| 2684805255 | Nucleotides | Building blocks of nucleic acids |  | 0 |
| 2684807142 | Base pairing | Principle that bonds in DNA can form only between adenine and thymine and between guanine and cytosine |  | 1 |
| 2684807960 | Phosphate-Deoxyribose | The two molecules that when added to A, T, G, or C make up a nucleotide |  | 2 |
| 2684811941 | Properties of Life | Order, Evolutionary Adaptation, Response to the Environment, Regulation, Energy Processing, Growth and Development, Reproduction. |  | 3 |
| 2684814097 | Example of Order | human genetic makeup, or the structure of DNA |  | 4 |
| 2684816840 | Example of Growth and Development | the cycle of a blowfly (application: forensic science) |  | 5 |
| 2684818751 | Example of Response to Environment | phototropism (stimulus: light, tropism: orientation towards light). also: Venus flytrap closing on a fly (stimulus: touch; response: activating feeding mechanism, or closing) |  | 6 |
| 2684822564 | Example of Regulation or Homeostasis | insulin and blood glucose level maintenance (negative feedback mechanism) |  | 7 |
| 2684826659 | Types of Energy | Kinetic, potential, chemical |  | 8 |
| 2684830957 | Kinetic energy | Energy of motion |  | 9 |
| 2684831827 | Potential energy | Energy stored in matter due to position |  | 10 |
| 2684832589 | Chemical energy | Energy stored in chemical bonds (ATP) |  | 11 |
| 2684833833 | Energy | the capacity to do work |  | 12 |
| 2684835083 | ATP | Adenosine tri-phosphate - the molecule that cells recognize and tap into for energy in the brain, muscles, etc. ATP releases energy for cellular work, such as respiration, reproduction, etc. |  | 13 |
| 2684838446 | Uncharged ATP | An ATP molecule with only 2 phosphates becomes ADP and is not usable for energy. It needs to be recharged with another phosphate. |  | 14 |
| 2684842667 | Two forms of Cellular Reproduction | Asexual & sexual |  | 15 |
| 2684844618 | Asexual Reproduction | Doesn't involve gametes |  | 16 |
| 2684845366 | Sexual Reproduction | Involves gametes |  | 17 |
| 2684846068 | Gametes | Sex cells. Male: sperm. Female: ova. |  | 18 |
| 2684847808 | Asexual reproduction examples | Binary fission (bacteria), mitosis (humans, cats, dogs, plants) |  | 19 |
| 2684849206 | Sexual reproduction examples | Meiosis (occurs in gonads to produce gametes) |  | 20 |
| 2684851157 | Evolutionary Adaptation | natural selection or "survival of the fittest." |  | 21 |
| 2684852235 | Example of evolutionary adaptation | Sickle cell mutation - one gene provides malaria resistance, both genes creates sickle cell anemia. |  | 22 |
| 2684855786 | Natural Selection Premise | Organisms with the desired trait will reproduce more successfully than organisms without the trait. Changes occur in DNA (mutation) to create the desired trait. |  | 23 |
| 2684858836 | Viruses | Viruses are 20x smaller than bacteria; made up of DNA or RNA; made of proteins (non-cellular); reproduce only thru host cell |  | 24 |
| 2684860472 | Bacteria | 20x larger than viruses; made up of DNA; unicellular; asexual reproduction, independent of host |  | 25 |
| 2684882186 | Emergent Properties | novel properties that appear at higher levels of organization due to the interaction of individual components (ex: cake ingredients become batter become cake, and each stage has different properties tho made up of the same things) |  | 26 |
| 2684904547 | Cell | The basic unit of life that retains the properties of life. |  | 27 |
| 2684912379 | How long can viruses survive outside the host? | A few seconds to minutes. |  | 28 |
| 2684915800 | True or False: Many bacteria don't cause infection. | True. |  | 29 |
| 2684919677 | True or False: Both viruses and bacteria can cause infection. | True. |  | 30 |
| 2684923377 | True or False: Antibiotics are effective against viruses. | False. |  | 31 |
| 2684925660 | True or False: Viral infections never go away without treatment. | False. |  | 32 |
| 2684942252 | Emergent Properties of Multicellular Organisms | Cell ---> Tissue ---> Organ ---> Organ System ---> Mollecular Organism |  | 33 |
