| 12203858630 | Trans -Saharan Trade | Trade of goods through the Sahara dessert Goods: Salt, gold, animal hides, slaves Important points: Timbuktu, Goa,Djenne |  | 0 |
| 12203858631 | Islam | Monotheistic religion created in the 7th century by Arabic merchant, Muhammed |  | 1 |
| 12203858632 | Caliphate | A regional state unified by Islam |  | 2 |
| 12203858633 | Crusades | A series of Christian vs Muslim military campaigns for the "holy land" |  | 3 |
| 12203858634 | Dar-al-Islam | territory of Islam |  | 4 |
| 12203858635 | Byzantine Empire | Eastern Roman empire extending to the Eastern Mediterranean and Southwest Asia |  | 5 |
| 12203858636 | Sinification | Chinese-ification of Japan, Korea, and Southeast Asia |  | 6 |
| 12203858637 | Mongols | nomadic invaders that conquered Eurasia with force and diplomacy |  | 7 |
| 12203858638 | Black Death | Plague that killed 1/3 of European population |  | 8 |
| 12203858639 | Maya | MesoAmerican civilization that had pyramids, large cities, a written system, and complex society |  | 9 |
| 12203858640 | Coerced labor | slavery, serfdom, corvee (government-recquired labor on public works projects), and indentured servitude |  | 10 |
| 12203858641 | Feudalism | Agricultural workers serving landowners or lords (knights and samurai) |  | 11 |
| 12203858642 | Zheng He | Ming explorer that crossed the Indian Ocean |  | 12 |
| 12203858643 | Silk | highly-priced luxury commodity mainly exported from China |  | 13 |
| 12203858644 | Chinese Inventions | gunpowder, compass, paper, astrolabe |  | 14 |
| 12203858645 | Tang Dynasty | (618-907 CE) The Chinese dynasty that was much like the Han, who used Confucianism. This dynasty had the equal-field system, a bureaucracy based on merit, and a Confucian education system. | 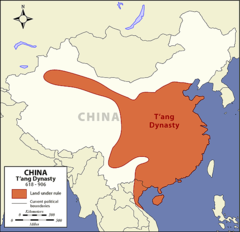 | 15 |
| 12203858646 | Song Dynasty | (960 - 1279 AD); started by Tai Zu; by 1000, a million people were living there; started feet binding; had a magnetic compass, navy, traded with india and persia (brought pepper and cotton), first to have paper money, explosive gun powder |  | 16 |
| 12203858647 | Central Asia | A region that includes the republics of Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan |  | 17 |
| 12203858648 | Indian Ocean trade | trade between Arab, Persian, Turkish, Indian, African, Chinese, and Europe merchants |  | 18 |
| 12203858649 | Ming Dynasty | Succeeded Mongol Yuan dynasty in China in 1368; lasted until 1644; initially mounted huge trade expeditions to southern Asia and elsewhere, but later concentrated efforts on internal development within China. |  | 19 |
| 12203858650 | Grand Canal | an inland waterway 1000 miles long in eastern China |  | 20 |
| 12203858651 | Pax Mongolica | Mongol peace from mid-1200's through mid-1300's imposed stability and law and order across Eurasia. Guaranteed safe passage for trade caravans, travelers, and missionaries from one end of empire to other. |  | 21 |
| 12203858652 | Vikings | A nomadic group that conquered ex: Normans |  | 22 |
| 12203858653 | Syncretism | A blending of two or more religious traditions |  | 23 |
| 12203858654 | Marco Polo | Italian explorer and author who made numerous trips to China and returned to Europe to write of his journeys, responsible for much of the knowledge exchanged between Europe and China during this time period. |  | 24 |
| 12203858655 | Ibn Battuta | (1304-1369) Morrocan Muslim scholar, the most widely traveled individual of his time. He wrote a detailed account of his visits to Islamic lands from China to Spain and the western Sudan. His writings gave a glimpse into the world of that time period. |  | 25 |
| 12203858656 | Mansa Musa | Emperor of the kingdom of Mali in Africa. He made a famous pilgrimage to Mecca and established trade routes to the Middle East. |  | 26 |
| 12203858657 | The Renaissance | (1350-1600) bagan in Italy. Rebirth of learning, science, art, music, literature, and culture. Rediscovery of Ancient Greece and Rome |  | 27 |
| 12203858658 | Secular | Non-religious |  | 28 |
| 12203858659 | Missionary | A person who spreads his or her religious beliefs to others |  | 29 |
| 12203858660 | Charlemagne | 768-843; reunited western Europe for the first time since the Roman Empire. |  | 30 |
| 12203858661 | Justinian | 6th century Byzantine emperor; failed to reconquer the western portions of the empire; rebuilt Constatinople; codified Roman law |  | 31 |
