| 2984480803 | ATP* (3.2) | (adenosine triphosphate) main energy source that cells use for most of their work |  | 0 |
| 2984480804 | active transport* (3.3) | Energy-requiring process that moves material across a cell membrane against a concentration difference |  | 1 |
| 2984480805 | bilayer | two layers |  | 2 |
| 2984480806 | cell membrane* | A cell structure that controls which substances can enter or leave the cell. |  | 3 |
| 2984480808 | cell wall* (3.2) | A rigid structure that surrounds the cell membrane and provides support to the cell |  | 4 |
| 2984480809 | chlorophyll | A green pigment found in the chloroplasts of plants, algae, and some bacteria |  | 5 |
| 2984480810 | chloroplast* (3.2) | An organelle found in plant and algae cells where photosynthesis occurs |  | 6 |
| 2984480811 | cilia | The hairlike projections on the outside of cells that move in a wavelike manner |  | 7 |
| 2984480812 | cytoplasm (3.1) | Gel-like fluid where the organelles are found |  | 8 |
| 2984480813 | cytoskeleton (3.2) | A network of fibers that holds the cell together, helps the cell to keep its shape, and aids in movement |  | 9 |
| 2984480814 | nucleus* (3.1) | A part of the cell containing DNA and RNA and responsible for growth and reproduction |  | 10 |
| 2984480815 | osmosis | Diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane |  | 11 |
| 2984480816 | differentiation | Process in which cells become specialized in structure and function |  | 12 |
| 2984480817 | diffusion (3.3) | Movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. |  | 13 |
| 2984480818 | phospholipid bilayer* | Plasma membrane layers composed of phospholipid molecules arranged with polar heads facing the outside and nonpolar tails facing the inside. | 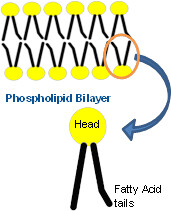 | 14 |
| 2984480819 | endocytosis (3.3) | Active transport process where a cell engulfs materials with a portion of the cell's plasma membrane and releases the contents inside of the cell. |  | 15 |
| 2984480820 | endoplasmic reticulum (smooth and rough) (3.2) | The organelle that transports proteins around the cell. |  | 16 |
| 2984480821 | hydrophilic | Water loving |  | 17 |
| 2984480822 | endosymbiosis / endosymbiotic theory (3.2) | A process in which a unicellular organism (the "host") engulfs another cell, which lives within the host cell and ultimately becomes an organelle in the host cell; also refers to the hypothesis that mitochondria and plastids were formerly small prokaryotes that began living within larger cells. |  | 18 |
| 2984480823 | equilibrium | A condition in which a system is experiencing no net change |  | 19 |
| 2984480824 | eukaryote* (3.1) | A cell that contains a nucleus and membrane bound organelles |  | 20 |
| 2984480826 | exocytosis (3.3) | a process by which the contents of a cell vacuole are released to the exterior through fusion of the vacuole membrane with the cell membrane. |  | 21 |
| 2984480827 | facilitated diffusion (3.3) | A process in which substances are transported across a plasma membrane with the concentration gradient with the aid of carrier (transport) proteins; does not require the use of energy. |  | 22 |
| 2984480828 | flagellum | A long, whiplike structure that helps a cell to move |  | 23 |
| 2984480830 | Golgi body | The organelle that packages proteins before they leave the cell. |  | 24 |
| 2984480831 | Homeostasis | Cells and systems maintain a constant internal balance |  | 25 |
| 2984480832 | Hydrophobic | Water fearing |  | 26 |
| 2984480834 | hypertonic solution | When comparing two solutions, the solution with the greater concentration of solutes |  | 27 |
| 2984480835 | hypotonic | In comparing two solutions, referring to the one with a lower solute concentration. |  | 28 |
| 2984480836 | lysosome | In an ANIMAL CELL. Contain chemicals that break down certain materials. Breaks down dead cells. |  | 29 |
| 2984480837 | isotonic | Describes a solution whose solute concentration is equal to the solute concentration inside a cell |  | 30 |
| 2984480838 | fluid mosaic model | The currently accepted model of cell membrane structure, which envisions the membrane as a mosaic of individually inserted protein molecules drifting laterally in a fluid bilayer of phospholipids. |  | 31 |
| 2984480839 | unicellular | One cell |  | 32 |