| 2684948028 | Biosphere | Consists of all life on Earth and all parts of the Earth in which life exists, including land, water, and the atmosphere. |  | 34 |
| 2684958887 | Ecosystem | All the living things in a particular area, along with all the nonliving components of the environment with which life interacts. |  | 35 |
| 2684964447 | Community | The array of organisms inhabiting a particular ecosystem. |  | 36 |
| 2684967024 | Population | All the members of one species in a particular ecosystem. |  | 37 |
| 2684969488 | Organelle | A functional component present in a cell. Organelle is to cell as organ is to organ system. Example: mitochondria |  | 38 |
| 2685001963 | Eukaryote | Cells containing membrane-enclosed organelles | 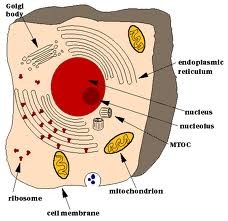 | 39 |
| 2685003560 | Prokaryote | Cells lacking a nucleus or other membrane-enclosed organelles. |  | 40 |
| 2685007485 | Taxonomic Levels of Organization | Domain - Kingdom - Phylum - Class - Order - Family - Genus - Species |  | 41 |
| 2685014599 | Domains | The highest level of classification of living organisms. Eukarya, Archaea, Bacteria |  | 42 |
| 2685015467 | Archaea | The domain that includes prokaryotes that live in Earth's most extreme environments. |  | 43 |
| 2685018647 | Kingdoms | High-level classification of organisms distinguished partly by their modes of nutrition. |  | 44 |
| 2685027122 | Eukarya | The domain that includes Kingdoms Plantae, Animalia, and Fungi. |  | 45 |
| 2685041163 | Bacteria (Domain) | The domain that includes prokaryotes which are the most diverse and widespread of all kingdoms. |  | 46 |
| 2685043430 | Independent Variable | The experimental factor that is manipulated; the variable whose effect is being studied. |  | 47 |
| 2685045489 | Dependent Variable | The outcome factor; the variable that may change in response to manipulations of the independent variable. |  | 48 |
| 2685046672 | Control | The group in an experiment which is used as a standard for comparison. |  | 49 |
| 2685047875 | Constant | A factor in an experiment that does not change. |  | 50 |
| 2685053055 | Feedback Regulation | A process in which the output, or product, of a process regulates the very process itself. |  | 51 |
| 2685055947 | Negative Feedback Mechanism | A loop in which the response reduces the initial stimulus. |  | 52 |
| 2685056959 | Positive Feedback Mechanism | A loop in which the response speeds up its own production. |  | 53 |
| 2685057990 | Null Hypothesis | States that there is no significant difference between specified populations, any observed difference being due to sampling or experimental error. |  | 54 |
| 2685058694 | Metric Conversion Chart | Kilo Hecto Deka (Base Unit m/l/g) Deci Centi Milli Micro Nano Pico |  | 55 |
| 2685080338 | Converting Fahrenheit to Celsius | (F-32) x .556 |  | 56 |
| 2685081634 | Converting Celsius to Fahrenheit | C x 1.8 + 32 |  | 57 |
| 2685086385 | Scientific Method | Prior Knowledge Observations Questions Hypothesis Prediction Experiment Conclusion/Analysis |  | 58 |
| 2685115896 | Classic Experimental Design | Test Population (100 identical rats) Experimental Group (given DDT in food) Controlled Group (no DDT, everything else constant) Independent Variable (under study, manipulated & changing) Dependent Variable (variable that changes based on independent variable) Controlled variables (water, amt. of food, everything not manipulated) |  | 59 |
| 2685123606 | Mean | Average of a group of measurements |  | 60 |
| 2685125967 | Median | The value that is in the middle of a group of measurements. |  | 61 |
| 2685127461 | Range | The difference between the smallest and the largest measurements. R = Max - Min |  | 62 |
| 2685130530 | Deviation | Measures how the measurements vary from the mean (+ or -). In other words, what is the difference between an actual measurement and the mean, or average, of the sample? |  | 63 |
| 2685133631 | Variance | Measures how much difference, or variation, there is between the values you have obtained. The smaller the variance, the closer the values will be to the mean. |  | 64 |
