| 10479088959 | Originally a vassal family of Shang China. The Zhou overthrew the Shang and established second historical Chinese dynasty. The Dynasty then Flourished from------------(1122 B.C.E to 256 B.C.E). First leader was King Wu Zhou. | Zhou (Dynasty) 1122 B.C.E to 256 B.C.E |  | 0 |
| 10479088960 | concerning farms, farmers, or the use of land | agrarian |  | 1 |
| 10479088961 | an alliance of nations joining together to fight a common enemy | allies |  | 2 |
| 10479088962 | a group of many islands in a large body of water | archipelago |  | 3 |
| 10479088963 | Characteristic of absolute rule or absolute ruler | autocratic / autocracy |  | 4 |
| 10479088964 | New name for the Western Pacific Rim where a significant regional realignment is now taking place. Includes rapidly-developing countries & parts of countries lining the Pacific from Japan's Hokkaido in the north to New Zealand in the South ________________________________________________________________________ | Austrasia |  | 5 |
| 10479088965 | How a minority group gradually adopts the customs and attitudes of the dominant/prevailing culture and becomes accepted. ________________________________________________________________________ | assimilation |  | 6 |
| 10479088966 | The number of births in a population in a certain amount of time | birth rate |  | 7 |
| 10479088967 | A world religion or philosophy based on the teaching of the Buddha and holding that a state of enlightenment can be attained by suppressing worldly desire ________________________________________________________________________ | Buddhism |  | 8 |
| 10479088968 | an economic system based on private ownership of capital | Capitalism |  | 9 |
| 10479088969 | farm crop grown to be sold or traded rather than used by the farm family | cash crop |  | 10 |
| 10479088970 | a social structure in which classes are determined by heredity | Caste system |  | 11 |
| 10479088971 | A monotheistic system of beliefs and practices based on the Old Testament and the teachings of Jesus as embodied in the New Testament and emphasizing the role of Jesus as savior ________________________________________________________________________ | Christianity |  | 12 |
| 10479088972 | A political system characterized by a centrally planned economy with all economic and political power resting in the hands of the central government. ________________________________________________________________________ | Communism |  | 13 |
| 10479088973 | The average weather a place has over a long period of time (usually 20 to 30 years) ________________________________________________________________________ | climate |  | 14 |
| 10479088974 | The largest main land masses of the globe | continent |  | 15 |
| 10479088975 | The ideas, beliefs, and customs that are shared and accepted by people in a society. ________________________________________________________________________ | culture |  | 16 |
| 10479088976 | something done by people in a particular society because it is traditional | custom |  | 17 |
| 10479088977 | the number of deaths per 1,000 people in an area | death rate |  | 18 |
| 10479088978 | a low triangular area where a river divides before entering a larger body of water | delta |  | 19 |
| 10479088979 | A political system in which the supreme power lies in a body of citizens who can elect people to represent them. ________________________________________________________________________ | democracy |  | 20 |
| 10479088980 | statistical characteristics of human populations, such as gender, age, income level, etc. | demographics |  | 21 |
| 10479088981 | Degradation of land, especially in semiarid areas, primarily because of human actions like excessive crop planting, animal grazing, and tree cutting. ________________________________________________________________________ | desertification |  | 22 |
| 10479088982 | the movement of customs or ideas from one place to another | diffusion |  | 23 |
| 10479088983 | height above (or below) sea level | elevation |  | 24 |
| 10479088984 | a distinct region or community enclosed within a larger territory | enclave |  | 25 |
| 10479088985 | An imaginary circle around the middle of the earth, halfway between the North Pole and the South Pole. ________________________________________________________________________ | Equator |  | 26 |
| 10479088986 | a social division based on national origin, religion, language, and often race | ethnicity |  | 27 |
| 10479088987 | Thinking about things based only on what your own culture/ethnicity does. Not valuing the culture, traditions, etc. of others. Belief your own ethnic group is superior. | ethnocentrism |  | 28 |
