| 8369749269 | Encomienda | Spanish got labor and tribute from indigenous people and required Spanish to look after welfare of workers. | 0 | |
| 8369749270 | Hernán Cortés | Spanish leader of the conquest of the Aztec empire in Mexico | 1 | |
| 8369749271 | Francisco Pizarro | Spanish leader of the conquest of the Incan empire in Peru | 2 | |
| 8369749272 | Viceroy | Spanish governors in Mexico and Peru that answered to the Monarchs in Spain | 3 | |
| 8369749273 | Audiencias | Courts that heard appeals against viceroys' decisions and conducted reviews of viceroys' performance at the end of terms | 4 | |
| 8369749274 | Treaty of Tordesillas | Divided the world along imaginary line and stated that Spain could claim land west of that line (Americas) and Portugal same rights for lands east of the line (Brazil, Africa, India and Spice Islands) | 5 | |
| 8369749275 | Zheng He | Chinese explorer who led missions into the Indian Ocean in order to establish relationships and show Chinese dominance in the region. | 6 | |
| 8369749276 | Ming Treasure Ships | Sent with Zheng He to bring gifts to neighboring countries and to show China's dominance. | 7 | |
| 8369749277 | Prince Henry the Navigator | Portuguese commander who captured trade ports in Morocco and established schools to navigation which led to early Portuguese dominance in Exploration. | 8 | |
| 8369749278 | Bartolomeu Dias | First to round the Cape of Good Hope in Africa from Europe | 9 | |
| 8369749279 | Vasco da Gama | First to sail to India around Africa from Europe. Opened up trade route to Asian goods that linked directly to Europe. | 10 | |
| 8369749280 | Christopher Columbus | Discovered the Americas while sailing to find a new trade route to India for Spain. | 11 | |
| 8369749281 | Astrolabe | Used by navigators to measure the position in the sky of a celestial body, day or night. Helped increase exploration | 12 | |
| 8369749282 | volta do mar | The circular wind and water currents of the Atlantic. Used by the Portuguese and later explorers to enable better sailing techniques. | 13 | |
| 8369749283 | Ferdinand Magellan | Led the first expedition to sail around the globe and first European to cross the Pacific Ocean. Sailed for Spain. | 14 | |
| 8369749284 | Captain James Cook | English Explored who mapped much of the Pacific and visited the Arctic and Antarctic. | 15 | |
| 8369749285 | Columbian exchange | Global diffusion of plants, food crops, animals, human populations, and disease pathogens that took place after voyages by Christopher Columbus and other European mariners | 16 | |
| 8369749286 | Manila Galleons | Ships that sailed from Spanish ports in Mexico carrying silver to the Philippines where they trades for spiced and other Asian goods. | 17 | |
| 8369749287 | Joint-Stock company | A business, often backed by a government charter, that sold shares to individuals to raise money for its trading enterprises and to spread the risks (and profits) among many investors. | 18 | |
| 8369749288 | Hegemony | leadership or dominance, especially by one country or social group over others. | 19 | |
| 8369749289 | Indentured Labor | Labor system used mainly in North America where a person would have their passage tot he Americas paid for and in return they would provide a term of service (7 years) | 20 | |
| 8369749290 | The Virgin of Guadalupe | Roman Catholic site in Mexico of a vision of the Virgin Mary that became a pilgrimage site. | 21 | |
| 8369749291 | Aboriginal | Indigenous Australian People | 22 | |
| 8369749292 | Polynesian | Indigenous people of Oceania | 23 | |
| 8369749293 | Triangular Trade | First leg carried European manufactured goods exchanged in sub-Saharan Africa for slaves. Second leg took enslaved Africans to Caribbean and Americas. Third leg took American products back to Europe. | 24 | |
| 8369749294 | Middle Passage | Trans-Atlantic journey made by slaves on crowded slave ships. Faced dire conditions. | 25 | |
| 8369749295 | Iberian | Peninsula where Spain and Portugal are located. | 26 | |
| 8369749296 | Mestizos | Born of European and Indigenous parents. Middle of Colonial Latin American Society. | 27 | |
| 8369749297 | Mulattoes | People of Spanish and African descent. | 28 | |
| 8369749298 | Zambos | People of Amerindian and African descent | 29 | |
| 8369749299 | Peninsulares | Spanish/Portuguese migrants born in Europe from the Iberian peninsula. Highest social class in colonial Latin America. Occupied highest positions of government. | 30 | |
| 8369749300 | Creoles | People born in the Americas of Iberian parents. Second highest social class in colonial Latin America. Made an elite class but bared from highest positions. | 31 | |
| 8369749301 | Mita system | Required labor for indigenous people used int he Andes by the Inca and later the Spanish for work in silver mines. | 32 | |
| 8369749302 | Quinto | 1/5 of silver from the Americas given to the Spanish crown. | 33 | |
| 8369749303 | Hacienda | The estate. Focus of Spanish agricultural production in colonial Americas. | 34 | |
| 8369749304 | Engenho | Portuguese sugar mills in Brazil which combined agriculture and industry. | 35 | |
| 8369749305 | African diaspora | The dispersal of African peoples and descendants; left a permanent mark throughout the western hemisphere. | 36 | |