| 12203858662 | hajj | A pilgrimage to Mecca, performed as a duty by Muslims |  | 32 |
| 12203858663 | Zakat | part of 4th Pillar, charitable giving of 2.5% of your net worth to community treasury |  | 33 |
| 12203858664 | jihad | A holy struggle or striving by a Muslim for a moral or spiritual or political goal |  | 34 |
| 12203858665 | Umayyad Caliphate | First hereditary dynasty of Muslim caliphs (661 to 750). From their capital at Damascus, the Umayyads ruled one of the largest empires in history that extended from Spain to India. Overthrown by the Abbasid Caliphate. |  | 35 |
| 12203858666 | Abbasid Caliphate | (750-1258 CE) The caliphate, after the Umayyads, who focused more on administration than conquering. Had a bureaucracy that any Mulim could be a part of |  | 36 |
| 12203858667 | Baghdad | Abbasid capital |  | 37 |
| 12203858668 | Sudanic States | Songhay Ghana and Mali. often led by patriarch or council of elders from a family or lineage |  | 38 |
| 12203858669 | Chinampas | Aztec floating gardens |  | 39 |
| 12203858670 | Alexander the Great | Alexander III of Macedon (356-323 B.C.E.), conqueror of the Persian Empire and part of northwest India. |  | 40 |
| 12203858671 | Ashoka | The most famous ruler of the Mauryan Empire (r. 268-232 B.C.E.), who converted to Buddhism and tried to rule peacefully and with tolerance. |  | 41 |
| 12203858672 | Caesar Augustus | The great-nephew and adopted son of Julius Caesar who emerged as sole ruler of the Roman state at the end of an extended period of civil war (r. 31 B.C.E.-14 C.E.). |  | 42 |
| 12203858673 | Cyrus (the Great) | Founder of the Persian Empire (r. 557-530 B.C.E.); a ruler noted for his conquests, religious tolerance, and political moderation. |  | 43 |
| 12203858674 | Darius I | Great king of Persia (r. 522-486 B.C.E.) following the upheavals after Cyrus's death; completed the establishment of the Persian Empire. |  | 44 |
| 12203858675 | Gupta Empire | An empire of India (320-550 C.E.). |  | 45 |
| 12203858676 | Han dynasty | Chinese dynasty that restored unity in China softened legalist policies. Begun in 202 B.C. by Liu Bang, the Han ruled China for more than 400 years. |  | 46 |
| 12203858677 | Hellenistic era | The period from 323 to 30 B.C.E. in which Greek culture spread widely in Eurasia in the kingdoms ruled by Alexander's political successors. |  | 47 |
| 12203858678 | hoplite | A heavily armed Greek infantryman. Over time, the ability to afford a military wares and to fight for the city came to define Greek citizenship. |  | 48 |
| 12203858679 | Mandate of Heaven | The ideological underpinning of Chinese emperors, this was the belief that a ruler held authority by command of divine force as long as he ruled morally and benevolently. |  | 49 |
| 12203858680 | Mauryan Empire | A major empire (322-185 B.C.E.) that encompassed most of India. | 50 | |
| 12203858681 | Patricians | Wealthy, privileged Romans who dominated early Roman society. | 51 | |
| 12203858682 | Pax Romana | The "Roman peace," a term typically used to denote the stability and prosperity of the early Roman Empire, especially in the first and second centuries C.E. |  | 52 |
| 12203858683 | Peloponnesian War | Great war between Athens (and allies) and Sparta (and allies), lasting from 431 to 404 B.C.E. The conflict ended in the defeat of Athens and the closing of Athens's Golden Age. |  | 53 |
| 12203858684 | Persepolis | The capital and greatest palace-city of the Persian Empire, destroyed by Alexander the Great. |  | 54 |
| 12203858685 | Persian Empire | A major empire that expanded from the Iranian plateau to incorporate the Middle East from Egypt to India; flourished from around 550 to 330 B.C.E. | 55 | |
| 12203858686 | Plebians | Poorer, less privileged Romans who gradually won a role in Roman politics. | 56 | |
| 12203858687 | Qin Dynasty | A short-lived (221-206 B.C.E.) but highly influential Chinese dynasty that succeeded in reuniting China at the end of the Warring States period. |  | 57 |
| 12203858688 | Qin Shihuangdi | Literally "first emperor" (r. 221-210 B.C.E.) forcibly reunited China and established a strong and repressive state. | 58 | |
| 12203858689 | Wudi | Han emperor (r. 141-86 B.C.E.) who began the Chinese civil service system by establishing an academy to train imperial bureaucrats. | 59 | |