| 10479088988 | To ship out (merchandise, resources, workers, ideas, etc.) to other countries for sale, exchange, etc. ________________________________________________________________________ | export |  | 29 |
| 10479088989 | A geographical area of fertile land in the Middle East stretching in a broad semicircle from the Nile to the Tigris and Euphrates ________________________________________________________________________ | Fertile Crescent |  | 30 |
| 10479088990 | A political and social system that developed during the Middle Ages; nobles offered protection and land in return for service ________________________________________________________________________ | feudalism |  | 31 |
| 10479088991 | A low plain adjacent to a river that is formed chiefly of river sediment and is subject to flooding and overflow. Perfect for agricultural needs. ________________________________________________________________________ | flood plain |  | 32 |
| 10479088992 | the study of where people, places, and things are located and how they relate to each other | geography |  | 33 |
| 10479088993 | A poor densely populated city district occupied by a minority ethnic group linked together by economic hardship and social restrictions ________________________________________________________________________ | ghetto |  | 34 |
| 10479088994 | half of the earth | hemisphere |  | 35 |
| 10479088995 | A religion and philosophy developed in ancient India, characterized by a belief in reincarnation and a supreme being who takes many forms. ________________________________________________________________________ | Hinduism |  | 36 |
| 10479088996 | a person who comes to a country where they were not born in order to settle there | immigrant/emigrant |  | 37 |
| 10479088997 | The policy of extending authority over several foreign countries to form an empire. Imperialism takes colonialism to the next level by holding many colonies, not just one. ________________________________________________________________________ | imperialism |  | 38 |
| 10479088998 | To bring in (merchandise, resources, ideas, workers, etc.) from a foreign country for use, trade, sale, and processing. ________________________________________________________________________ | import |  | 39 |
| 10479088999 | Something that is originally from an area: Native. | indigenous |  | 40 |
| 10479089000 | French colony made up of Cambodia, Laos, and Vietnam | Indochina |  | 41 |
| 10479089001 | When a country organizes factories, technology, and workers to manufacture (in order to mass-produce) things for sale. ________________________________________________________________________ | industrialization |  | 42 |
| 10479089002 | the system of public works of a country, state, or region, such as roads, electricity, sewers, running water, etc. | infrastructure |  | 43 |
| 10479089003 | The dependence of countries on goods, resources, and knowledge from other parts of the world. ________________________________________________________________________ | interdependence |  | 44 |
| 10479089004 | supplying dry land with water by means of ditches | irrigation |  | 45 |
| 10479089005 | a relatively narrow strip of land (with water on both sides) connecting two larger land areas | isthmus |  | 46 |
| 10479089006 | the monotheistic religion founded by Abraham and whose followers are called Jews | Judaism |  | 47 |
| 10479089007 | The way that the first people may have arrived in the Americas; connected Siberia and Alaska around 40,000 years ago. ________________________________________________________________________ | land bridge |  | 48 |
| 10479089008 | natural features of the earth's surface | landforms |  | 49 |
| 10479089009 | surrounded by land; cut off from the sea | landlocked |  | 50 |
| 10479089010 | The set of imaginary parallel lines that circle the earth parallel to the Equator and measure the distance north and south of the equator in degrees. ________________________________________________________________________ | latitude |  | 51 |
| 10479089011 | distance east or west of the Prime Meridian, measured in degrees | longitude |  | 52 |
| 10479089012 | A society in which the mother is the supreme authority in the family, clan or tribe and children belong to the mother's family or tribe; women have the governing authority. ________________________________________________________________________ | matriarchy | 53 | |
| 10479089013 | relating to or situated in or extending toward the middle | median |  | 54 |
