| 9682757949 | Development | A process of improvement in the material conditions of people through diffusion of knowledge and technology. In order to be in the last part of the demographic transition model a country needs to develop. |  | 0 |
| 9682757950 | Foreign direct investment | Investment made by a foreign company in the economy of another country. Usually companies invest where work is cheaper. |  | 1 |
| 9682757951 | Gross domestic product | The total value of goods and services produced within the borders of a country during a specific time period, usually one year. GDP is important to a countries economic world rating. |  | 2 |
| 9682757952 | Gross national product | The total value of goods ad services, including income received from abroad, produced by the residents of a country within a specific time period, usually one year. Like "gross domestic product," only the incomes that people earn abroad are also considered |  | 3 |
| 9682757953 | Human development index | Measure used by the United Nations that calculates development not in terms of money or productivity but in terms of human welfare. The HDI evaluates human welfare and costs of living. | 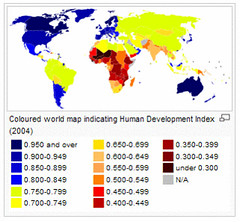 | 4 |
| 9682757954 | Measures of development | The process of achieving an optimum level of health and well-being. It includes physical, biological, mental, emotional, social, educational, economic, and cultural components. |  | 5 |
| 9682757955 | Rostows "Stages of Growth" model | Five stages a country goes through in developing their economy through international trade. Rostows "Stages of Growth" model shows how long and how much a country can develop its trade. |  | 6 |
| 9682757956 | World System model | Theorized that the modern network of countries engaged in trade and competition emerged when European nations began exploring the rest of the world. Immanuel Wallerstein developed model to explain a three level hierarchy in the world: core, periphery, and semi-periphery. |  | 7 |
| 9682757957 | Agglomeration | The term often refers to manufacturing plants and businesses that benefit from close proximity because they share skilled-labor pools and technological and financial amenities. This process involves the clustering or concentrating of people or activities. |  | 8 |
| 9682757958 | Fordism | The manufacturing economy and system derived from assembly-line mass production and the mass consumption of standardized goods. This type of work was named after Henry Ford. |  | 9 |
| 9682757959 | Break-of-bulk point | A location where goods are transferred from one type of carrier to another. For example from barge to railroad. |  | 10 |
| 9682757960 | Deindustrialization | Process by which companies move industrial jobs to other regions with cheaper labor, leaving the newly deindustrialized region to switch to a service economy and to work through a period of high unemployment. A synonym is outsourcing, since both deal with the moving of jobs. |  | 11 |
| 9682757961 | Industrial location theory | Alfred Weber, the selection of optimal factory locations has much to do with the minimization of land, labor, resource, and transportation costs, variable-cost framework that affects location of factory sites. This made back in the 1900s where there were only a couple of markets. |  | 12 |
| 9682757962 | Industrial Revolution | A period of rapid growth in the use of machines in manufacturing and production that began in the mid-1700s. Began in England with the invention of the steam engine. |  | 13 |
| 9682757963 | Infrastructue | The basic physical systems of transportation, communication, sewage water, and electric. Infrastructure is what we call interstates and roads. |  | 14 |
| 9682757964 | International division of labor | A division of work between rich and poor countries under which low-waged workers in the global South do assembly, manufacturing, and office work on contract to companies based in the global North. The process where the assembling procedures for a product are spread out through different parts of the world. |  | 15 |
| 9682757965 | Maquiladora | A foreign-owned assembly company located in the United States-Mexico border region in order to take advantage of cheaper labor, favorable tax breaks, and lax environmental regulations. This company was located near the border due to export processing zones. |  | 16 |
| 9682757966 | Outsourcing | Sending industrial processes out for external production. The term outsourcing increasingly applies not only to traditional industrial functions, but also to the contracting of service industry functions to companies to overseas locations, where operating costs remain relatively low. A decision by a corporation to turn over much of the responsibility for production to independent suppliers is an example of outsourcing. |  | 17 |
| 9682757967 | Postindustrial | People moving into the service sector, quaternary and quinary sectors of the economy. Information is created, processed, and stored in the postindustrial era. |  | 18 |
