Neuroscience and Behavior
| 10884659527 | biological psychology | branch of psychology concerned with the links between biology and behavior |  | 0 |
| 10884659528 | neuron | a nerve cell; the basic building block of the nervous system |  | 1 |
| 10884659529 | dendrite | bushy, branching extensions of a neuron that retrieve messages & conduct impulses toward the cell body |  | 2 |
| 10884659530 | axon | extension of a neuron, ending in branching terminal fibers, through which messages pass to other neurons or to muscles or glands |  | 3 |
| 10884659531 | myelin sheath | layer of fatty tissue segmentally encasing the fibers of many neurons; enables faster transmission speed of neural impulses |  | 4 |
| 10884659532 | action potential | a neuro impulse; the movement of positively charge atoms in and out of axon channels generates a brief electrical charge |  | 5 |
| 10884659533 | synapse | junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron |  | 6 |
| 10884659534 | neurotransmitters | chemical messengers that travel across the synaptic gap between and bind to receptor sites to possibly generate neuro impulses |  | 7 |
| 10884659535 | threshold | the level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse |  | 8 |
| 10884659537 | endorphins | natural, opiatelike neurotransmitters linked to pain control and to pleasure "morphine within" |  | 9 |
| 10884659538 | nervous system | the body's speedy, electromechanical communication network, consisting of all the nerve cells |  | 10 |
| 10884659539 | Central Nervous System (CNS) | the brain and spinal cord |  | 11 |
| 10884659540 | Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) | the sensory and motor neurons that connect the CNS to the rest of the body |  | 12 |
| 10884659541 | nerves | neural "cables" containing bundles of axons. They connect the central nervous system with muscles, glands, and sense organs in the PNS |  | 13 |
| 10884659542 | motor (efferent) neurons | neurons that carry outgoing info from the CNS to the muscles and glands |  | 14 |
| 10884659543 | sensory (afferent) neurons | neurons carry incoming informations from the sense receptors to the CNS |  | 15 |
| 10884659544 | interneurons | CNS neurons that internally communicate and intervene between sensory inputs and motor outputs |  | 16 |
| 10884659545 | Somatic Nervous System | the division of the PNS that controls the body's skeletal muscles aka the skeletal nervous system |  | 17 |
| 10884659546 | autonomic nervous system | the division of the PNS that controls the glands and muscles of internal organs |  | 18 |
| 10884659547 | sympathetic nervous system | division of autonomic nervous system that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations |  | 19 |
| 10884659548 | parasympathetic nervous system | the division of the autonomic nervous system that calms the body, conserving its energy |  | 20 |
| 10884659549 | reflex | a simple automatic inborn response to a sensory stimulus, such as the knee jerk response |  | 21 |
| 10884659550 | endocrine system | the body's "slow" chemical communication system; a set of glands that secrete hormones into the bloodstream | 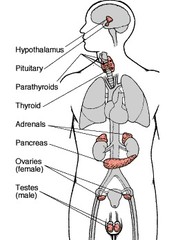 | 22 |
| 10884659551 | hormones | chemical messengers, mostly those manufactured by the endocrine glands, that are produced in one tissue and affect another |  | 23 |
| 10884659552 | adrenal glands | pair of endocrine glands above kidneys; secrete the hormones epinephrine and norepinephrine to arouse the body in times of stress |  | 24 |
| 10884659553 | pituitary gland | endocrine system's most influential gland. With the influence of the hypothalamus, it regulates growth and controls endocrine glands |  | 25 |
| 10884659554 | lesion | tissue destruction; naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue |  | 26 |
| 10884659555 | EEG (Electroencephalogram) | amplified recording of electrical activity waves that sweep across the brain's surface; waves are measured by electrodes placed on the scalp |  | 27 |
| 10884659556 | PET scan (positron emission topography) | visual display of brain activity that detects where a radioactive form of glucose goes while a brain performs a given task |  | 28 |
| 10884659557 | MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) | uses magnetic fields & radio waves to produce computer generated images of types of soft tissue; allows us to see brain structures |  | 29 |
| 10884659558 | fMRI (functional MRI) | technique for revealing blood flow and therefore brain activity by comparing successive MRI scans |  | 30 |
| 10884659559 | brainstem | oldest part and central core of brain, beginning where the spinal core swells as it enters the skull; responsible for automatic survival functions |  | 31 |