| 10479089014 | a very large urban complex (usually involving several cities and towns) | megalopolis |  | 55 |
| 10479089015 | a person of mixed Spanish and Native American ancestry | mestizo |  | 56 |
| 10479089016 | the transformation of traditional societies into industrial societies | modernization |  | 57 |
| 10479089017 | The term used in Spanish and Portuguese colonies to describe someone of mixed African and European descent ________________________________________________________________________ | mulatto |  | 58 |
| 10479089018 | an independent geopolitical unit of people having a common culture and identity | nation-state |  | 59 |
| 10479089019 | The natural wealth of a country, consisting of land, forests, mineral deposits, water, etc.; natural resources 1) make a country wealth, 2) have a limit 3) are not man-made | natural resources |  | 60 |
| 10479089020 | west; denoting or characteristic of countries of Europe and the Western Hemisphere | occidental |  | 61 |
| 10479089021 | a political system governed by a small group of people | oligarchy |  | 62 |
| 10479089022 | east; denoting or characteristic of the biogeographic region including southern Asia and the Malay Archipelago as far as the Philippines and Borneo and Java. ________________________________________________________________________ | oriental |  | 63 |
| 10479089023 | Disease that occurs over a wide geographic area and affects a very high proportion of the population. ________________________________________________________________________ | pandemic |  | 64 |
| 10479089024 | the super continent where all the continents were once joined | Pangaea |  | 65 |
| 10479089025 | a society in which the father is the supreme authority in the family, clan or tribe and children belong to the fathers family or tribe; men have authority over woman and children. | patriarchy |  | 66 |
| 10479089026 | body of land jutting into a lake or ocean, surrounded on three sides by water | peninsula |  | 67 |
| 10479089027 | a map that shows mountains, hills, plains, rivers, lakes, oceans, etc. | physical map |  | 68 |
| 10479089028 | an extensive area of level and rolling, treeless country, often covered by rich, fertile soil | plains |  | 69 |
| 10479089029 | an estate where cash crops are grown on a large scale (especially in tropical areas) | plantation |  | 70 |
| 10479089030 | a large area of flat land elevated high above sea | plateau |  | 71 |
| 10479089031 | a map showing units such as countries, states, provinces, districts, etc.l each is normally a different color | political map |  | 72 |
| 10479089032 | worshipping or believing in more than one god | polytheistic |  | 73 |
| 10479089033 | number of individuals per unit area | population density |  | 74 |
| 10479089034 | a line that runs north to south through Greenwich England; other meridians are measured from this | prime meridian |  | 75 |
| 10479089035 | the leader of the executive branch of a parliamentary government | prime minister | 76 | |
| 10479089036 | people who are believed to belong to the same genetic stock | race |  | 77 |
| 10479089037 | People who are forced to migrate from their home country and cannot return for fear of persecution because of their race, religion, nationality, membership in a social group, or political opinion ________________________________________________________________________ | refugees |  | 78 |
| 10479089038 | A ritual performed in some cultures at times when a individual changes his status (as from adolescence to adulthood) ________________________________________________________________________ | rite of passage |  | 79 |
| 10479089039 | another name for ceremonies or rites | rituals |  | 80 |
| 10479089040 | of, pertaining to, or characteristic of the country, country life, or country people; of or pertaining to agriculture: rural economy ________________________________________________________________________ | rural |  | 81 |
| 10479089041 | grassland with scattered trees; found in tropical regions of Africa, Australia, and South America | savanna |  | 82 |
| 10479089042 | not spiritual or religious; worldly | secular |  | 83 |
| 10479089043 | not migratory; settled | sedentary |  | 84 |
| 10479089044 | a usually poor town or section of a town consisting mostly of small wooden shacks | shantytown |  | 85 |
| 10479089045 | system in which landowners leased a few acres of land to farm workers in return for a portion of their crops ________________________________________________________________________ | sharecropping |  | 86 |