| 2685136017 | Standard Deviation | Standard deviation gives you an idea of how widely spread your values are about the mean. Smaller = closer values to the average. (Picture a tall, thin, bell-shaped curve. Larger - wide bell curve.) |  | 65 |
| 2685143233 | Inductive Reasoning | A type of logic in which generalizations are based on a large number of specific observations. Seeks to reduce uncertainty of claims. "Informal" - looks for probability, not certainty. |  | 66 |
| 2685145789 | Deductive Reasoning | A type of logic in which specific results are predicted from a general premise. Seeks absolute certainty of conclusions. "Formal" - seeks truth and certainty, not probability. |  | 67 |
| 2685153482 | Genes | Discrete units of hereditary information consisting of a special nucleotide sequence in DNA (or RNA, in some viruses) |  | 68 |
| 2685154899 | Gene expression | Process by which a gene produces its product and the product carries out its function. |  | 69 |
| 2685155942 | Genome | A "library" of genetic instructions that an organism inherits. |  | 70 |
| 2685157224 | Genomics | The systematic study of whole sets of genes (or other DNA) and their interactions within a species, as well as genome comparisons between species |  | 71 |
| 2685158409 | Proteomics | The study of sets of proteins and their properties. |  | 72 |
| 2685159582 | Producers | Plants and other photosynthetic organisms. |  | 73 |
| 2685160549 | Consumers | Organisms that feed on producers and other consumers. |  | 74 |
| 2685166531 | Inquiry | The search for information and explanation, often focusing on specific questions. |  | 75 |
| 2695666426 | Cell Theory | 1. The cell is the basic unit of life. 2. All cells arise from pre-existing cells. 3. All organisms are composed of one or more cells. |  | 76 |
| 2695667964 | Classification of organisms on the cellular level | 1. Unicellular: bacteria, some protists such as amoeba, paramecia, etc. 2. Multicellular: humans, trees, etc. 3. Prokaryiotic: bacteria, and blue-green algae only; no nucleus 4. Eukaryotic: animals, plants (multicellular), some protists (unicellular); have a nucleus |  | 77 |
| 2695670688 | 4 Common Cellular Features | 1. Plasma membrane 2. DNA Region 3. Cytoplasm 4. Free Ribosomes |  | 78 |
| 2695673067 | Plasma membrane | Regulates and controls what goes in and out of the cell |  | 79 |
| 2695673547 | DNA Region | DNA is organized into chromosomes; each segment of DNA that codes for a trait is a gene. In a eukaryotic cell, the DNA region is the nucleus. |  | 80 |
| 2695674338 | Cytoplasm | The contents of the cell bounded by the plasma membrane; in eukaryotes, the portion of the cell outside the nucleus. |  | 81 |
| 2695677599 | Free Ribosomes | Organelles that function in protein synthesis. |  | 82 |
| 2695678185 | Whittaker System - 5 Kingdoms | 1. Monera (Bacteria) 2. Protista 3. Fungi 4. Plantae 5. Animalia |  | 83 |
| 2695678862 | Taxonomy | The science of classification and nomenclature (naming) |  | 84 |
| 2695679222 | Ecology | The study of organisms in their physical and chemical environment |  | 85 |
| 2695680926 | Autotroph | Self-feeder |  | 86 |
| 2695681336 | Heterotroph | Other-feeder |  | 87 |
Campbell Biology 10th Edition Chapter 1 Flashcards
Primary tabs
Need Help?
We hope your visit has been a productive one. If you're having any problems, or would like to give some feedback, we'd love to hear from you.
For general help, questions, and suggestions, try our dedicated support forums.
If you need to contact the Course-Notes.Org web experience team, please use our contact form.
Need Notes?
While we strive to provide the most comprehensive notes for as many high school textbooks as possible, there are certainly going to be some that we miss. Drop us a note and let us know which textbooks you need. Be sure to include which edition of the textbook you are using! If we see enough demand, we'll do whatever we can to get those notes up on the site for you!