| 12203858690 | Aristotle | A Greek polymath philosopher (384-322 B.C.E.); student of Plato and teacher of Alexander the Great. | 60 | |
| 12203858691 | Bhagavad Gita | A great Hindu epic text, part of the much larger Mahabharata, which affirms the performance of caste duties as a path to religious liberation. | 61 | |
| 12203858692 | Brahman | The "World Soul" or final reality in upanishadic Hindu belief. | 62 | |
| 12203858693 | Brahmins | The priestly caste of India. | 63 | |
| 12203858694 | Buddhism | The cultural/religious tradition first enunciated by Siddhartha Gautama | 64 | |
| 12203858695 | Confucianism | The Chinese philosophy first enunciated by Confucius, advocating the moral example of superiors as the key element of social order. | 65 | |
| 12203858696 | Confucius | The founder of Confucianism (551-479 B.C.E.); an aristocrat of northern China who proved to be the greatest influence on Chinese culture in its history. | 66 | |
| 12203858697 | Constantine | Roman emperor (r. 306-337 C.E.) whose conversion to Christianity paved the way for the triumph of Christianity in Europe. |  | 67 |
| 12203858698 | Daoism | A Chinese philosophy/popular religion that advocates simplicity and understanding of the world of nature, founded by the legendary figure Laozi. | 68 | |
| 12203858699 | Filial piety | The honoring of one's ancestors and parents, a key element of Confucianism. | 69 | |
| 12203858700 | Hinduism | A word derived from outsiders to describe the vast diversity of indigenous Indian religious traditions. | 70 | |
| 12203858701 | Hippocrates | A very influential Greek medical theorist (ca. 460-ca. 370 B.C.E.); regarded as the father of medicine. | 71 | |
| 12203858702 | Jesus of Nazareth | The prophet/god of Christianity(ca. 4 B.C.E.-ca. 30 C.E.). | 72 | |
| 12203858703 | Karma | In Hinduism, the determining factor of the level at which the individual is reincarnated, based on purity of action and fulfillment of duty in the prior existence. |  | 73 |
| 12203858704 | Laozi | A legendary Chinese philosopher of the sixth century B.C.E.; regarded as the founder of Daoism. | 74 | |
| 12203858705 | Legalism | A Chinese philosophy distinguished by an adherence to clear laws with vigorous punishments. | 75 | |
| 12203858706 | Moksha | In Hindu belief, liberation from separate existence and union with Brahman. | 76 | |
| 12203858707 | Nirvana | The end goal of Buddhism, in which individual identity is "extinguished" into a state of serenity and great compassion. | 77 | |
| 12203858708 | Siddhartha Gautama (the Buddha) | The Indian prince turned ascetic (ca. 566-ca. 486 B.C.E.) who founded Buddhism. | 78 | |
| 12203858709 | Socrates | The first great Greek philosopher to turn rationalism toward questions of human existence (469-399 B.C.E.). | 79 | |
| 12203858710 | Theravada | "The Teaching of the Elders," the early form of Buddhism according to which the Buddha as a wise teacher but not divine and which emphasizes practices rather than beliefs. | 80 | |
| 12203858711 | Upanishads | Indian mystical and philosophical works, written between 800 and 400 B.C.E. | 81 | |
| 12203858712 | Vedas | The earliest religious texts of India, a collection of ancient poems, hymns, and rituals that were transmitted orally before being written down ca. 600 B.C.E. | 82 | |
| 12203858713 | Yin and Yang | Expression of the Chinese belief in the unity of opposites. | 83 | |
| 12203858714 | Zarathustra | A Persian prophet, traditionally dated to the sixth or seventh century B.C.E. (but perhaps much older), who founded Zoroastrianism. | 84 | |
| 12203858715 | Zoroastrianism | Persian monotheistic religion founded by the prophet Zarathustra. | 85 | |
| 12203858716 | caste system | The system of social organization in India that has evolved over millennia; it is based on an original division of the populace into four inherited classes, with the addition of thousands of social distinctions based on occupation, which became the main cell of social life in India. | 86 | |
| 12203858717 | dharma | In Indian belief, performance of the duties appropriate to an individual's caste; good performance will lead to rebirth in a higher caste. | 87 | |
| 12203858718 | helots | The dependent, semi-enslaved class of ancient Sparta whose social discontent prompted the militarization of Spartan society. | 88 | |
| 12203858719 | Kshatriya | The Indian social class of warriors and rulers. | 89 | |
