| 6017246835 | Harlow | studied monkeys to determine what livings things need in order to form attachment; changed the perspective of how babies are born and raised; not nourishment but comfort is what is needed |  | 0 |
| 6017247182 | Kohlerberg | stages of morality | 1 | |
| 6020505699 | Erikson | psychosocial roles: | 2 | |
| 6020505700 | Ainsworth | a child has a sense of safety in room with mom. And without the mom they feel insecure. | 3 | |
| 6020509772 | Kubler-Ross | stages of greif | 4 | |
| 6020512543 | Developmental Psychology | a branch of psychology that studies physical, cognitive, and social change throughout the life span. |  | 5 |
| 6020513963 | Industrial Psychology | 6 | ||
| 6020522224 | Identical Twins | develop from a single fertilized egg that splits into 2 forming 2 genetically identical humans |  | 7 |
| 6020524174 | Fraternal Twins | develop from separate eggs and are genetically no more similar than an ordinary broth or sister |  | 8 |
| 6020524175 | Sex vs. gender | vs. the biologically and socially influenced characteristics by which people define male and female | 9 | |
| 6020527588 | Zygote | the fertilized egg, it enters a 2 week period of rapid cell division and develops |  | 10 |
| 6020527589 | Embryo | the developing human organism from about 2 weeks after fertilization through the second month |  | 11 |
| 6020527590 | Fetus | developing human organism from 9 weeks after conception | 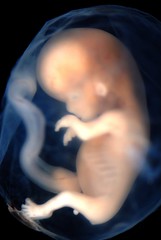 | 12 |
| 6020531688 | Nature vs. Nurture | 13 | ||
| 6020533479 | Stability or change | 14 | ||
| 6020533480 | gender difference | gender is social / sex is physical | 15 | |
| 6020536237 | Teratogens | agents, such as chemicals and viruses, that can reach the embryo of fetus during prenatal development and cause harm. | 16 | |
| 6020536238 | FAS | physical and cognitive abnormalities in children caused by a pregnant woman's heavy drinking. In severe cases, symptoms include noticeable facial abnormalities |  | 17 |
| 6020536239 | Rooting reflex | a baby's tendency when toughed on the cheek to turn towards the touch, open mouth, and search for the nipple |  | 18 |
| 6020538570 | Moro | baby gets "big" when frightened; a defence mechanism or evolutionary |  | 19 |
| 6020538571 | Imprinting | the process by which certain animals form attachments during a critical period very early in life. | 20 | |
| 6020541251 | Critical Periods | an optimal period shortly after birth when an organism's exposure to certain stimuli or experiences produces peoper development | 21 | |
| 6020541252 | Maturation | biological growth processes that enable orderly changes in behavior, relatively uninfluenced by experience - of motor development (roll over, crawl, walk) | 22 | |
| 6020545984 | Piaget Stages of Cognitive Development | Sensorimotor Preoperational Concrete Operational Formal Operational | 23 | |
| 6020545985 | Schema | a concept or framework that organizes and interprets information. | 24 | |
| 6020548213 | Assimilation | interperting one's new experiences in terms of one's existing schema's | 25 | |
| 6020548214 | Accommodations | adapting one's current understanding(schema) to incorperate new information | 26 | |
| 6020551060 | Holophrastic | one word; 4 months to babble sounds | 27 | |
| 6020557225 | Telegraphic | two words; 10 months to babble resembling language | 28 | |
| 6020557226 | Sensorimotor | in Piaget's theory, the stage (from birth -2 years) during which infants know the world mostly in terms of their sensory impressions and motor activities |  | 29 |
| 6020560833 | Stranger Anxiety | the fear of strangers that infants commonly display, beginning by about 8 months old |  | 30 |
| 6020563128 | Object Permanence | the awareness that things continue to exist even when not persieved (peek-a-boo) |  | 31 |
| 6020568747 | Pre-operational Stage | in Piaget's theory, the stage (from 2-7 years) during which a child learns to use language but does not yet comprehend the mental operations of concrete logic | 32 | |
| 6020568748 | Egocentric | in Piaget's theory, the pre-operational child's difficulty taking another's point of view |  | 33 |
| 6020573914 | Theory of Mind | People's ideas about their own and others mental states - about their feelings, perceptions, and thoughts and the behavior these might predict. | 34 | |
| 6020575659 | Concrete Operational | in Piaget's theory, the stages of cognitive development (7-11 years) during which children gain the mental operations that enable them to think logically about concrete events. | 35 | |
| 6020575680 | Law of Conservation | principle (which Piaget believed to be a part of concrete operational reasoning) that properties such as mass, volume, and number remain the same despite changes in the forms of objects |  | 36 |
| 6020578160 | Formal Operational | Piaget's theory, the stages of cognitive development (12+ years) during which people begin to think logically about abstract concepts | 37 | |
| 6020580877 | Kohlberg's Moral Development | Preconventional Morality (egocentric) > Conventional Morality (sociocentric) > Post Conventional Morality (greater good) | 38 | |
