| 8121237048 | The French and Indian War | 1754-1763 War between French and British in American colonies part of 7 years |  | 0 |
| 8121237049 | The Proclamation of 1763 | Line drawn by British Parliament, colonists not allowed to settle past Appalachian mountains |  | 1 |
| 8121237050 | Stamp Act | 1765 direct tax on a stamp that must be put on paper, office documents, etc. |  | 2 |
| 8121237051 | The Coercive Acts | 1774 intolerable acts |  | 3 |
| 8121237052 | Common Sense | 1776 pamphlet written by Thomas Paine to get people to want independence |  | 4 |
| 8121237053 | The Declaration Of Independence | 1776 document written by colonist elites to British King and Parliament stating independence and what all was wrong with British rule and the King |  | 5 |
| 8121237054 | Battle of Saratoga | Head to head battle between the British and Americans in country side, Americans win by a lot and show they have a chance |  | 6 |
| 8121237055 | French American Alliance | Formed after battle of Saratoga when Americans proved to French they can win and French are allies because they want to damage an age old enemy |  | 7 |
| 8121237056 | Treaty of Paris | 1783 ended the American Revolutionary War Granted the land British gave Indians as American land now American colonies recognized as their own independent country |  | 8 |
| 8121237057 | Articles of confederation | First form of government A lot of weaknesses No strong central government Strong state governments Causes economical problems and failure |  | 9 |
| 8121237058 | The Northwest Ordinance of 1787 | Land in Northwest is divided into 5 states (Michigan, Illinois, Ohio, Wisconsin, Indiana) they are all seen as equal to the 13 original states Reach a certain pop you can apply for statehood and be part of congress and slavery was outlawed |  | 10 |
| 8121237059 | Shay's Rebellion | 1786 farmers debt rebellion agriculture depression, economical failure and 2 out of 3 were being sued |  | 11 |
| 8121237060 | The Constitution | New format of government focuses more on a central national power and less on states 3 branch government that limit each other |  | 12 |
| 8121237061 | Federalism | One central power over all |  | 13 |
| 8121237062 | The Great Compromise | New Jersey and Virginia plans together and create the senate and House of Representatives senate equal vote house of rep by population |  | 14 |
| 8121237063 | The Three-Fifths compromise | Slaves count as population for vote in congress 3 slaves for every 5 white were counted |  | 15 |
| 8121237064 | The Federalists papers | Essays written by Federalists to get people to ratify the constitution plubis |  | 16 |
| 8121237065 | Federalists | Supported the ratification of the constitution one central strong government |  | 17 |
| 8121237066 | Anti federalists | Against ratification of the constitution |  | 18 |
| 8121237067 | The Bill of rights | First ten amendments of the constitution |  | 19 |
| 8121237068 | George Washington's presidency | 1st president formed the cabinets 2nd term strictly followed constitution left office to tell everyone they needed to be unified established framework of Supreme Court and how they will be decided judiciary |  | 20 |
| 8121237069 | Hamilton | Tackle debt- grant money back to people, national bank create national government, manufacturing establish tax revenue |  | 21 |
| 8121237070 | Jefferson | Wanted state governments against Hamilton 3rd president vice under John Adams voting process not fix yet and he got 2nd place |  | 22 |
| 8121237071 | Washington's farewell address | Unity and against foreign policies |  | 23 |
| 8121237072 | XYZ Affair | 3 agents from France try to bribe Americans who came as ambassadors to see the rulers of France common in Europe but Americans took offense and John Adams published what happened for all Americans to see decreasing support of republicans because they are Franco files | 24 | |
| 8121237073 | Alien and Sedition Acts | Sedition- speaking false against congress or president Alien- allow president to prison or deport suspicious foreign during war Cut of increase of republicans |  | 25 |
| 8121237074 | Kentucky and Virginia Resolutions | Idea of nullification Legislatures that constitution was written by sovereign states so they could revoke the unconstitutional laws |  | 26 |
| 8121237075 | Enslaved Africans / Free Africans(Atlantic Slave Trade) | African peoples have been subjected to many different types of slavery both within Africa and externally. Slavery is an economic system, which relies on the free labor of enslaved people. This may be for a fixed period of time, or, as in the case of the transatlantic slave trade(the buying, transporting, and selling of Africans for work in the Americas), for life. |  | 27 |
| 8121237076 | Virginia House of Burgesses | The first elected assembly in the New World, established in 1619 |  | 28 |