| 9682757968 | Transnational corporation | A company that conducts research, operates factories, and sells products in many countries, not just where its headquarters or shareholders are located. Apple is a real life example of a transnational corporation company. |  | 19 |
| 9682757969 | Bulk-gaining industry | An industry in which the final product weighs more or comprises a greater volume than the inputs. Coca-cola is an example of bulk-gaining product. |  | 20 |
| 9682757970 | Bulk-reducing industry | An industry in which the final product weighs less or comprises a lower volume than the inputs. Copper factories have to be close to the mine because of bulk-reducing industry. |  | 21 |
| 9682757971 | Market oriented | The degree to which a company follows the marketing concept. At one point in the evolution of marketing, the United States entered a buyer's market and the customer became king. Which era is being described. |  | 22 |
| 9682757972 | Resource oriented | Weight-losing; lower cost of transportation for finished product. Industries that are located close to the resource because it is too heavy/bulky to transport in resource oriented industries. |  | 23 |
| 9682757973 | Categories of wealth | MDC's are more developed countries with better quality of life and LDC's are the opposite. MDC's have a higher fraction of wealth and are in the final state of the demographic model. |  | 24 |
| 9682757974 | Industrial regions | A region with extremely dense industry. It is usually heavily urbanized. Western Europe, Eastern Europe, North America, East Asia are the industrial regions of the world. |  | 25 |
| 9682757975 | Cottage Industry | Weaving, sewing, carving, and other small-scale industries that can be done in the home. The laborers, frequently women, are usually independent. Most manufacturing was done this way before the industrial revolution. An industry in which the production of goods and services is based in homes, as opposed to factories. |  | 26 |
| 9682757985 | Comparison of transportation systems |  | 27 | |
| 9682757976 | Site factors of industrial locations | Three economic factors based on the location of a factory: land, labor, and capital. One of the two geographic costs an ordinary company will face and results from the unique characteristics of location. |  | 28 |
| 9682757977 | Situational factors of industrial location | Proximity(physical distance), Familiarity(mere exposure effect). The less money there is in a place the lower the wages can be. |  | 29 |
| 9682757978 | Brandt line | Imaginary line that separates the rich "Global North" from the poor "Global South". The Brandt line is a line created 30 years ago so it is very ineffective. |  | 30 |
| 9682757979 | Changing geography of jobs | Shift from extracting natural resources from the earth, to converting raw materials into goods and services, to selling the goods and services. There are more computer and technologies created than ever before. |  | 31 |
| 9682757980 | Just-in-time delivery | Method of inventory management made possible by efficient transportation and communication systems, whereby companies keep on hand just what they need for near-term production, planning that what they need for longer-term production will arrive when needed. Shipment of parts and materials to arrive at a factory moments before they are needed usually by mail companies. |  | 32 |
| 9682757981 | International trade approach | Method of improving a country's development that pushes the country to identify its unique set of strengths in the world and to channel investment toward building on these strengths. To compete internationally, this approach argues, a country must find out what it can offer the world and capitalize on that good or service. |  | 33 |
| 9682757982 | Self-suffiency model | Focus on local economy-wide growth (promote internal development. More focus on making the most profit for the country. |  | 34 |
| 9682757983 | Informal economy | Economic activity that is neither taxed nor monitored by a government; and is not included in that government's Gross National Product; as opposed to a formal economy. This is another word for the black market. |  | 35 |
| 9682757984 | Gender Inequality Index | A United Nations index, introduced in 2010, which measures a country's loss of achievement due to gender inequality, based on reproductive health, employment, and general empowerment. The UN index which measures a country's loss of achievement due to gender inequality. |  | 36 |
AP Human Geography Industry Flashcards
Primary tabs
Need Help?
We hope your visit has been a productive one. If you're having any problems, or would like to give some feedback, we'd love to hear from you.
For general help, questions, and suggestions, try our dedicated support forums.
If you need to contact the Course-Notes.Org web experience team, please use our contact form.
Need Notes?
While we strive to provide the most comprehensive notes for as many high school textbooks as possible, there are certainly going to be some that we miss. Drop us a note and let us know which textbooks you need. Be sure to include which edition of the textbook you are using! If we see enough demand, we'll do whatever we can to get those notes up on the site for you!