| 8369749306 | Maroons | Runaway slaves from Latin and South America that created their own communities. | 37 | |
| 8369749307 | Syncretic | Blending of religions; specifically Christianity in the Americas and Oceania. | 38 | |
| 8369749308 | Sunni Ali | Leader of the Songhay emperor in Westen Africa | 39 | |
| 8369749309 | Timbuktu | Major trading city in Western Africa | 40 | |
| 8369749310 | King Nzinga Mbemba/ King Afonso I | Leader of the Kongo who converted to Christianity to do better business with the Portuguese and endorse his rule | 41 | |
| 8369749311 | Queen Nzinga | Rules kingdom of Ndongo and resisted the Portuguese for 40 years | 42 | |
| 8369749312 | Dona Beatriz | Kongolese woman who proclaimed St. Anthony of Padua possessed her and chose her to communicate his messages. Taught syncretic Antonian movement to Africans. | 43 | |
| 8369749313 | Martin Luther | German monk whose grievances against the Church began the Protestant Reformation. | 44 | |
| 8369749314 | 95 Thesis | Luther's document that stated grievances with the church such as corruption, the selling of indulgences and a secularized ruling elite. | 45 | |
| 8369749315 | Johannes Gutenberg | Inventor of the printing press which helped spread Protestant literature and contributed to the Reformation | 46 | |
| 8369749316 | John Calvin/ Calvinism | Founder of sect of Protestantism based in Geneva. Believed in strict adherence to the Bible and Predestination. | 47 | |
| 8369749317 | Council of Trent | Catholic meeting about what to do in response to the Protestant reformation. Decided to uphold beliefs of the Catholic Church and cut down on secularism. | 48 | |
| 8369749318 | St. Ignatius Loyola | Founder of the Jesuits. Catholic group that worked a missionaries to spread the Catholic faith using education. | 49 | |
| 8369749319 | The Thirty Years' War | War fought in Central Europe between Catholics and Protestants and the deadliest European religious war in history | 50 | |
| 8369749320 | Geocentric | Earth centered universe | 51 | |
| 8369749321 | Nicolas Copernicus | Proposed a heliocentric universe and helped begin the Scientific Revolution. | 52 | |
| 8369749322 | Heliocentric | Sun centered universe | 53 | |
| 8369749323 | Johannes Kepler | Discovered the laws of planetary motion. | 54 | |
| 8369749324 | Isaac Newton | Invented calculus and the laws of motion. | 55 | |
| 8369749325 | Leonardo da Vinci | Italian Renaissance painter and scientist whose works include the Mona Lisa and the Last Supper. | 56 | |
| 8369749326 | Donatello | Renaissance sculptor from Florence | 57 | |
| 8369749327 | Michelangelo Buonarroti | Renaissance Painter and Sculptor whose works include the Sistine Chapel and the David. | 58 | |
| 8369749328 | Desiderius Erasmus | Early Humanist scholar who translated many works | 59 | |
| 8369749329 | Petrarch | Known as the father of humanism traveled around Europe searching for Classical Greek and Roman manuscripts | 60 | |
| 8369749330 | Humanism | Philosophy that emphasizes the value of human beings and prefers critical thinking and evidence over acceptance of superstition. | 61 | |
| 8369749331 | Renaissance | Cultural rebirth that occurred in Europe from the 14th through the 17th centuries, based on the rediscovery of the literature of Greece and Rome | 62 | |
| 8369749332 | Reformation | A 16th-century movement for the reform of abuses in the Roman Catholic Church ending in the establishment of the Reformed and Protestant Churches. | 63 | |
| 8369749333 | Silk Roads | the most famous of the trading routes established by pastoral nomads connecting the European, Indian, and Chinese; transmitted goods and ideas among civilizations | 64 | |
| 8369749334 | Black Death | The common name for a major outbreak of plague that spread across Asia, North Africa, and Europe in the mid-fourteenth century, carrying off vast numbers of persons. | 65 | |
| 8369749335 | Indian Ocean trading network | The world's largest sea-based system of communication and exchange before 1500 C.E., stretched from southern China to eastern Africa and included exchange of goods also ideas and crops. |  | 66 |
| 8369749337 | Swahili civilization | an East African civilization that emerged in the 8th century ce from a blending of Bantu, Islamic, and other Indian Ocean trade elements |  | 67 |
| 8369749338 | Great Zimbabwe | City whose many stone structures were built between about 1250 and 1450, when it was a trading center and the capital of a large state. | 68 | |
| 8369749339 | Ghana, Mali, Songhay | Capitalizing on new Saharan trade these monarchies were established trading gold for salt and slaves |  | 69 |
| 8369749340 | Trans-Saharan slave trade | A fairly small-scale trade exporting West African slaves across the Sahara as household servants in Islamic North Africa | 70 | |
| 8369749341 | Sui dynasty | The short dynasty between the Han and the Tang; built the Grand Canal, strengthened the government, and introduced Buddhism to China |  | 71 |
| 8369749342 | Tang dynasty | 618-907 CE. Had the equal field system, a bureaucracy based on merit and a Confucianism education system. Trained strong armies to fight off nomadic powers from Asia. Cultural influence over Korea and Vietnam. |  | 72 |