| 12203858720 | latifundia | Huge estates operated by slave labor that flourished in parts of the Roman Empire | 90 | |
| 12203858721 | Pericles | A prominent and influential statesman of ancient Athens (ca. 495-429 B.C.E.); presided over Athens's Golden Age. | 91 | |
| 12203858722 | scholar-gentry class | A term used to describe members of China's landowning families, reflecting their wealth from the land and the privilege that they derived as government officials. | 92 | |
| 12203858723 | Sudra | The lowest Indian social class of varna; regarded as servants of their social betters; eventually included peasant farmers | 93 | |
| 12203858724 | the "three submissions" | In Chinese Confucian thought, the notion that a woman is permanently subordinate to male control: first that of her father, then of her husband, and finally of her son. | 94 | |
| 12203858725 | Untouchables | An Indian social class that emerged below the Sudras and whose members performed the most unclean and polluting work. | 95 | |
| 12203858726 | Vaisya | The Indian social class that was originally defined as farmers but eventually comprised merchants. | 96 | |
| 12203858727 | Axum | Classical-era kingdom of East Africa, in present-day Eritrea and northern Ethiopia; flourished from 100 to 600 C.E. and adopted Christianity. | 97 | |
| 12203858728 | Bantu expansion | Gradual migration of peoples from their homeland in what is now southern Nigeria and the Cameroons into most of eastern and southern Africa, a process that began around 3000 B.C.E. and continued for several millennia. The agricultural techniques and ironworking technology of these farmers gave them an advantage over the gathering and hunting peoples they encountered. | 98 | |
| 12203858729 | Silk Road | Trade route stretching from China into Europe. | 99 | |
| 12203858740 | hunting and gathering | Means of obtaining subsistence by humans before the mastery of sedentary agriculture; normally typical of tribal social organization |  | 100 |
| 12203858741 | civilization | Societies with reliance on sedentary agriculture, ability to produce food surpluses, and existence of nonfarming elites, along with merchant and manufacturing groups | 101 | |
| 12203858742 | neolithic | The New Stone Age between 8000 and 5000 B.C.E.; period in which adaptation of sedentary agriculture occurred; domestication of plants and animals accomplished |  | 102 |
| 12203858743 | nomadic societies | livestock hearding societies that do not have a permanent settlement. normally found on the fringes of civilized (urban) societies; commonly referred to as "barbarian" by civilized societies |  | 103 |
| 12203858744 | culture | Combination of ideas, objects, and patterns of behavior that result from human social interaction |  | 104 |
| 12203858745 | agrarian revolution | Occurred between 8000 and 5000 B.C.E.; transition from hunting and gathering to sedentary agriculture |  | 105 |
| 12203858746 | pastoralism | A nomadic agricultural lifestyle based on herding domesticated animals; tended to produce independent people capable of challenging sedentary agricultural societies |  | 106 |
| 12203858747 | Mesopotamia | Literally "between the rivers"; the civilization that arose in the alluvial plain of the Tigris-Euphrates river valleys |  | 107 |
| 12203858748 | potter's wheel | A technological advance in pottery making; invented circa 6000 B.C.E.; encouraged faster and higher-quality ceramic pottery products |  | 108 |
| 12203858749 | Sumerians | People who migrated into Mesopotamia circa 4000 B.C.E.; created the first civilization within the region; organized area into city-states |  | 109 |
| 12203858750 | cuneiform | A form of writing developed by the Sumerians using a wedge-shaped stylus and clay tablets |  | 110 |
| 12203858751 | city-state | A form of political organization typical of Mesopotamian civilization; consisted of agricultural hinterlands ruled by an urban-based king |  | 111 |
| 12203858752 | Babylonian Empire | Unified all of Mesopotamia circa 1800 B.C.E.; collapsed due to foreign invasion circa 1600 B.C.E. |  | 112 |
| 12203858753 | Hammurabi | The most important Babylonian ruler; responsible for codification of the law |  | 113 |
| 12203858754 | Pharaoh | The term used to denote the kings of ancient Egypt; the term, "great house" refers to the palace of the pharaohs |  | 114 |
| 12203858755 | pyramids | Monumental architecture typical of Old Kingdom Egypt; used as burial sites for pharaohs |  | 115 |