| 10479089046 | group of people who hold similar positions in society, share similar wealth, and receive similar respect from other members of society ________________________________________________________________________ | social classes |  | 87 |
| 10479089047 | the level of material comfort as measured by the goods, services, and luxuries available to an individual, group, or nation ________________________________________________________________________ | standard of living |  | 88 |
| 10479089048 | farming that provides for the basic needs of the farmer without surpluses for marketing | subsistence farming |  | 89 |
| 10479089049 | a noble title for the ruler of a Muslim country (especially of the former Ottoman Empire) | sultan |  | 90 |
| 10479089050 | a government tax on imports or exports | tariff |  | 91 |
| 10479089051 | a government controlled by religious leaders | theocracy |  | 92 |
| 10479089052 | the business of buying and selling or exchanging items | trade |  | 93 |
| 10479089053 | a stream or river that flows into a larger river | tributary |  | 94 |
| 10479089054 | sameness; monotony; (adj.) uniform: the same all over | uniformity |  | 95 |
| 10479089055 | of, relating to, or located in a city; characteristic of the city or city life | urban |  | 96 |
| 10479089056 | the growth of cities and the migration of people into them | urbanization |  | 97 |
| 10479089057 | the temperature and humidity of a place at a specific time | weather |  | 98 |
| 10479089058 | The adoption of Western culture, government, food, clothing, and religion | Westernization |  | 99 |
| 10479089059 | The Old Stone Age ending in 12,000 B.C.E.; typified by use of crude stone tools and hunting and gathering for subsistence. ________________________________________________________________________ | Paleolithic Age Until~ 12,000 B.C.E |  | 100 |
| 10479089060 | The New Stone Age between 8000 and 5000 B.C.E.; period in which adaptation of sedentary agriculture occurred; domestication of plants and animals accomplished. ________________________________________________________________________ | Neolithic Age ~8,000 B.C.E to 5,000 B.C.E |  | 101 |
| 10479089061 | From about 4000 B.C.E.; when bronze tools were first introduced in the Middle East, to about 1500 B.C.E., when iron began to replace it. ________________________________________________________________________ | Bronze Age ~4,000 B.C.E to 1,500 B.C.E |  | 102 |
| 10479089062 | A level of social organization normally consisting of 20-30 people; nomadic hunters and gatherers; labor divided on a gender basis. ________________________________________________________________________ | Band |  | 103 |
| 10479089063 | Societies distinguished by reliance on sedentary agriculture, ability to produce food surpluses, and existence of non-farming elites, as well as merchant and manufacturing groups. ________________________________________________________________________ | Civilization ~3,200 B.C.E to Current period |  | 104 |
| 10479089064 | A form of writing developed by the Sumerians using a wedge-shaped stylus and clay tablets. ________________________________________________________________________ | Cuneiform 3,500 B.C.E to 100 B.C.E |  | 105 |
| 10479089065 | Cattle- and sheep-herding societies normally founded on the fringes of civilized societies; commonly referred to as "barbarian' by civilized societies. ________________________________________________________________________ | Nomads |  | 106 |
| 10479089066 | Literally "between the rivers"; the civilizations that arose in the alluvial plain of the Tigris and Euphrates river valleys. ________________________________________________________________________ | Mesopotamia ~5000 B.C.E to ~3500 B.C.E |  | 107 |
| 10479089067 | People who migrated in to Mesopotamia c. 4000 B.C.; created first civilization within region; organized area into city-states. ________________________________________________________________________ | Sumerians ~4000 B.C.E to 2200 B.C.E |  | 108 |
| 10479089068 | Massive towers usually associated with Mesopotamian temple complexes. | Ziggurauts |  | 109 |
| 10479089069 | A form of political organization typical of Mesopotamian civilizations; consisted of agricultural hinterlands ruled by an urban-based king. ________________________________________________________________________ | city-state |  | 110 |
| 10479089070 | Unified all of Mesopotamia c. 1800 B.C.E.; collapsed due to foreign invasion c. 1600 B.C.E ________________________________________________________________________ | Babylonian Empire 1792 B.C.E to 539 B.C.E |  | 111 |
