PART 2
This covers:
-The Cell Cycle and Cell Division[CH.18,19]
-Cell Defense and Cell Death
-Stem Cells and Cancer Cells [20]
-Evolution of Cells [CH.1, 7, 14, 15]
flash cards for the 4rd test in Cell Biology, Dr. Bill Campbell's class at LA Tech.
[complete collection of flash cards]
| 1928969066 | CELL CYCLE: The life of a cell is called the ___ _____. | cell cycle |  | 0 |
| 1928969095 | Eukaryotic cell division is generally more complex than prokaryotic division for 3 reasons: - Organelles - more ________ - larger genome | chromosomes | 1 | |
| 1928969067 | How do prokaryotes divide? -By binary _______. | fission |  | 2 |
| 1928969096 | Does fission happen in Eukaryotic cells? YES. The ________ (organelle, animals) and _______ (organelle, plants) divide this way. | mitochondria, chloroplast | 3 | |
| 1928969097 | Cell cycle has 2 phases: ______ phase and __ phase. | growth, M | 4 | |
| 1928969068 | Growth phase is also called __________. | Interphase |  | 5 |
| 1928969098 | Growth phase consists of: - __1 - __ - __2 | G, S, G | 6 | |
| 1928969099 | Growth phase involves - DNA replication (___ phase) - membrane synthesis - distribution of cell contents - protein synthesis | S | 7 | |
| 1928969100 | In both G1 and G2 there is cell growth (G= Growth) but it is in ___ of interphase (growth phase) the new daughter cells begin and increases cytoplasmic contents. | G1 | 8 | |
| 1928969101 | In ___ of interphase (growth phase) there is preparation for division. | G2 | 9 | |
| 1928969102 | In 3 of the 4 stages (G1, M, G2, S) there is a check point except in what stage? | S | 10 | |
| 1928969103 | _____ and ___ ____ _____ (cdKs) regulate the cell cycle. | cyclins, cyclin dependent kinases | 11 | |
| 1928969104 | _____ bind to cyclin dependent kinases (cdKs) to activate them. | Cyclins | 12 | |
| 1928969069 | M phase or division phases involve - ______ division - ________ (cytoplasm division) | nuclear, cytokinesis |  | 13 |
| 1928969105 | Although this phase involves cytokinesis.. cytokinesis is NOT part of __ phase. | M | 14 | |
| 1928969106 | M phase has 2 kinds (for different kinds of cells: germ&somatic). These are called _______ (germ) and _______. | Meiosis, Mitosis | 15 | |
| 1928969107 | Mitosis (or meiosis) is NOT cell division. Only the ______ has divided. | nucleous | 16 | |
| 1928969108 | There are 5 steps in m phase: | prophase prometaphase metaphase anaphase telophase | 17 | |
| 1928969070 | the nuclear envelope breaks down during _________. | prometaphase |  | 18 |
| 1928969071 | Paired chromotids separtate and move to opposite poles during ________. | anaphase |  | 19 |
| 1928969072 | the nuclear envelope reforms during _________. | telophase |  | 20 |
| 1928969109 | cytokinesis in animal cells involves a ______ _______ and a _____ ____ made up of actin and myosin. | cleavage farrow, contractile ring | 21 | |
| 1928969110 | Cells with cell walls (plants) do not undergo cytokinesis with a cleavage furrow. instead they form a new ___ ___ between the two daughter cells. | cell wall | 22 | |
| 1928969111 | In plant cytokineses: At the beginning of telophase a specialized structure call a __________ forms to create a new cell wall. | phragmoplast | 23 | |
| 1928969112 | cytokinesis is different in animal cells than plant cells. Plant cells form a structure called a _________ where the new cell wall will divide the new cells. | phragmoplast | 24 | |
| 1928969113 | With a cell wall is it difficult for a plant cell to expand and grow. How is this accomplished? Acid Growth Hypothesis: - H+ is pumped _____(in/out) of the cell - water pressure causes cell to expand. | into | 25 | |
| 1928969073 | mitosis results in ___ daughter cells while meiosis results in ___ daughter cells. | 2, 4 | 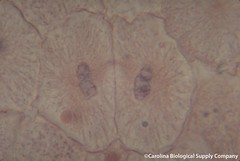 | 26 |
| 1928969114 | mitosis results in daughter cells called ______ cells while meiosis results in daughter cells called _______. | somatic, gamates | 27 | |
| 1928969115 | Which is --false-- regarding Gamates: (a) are sex cells (b) are also called germ cells (c) are haploid (d) are dividing cells | d | 28 | |
| 1928969116 | Eukaryotic cell cycle times vary fro 30 minutes to one full year Tue/Flase | TRUE | 29 | |
| 1928969117 | CELL DEFENSE: Pathogens may involve invading and feeding on a cell however pathogens will ________ (always/ not always) kill the cell. | not always | 30 | |
| 1928969074 | What are some physical mechanisms of defense for plant cells{3}? ___ ____, ________, ___ ____ | cell wall, cuticles, leaf hairs |  | 31 |