| 8369749343 | Song dynasty | 960 - 1279 AD. Important inventions such as magnetic compass; had a navy; traded with India and Persia; paper money, gun powder; |  | 73 |
| 8369749345 | foot binding | Practice in Chinese society to mutilate women's feet in order to make them smaller; produced pain and restricted women's movement; made it easier to confine women to the household. | 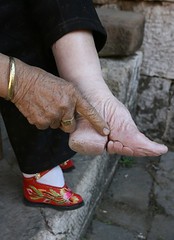 | 74 |
| 8369749346 | tribute system | Chinese method of dealing with foreign lands and people's that assumed the subordination of all non-Chinese authorities and required payment | 75 | |
| 8369749349 | Silla Dynasty | Korean dynasty that resisted Tang for first time. Respected China, studied Buddhism/Confucianism | 76 | |
| 8369749350 | bushido | "the way of the warrior"; Japanese word for the Samurai life ; Samurai moral code based on loyalty, chivalry, martial arts, and honor until the death |  | 77 |
| 8369749351 | Chinese Buddhism | Entered China from India through a series of cultural accommodations. At first supported by the state suffered persecution during the 9th century but continued to play a role in Chinese society. | 78 | |
| 8369749352 | Quran | The holy book of Islam | 79 | |
| 8369749353 | umma | The community of all Muslims. Innovation where traditionally kinship rather than faith determined membership in a community. | 80 | |
| 8369749354 | Pillars of Islam | The five core practices required of Muslims: a profession of faith, regular prayer, charitable giving, fasting during Ramadan, and a pilgrimage to Mecca (if physically and financially possible). | 81 | |
| 8369749355 | hijra | The Migration of Muhammad from Mecca to Medina in A.D. 622, marking the founding of Islam |  | 82 |
| 8369749356 | sharia | Body of Islamic law that includes interpretation of the Quran and applies Islamic principles to everyday life | 83 | |
| 8369749357 | jizya | tax paid by Christians and Jews who lived in Muslim communities to allow them to continue to practice their own religion | 84 | |
| 8369749358 | ulama | Muslim religious scholars. From the ninth century onward, the primary interpreters of Islamic law and the social core of Muslim urban societies. | 85 | |
| 8369749359 | Umayyad Caliphate | (661-750 CE) Islamic; established a capital at Damascus, conquered North Africa, the Iberian Peninsula, Southwest Asia, and Persia; had a bureaucracy with only Arab Muslims able to be a part of it. |  | 86 |
| 8369749360 | Abbasid Caliphate | (750-1258 CE) Islamic; after the Umayyads; focused on administration rather than conquering; bureaucracy any Muslim could be a part of. |  | 87 |
| 8369749361 | Sufism | A branch of Islam, defined by adherents as the inner, mystical dimension of Islam; |  | 88 |
| 8369749363 | Ibn Battuta | (1304-1369) Morrocan Muslim scholar, the most widely traveled individual of his time. Wrote account of his visits to Islamic lands from China to Spain and the western Sudan. |  | 89 |
| 8369749365 | Mansa Musa | Ruler of Mali (r. 1312-1337). Extravagant pilgrimage through Egypt to Mecca in 1324-1325 established the empire's reputation for wealth in the Mediterranean world. |  | 90 |
| 8369749367 | madrassas | Formal colleges for higher institutions in the teaching of Islam as well as in secular subjects founded throughout the Islamic world in beginning in the 11th century | 91 | |
| 8369749368 | House of Wisdom | Combination library, academy, and translation center in Baghdad established in the 800s. |  | 92 |
| 8369749369 | Nubian Christianity | Christianity was introduced by traders and missionaries. Preserved Christianity for 600 years. | 93 | |
| 8369749370 | Ethiopian Christianity | Christian island surrounded by Muslims sea; focused on banishing of evil spirits and amulets. |  | 94 |
| 8369749371 | Byzantine Empire | (330-1453) The eastern half of the Roman Empire;survived after the fall of the Western Empire; capital was Constantinople, named after the Emperor Constantine. |  | 95 |
| 8369749372 | Constantinople | A large and wealthy city that was the imperial capital of the Byzantine empire and later the Ottoman empire, now known as Istanbul | 96 | |
| 8369749373 | Justinian | Byzantine emperor in the 6th century A.D.; reconquered territory previously ruled by Rome, initiated a building program , including Hagia Sofia, as well as a new legal code |  | 97 |
| 8369749374 | caesarpapism | a political-religious system where the secular ruler is also the head of the religious establishment (Byzantine Empire) | 98 | |
| 8369749375 | Eastern Orthodox Christianity | Branch of Christianity that evolved following the division of the Roman Empire and development of the Byzantine Empire; Church recognized the primacy of the patriarch of Constantinople | 99 | |
| 8369749376 | icons | A painting of Christ or another holy figure, used as an aid to devotion in the Byzantine and other Eastern Churches. | 100 | |
| 8369749377 | Kievan Rus | Monarchy established in present day Russia in the 6th and 7th centuries. Ruled through loosely organized alliances with regional aristocrats from surrounding lands | 101 | |
| 8369749378 | Charlemagne | King of the Franks (r. 768-814); emperor (r. 800-814). Through military conquests established the Carolingian Empire; all of Gaul and parts of Germany and Italy. | 102 | |