| 10884659560 | medulla | the base of the brain stem; controls heartbeat and breathing |  | 32 |
| 10884659561 | reticular formation | a nerve network in the brainstem that plays an important role in controlling arousal |  | 33 |
| 10884659562 | thalamus | brain's sensory switchboard located on top of the brainstem; directs messages to the cortex, cerebellum, and medulla |  | 34 |
| 10884659563 | cerebellum | "little brain" attached to the rear of the brainstem; processes sensory input and coordinates movement output and balance |  | 35 |
| 10884659564 | limbic system | doughnut shaped system between brainstem and cerebral hemispheres; controls basic emotions and drives (food and sex) |  | 36 |
| 10884659565 | amygdala | two lima bean-sized neutral clusters that are components of the limbic system and are linked to emotions |  | 37 |
| 10884659566 | hypothalamus | neuro structure below the thalamus; directs maintenance activities (eating, temperature), the endocrine system, and some emotion |  | 38 |
| 10884659567 | cerebral cortex | intricate fabric of interconnected neural cells that covers the cerebral hemispheres; ultimate control and information processing center |  | 39 |
| 10884659568 | glial cells (glia) | cells in the nervous system that support, nourish, and protect neurons |  | 40 |
| 10884659569 | frontal lobes | portion of the cerebral cortex behind the forehead; involved in speaking and muscle movements and in making plans/judgements |  | 41 |
| 10884659570 | occipital lobes | portion of the cerebral cortex at the back of the head; includes the visual areas, which receive information from the opposite visual field |  | 42 |
| 10884659571 | temporal lobes | portion of the cerebral cortex above the ears; includes auditory areas each of which receives information from the opposite field |  | 43 |
| 10884659572 | parietal lobe | the portion of the cerebral cortex lying at the top of the head and toward the rear; receives sensory input for touch and body position |  | 44 |
| 10884659573 | motor cortex | an area at the rear of the frontal lobes that controls voluntary movements |  | 45 |
| 10884659574 | sensory cortex | the area at the front of the parietal lobes that registers and processes body touch and movement sensations |  | 46 |
| 10884659575 | association areas | areas of the cerebral cortex involved in higher mental functions such as learning, remembering, thinking, or speaking |  | 47 |
| 10884659578 | plasticity | brain's capacity for modification, as evident in brain reorganization following damage and in experiments on brain development |  | 48 |
| 10884659579 | corpus callosum | the large band of neural fibers connecting the 2 brain hemispheres and carrying messages between them |  | 49 |
| 10884659580 | split brain | condition where the 2 hemispheres of the brain are isolated by cutting the connecting fibers (mostly the corpus callosum) between them |  | 50 |
| 10884813127 | neurogenesis | the formation of new neurons | 51 | |
| 10884817791 | environment | every nongenetic influence, from prenatal nutrition to the people and things around us | 52 | |
| 10884824276 | behavior genetics | the study of the relative power and limits of genetic and environmental influences on behavior | 53 | |
| 10884828342 | chromosomes | threadlike structures made of DNA molecules that contain the genes | 54 | |
| 10884834427 | DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) | A complex molecule containing the genetic information that makes up the chromosomes. | 55 | |
| 10884839696 | genes | DNA segments that serve as the key functional units in hereditary transmission. | 56 | |
| 10884839698 | identical twins | twins who develop from a single fertilized egg that splits in two, creating two genetically identical organisms | 57 | |
| 10884844335 | fraternal twins | twins who develop from separate fertilized eggs. They are genetically no closer than brothers and sisters, but they share a fetal environment. | 58 | |
| 10884847672 | interaction | the interplay that occurs when the effect of one factor (such as environment) depends on another factor (such as heredity) | 59 | |
| 10884851554 | Epigenetics | the study of environmental influences on gene expression that occur without a DNA change | 60 | |
| 10884855421 | evolutionary psychology | the study of the evolution of behavior and the mind, using principles of natural selection | 61 | |
| 10884858690 | natural selection | A process in which individuals that have certain inherited traits tend to survive and reproduce at higher rates than other individuals because of those traits. | 62 | |
| 10884862675 | mutation | A change in a gene or chromosome. | 63 |