| 1928969118 | What are 2 chemical mechanisms of defense for plant cells? chemical __________ _________ _________ (many plant cells die in the area) | secretions, hypersensitive response | 32 | |
| 1928969075 | During the hyper sensitive response cells in an area accumulate ____ and the cells die. This results in dark, dead, spots on leaves. This is a form of plant apoptosis. | toxins |  | 33 |
| 1928969076 | The adaptive and innate immune responses both serve important purposes. One major different difference involving the innate immune repose is that it is present at ___ times in the organisms life. | ALL |  | 34 |
| 1928969119 | Antibodies are part of the ______ immune response. | adaptive | 35 | |
| 1928969120 | Antigens on the surface of pathogens prompt __ cells to produce _______. | B, antibodies | 36 | |
| 1928969121 | an antibody can bind up to ____ antigens. | 2 | 37 | |
| 1928969077 | Antibody structure: 2 identical ____ chains and 2 identical ____ chains | heavy, light |  | 38 |
| 1928969122 | CELL DEATH: What are 2 types of cell death? _____ and ______ | necrosis, apoptosis | 39 | |
| 1928969123 | _____ is death due from damage or injury (a) necrosis (b) apoptosis | a | 40 | |
| 1928969124 | Necrosis affects __ while apoptosis affects __ (a) groups of cells (b) one cell/individual cells | a,b | 41 | |
| 1928969078 | cells swell and burst/ruptures the plasma membrane in ______. | necrosis |  | 42 |
| 1928969125 | _______ (enzymes) initiate apoptosis. | caspases | 43 | |
| 1928969079 | What types of cells does apoptosis affect? cells that: -are generated in ______ -develop _________ -have _______ their function | excess, improperly, completed |  | 44 |
| 1928969080 | apoptosis in plants is involved in the formation of the ______ and _____. | xylem; phloem |  | 45 |
| 1928969126 | STEM CELLS: There are two types of stem cells? _____ stem cells (ESCs) and _____ stem cells | embryonic and adult | 46 | |
| 1928969127 | cells differentiate due to differences in _____ ________. | gene expression | 47 | |
| 1928969128 | Stem cells are like regular body cells not they are not _________. | differentiated | 48 | |
| 1928969129 | When stem cells divide BOTH (2) daughter cells will: (a) become stem cells as well (b) become another kind of cell other than a stem cell (c) become less able to give rise to other cells (totipotent will have pluripotent daughter cells; pluripotent will have multipotent daughter cells) (d) have the potential to differentiate or become stem cells together or separately. They do not both have to become the same cell type but they can. | d | 49 | |
| 1928969130 | embryonic stem cells are _______ and adult stem cells are ______. | pluripotent, multipotent | 50 | |
| 1928969131 | Adult stem cells include the lining of ______ and _____ stem cells (HSCs). | intestines, hemopoetic | 51 | |
| 1928969132 | HSCs give rise to ____ blood cell types. | all | 52 | |
| 1928969133 | damage to HSCs can be treated with ____ _______ transplant. | bone marrow | 53 | |
| 1928969081 | plant stem cells: In plants, the only sites of division are meristems. These include 3 sites: _____ apicle, _____apicle, ____ ____ | shoot, root, axillary bud |  | 54 |
| 1928969082 | CANCER CELLS: What 2 properties define a cancer cell? - reproduce without _________ - invade and ______ places normally reserved for other cells | restraints, colonize |  | 55 |
| 1928969134 | What traits make a cell capable of cancerous growth? - _______ signals regulating division - avoids ________ - ________ unstable - _________ (relocates and grows) | disregards, apoptosis, genetically, metastasizes | 56 | |
| 1928969083 | A tumor is a _______. which is a mass of abnormal cells. | neoplasm |  | 57 |
| 1928969084 | Define benign: Benign is when the growth is ________. The cells are not relocating but there is abnormal growth in the area. | localized |  | 58 |
| 1928969085 | Define malignant: malignant is when the growth is abnormal and the cells are ________ surrounding tissues. | invading |  | 59 |
| 1928969135 | ____-________ a normal gene that has the potential to become a cancer causing gene. | proto oncogenes | 60 | |
| 1928969136 | _________ is a cancer causing gene. | oncogenes | 61 | |
| 1928969137 | ______ _________ _____ inhibits progress throughout cell cycle, loss of gene causes cell to divide unregulated, recessive mutation is loss of function | tumor supressor genes | 62 | |
| 1928969138 | EVOLUTION OF CELLS: All life forms are composed of ____. | cells | 63 | |
| 1928969139 | Properties emerge at the ____ level. | cell | 64 | |
| 1928969140 | How cells evolved is not known with certainty but the major focus on how cells evolved is on the evolution of ______ information. | genetic | 65 | |