| 8369749379 | Holy Roman Empire | A medieval and early modern central European Germanic empire, which consisted of hundreds of separate Germanic and Northern Italian states. So decentralized it played a role in perpetuating the fragmentation of central Europe. | 103 | |
| 8369749380 | Roman Catholic church | One of three major branches of Christianity; arose out of division of the Roman empire in the Western portion; pope is the head | 104 | |
| 8369749381 | Western Christendom | On the margins of world history for most postclassical era; Removed from world trade routes; Geography made political unity difficult; Coastlines and river systems facilitated internal exchange; | 105 | |
| 8369749382 | Crusades | Armed pilgrimages to the Holy Land by Christians determined to recover Jerusalem from Muslim rule. The Crusades brought an end to western Europe's centuries of intellectual and cultural isolation. |  | 106 |
| 8369749383 | pastoralism | A type of agricultural activity based on nomadic animal husbandry or the raising of livestock to provide food, clothing, and shelter. | 107 | |
| 8369749384 | Turks | 6th-10th centuries C.E.; Pastoral ethnic group that originated in northern Eurasia and spread into Central Asia and the Middle East; cultural and political interactions with China, Persia, Byzantium; conversion to Islam 10th-14th centuries and diffused it throughout Middle East, India, Anatolia(Turkey) | 108 | |
| 8369749385 | Temujin | leader of the largest Mongol clans; he united them all; receives title Genghis Khan(universal ruler) | 109 | |
| 8369749386 | the Mongol world | Eurasia, 13th-15th centuries; 50-year period conquests across Eurasia that created Mongol; Subjected huge populations to rule; Military strength allowed for rapid conquest; created interactions between diverse groups; diffused technology, culture, political and economic systems |  | 110 |
| 8369749387 | Yuan Dynasty | (1279-1368 CE) The dynasty with Mongol rule in China; centralized with bureaucracy but structure is different: Mongols on top->Persian bureaucrats->Chinese bureuacrats. | 111 | |
| 8369749388 | Kublai Khan | (1215-1294) Grandson of Genghis Khan and founder of the Mongol Yuan Dynasty in China. | 112 | |
| 8369749389 | Hulegu | Ruler of the Ilkhan khanate; grandson of Chinggis Khan; responsible for capture and destruction of Baghdad in 1257 | 113 | |
| 8369749390 | Kipchak Khanate | Name given to Russia by the Mongols after they conquered it and incorporated it into the Mongol Empire in the mid-thirteenth century; known to Russians as the "Khanate of the Golden Horde." |  | 114 |
| 8369749391 | Timur | Sometimes known as Tamerlane, Central Asian leader of a Mongol tribe who attempted to re-establish the Mongol Empire in the late 1300's. Empire included Persia. | 115 | |
| 8369749392 | European Renaissance | a "rebirth" of classical learning that is most often associated with the cultural blossoming of Italy is the period 1350-1500 and included Greek learning and growing secularism | 116 | |
| 8369749393 | Ottoman Empire | Islamic state founded by Osman in northwestern Anatolia. After the fall of the Byzantine Empire, the Ottoman Empire was based at Istanbul Encompassed lands in the Middle East, North Africa, the Caucasus, and eastern Europe. |  | 117 |
| 8369749394 | Seizure of Constantinople | Fell to army of Ottoman sultan Mehmed II in 1453, marking end of Christian Byzantium | 118 | |
| 8369749395 | Songhay Empire | A state located in western Africa. From the early 15th to the late 16th century, it was one of the largest Islamic empires in history. | 119 | |
| 8369749396 | Malacca | Port city in the modern Southeast Asian country of Malaysia, founded 1400 as a trading center on the Strait of Malacca. |  | 120 |
| 8369749397 | Bantu Migration | Causes spread of agriculture in Africa, spread of iron metallurgy, population growth and spread of the Bantu Language | 121 | |
| 8369749398 | Vikings | Norse raiders who terrorized Europe due to their own lack of resources; advanced ship technology; helped spread culture; kept Europe decentralized | 122 | |
| 8369749399 | Technological Diffusion Examples | magnetic compass; crops (fast growing rice, cotton, sugercane); horse collar; three field system; gunpowder | 123 | |
| 8369749400 | Marco Polo | Venetian merchant traveler who spent 20 years in China and wrote about his travels is a widely popular book | 124 | |
| 8369749401 | Chinese influence on Japan | Buddhism; bureaucracy; trade; Social Structure | 125 | |
| 8369749402 | Syncretism | combining of different beliefs (religions); ex. Ethiopian Christianity, | 126 | |
| 8369749403 | Confucianism | Philosophical "religion", based on the teachings of the Chinese philosopher King Fuzi (551-479 BCE), or Confucius, that emphasizes order, the role of the gentleman, obligation to society, and reciprocity; | 127 | |
| 8369749404 | Daodejing | Book that is the fundamental work of Daoism; | 128 | |
| 8369749405 | Daoism | Chinese philosophy with origins in the Zhou dynasty. It associated with legendary philosopher Laozi, and it called for a policy of non competition; | 129 | |
| 8369749406 | Han Dynasty | One of the longest and most influential dynasties, lasting over 400 years (206 BCE-220 CE) ; | 130 | |