| 10479089071 | (r. 1792-1750 B.C.E.) The most important ruler of the Babylonian empire; responsible for codification of the law. ________________________________________________________________________ | Hammurabi 1640 B.C.E to 1750 B.C.E |  | 112 |
| 10479089072 | Monumental architecture typical of Old Kingdom Egypt; used as burial sites for pharaohs. | pyramids |  | 113 |
| 10479089073 | An African state that developed along the upper reaches of the Nile c. 1000 B.C.E; conquered Egypt and ruled it for several centuries. ________________________________________________________________________ | Kush civilization |  | 114 |
| 10479089074 | River sources in Himalayas to mouth in Arabian Sea; location of Harappan civilization. | Indus River Valley ~2600 B.C.E to 1900 B.C.E |  | 115 |
| 10479089075 | Along with Mohenjo daro, major urban complex of the Harappan civilization; laid out on planned grid pattern. ________________________________________________________________________ | Harappa ~2500 B.C.E to ~2000 B.C.E |  | 116 |
| 10479089076 | Also known as the Huanghe; site of development of sedentary agriculture in China. | Yellow River |  | 117 |
| 10479089077 | First Chinese dynasty for which archeological evidence exists; capital located in Ordos bulge of the Huanghe; flourished 1600 to 1046 B.C.E. ________________________________________________________________________ | Shang ~1600 B.C.E to ~1000 B.C.E |  | 118 |
| 10479089078 | Pictographic characters grouped together to create new concepts; typical of Chinese writing. | ideographs |  | 119 |
| 10479089079 | Seafaring civilization located on the shores of the eastern Mediterranean; established colonies throughout the Mediterranean. ________________________________________________________________________ | Phoenicians ~1500 B.C.E to ~300 B.C.E |  | 120 |
| 10479089080 | The exclusive worship of a single god; introduced by the Jews into Western civilization. | monotheism |  | 121 |
| 10479089081 | Founder of the brief Qin dynasty in 221 B.C.E. | Shi Huangdi 259 B.C.E to 210 B.C.E |  | 122 |
| 10479089082 | Established in 221 B.C.E. at the end of the Warring States period following the decline of the Zhou dynasty; fell in 207 B.C.E ________________________________________________________________________ | Qin dynasty 221 B.C.E to 207 B.C.E |  | 123 |
| 10479089083 | Chinese dynasty that succeeded the Qin in 202 B.C.E.; rules for next 400 years. | Han dynasty 206 B.C.E to 220 C.E |  | 124 |
| 10479089084 | Also known as Kung Fuzi; major Chinese philosopher born in 6th century B.C.E. Philosophy based on need for restoration of order through advice of superior men. ________________________________________________________________________ | Confucius 551 B.C.E to 479 B.C.E |  | 125 |
| 10479089085 | Chinese defensive fortification in tended to keep out the nomadic invaders from the north; initiated during Qin dynasty and reign of Qin Shi Huangdi. ________________________________________________________________________ | The Great Wall Built from: 220 B.C.E to 206 B.C.E |  | 126 |
| 10479089086 | Creator of a major Indian and Asian religion; born in 6th century B.C.E. as son of local ruler among Aryan tribes. Found enlightenment;taught enlightenment could be achieved only by abandoning desires for all earthly things. | Buddha |  | 127 |
| 10479089087 | Indo-European nomadic pastoralists who replaced Harappan civilization; militarized society. | Aryans |  | 128 |
| 10479089088 | The sacred and classical Indian language. | Sanskrit Created: ~1500 B.C.E |  | 129 |
| 10479089089 | Aryan hymns originally transmitted orally but written down in sacred books. | Vedas Written: ~1200 B.C.E |  | 130 |
| 10479089090 | Clusters of caste group in Aryan society; four social castes - Brahmans (priests) warriors, merchants, and peasants; beneath four Aryan castes was group of socially untouchable Dasas. ________________________________________________________________________ | Varnas |  | 131 |
| 10479089091 | Low social caste in Hindu culture; performed tasks that were considered polluting - street sweeping, removal of human waste, and tanning ________________________________________________________________________ | untouchables |  | 132 |
| 10479089092 | Dynasty established in Indian subcontinent in 4th century B.C.E. following invasion by Alexander the Great. ________________________________________________________________________ | Mauryan ~320 B.C.E to ~180 B.C.E |  | 133 |