| 1928969086 | Our universe is about 13.7 billion years old (byo) Our Earth is about 4.6 byo. The 1st cell we believe appeared about ___ billion years ago. | 3.6 |  | 66 |
| 1928969141 | The 1st cell(s) were thought to have been __________ (prokaryotic/eukayrotic) and _________ (heterotrophic/autotrophic). | prokaryotic, heterotrophic | 67 | |
| 1928969142 | ____ is thought to have evolved before DNA. Living systems likely began with ______ ___ molecules. | RNA, catalyic RNA | 68 | |
| 1928969143 | Why would we think RNA evolved before DNA? DNA cannot self replicate while RNA can. RNA can also direct ______ synthesis. | protein | 69 | |
| 1928969144 | Ribozymes = RNA molecules that can catalize reactions. - (Are/are not) proteins - (Are/are not) enzymes | are not, are | 70 | |
| 1928969145 | If RNA has advantages like self-replication. What are the advantages that lead to the DNA based systems? - DNA is more stable because it is a _______ ______ molecule. - Unlike RNA, DNA has _____ systems | double stranded, repair | 71 | |
| 1928969146 | The 1st cells were prokaryotic. How did they get organelles?: ----------------------------------------- [nucleus] The nuclear membrane and the __ membrane may have evolved from the invagination of the _____ membrane. | ER, plasma | 72 | |
| 1928969147 | Once cells gamed a nucleus they became __________ cells. | Eukaryotic | 73 | |
| 1928969148 | The 1st cells were prokaryotic. How did they get organelles?: ----------------------------------------- [mitochondria/chloroplast] A ________ cell may have been engulfed by a Eukaryotic cell. This is called ____________. | Prokaryotic, endosymbiosis. | 74 | |
| 1928969149 | mitochondria are thought to have come from a _________ Prokaryote that was engulfed by a Eukaryotic cell. | aerobic | 75 | |
| 1928969087 | chloroplast are thought to have come from a _________ Prokaryote that was engulfed by a Eukaryotic cell. | Photosynthetic |  | 76 |
| 1928969150 | Evidence that mitochondria/chloroplast come from endosymbiosis: - _________ membrane - divide by _________ (like bacteria) - _______ similar to those in bacteria - have their own _______ (smaller than nuclear) | double, fission, ribosomes, genome | 77 | |
| 1928969088 | Why would the 1st cells be heterotrophic instead of autotrophic?: At the time of the earliest cells, levels of CO2 were ___ (high low). Photosynthetic autotrophs, such as plants today, use CO2 in the process to create their own energy. (as a carbon source) ________ processes of heterotrophs release CO2. | low, Anearobic |  | 78 |
| 1928969089 | Anearobic heterotrophs released ____ (gas) into the atmosphere while Photosynthetic autotrophs begane to release ___ (gas) into the atmosphere. | CO2, O2 |  | 79 |
| 1928969151 | Surprisingly the 1st natural disaster to the atmosphere involved the accumulation of ____ (gas). | O2 | 80 | |
| 1928969152 | Why is oxygen in the atmosphere bad for Earths early life?: O2 can be toxic to _________ cells. | anaerobic | 81 | |
| 1928969153 | atmosphere gaining O2 caused: - New _______ systems - Formation of atmospheric ____ - oxygen toxicity problems for life on Earth | Metabolic, ozone | 82 | |
| 1928969154 | New Metabolic systems improved life on Earth because life forms that use ______ respiration can create much more energy for themselves. | aerobic | 83 | |
| 1928969090 | atmospheric Ozone was a good thing for life on earth because it protects from __ _______. | UV radiation |  | 84 |
| 1928969091 | Atmospheric ozone = 'good' Ground level ozone = 'bad' Ozone above ground level protects us from __ radiation. Ozone at ground level causes damage to cells. | UV | 85 | |
| 1928969092 | Ozone (O3) can be reduced to highly reactive forms called ______ _____ ______(ROs). | reactive oxygen species |  | 86 |
| 1928969093 | Atmospheric ozone = 'good' Ground level ozone = 'bad' How are cars/pollution involved?: Pollution in the air (in the presence of sunlight) turns into _____ (at ground level; where the pollution is). Ozone turns into ______ _____ ______(ROs) which cause damage to cells. | Ozone, reactive oxygen species |  | 87 |
| 1928969155 | reactive oxygen species (ROS) can harm life by causing damage to 3 biological molecules: - _____, _____, and ___ | Lipids, proteins, DNA | 88 | |
| 1928969094 | How do biological organisms combat reactive oxygen species (ROS) and live in an environment with potentially dangerous oxygen? _______ defense mechanisms. | Antioxidant |  | 89 |
| 1928969156 | Some Antioxidants include: Vitamin __ and enzymes like _____ | C, catalase | 90 |