| 8121237077 | North Carolina | In the 1600s permanent settlers from Virginia began to move to North Carolina, and it eventually became part of a British colony known as "Carolina." | 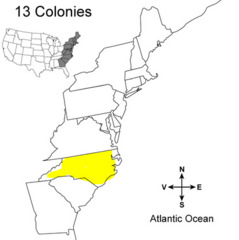 | 29 |
| 8121237078 | New England Colonies | The FOUNDERS of the New England colonies had an entirely different mission from the Jamestown settlers. Although economic prosperity was still a goal of the New England settlers, their true goal was spiritual. Fed up with the ceremonial Church of England, Pilgrims and Puritans sought to recreate society in the manner they believed God truly intended it to be designed. |  | 30 |
| 8121237079 | Puritans/Pilgrims | Protestants who hoped to reform the Church of England |  | 31 |
| 8121237080 | Mayflower Compact | 1620. First Social Contract provided a basis for government at Plymouth |  | 32 |
| 8121237081 | John Winthrop | Puritan governor of Massachusetts Bay Colony. Speaker of "City Upon a Hill" |  | 33 |
| 8121237082 | Anne Hutchinson | Woman who was banished from Massachusetts colony for criticizing Puritan ministers |  | 34 |
| 8121237083 | Pequot War | Fought by the ____________people against a coalition of English settlers from the Massachusetts Bay, Connecticut, and Saybrook colonies and their Native American allies (including the Narragansett and Mohegan) that eliminated the ______________ as an impediment to English colonization of southern New England. It was an especially brutal war and the first sustained conflict between Native Americans and Europeans in northeastern North America. |  | 35 |
| 8121237084 | Middle Colonies | Diversity! The MIDDLE COLONIES of Pennsylvania, New York, New Jersey, and Delaware. European ethnic groups as manifold as English, Swedes, Dutch, Germans, Scots-Irish and French lived in closer proximity than in any location on continental Europe. The middle colonies contained Native American tribes of Algonkian and Iroquois language groups as well as a sizable percentage of African slaves during the early years. Unlike solidly Puritan New England, the middle colonies presented an assortment of religions. The presence of Quakers, MENNONITES, LUTHERANS, DUTCH CALVINISTS, and PRESBYTERIANS made the dominance of one faith next to impossible. |  | 36 |
| 8121237085 | New Amsterdam | Original Dutch settlement in New Netherlands; later became New York City. Known for trade. |  | 37 |
| 8121237086 | Southern Colonies | Virginia, the First Southern Colony in the South was turning to cash crops. Geography and motive rendered the development of these colonies distinct from those that lay to the North. Immediately to Virginia's north was MARYLAND. Begun as a Catholic experiment, the colony's economy would soon come to mirror that of Virginia, as tobacco became the most important crop. To the south lay the Carolinas, created after the English Civil War had been concluded. In the Deep South was GEORGIA, the last of the original thirteen colonies. Challenges from Spain and France led the king to desire a buffer zone between the cash crops of the Carolinas and foreign enemies. Georgia, a colony of debtors, would fulfill that need. |  | 38 |
| 8121237087 | Maryland Act Concerning Religion | Was a law mandating religious tolerance for Trinitarian Christians. Passed on April 21, 1649, by the assembly of the Maryland colony, in St. Mary's City. It was the second law requiring religious tolerance in the British North American colonies and created one of the pioneer statutes passed by the legislative body of an organized colonial government to guarantee any degree of religious liberty. Specifically, the bill, now usually referred to as the Toleration Act, granted freedom of conscience to all Christians. |  | 39 |
| 8121237088 | British West Indies | To start with, British traders supplied slaves for the Spanish and Portuguese colonists in America. However, as British settlements in the Caribbean and North America grew, often through wars with European countries such as Holland, Spain and France, British slave traders increasingly supplied British colonies |  | 40 |
| 8121237089 | Metacom's War / King Phillip's War | 1637 Conflict between an alliance of Massachusetts Bay and Plymouth colonies, with American Indian allies (the Narragansett, and Mohegan Indians), against the Pequot Indians. This war saw the elimination of the Pequot in New England, and is exemplary of the Puritan use of genocide towards Native Americans. |  | 41 |
| 8121237090 | Bacon's Rebellion | 1676; VA frontiersmen seeking land clashed with Native Americans; Frontiersmen demanded help from the government; Jamestown refused aid, fearing Native American War; Bacon and his men lived on frontier; Bacon & men stormed Jamestown; Bacon died of fever; Rebellion collapsed; Colonial rebellion against government authority; Clash between east/west, rich/poor; Tidewater's discrimination against frontiersmen; Revision of indentured servant system, greater reliance on slave labor |  | 42 |