| 10479089093 | Grandson of Chandragupta Maurya; completed conquests of Indian subcontinent; converted to Buddhism and sponsored spread of new religion though his empire. ________________________________________________________________________ | Ashoka 340 B.C.E to 232 B.C.E (r. 273 - 232 B.C.E.) |  | 134 |
| 10479089094 | The caste position and career determined by a person's birth; Hindu culture required that one accept one's social position and perform occupation to the best of one's ability in order to have a better situation in the next life. | Dharma |  | 135 |
| 10479089095 | Dynasty that succeeded the Kushans in the 3rd century B.C.E.; built empire that extended to all but the southern regions of Indian sub-continent; less centralized that Mauryan Empire. ________________________________________________________________________ | Guptas 240 C.E to 590 C.E |  | 136 |
| 10479089096 | Animist religion that saw material existence as battle between forces of good and evil; stressed the importance of moral choice; righteous lived on or after death in "house of Song"; chief religion of Persian Empire. | Zoroastrianism Created: ~600 B.C.E |  | 137 |
| 10479089097 | Athenian political leader during the 5th century B.C.E.; guided development of Athenian empire; died during early stages of Peloponnesian War. ________________________________________________________________________ | Pericles 494 B.C.E to 429 B.C.E |  | 138 |
| 10479089098 | That culture associated with the spread of Greek influence as a result of Macedonian conquests; often seen as the combination of Green culture with eastern political forms. ________________________________________________________________________ | Hellenistic Period ~320 B.C.E to ~30 B.C.E |  | 139 |
| 10479089099 | The balanced constitution of Rome from c. 510 to 47 B.C.E.; featured an aristocratic Senate, a pane of magistrates, and several popular assemblies. ________________________________________________________________________ | Roman republic ~800 B.C.E to ~470C.E |  | 140 |
| 10479089100 | Roman general responsible for conquest of Gaul; brought back to Rome and overthrew republic; assassinated in 44 B.C.E. by conservative senators. ________________________________________________________________________ | Julius Caesar 100 B.C.E to 44 B.C.E |  | 141 |
| 10479089101 | Roman emperor from 312 to 337 C.E.; established second capital at Constantinople; attempted to use religious force of Christianity to unify empire spiritually. ________________________________________________________________________ | Constantine 272 C.E to 337 C.E |  | 142 |
| 10479089102 | Where people participate directly in assemblies that make laws and select leaders, rather than electing representatives. ________________________________________________________________________ | Direct Democracy Created: ~500 B.C.E |  | 143 |
| 10479089103 | Assembly of Roman aristocrats; advised on policy within the republic; one of the early elements of the Roman constitution. ________________________________________________________________________ | Senate |  | 144 |
| 10479089104 | Two chief executives or magistrates of the Roman republic; elected by an annual assembly dominated by aristocracy ________________________________________________________________________ | consuls |  | 145 |
| 10479089105 | (384-322 B.C.E.) Greek philosopher; teacher of Alexander the Great; knowledge based on observation of phenomena in material world. ________________________________________________________________________ | Aristotle 384 B.C.E to 322 B.C.E |  | 146 |
| 10479089106 | Athenian philosopher of later 5th century B.C.E.; tutor of Plato; urged rational reflection of moral decisions; contemned to death of corrupting minds of Athenian young. ________________________________________________________________________ | Socrates 470 B.C.E to 399 B.C.E |  | 147 |
| 10479089107 | Greek epic poem attributed to Homer but possibly he work of many authors; defined gods and human nature that shaped Greek mythos. ________________________________________________________________________ | Iliad |  | 148 |
| 10479089108 | Greek epic poem attributed to Homer but possibly he work of many authors; defined gods and human nature that shaped Greek mythos ________________________________________________________________________ | Odysssey |  | 149 |
| 10479089109 | Kingdom located in Ethiopian highlands; replaced Meroë in 1st century C.E.; received strong influence from Arabian peninsula; eventually converted to Christianity. ________________________________________________________________________ | Axum |  | 150 |