| 8369749407 | Han Wudi | Enthusiastic emperor who ruled with the principles of administrative centralization and imperial expansion Ruled the Han dynasty for 54 years (141-87 BCE); | 131 | |
| 8369749408 | Legalism | Chinese philosophy from the Zhou dynasty that called for harsh suppression of the common people; | 132 | |
| 8369749409 | Liu Bang | Chinese ruler who restored centralised imperial rule to start the Han dynasty ; | 133 | |
| 8369749410 | Period of the Warring States | Last centuries of the Zhou dynasty (403-221 BCE) where wars divided the region until the establishment of the Qin dynasty ended the disunity; | 134 | |
| 8369749411 | Qin | Chinese dynasty (221-207 BCE) that was founded by Qin Shihuangdi and was marked by the first unification of China and the early construction of defensive walls; | 135 | |
| 8369749412 | Qin Shihuangdi | First emperor of the Qin dynasty (221-207 BCE); | 136 | |
| 8369749413 | Ren | Confucian concept of kindness and benevolence or a sense of humanity; | 137 | |
| 8369749414 | Terracotta Army | Thousands of statues made for Qin Shihuangdi's burial | 138 | |
| 8369749416 | Xiongnu | Nomadic people, warriors killed Liu Bang in 200 BCE; | 139 | |
| 8369749417 | Yellow Turban uprising | Peasant revolt in the later Han dynasty because of the unfair difference between rich and poor; | 140 | |
| 8369749418 | Early Development of Greek Society | during 3rd millennium BCE, early Greek people traveled throughout the Mediterranean Basin and met and traded with various early civilizations, built societies based off Egyptian, Mesopotamian, and Phoenician models; organize into series of city states by 9th century BCE | 141 | |
| 8369749419 | Minoan Society | arose in island of Crete, named after Minoan King Minos, build elaborately decorated palaces throughout island to serve as nerve centers of society | 142 | |
| 8369749421 | Linear A | writing system used in Minoan society, developed by palace officials, stood for syllabled rather than words, vowels, consonants, or ideas; used for record keeping of economic and commercial matters | 143 | |
| 8369749423 | Mycenaean Society | Indo-European migrations of people from Balkans move into Greek peninsula, began trade with Minoan merchants and visited Crete where they learned about Linear A and developed Linear B; built massive stone fortresses and palaces in Peloponnesus which attracted settlers from the north who built small agricultural communities | 144 | |
| 8369749424 | The Polis | local institutions reorder Greece politically since there was no centralized state or empire; people retreated to citadels/fortresses (polis) for security, polis attract many people and become commercial centers and defensive positions, become increasingly urban, Poleis become city-states of Greek society | 145 | |
| 8369749425 | Sparta | located in fertile region of Peloponnesus and gradually extend authority over the region, turned conquered people into helots | 146 | |
| 8369749427 | Athens | government based on democratic principles (only free, adult males palyed a role), established order by considering the interest of the polis' different groups | 147 | |
| 8369749428 | Solon and Athenian Democracy | ended civil war, served as mediator between rich and poor, allowed rich to keep land, but said they must pardon all debts and forbade slavery due to debt; provided representation of common classes to ensure aristocrats would not undo reforms which eventually turned Athens into a Democratic state | 148 | |
| 8369749429 | Pericles | leader of Athen during height, came from common background, supported building programs that provided work for thousands; Athens becomes most sophisticated Polis made up of scientists, philosophers, poets, dramatists, artists, and architects | 149 | |
| 8369749431 | Effects of Greek Colonization | people of Mediterranean experienced more communication, interaction, and change, colonies facilitated trade, colonization spread Greek language and tradition, brought wealth to regions | 150 | |
| 8369749432 | Persian Wars | pre-emptive strike launched by Darius against Athens, Athens defeat Persians at Marathon and race back to fend off Persian navy, Xerxes later launches another attack against Greece 10 years later; Persians captured and burned Athens, Persian fleet destroyed by Athenian led Greek fleet at Battle of Salamis, border clashes continue | 151 | |
| 8369749433 | Delian League | formed to create an alliance system among the Poleis to help fight in case of new Persian invasion, Athens is leader of League and provided military while other Poleis provided financial support, funds used for infrastructure development in Athens, soon other Poleis become resentful of Athens newfound wealth | 152 | |
| 8369749434 | Peloponnesian War | tensions in Delian League resulted in civil war, divided between Athens and Sparta, and Athens was forced to surrender to Sparta which spawned renewed jealousies and resulted in renewed fighting, Thucydides wrote history of war and reported that both sides engaged in brutal behavior, Athens lost high moral position | 153 | |