| 8121237091 | William Penn | The founder of Pennsylvania. The British government repaid a debt to Penn by giving him title to what is now Pennsylvania, where he established a colony with broad religious toleration. Many Quakers, who were persecuted in England, settled in Pennsylvania. _________ was known for his friendly relations with the Native American tribes in his colony. |  | 43 |
| 8121237092 | Pueblo Revolt | The most successful Indian revolt against the Europeans: Pueblo Indians in 1680, led by Pope, attacked Spanish settlers (Onante and his aggressive conlonisation) and killed some 400; maintained independence in New Mexico until ten years later. When the Spanish returned and reconquered the Indians. |  | 44 |
| 8121237093 | Southwest | Native Americans lived in villages with farming as their source of food, included Apache, Hopi, Navajo, Pueblo, and Zuni |  | 45 |
| 8121237094 | Navigation Acts | Passed under the mercantilist system, the Navigation Acts (1651-1673) regulated trade in order to benefit the British economy. The acts restricted trade between England and its colonies to English or colonial ships, required certain colonial goods to pass through England before export, provided subsidies for the production of certain raw goods in the colonies, and banned colonial competition in large-scale manufacturing. |  | 46 |
| 8121237095 | Dominion of New England | 1686-The British government combined the colonies of Massachusetts, Rhode Island, New Hampshire, and Connecticut into a single province headed by a royal governor (Andros). Ended in 1692, when the colonists revolted and drove out Governor Andros. |  | 47 |
| 8121237096 | New England Confederation | New England colonists formed the New England Confederation in 1643 as a defense against local Native American tribes and encroaching Dutch. The colonists formed the alliance without the English crown's authorization. |  | 48 |
| 8121237097 | Glorious Rebellion | The Glorious Revolution of 1688-1689 replaced the reigning king, James II, with the joint monarchy of his protestant daughter Mary and her Dutch husband, William of Orange. It was the keystone of the Whig (those opposed to a Catholic succession) history of Britain. |  | 49 |
| 8121237098 | Leisler's Rebellion | The uprising took place in the aftermath of Britain's Glorious Revolution and the 1689 Boston revolt in the Dominion of New England, which had included New York. The rebellion reflected colonial resentment against the policies of deposed King James II. |  | 50 |
| 8121237099 | First Great Awakening | The Great Awakening or First Great Awakening was an evangelical and revitalization movement that swept Protestant Europe and British America, especially the American colonies, in the 1730s and 1740s, leaving a permanent impact on American Protestantism. |  | 51 |
| 8121237100 | Salem Witch Trials | Began during the spring of 1692, after a group of young girls in Salem Village, Massachusetts, claimed to be possessed by the devil and accused several local women of witchcraft. A wave of hysteria spread throughout colonial Massachusetts. |  | 52 |
| 8121237101 | Royal African Company Monopoly | King James I had granted a patent to a company that wanted to trade for gold and precious woods in Africa. Other groups also received rights to trade in Africa, but never dealt with slaves in any major way. English involvement in the slave trade would intensify after 1663, when a new patent was issued to the Company of Royal Adventurers. England had realized the money to be made trading slaves to the West Indies and Virginia. |  | 53 |
| 8121237102 | European Enlightenment | The AGE OF REASON, as it was called, was spreading rapidly across Europe. In the late 17th century, scientists like ISAAC NEWTON and writers like JOHN LOCKE were challenging the old order. Newton's laws of gravity and motion described the world in terms of natural laws beyond any spiritual force. In the wake of political turmoil in England, Locke asserted the right of a people to change a government that did not protect natural rights of life, liberty and property. |  | 54 |
| 8121237103 | Protestant Evangelicalism | Its origins are usually traced back to English Methodism, the Moravian Church , and German Lutheran Pietism. While all these phenomena contributed greatly, John Wesley and other early Methodists were at the root of sparking this new movement during the First Great Awakening. The movement gained great momentum during the 18th and 19th centuries with the Great Awakenings in the United Kingdom and North America. |  | 55 |
| 8121237104 | Mercantilism | Economic theory and practice common in Europe from the 16th to the 18th century that promoted governmental regulation of a nation's economy for the purpose of augmenting state power at the expense of rival national powers. It was the economic counterpart of political absolutism. |  | 56 |
