | Dominated by agriculture Ex. The Great Plains Of America more resources than people | 36 | |
| 8400944969 | World population centers (regions) | The largest cities in the world by land area, population and density | 37 | |
| 8401013973 | Thomas Malthus | concluded that the rate of population was growing at a faster rate than agriculture productivity- scared we were going to run out of food | 38 | |
| 8401199351 | Linear growth | simply growth that occurs evenly across each unit of time |  | 39 |
| 8401279440 | Exponential growth | looks at growth as a percentage of the total population |  | 40 |
| 8401397845 | The demographic transition model | describes human activities in the past and predicts human activities in the future |  | 41 |
| 8401483529 | Infant mortality rate | number of babies per 1,000 that die before their first birthday | 42 | |
| 8401522687 | Total fertility rate | number of babies on average women delivers during her childbearing years |  | 43 |
| 8401899904 | Replacement rate | the amount of fertility needed to keep the population the same from generation to generation | 44 | |
| 8401996936 | Population pyramid | way to identify a population's sex ratio |  | 45 |
| 8402085890 | Dependency ratio | those aged 0-14 and over 65 depend on the workforce for support | 46 | |
| 8402121892 | Demographic momentum | continued population increase as a result of a large segment being young | 47 | |
| 8402175723 | Dowry death | when the grooms family kills the bride bc of her inability to pay the dowery- womens family must pay the grooms for the right to marry | 48 | |
| 8403082487 | Doubling time | the number of years that it takes for a country to double its population | 49 | |
| 8403102524 | J- curve | places countries on a scale based on their openess & stability | 50 | |
| 8403133339 | Pull factors | conditions that attract people to move to a region Ex. regular pay check-medical care- 1 reason people move is for jobs |  | 51 |
| 8403185264 | Push factors | condition that causes people to want to leave a region Ex. environmental hazards, high cost of land |  | 52 |
| 8420479867 | Refugees | someone who has been forced to flee their country | 53 | |
| 8420538698 | Asylum seeker | asking the government the government to keep you safe/protection- seeking safety in another country |  | 54 |
| 8420601600 | Forced migrants | literally forced out of their homes for either political or environmental reasons Ex. Jews moving from Europe to US- fled the Nazis for dear of death | 55 | |
| 8420662162 | Voluntary migration | people have a choice to move Ex. many people from the north who are retired move to Florida bc of the warmer climate |  | 56 |
| 8420780233 | Ravenstein's law of migration | -most migrants travel only a short distance -migrants travelling long distances usually settle in urban areas bc of the jobs -most migration occurs in steps -not true in today's society -most migration is rural to urban - each migration flow produces a movement in the opposite direction (counter flow)-ppl sometimes move back home -most migrants are single adults -females are more migratory than males within a country |  | 57 |
| 8420916393 | Chain migration | usually voluntary in nature and functions to reunite families and cultures- send money back to family members | 58 | |
| 8420984275 | Rural to Urban migration | most typical type of intraregional migration- movement of people within the same region | 59 | |
| 8421074692 | Urban to Suburban migration | brickell to homestead | 60 | |
| 8421127982 | Cyclic movement | seasonal migration of livestock to areas where food is more available | 61 | |
| 8421180552 | Transhumance | movement of livestock to higher elevation during the summer to escape the heat in the valleys and to lower elevations during the winter to escape the severe cold of the mountains | 62 | |
| 8421250490 | Intervening obstacles | halt and change migrations plans due to some negative factor cultural to physical | 63 | |
| 8421282560 | Quotas | limits that governments put on the number of immigrants they allow into their county |  | 64 |
| 8421307038 | Remittances | legal and illegal immigrants often send their earnings to their families back in their home country |  | 65 |
| 8421346468 | Cencus | a detailed counting of the population has occurred in the US every 10 years | 66 | |
| 8300811882 | Folk culture | practice of a particular custom by a relatively small group of people in a focused area Ex. father teaches son to how to harvest crops the way it has been done for hundreds of years | 67 | |
| 8296586188 | Popular culture | large societies that share certain habits despite difference in other personal characteristics Ex. Tex-Mex music | 68 | |
| 8300903206 | Built enviroment | tangible impact of human beings on the lansdcape Ex. buildings, parks, man made lakes | 69 | |
| 8300954762 | Folklore | stories that are passed on from generation to generation Ex. bedtime stories |  | 70 |
| 8301020037 | Cultural landscape | interactions of a group in relation to their own cultural practices as well as to the values of society as reflected through artifacts and architecture Ex. mosques, churches, temples |  | 71 |
| 8301073254 | Adaptive stragety | how a person adapts to a new culture Ex. move from FL->NYC - encounter snow | 72 | |