| 8369749435 | Philip of Macedon | King Philip II built a powerful military that allowed him to overcome the clans and make himself rule of Macedon, next turned attention to Greece and Persia and was able to conquer Greek city-states with ease, planned on invading Persia but was assassinated ` | 154 | |
| 8369749436 | Alexander of Macedon | succeeded his father at age 20, led army of 48,000 men into Persia, conquered Ionia, then Anatolia, then Syria, Palestine and Egypt, then Mesopotamia and lastly the Persian homeland, captured Pasargadae, burned Persepolis, Persian army defeated at Gaugamela and Alexander established himself as ruler of Persia; planned on invading India but soldiers began to mutiny so returned to Mesopotamia; died at age 33 | 155 | |
| 8369749437 | Hellenistic Empires | Antigonus: Greece and Macedon (worst) Ptolemy- Egypt (best) Seleucus- former Achaemenid (biggest) | 156 | |
| 8369749438 | Hellenistic Era | age of Alexander and his successors, era when Greek cultural traditions expand past Greece, governed cosmopolitan societies and promoted interaction between people from Greece to India, helped integrate economies of distant regions, facilitated trade and made it possible for beliefs , values, and religions to spread over greater distances | 157 | |
| 8369749439 | Antigonid Empire | smallest and poorest of Hellenistic Empires, tension between leaders and Greek cities wishing to remain independent, made arrangements to recognize their rule but local self rule | 158 | |
| 8369749440 | Ptolemaic Empire | wealthiest of Hellenistic Empires, Greek and Macedonian leaders did not interfere with Egyptian society, spent time organizing agriculture, industry, and tax collection, established monopolies over most lucrative businesses | 159 | |
| 8369749441 | Alexandria | located at mouth of Nile River, served as bureaucratic and financial center of Ptolemaic Empire, wealth attracted migrants, city was a megalopolis with different cultures, religions, and ethnic backgrounds, cultural center of Hellenistic World | 160 | |
| 8369749442 | Seleucid Empire | Greek influence at its highest, fortress cities established by Alexander become home to droves of Greek and Macedonian colonists who transformed them into commercial centers, Greeks and Macedonians gained positions in the imperial bureaucracy and administration, were minorities | 161 | |
| 8369749443 | Sappho | wrote poems of attraction to women, promoted education for women, charged with homosexual activity | 162 | |
| 8369749444 | Socrates | encouraged reflection on questions of ethics and morality | 163 | |
| 8369749445 | Plato | disciple of Socrates, theory for Forms or Ideas-- world of ideal qualities; world is imperfect reflection of world of forms, Republic expressed ideal of philosophical kings | 164 | |
| 8369749446 | Aristotle | Plato's student, did not trust theory of Forms, devised rules of logic to construct powerful arguments, should rely on senses to provide accurate information | 165 | |
| 8369749447 | Skeptics | doubted certainty of knowledge, sought equanimity | 166 | |
| 8369749448 | Stoics | taught individuals duty to aid others and lead virtuous lives | 167 | |
| 8369749449 | Cyrus | r. 558-530 BCE; launched the Persians' imperial venture; came from a mountainous region of SW Iran; his conquers laid the foundation of the first Persian empire, aka the Achaemenid empire because its rulers claimed descent from his Achaemenid clan | 168 | |
| 8369749450 | Darius | r. 521-486 BCE; a younger kinsman of Cyrus who extended the empire both E and W; by the late sixth century, he presided over an empire stretching 3,000 km (1,865 mi) from the Indus River (E) to the Aegean Sea (W), and 1,500 km (933 mi) from Armenia (N) to the first catarct of the Nile (S) | 169 | |
| 8369749451 | Xerxes | r. 486-465 BCE; Darius's successor who retreated from the policy of toleration and sought to impose his own values on conquered lands | 170 | |
| 8369749452 | Seleucus | r. 305-281 BCE; formerly commander of an elite corps of guards in Alexander's army; he and his successors retained the Achaemenid systems of administration and taxation as well as the imperials roads and postal service | 171 | |
| 8369749454 | Zarathustra | Persian prophet (ca. 628-551 BCE) who founded Zoroastrianism | 172 | |
| 8369749455 | Achaemenids | First great Persian empire (558-330 BCE), which began under Cyrus and reached its peak under Darius | 173 | |
| 8369749457 | Satrapy | an administrative and taxation district governed by a satrap; used by the Persians | 174 | |
| 8369749458 | Parthians | Persian dynasty (247 BCE-224 CE) that reached its peak under Mithradates I | 175 | |
| 8369749459 | Sasanids | Later powerful Persian dynasty (224-651) that would reach its peak under Shapur I and later fall to Arabic expansion | 176 | |
| 8369749460 | Qanat | underground canals which allowed cultivators to distribute water to fields without losing large quantities to evaporation through exposure to the sun and open air | 177 | |
| 8369749461 | Zoroastrianism | Persian religion based on the teaching of the sixth-century-BCE prophet Zarathustra; its emphasis in the duality of good and evil and on the role of individuals in determining their own fate would influence later religions | 178 | |
| 8369749462 | Magi | Zoroastrian priests | 179 | |