| 8121237105 | Molasses Act | The Molasses Act of March 1733 was an Act of the Parliament of Great Britain (citation 6 Geo II. c. 13), which imposed a tax of six pence per gallon on imports of molasses from non-English colonies. Parliament created the act largely at the insistence of large plantation owners in the British West Indies |  | 57 |
| 8121237106 | John Peter Zenger | The trial of JOHN PETER ZENGER, a New York printer, was an important step toward this most precious freedom for American colonists. In 1733, it was libel when you published information that was opposed to the government. Truth or falsity were irrelevant. He never denied printing the pieces. The judge therefore felt that the verdict was never in question. But was found innocent, Although true freedom of the press was not known until the passage of the FIRST AMENDMENT, newspaper publishers felt freer to print their honest views |  | 58 |
| 8121237107 | Stono Rebellion | Conspiracy or Cato's Rebellion) was a slave rebellion that began on 9 September 1739, in the colony of South Carolina. It was the largest slave uprising in the British mainland colonies, with 42-47 whites and 44 blacks killed. |  | 59 |
| 8121237108 | Iron Act | The Iron Act of 1750 was a British Law, passed by the Parliament of Great Britain, that was designed to encourage the American manufacture of more pig iron and iron bars by the American colonists in the 13 Colonies to be sent to England, tax free. But the Act of 1750 also prohibited the colonies from producing finished iron goods. |  | 60 |
| 8121237109 | How did early Americans reach North and South America? | They crossed a land bridge from Asia | 61 | |
| 8121237110 | When was the land bridge formed? What was it made of? | During the ice age, ice/land | 62 | |
| 8121237111 | What were the Indians doing when they crossed the land bridge? | Following food or herds | 63 | |
| 8121237112 | What were the most complex Indian communities? | Mayan, Inca and Aztecs | 64 | |
| 8121237113 | What did the cultivation of maize do? | Transform nomadic hunter-gather societies into settled farming communities | 65 | |
| 8121237114 | What kinds of items did Europeans desire from Persia and China? | Silk, Spices, Oils/Perfumes | 66 | |
| 8121237115 | What were the Spanish 3 motives for exploration? | 1. God 2. Gold 3. Glory | 67 | |
| 8121237116 | Which direction did Portugal head to reach Asia and India? | South along the West coast of Africa. | 68 | |
| 8121237117 | Who married to make Spain whole? | Ferdinand of Aragon and Isabella of Castille | 69 | |
| 8121237118 | Where did Columbus land? | Hispainola | 70 | |
| 8121237119 | Columbus died thinking what? | That he had found a trade route to Asia and that he had landed on the outskirts of India | 71 | |
| 8121237120 | When Spain and Portugal went to the pope to see how to divide the world, the pope made what? | The Treaty of Tordesillas | 72 | |
| 8121237121 | What did the Treaty of Tordesillas say? | Divided the trade routes to Asia: Spain gets the route across the Atlantic and Portugal gets the route around Africa. Also, Spain got a lot of land in the New World and Portugal got present-day Brazil. | 73 | |
| 8121237122 | Who came to the New World once it was discovered? | Spanish conquistadors | 74 | |
| 8121237123 | Who conquered the Aztecs? Who conquered the Incas? | Cortes-Aztecs Pizzaro- Incas | 75 | |
| 8121237124 | What are the 2 things the Spanish give the Indians in exchange for their work (in the Encomienda System) | 1. Provide food, shelter, and good treatment to the Indians 2. Convert them to Christians | 76 | |
| 8121237125 | What was the Encomienda System basically? | Slavery | 77 | |
| 8121237126 | Who worked for Indian's rights? | Bartolome de las Casas | 78 | |
| 8121237127 | What happened when the Spanish ran out of Indians to do work? | They went and got Africans | 79 | |
| 8121237128 | Who was the explorer sent by England to the New World? Where did he explore? | John Cabot- coastline of North America | 80 | |
| 8121237129 | Who was an explorer sent by Spain to the New World? (not Columbus) Where did he explore? | Vasco Nunez de Balboa- Pacific Ocean | 81 | |
| 8121237130 | What is Ferdinand Magellan credited with? | The 1st circumnavigation of the earth | 82 | |
| 8121237131 | When the Spanish moved north, what did they establish? Where? | A fort (outpost) in St. Augustine, Fl | 83 | |
| 8121237132 | What is the Biological (Columbian) Exchange? | Exchange of plants, animals, and diseases between Old World and New World after the time of Columbus. | 84 | |
| 8121237133 | What 3 crops from the Americas ended up being staple crops in Europe? | 1. Corn 2. Beans 3. Potatoes | 85 | |
| 8121237134 | What was the "big" animal brought to the Americas that changed Indian life? | Horses | 86 | |
| 8121237135 | What diseases were from the Old World and went to the New World? | Smallpox, malaria, yellow fever, influenza | 87 | |
| 8121237136 | What disease did the Indians give Europeans? | Syphillis | 88 | |