| 8301111874 | Culture region core domain | a region defined by similar culture traits and cultural landscape features the zone of greatest concentration that characterize a region area outside of the core of a culture region in which the culture is still dominant but less intense * the domain & sphere togeather are sometimes called the periphery | 73 | |
| 8421438997 | Cultural identity | a sense of personal connection with a particular cultural group | 74 | |
| 8301299353 | Nation | not a country - a group of people Ex. cherokee, french are nations but they live in the countries US, France | 75 | |
| 8301350255 | State | a political entity Ex the government- secetary of state | 76 | |
| 8301368282 | Nation-State | boundaries of a nation and state match up almost perfectly Ex. France, England, Norway | 77 | |
| 8301390592 | Acculturation | when one group of people adopt the culture traits of another culture |  | 78 |
| 8301481530 | Assimilation | process of less dominant cultures losing their culture to a more dominant culture Ex. hebrew | 79 | |
| 8301517299 | Folk music | conveys information about daily activities, life cycle events and are familiar to a group of people (village). Ex. In Vietnam there are songs that convey farming techniques (agriculture technology). | 80 | |
| 8301664948 | Folk songs | traditionally sung by the common people of a region and forms part of their culture | 81 | |
| 8301682391 | Sequent occupance | succesive groups of populations occupy a territory and modify the previous landscapes- group leaves their imprint on a place | 82 | |
| 8301757533 | Cultural globalization | city scape of the world- starting to look the same - people have shared ideas as to what is urban landscape Ex. Shanghi looks like Seattle | 83 | |
| 8301787766 | Uniform landscape | all over the world the land looks the same Ex. highways, gas stations, malls- Mc donalds logo does not change anywhere in the world | 84 | |
| 8301915601 | Mediterranean agriculture | olives, figs, dates farming of fruits and vegtables | 85 | |
| 8301885367 | Fusion cusine | mixing more than one global food tadition into one dish Ex. sokai place at falls- Japaneese & Pervuian | 86 | |
| 8301964232 | Folk food | sushi- Japan tacos-mexico | 87 | |
| 8301978946 | taboo | a restriction on behavior imposed by social custom Ex. muslims have a taboo agnist heating pork hindus have a taboo agnist eating beef | 88 | |
| 8302010592 | terrior | contribution of a location distinctive physical features to the way food tastes Ex. coffee, wine | 89 | |
| 8302987332 | Monolingual country | only has 1 official language all govenment buisness is conducted Ex. Italy- Itallian France-French | 90 | |
| 8303011302 | Multilingual country | has more than one official language Ex. Switzerland has German, French, Italian, Roman | 91 | |
| 8303028876 | Lingua Franca | a language used as a common tounge among people who speak diverse languages- often to conduct business - different parts of the world have different lingua franca -English is a global LF -2 reasons for LF -buisness/trade - travel purposes pilots travel around the world have to speak english | 92 | |
| 8303073081 | Dialect | regional variation of a language distinguished by distinctive vocab, spelling, and pronunciation -English has a variety of dialects Ex. in England the standard form of English spoken by the queen, politicians,actors is called the BRP | 93 | |
| 8303130882 | Isogloss | boundary of a dialect -people pronounce diff words diff ways- boundaries lines for words like "yall"(south) "you guys"(north) are established through an isogloss | 94 | |
| 8303185829 | Pidgin language | mix of languages- nonnative speakers- happens when one one speaks the same language but have to communicate-people were forced to communicate for trade | 95 | |
| 8303223439 | Creole language | have native speakers-has a name- know rules but not written yet- after 3-4 generations | 96 | |
| 8303268778 | Indo-european languages | Branch- Germanic Group- west Germanic Individual lang-Endlish Indo-india European-europe | 97 | |
| 8303309090 | Official language | lang. in which all government business is conducted in -taught in schools -*official/native lang. can be diff | 98 | |
| 8303346588 | Language family | groups of languages organized by their common heritage | 99 | |
| 8303367097 | Language group | people whos languages are decended from a common tounge Ex. France & Spain- Romance languages | 100 | |
| 8303396432 | Toponymy | a word that means a name of a place Ex. Los Angles-> Los Angles( spanish) | 101 |
AP HUG MIDTERM Flashcards
Primary tabs
Need Help?
We hope your visit has been a productive one. If you're having any problems, or would like to give some feedback, we'd love to hear from you.
For general help, questions, and suggestions, try our dedicated support forums.
If you need to contact the Course-Notes.Org web experience team, please use our contact form.
Need Notes?
While we strive to provide the most comprehensive notes for as many high school textbooks as possible, there are certainly going to be some that we miss. Drop us a note and let us know which textbooks you need. Be sure to include which edition of the textbook you are using! If we see enough demand, we'll do whatever we can to get those notes up on the site for you!