| 8369749463 | Chandragupta Maurya | an ambitious explorer who laid the foundation for the Mauryan empire; by the end of the fourth century BCE, his empire embraced all of N India from the Indus to the Ganges | 180 | |
| 8369749464 | Ashoka | r. 268-232 BCE; Chandragupta Maurya's grandson; his first major undertaking as emperor was to conquer Kalinga, a kingdom actively hostile to Mauryan expansion; better known as a governor than a conqueror | 181 | |
| 8369749466 | Chandra Gupta | laid foundations for the Gupta empire; forged alliances with pwoerful families in the Ganges region and established a dynamic kingdom about th year 320 CE | 182 | |
| 8369749467 | Vardhamana Mahavira | a great teacher who turned to Jainism in the late century BCE, making the religion popular | 183 | |
| 8369749468 | Siddhartha Guatama | Indian kshatriya who achieved enlightenment and became known as the Buddha, the founder of Buddhism | 184 | |
| 8369749469 | Kingdom of Magadha | filled the void left by Alexander of Macedon when he left Punjab without a government | 185 | |
| 8369749470 | Mauryan Empire | 321-185 BCE; empire founded by Chandragupta Maurya in India | 186 | |
| 8369749471 | Arthashastra | Ancient Indian political treatise from the time of Chandragupta Maurya; its authorship was traditionally ascribed to Kautalya, and it stresses that war was inevitable | 187 | |
| 8369749473 | Kushan empire | empire founded by the most successful of the central Asian conquerors who attacked Bactria and put an end to the Indo-Greek kingdom there; embraced much of N India and central Asia from about 1 to 300 CE | 188 | |
| 8369749474 | Gupta dynasty | dynasty founded by Chandra Gupta; based in Magadha | 189 | |
| 8369749475 | Caste | term comes from the Portuguese "casta"; it refers to a social class of heredity and usually unchangeable status | 190 | |
| 8369749476 | Jainism | Indian religion associated with the teacher Vardhamana Mahavira (ca. 540-468 BCE) in which every physical object possessed a soul; Jains believe in complete nonviolence to all living beings | 191 | |
| 8369749477 | Buddhism | religion, based on Four Noble Truths, associated with Siddhartha Guatama (563-483 BCE), or the Buddha; its adherents desired to eliminate all distracting passion and reach nirvana | 192 | |
| 8369749478 | Hinduism | Main religion of India, a combination of Dravidian and Aryan concepts; its goal is to reach spiritual purity and union with the great world spirit; its important concepts include dharma, karma, and samsara | 193 | |
| 8369749479 | Dharma | Hindu concept of obedience to religious and moral laws and order | 194 | |
| 8369749480 | Karma | Hindu concept that the sum of good and bad in a person's life will determine his or her status in the next life | 195 | |
| 8369749481 | Noble Eightfold Path | final truth of the Buddhist Four Noble Truths that called for leading a life of balance and constant contemplation | 196 | |
| 8369749482 | Etruscans | Northern Italian tribe that dominated Rome in its early history Dominate Italy 8th-5th centuries Originally from Anatolia Colonized Roman regions Society declines late 6th c. BCE Greek maritime attacks Celtic invasions from north | 197 | |
| 8369749483 | Romulus and Remus | founded Rome in 753 BC | 198 | |
| 8369749484 | Roman republic | depose last Etruscan king in 509 BC, replace monarchy with aristocratic republic, Roman forum at heart of city | 199 | |
| 8369749485 | forum | political and civic center with temples and public buildings | 200 | |
| 8369749486 | tribunes | power by plebeians to intervene and veto decisions, dominated Roman politics | 201 | |
| 8369749487 | Punic Wars | Rome conflict with Carthage over Sicily for grain to finance more expansion, Romans win; conflict with Hellenistic realms when armies dispatched to protect Roman citizens from pirates | 202 | |
| 8369749488 | Julius Caesar | Names self Dictator for life of Rome in 46 BCE | 203 | |
| 8369749489 | Pax romana | Roman Peace, under Augustus, Roman roads, postal system | 204 | |
| 8369749490 | Roman law | Twelve Tables, c. 450 BCE Adapted to diverse populations under Roman Rule -Innocent until proven guilty -Right to challenge accusers in court | 205 | |
| 8369749492 | Cicero | writer on Stoicism | 206 | |
| 8369749493 | religions of salvation | appeal to masses, promised afterlife | 207 | |
| 8369749495 | Judaism | monotheistic, Yahweh = only god, Essenes (sect), defeated in Jewish War (66-70 CE) | 208 | |
| 8369749496 | Jesus of Nazareth | Christians' savior, Jewish teacher, love for human beings, popular Romans fear instigation of rebellion Crucifixion in early 30s CE (Romans execute him), became "Christ" | 209 | |
| 8369749497 | Old Testament | Jews' Hebrew scriptures | 210 | |
| 8369749498 | New Testament | accounts of Jesus' life, outlines Christian teachings | 211 | |
| 8369749499 | Paul of Tarsus | principal figure in spread of Christianity*, executed by Roman emperor Extends teachings far beyond Jewish circles Traveled widely throughout the Roman Empire Missionary activity | 212 | |