| 8121237137 | Columbian Exchange | An exchange of goods, ideas and skills from the Old World (Europe, Asia and Africa) to the New World (North and South America) and vice versa. |  | 89 |
| 8121237138 | Encomienda | A grant of land made by Spain to a settler in the Americas, including the right to use Native Americans as laborers on it |  | 90 |
| 8121237139 | Atlantic slave trade | Lasted from 16th century until the 19th century. Trade of African peoples from Western Africa to the Americas. 98% of Africans were sent to the Caribbean, South and Central America. | 91 | |
| 8121237140 | Bartolome de las Casas | First bishop of Chiapas, in southern Mexico. He devoted most of his life to protecting Amerindian peoples from exploitation. His major achievement was the New Laws of 1542, which limited the ability of Spanish settlers to compel Amerindians to labor; however his suggestion to replace Natives with Africans was won he would regret. |  | 92 |
| 8121237141 | Maize | An early form of corn grown by Native Americans |  | 93 |
| 8121237142 | Anasazi | A Native American who lived in what is now southern Colorado and Utah and northern Arizona and New Mexico and who built cliff dwellings |  | 94 |
| 8121237143 | Iroquois | A later native group to the eastern woodlands. They blended agriculture and hunting living in common villages constructed from the trees and bark of the forests |  | 95 |
| 8121237144 | Cherokee | Are a Native American people historically settled in the Southeastern United States (principally Georgia, the Carolinas and Eastern Tennessee). Linguistically, they are part of the Iroquoian-language family. In the 19th century, historians and ethnographers recorded their oral tradition that told of the tribe having migrated south in ancient times from the Great Lakes region, where other Iroquoian-speaking peoples were located. |  | 96 |
| 8121237145 | Inuit | A member of a people inhabiting the Arctic (northern Canada or Greenland or Alaska or eastern Siberia) |  | 97 |
| 8121237146 | Maya | Mesoamerican civilization concentrated in Mexico's Yucatan Peninsula and in Guatemala and Honduras but never unified into a single empire. Major contributions were in mathematics, astronomy, and development of the calendar. |  | 98 |
| 8121237147 | Aztec | (1200-1521) 1300, they settled in the valley of Mexico. Grew corn. Engaged in frequent warfare to conquer others of the region. Worshipped many gods (polytheistic). Believed the sun god needed human blood to continue his journeys across the sky. Practiced human sacrifices and those sacrificed were captured warriors from other tribes and those who volunteered for the honor. |  | 99 |
| 8121237148 | Inca | Their empire stretched from what is today Ecuador to central Chili in the Andes Mountain region of South America. Called the Children of the Sun. |  | 100 |
| 8121237149 | Tenochtitlan | Capital of the Aztec Empire, located on an island in Lake Texcoco. Its population was about 150,000 on the eve of Spanish conquest. Mexico City was constructed on its ruins. |  | 101 |
| 8121237150 | Aztec calendar | 365 days, divided into 18 months each with 20 days. |  | 102 |
| 8121237151 | Terrace farming | The cutting out of flat areas (terraces) into near vertical slopes to allow farming. Terrace farms appears as steps cut into a mountainside. This adaptation allowed both the early Chinese, and the Inca of Mesoamerica to grow enough food for their large populations. |  | 103 |
| 8121237152 | Nomad | Early, simplistic man that migrated across the land bridge. | 104 | |
| 8121237153 | Causes for European interest in exploration? | The Holy Crusades, Renaissance and The Protestant Reformation. | 105 | |
| 8121237154 | Martin Luther | Broke away from the Catholic Church because of his 95 problems with the Catholic Church. | 106 | |
| 8121237155 | King Henry VIII | Broke away from the Catholic Church because of his disagreement with his inability to get divorced; which eventually led to civil unrest in his country. | 107 | |
| 8121237156 | New France | Established in Canada and along the Mississippi River, focused on fur trade. | 108 |
Ap US History period 3, AP US History Period 2 (1607-1754), US AP History Period 1 (Review) Flashcards
Primary tabs
Need Help?
We hope your visit has been a productive one. If you're having any problems, or would like to give some feedback, we'd love to hear from you.
For general help, questions, and suggestions, try our dedicated support forums.
If you need to contact the Course-Notes.Org web experience team, please use our contact form.
Need Notes?
While we strive to provide the most comprehensive notes for as many high school textbooks as possible, there are certainly going to be some that we miss. Drop us a note and let us know which textbooks you need. Be sure to include which edition of the textbook you are using! If we see enough demand, we'll do whatever we can to get those notes up on the site for you!