| 6020580878 | Pre-conventional | before age 9, most children have self-interest. they obey either to avoid punishment or to gain reward. | 39 | |
| 6020585368 | Conventional | by early adolescence, morality usually evolves to a level that cares for others and upholds the law and social rules simply because they are laws. | 40 | |
| 6020585369 | Post-conventional | some of those who develop the abstract reasoning of thought may come to a third level. Affirms people's agreed upon rights or follows what one personally percieve | 41 | |
| 6020590161 | Attachment | an emotional tie with another person; shown in young children by their seeking closeness to the caregiver and showing distress on separation | 42 | |
| 6020591984 | Secure Attachment | caregiver is consistent and appropriate therefore the child is willing to explore | 43 | |
| 6020597096 | Ambivalent / Resistant (insecure Attachment) | caregiver is inconsistent with responses (can't count of parent) > child will be anxious, clingy, need for attention, struggle with relationships | 44 | |
| 6020602039 | Disorganized (insecure attachment) | Caregiver show neglect & abuse (physical / emotional) consequences show lack of conscience, animal cruelty, self-harming, theft, crime, poor relationships and self esteem | 45 | |
| 6020604093 | "Strange Situation" | Mary Ainsworth in 1969 to observe attachment relationships between a caregiver and a child | 46 | |
| 6020606270 | Temperament | a person's characteristic emotional reactivity and intensity | 47 | |
| 6020606271 | Parenting styles | permissive, authoritarian, authoritative | 48 | |
| 6020609283 | Permissive | parents submit to their children's desires, make few demands, and use little punishment. |  | 49 |
| 6020612262 | Authoritarian | parents impose rules and experts obidience |  | 50 |
| 6020612263 | Authoritative | parents are both demanding and responsive. They control not only by setting rules and enforcing them but also by explaining the reasons and especially with older children, encouraging open discussion and allowing exceptions when making the rules. |  | 51 |
| 6020616869 | Erkison Psychosocial Development | "Identity Crisis" - each stage we face a crisis that is determined by our environment, we learn through our experiences. | 52 | |
| 6020619856 | Trust vs. Mistrust | either parent is consistent and is always there we learn to trust or not consistant and mistrust | 53 | |
| 6020623125 | Autonomy vs. Shame and doubt | kids feel comfortable to start some independency without shame because they know its concrete | 54 | |
| 6020626383 | Initiative vs. Guilt | "it's all about me" - kids feel more independence and safe towards change (asking why) | 55 | |
| 6020631746 | Industry vs. Inferiority | eliminatory school that effects child's confidence | 56 | |
| 6020637975 | Identity vs. role sonfusion | forming an identity but if you are inferior personality you won't go to far out of the box | 57 | |
| 6020641747 | intimacy vs. isolation | choosing to be in a relationship / not or your intimacy levels. | 58 | |
| 6020648156 | Generativity vs. Stagnation | mid life crisis the focus going from kids to either "go to work" or "do something for others" | 59 | |
| 6020651813 | Integrity vs. despair | either they have integrity and enjoyed life and are content with it or they have despair and dont feel content and always are complaining | 60 | |
| 6020651814 | Personal Fable | type of (teen) reasoning that uses egocentric aspect "you don't understand" | 61 | |
| 6020654777 | Invincibility | type of (teen) reasoning that nothing is going to hurt you and you always feel in control | 62 | |
| 6020723044 | Rationalization | type of (teen) reasoning to make yourself feel better | 63 | |
| 6020724963 | Longitudinal Study | research in which the same people are restudied and retested over a long period. | 64 | |
| 6020727105 | Cross-cultural Study | a study in which people of different ages are compared with one another | 65 | |
| 6020829207 | Crystallized Intelligence | is wisdom and increases as you are | 66 | |
| 6020992025 | Fluid Intelligance | reaction time and ability to learn decreases as you age | 67 | |
| 6021008688 | Stages of Grief | Before 1. Denial 2. Anger 3. Bargaining 4. Depression 5. Accepting After 1. Shock 2. Anger 3. Depression 4. Acceptance | 68 |
AP Psychology: Test 5 Flashcards
Primary tabs
Need Help?
We hope your visit has been a productive one. If you're having any problems, or would like to give some feedback, we'd love to hear from you.
For general help, questions, and suggestions, try our dedicated support forums.
If you need to contact the Course-Notes.Org web experience team, please use our contact form.
Need Notes?
While we strive to provide the most comprehensive notes for as many high school textbooks as possible, there are certainly going to be some that we miss. Drop us a note and let us know which textbooks you need. Be sure to include which edition of the textbook you are using! If we see enough demand, we'll do whatever we can to get those notes up on the site for you!