| 10479089110 | A Christian kingdom that developed int eh highlands of eastern Africa under the dynasty of King Lalaibela; retained Christianity in the face of Muslim expansion elsewhere in Africa. ________________________________________________________________________ | Ethiopia ~980 B.C.E to Present |  | 151 |
| 10479089111 | Religion of early Japanese culture; deveotees worshipped numerous gods and spirits associated with the natural world; offers of food and prayers made to gods and nature spirits. ________________________________________________________________________ | Shinto 800 B.C.E to 1945 C.E |  | 152 |
| 10479089112 | Cultural tradition that arose at San Lorenzo and La Venta in Mexico c. 1200 B.C.E.; featured irrigated agriculture, urbanism, elaborate religion, beginnings of calendrical and writing systems. | Olmec culture 1200 B.C.E to 400 B.C.E |  | 153 |
| 10479089113 | Site of classic culture in central Mexico; urban center with important religious functions; supported by intensive agriculture in surrounding regions; population of as much as 200,000. ________________________________________________________________________ | Teotihuacan Built: 100 B.C.E |  | 154 |
| 10479089114 | Classic culture in southern Mexico and Central America contemporary with Teotihuacan; extended over broad region; featured monumental architecture, written language, and highly developed: Math, Calendrical and religion systems. | Maya 1800 B.C.E to 250 C.E |  | 155 |
| 10479089115 | Group of clans centered at Cuzco that were able to create empire incorporating various Andean cultures; term also used for leader of empire. ________________________________________________________________________ | Inca ~1400 C.E to ~1500 C.E |  | 156 |
| 10479089116 | Islands contained in a rough triangle whose points lie inHawaii, New Zealand, and Easter Island. | Polynesia |  | 157 |
| 10479089117 | Chinese Daoists who launched a revolt in 184 C.E. in China promising a golden age to be brought about by divine magic. ________________________________________________________________________ | Yellow Turbans 184 C.E to 205 C.E |  | 158 |
| 10479089118 | Dynasty that succeeded the Han in China; emerged from strong rulers in northern China; united all of northern China and reconquered southern China. ________________________________________________________________________ | Sui (Dynasty) 581 C.E to 610 C.E |  | 159 |
| 10479089119 | Dynasty that succeedd the Sui in 618 C.E.; more stable than previous dynasty. | Tang (Dynasty) 618 C.E to 918 C.E | 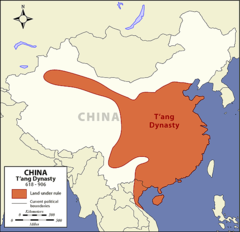 | 160 |
| 10479089120 | Major world religion having its origins in 610 c.e. in the Arabian peninsula; meaning literally submission; based on prophecy of Muhammad. ________________________________________________________________________ | Islam Created: 700 C.E |  | 161 |
| 10479089121 | Eastern half of Roman Empire following collapse of western half of old empire; retained Mediterranean culture, particularly Greek; later lost Palestine, Syria, and Egypt to Islam; capital at Constantinople. | Byzantine Empire 330 C.E to 1453 C.E |  | 162 |
| 10479089122 | Christian sect in Egypt, later tolerated after Islamic takeover. | Coptic Created: 42 C.E |  | 163 |
| 10479089123 | A religious outlook that sees gods in many aspects of nature and propitiates them to help control and explain nature; typical of Mesopotamian religions. ________________________________________________________________________ | animism |  | 164 |
| 10479089124 | Name given to Octavian following his defeat of Mark Anthony and Cleopatra; first emperor of Rome. ________________________________________________________________________ | Augustus Caesar 63 B.C.E. to 14 C.E. |  | 165 |
AP World History - Summer Assignment Terms & Concepts Flashcards
Primary tabs
Need Help?
We hope your visit has been a productive one. If you're having any problems, or would like to give some feedback, we'd love to hear from you.
For general help, questions, and suggestions, try our dedicated support forums.
If you need to contact the Course-Notes.Org web experience team, please use our contact form.
Need Notes?
While we strive to provide the most comprehensive notes for as many high school textbooks as possible, there are certainly going to be some that we miss. Drop us a note and let us know which textbooks you need. Be sure to include which edition of the textbook you are using! If we see enough demand, we'll do whatever we can to get those notes up on the site for you!