| 8369749500 | Christianity | Spiritual equality of the sexes Appeal to lower classes, urban population, women Influence faith in Mediterranean* by 200s CE Orthodox and Catholic believers describe Worship in terms of the seven sacraments or "mysteries." These include baptism, the Eucharist (communion), matrimony, Holy Orders, confirmation, penance and reconciliation, and the Anointing of the Sick. Priests conducted local services and ceremonies. Above the priests were bishops who headed the church in each major city. Bishops in Rome, Antioch, Constantinople, Alexandria and Jerusalem became known as patriarchs. Over time the patriarch of Rome took the title pope, claiming to be supreme over the patriarchs. | 213 | |
| 8369749502 | Augustus | Civil conflict follows death of Caesar Power belongs to Octavian Octavian defeats Mark Antony & Cleopatra Titled himself Princeps, which is Latin for "first citizen." Takes title Augustus 27 BCE Marks the official end of the Roman Republic and the beginning of the Roman Empire. | 214 | |
| 8369749503 | Public Works During the Republic | The Appian Way - was the most important ancient Roman road. It connected Rome to southeast Italy. Aqueducts were built to supply water to cities and industrial sites. These aqueducts were among the greatest engineering feats of the ancient world, and set a standard not equaled for over a thousand years after the fall of Rome. Many cities still maintain and use the ancient aqueducts for their water supply even today. | 215 | |
| 8369749504 | monsoon system | used to determine different sea routes to use throughout the year | 216 | |
| 8369749510 | Manichaeism | syncretic blend of 3 religions: Christianity, Buddhism, Zoroastrianism; HATED by Zoroastrians | 217 | |
| 8369749512 | Fall of the Han | crop shortage + disease, Yellow Turban Uprising, gone by 220 CE | 218 | |
| 8369749513 | Fall of Rome | 476 CE, no single cause. internal problems: lack of money + disease. external problems: Attila the Hun. | 219 | |
| 8369749515 | Diocletian | DIVIDES. splits rome into two and assigns 4 tetrarchs: his officials leading under him. tried to make reforms to administration and economy. | 220 | |
| 8369749516 | Constantine | CONSOLIDATES. Constantinople, unity, Christianity, promoted Edict of Milan. | 221 | |
| 8369749517 | The Huns | Attila attacking the Visigoths, Vandals and Franks; sent them all packing to Rome | 222 | |
| 8369749518 | Theodosius | made Christianity the official religion of the Roman empire | 223 | |
| 8369749519 | St. Augustine | the bishop of Hippo, instrumental in bringing Christianity to the people of the Mediterranean | 224 | |
| 8369749520 | Council of Nicaea | Jesus is both fully divine and fully human | 225 | |
| 8369749522 | Byzantine empire | Eastern roman empire, Constantinople | 226 | |
| 8369802147 | Animism | Religion based on the attribution of a soul to plants, inanimate objects, and natural phenomena. | 227 | |
| 8369804073 | Paleolithic Era | Cultural period of the Stone Age; began about 2.5 to 2 million years ago, marked by the earliest use of tools made of stone. | 228 | |
| 8369811643 | Neolithic Revolution | Transition of many human cultures from a lifestyle of hunting and gathering to one of agriculture and settlement, making possible an increasingly larger population. | 229 | |
| 8369813410 | Summarians | Early civilization based in the fertile crescent; used agriculture for form settled society and specialization of Labor | 230 | |
| 8369816612 | Egyptions | Early civilization developed along the Nile River valley characterized by Pharaohs and pyramids. | 231 | |
| 8369823001 | Shang | Early Civilization developed in the Yellow River Valley in China | 232 | |
| 8369825735 | Aztecs | Ancient civilization (1200-1521AD) that was located in what is present-day Mexico City; used a tribute system and human sacrifice | 233 | |
| 8369827802 | Maya | Developed in central America has great temples and disappeared for unknown reasons | 234 | |
| 8369833804 | Inca | Civilization that developed int he Andes Mountains used the mita system and were great road builders. | 235 | |
| 8369839350 | Ziggurat | a rectangular stepped tower, sometimes surmounted by a temple. Used in religious celebrations by early civilizations | 236 | |
| 8395903016 | Cuneiform | World's first writing system called developed by Sumerians in order to manage their surplus crops and manufacturing. | 237 | |
| 8395919251 | Hammurabi's Code | A set of 282 laws carved into stone monuments and one of the first of laws being put into writing for everyone to see; based on an eye for an eye. | 238 | |
| 8395932514 | Pastoralism | Based on people moving herds of animals from pasture to pasture | 239 |
AP World History Midterm Quizlet Flashcards
Primary tabs
Need Help?
We hope your visit has been a productive one. If you're having any problems, or would like to give some feedback, we'd love to hear from you.
For general help, questions, and suggestions, try our dedicated support forums.
If you need to contact the Course-Notes.Org web experience team, please use our contact form.
Need Notes?
While we strive to provide the most comprehensive notes for as many high school textbooks as possible, there are certainly going to be some that we miss. Drop us a note and let us know which textbooks you need. Be sure to include which edition of the textbook you are using! If we see enough demand, we'll do whatever we can to get those notes up on the site for you!

