Unit Three Part Three
| 11316494104 | Sui Dynasty | *Definition:* Short dynasty between Han and Tang. *Significance:* Built Grand Canal, strengthened government, and introduced Buddhism to China. |  | 0 |
| 11316494105 | Tang Dynasty | *Definition:* Dynasty often referred to as "China's Golden Age". (618 CE - 907 CE) *Significance:* China expands to Vietnam, Imperial examination perfected. New technologies (paper money, gunpowder, junks, etc...) through silk road. | 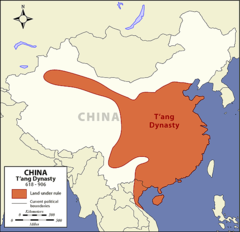 | 1 |
| 11316494106 | Song Dynasty | *Definition:* (960 CE - 1279 CE) Started by Tai Zu. *Significance:* Million people there. Foot binding, magnetic compass, navy, and traded with India and Persia. |  | 2 |
| 11316494107 | Hangzhou | *Definition:* Capital of later Song Dynasty. *Significance:* Permitted overseas trading with population exceeding 1 million. |  | 3 |
| 11316494108 | Economic Revolution | *Definition:* Rapid population growth, economic speculation, increase in industrial production and innovations (Song dynasty). *Significance:* Made China "by far the richest, most skilled, and most populous country on Earth." |  | 4 |
| 11316494109 | Foot Binding | *Definition:* Practice in Chinese society to mutilate women's feet to make them smaller. *Significance:* It was associated with images of female beauty and eroticism. |  | 5 |
| 11316494110 | Tribute System | *Definition:* Chinese method of dealing with foreign lands and people that assumed subordination of all non-chinese authorities. They required all foreigners wanting access to China to pay tribute. *Significance:* System the attempted to regulate their relationships with Northern Nomads. |  | 6 |
| 11316494111 | Khitan/Jurchen People | *Definition:* Nomadic people who established a state that included parts of Northern China. *Significance:* Was a nomadic group who "picked up the pieces" after collapse of Tang Dynasty. |  | 7 |
| 11316494112 | Silla Dynasty (Korea) | *Definition:* First ruling dynasty to bring a measure of political unity to Korean Peninsula. *Significance:* Allied with China to bring political unity to the peninsula for the first time. |  | 8 |
| 11316494113 | Hangul | *Definition:* Phonetic alphabet in Korea (14th century). *Significance:* Helped Korea move toward greater cultural independence. | 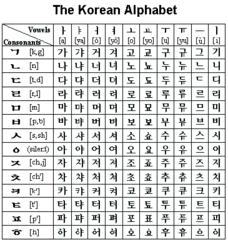 | 9 |
| 11316494114 | Shotoku Taishi | *Definition:* Japanese statesman who launched the drive to make Japan into centralized bureaucratic state modeled on China. *Significance:* Launched a series of large-scale missions to China. |  | 10 |
| 11316494115 | Bushido | *Definition:* "Way of the Warrior". *Significance:* A distinct set of values for Samurais. |  | 11 |
| 11316494116 | Chinese Buddhism | *Definition:* Entered China through cultural accommodations. *Significance:* Useful to helping nomadic rulers govern northern China because it was foreign. |  | 12 |
| 11316494117 | Emperor Wendi | *Definition:* Sui Emperor who patronized Buddhism. *Significance:* He was responsible for the monasteries constructed at the base of China's 5 sacred mountains. |  | 13 |
| 11316494119 | Chu nom | *Definition:* The writing system of Vietnam *Significance:* United Vietnam even during times of civil war |  | 14 |
| 11316525121 | gun powder | Explosive substance that gave Chinese an advantage over Mongals | 15 | |
| 11316525122 | Xiognu | A largely nomadic confederacy that raided Northern China. Chinese emperor was forced to regard this group as equals and supply them with grain, wine, and silk in return for the termination of their invasions. | 16 | |
| 11316525123 | Izumi Shikibu | - Heian period poet known for her love poems and romance | 17 |