| 12203858756 | hieroglyphs | Form of writing developed in ancient Egypt; more pictorial than Mesopotamian cuneiform |  | 116 |
| 12203858757 | monotheism | The exclusive worship of one god; introduced by Jews into Middle Eastern civilization |  | 117 |
| 12203858758 | Aryans | Indo-European nomadic, warlike, pastorialists who replaced Harappan civilization |  | 118 |
| 12203858759 | Huanghe (Yellow) River Basin | Site of the development of sedentary agriculture in China |  | 119 |
| 12203858760 | Shang | 1st Chinese dynasty (after the legendary Xia) |  | 120 |
| 12203858761 | Oracles | Shamans or priests in Chinese society who foretold the future through interpreting animal bones cracked by heat; inscriptions on bones led to Chinese writing |  | 121 |
| 12203858762 | Big Geography | A term that draws attention to the global nature of world history. |  | 122 |
| 12203858763 | Paleolithic | The period that ended about 3,000 years after the end of the last Ice Age, it lasted until about 10,000 years ago. (Old Stone Age) The period of the Stone Age associated with the evolution of humans. It predates the Neolithic period. |  | 123 |
| 12203858764 | Human migration during Paleolithic era | movement of humans from Africa to Eurasia, Australia, and the Americas | 124 | |
| 12203858765 | eglitarian | equality among people (no social levels) | 125 | |
| 12203858766 | tools | Humans developed a wider range of ____ specially adapted to different environments from tropics to tundra | 126 | |
| 12203858767 | Neolithic Revolution | period of change from hunter-gatherer lifesyle to agricultural lifestyles associated with domestication, farming, and settlement |  | 127 |
| 12203858768 | patriarchy | father based/male dominated society |  | 128 |
| 12203858769 | climatic change | Permanent agricultural villages emerged first in the lands of the eastern Mediterranean, possibly as a response to what? | 129 | |
| 12203858770 | weapons | Pastoralists were often the developers and disseminators of of ____ and forms of transportation that transformed warfare in agrarian civilizations | 130 | |
| 12203858771 | horses | name one mode of new transportation by the pastoralists | 131 | |
| 12203858772 | art | Elites, both political and religious, promoted ____. | 132 | |
| 12203858773 | record-keeping systems | ___ arose independently in all early civilization sand subsequently were diffused | 133 | |
| 12203858730 | Nile River | This river flooded regularly. |  | 134 |
| 12203858731 | Tigris River | This river's floods were unpredictable. |  | 135 |
| 12203858732 | Mesopotamian | Unpredictable weather patterns affected the development of the _____ civilization. | 136 | |
| 12203858733 | Egyptian | _______art demonstrated little change for nearly 1000 years. | 137 | |
| 12203858734 | Euro diseases | Smallpox, measles, diphtheria, influenza, malaria, yellow fever and typhoid nearly wiped put entire indian villages | 138 | |
| 12203858735 | Spanish Silver | commercial and new global economic | 139 | |
| 12203858736 | cod hot spot | northern european in america | 140 | |
| 12203858737 | Confucianism | The system of ethics, education, and statesmanship taught by Confucius and his disciples, stressing love for humanity, ancestor worship, reverence for parents, and harmony in thought and conduct. | 141 | |
| 12203858738 | Doaism | Religion that teaches people to give up earthly desires in favor of nature | 142 | |
| 12203858739 | Legalism | A Chinese philosophy that was devoted to strengthen and expand the state through increased agricultural work and military service. | 143 |
AP World History Flashcards
Primary tabs
Need Help?
We hope your visit has been a productive one. If you're having any problems, or would like to give some feedback, we'd love to hear from you.
For general help, questions, and suggestions, try our dedicated support forums.
If you need to contact the Course-Notes.Org web experience team, please use our contact form.
Need Notes?
While we strive to provide the most comprehensive notes for as many high school textbooks as possible, there are certainly going to be some that we miss. Drop us a note and let us know which textbooks you need. Be sure to include which edition of the textbook you are using! If we see enough demand, we'll do whatever we can to get those notes up on the site for you!