| 2984480840 | macromolecule | A type of giant molecule formed by joining smaller molecules which includes proteins, polysaccharides, lipids, and nucleic acids. |  | 33 |
| 2984480841 | mitochondrion (singular)* (3.2) mitochonria (plural) | A membrane‐bound organelle found in most eukaryotic cells; site of cellular respiration. |  | 34 |
| 2984480842 | multicellular | Many cells |  | 35 |
| 2984480843 | nucleolus | Found inside the nucleus and produces ribosomes |  | 36 |
| 2984480844 | organelle* (3.1) | Small structures within cells that perform specific functions (ex. mitochondria, nucleus, ER). |  | 37 |
| 2984480845 | osmosis (3.3) | Diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane |  | 38 |
| 2984480846 | passive transport* (3.3) | Requires NO energy, Movement of molecules from high to low concentration, Moves with the concentration gradient |  | 39 |
| 2984480847 | phospholipid bilayer (3.2) | structure of the cell membrane |  | 40 |
| 2984480848 | plasmolysis | the contraction or shrinking of the cell membrane of a plant cell in a hypertonic solution in response to the loss of water by osmosis |  | 41 |
| 2984480849 | plasma membrane (3.1) | A selectively-permeable phospholipid bilayer forming the boundary of the cells |  | 42 |
| 2984480850 | prokaryote* (3.1) | Unicellular organism that lacks a nucleus |  | 43 |
| 2984480851 | pseudopod | false foot which amoebas use to move |  | 44 |
| 2984480852 | ribosome* (3.1) | Make protein |  | 45 |
| 2984480853 | semi-permeable | characteristic of a cell membrane which allows some molecules to pass through but not others |  | 46 |
| 2984480854 | simple diffusion | Net movement of dissolved particles from higher concentration to a region of lower concentration |  | 47 |
| 2984480855 | sodium-potassium pump (3.3) | a carrier protein that uses ATP to actively transport sodium ions out of a cell and potassium ions into the cell. |  | 48 |
| 2984480856 | solution | A homogeneous mixture of two or more substances |  | 49 |
| 2984480857 | solute | Substance being dissolved |  | 50 |
| 2984480858 | solvent | In a solution, the substance in which the solute dissolves. |  | 51 |
| 2984480859 | transport protein (3.3) | A membrane protein that is responsible for moving hydrophilic substances from one side to the other. |  | 52 |
| 2984480860 | turgor pressure | water pressure inside a plant cell's central vacuole |  | 53 |
| 2984480861 | vacuole (3.2) | Cell organelle that stores materials such as water, salts, proteins, and carbohydrates |  | 54 |
| 2984480862 | vesicle (3.2) | Small membrane-bound sac that functions in moving products into, out of, and within a cell. |  | 55 |
| 2984480863 | virus (3.1) | A tiny, nonliving particle that invades and then reproduces inside a living cell. |  | 56 |
| 2984503580 | ameoba | protist that moves and feeds with the help of pseudopods |  | 57 |
| 2984521587 | hydrophobic | Water fearing |  | 58 |
| 2984526072 | Modern Cell Theory* | All organisms are composed of cells, the cell is the simplest of all units of life, only come from preexisting cells and all cell species have many fundamental similarities in chemical composition and metabolic mechanisms | 59 | |
| 2984526073 | Leeuwenhoek | A Dutch merchant, who in the late 1600s made the first simple microscope and observed microscopic life (protozoa). |  | 60 |
| 2984528106 | Compound Microscope | Magnifies the image using two lenses at once |  | 61 |
| 2986350964 | organelles | A membrane-enclosed structure with a specialized function within a cell. |  | 62 |
| 2986350965 | selective permeability* | a process in which a membrane allows some molecules to pass through while keeping others out. |  | 63 |
| 2986364680 | chloro- | green |  | 64 |
| 2986364681 | cyto- | cell (prefix) cell; cytoplasm |  | 65 |
| 2986366003 | pro- | before |  | 66 |
| 2986366004 | eu- | true |  | 67 |
| 2986395789 | hypo- | Under, below | 68 | |
| 2986395790 | hyper- | over | 69 | |
| 2986395791 | iso- | equal |  | 70 |
| 2986392200 | hypo- | below |  | 71 |
| 2988146405 | bi- | two, double |  | 72 |
| 2988150637 | -tonic | Strength,concentration |  | 73 |
| 2999005280 | -philic | loving |  | 74 |
| 2999008454 | -phobic | fearing |  | 75 |
| 3010448009 | eukaryotic cell (3.1) | A type of cell with a membrane-enclosed nucleus and membrane-enclosed organelles. Examples of organisms with these cells are protists, plants, fungi, and animals. |  | 76 |
| 3010477346 | prokaryotic cell (3.1) | A type of cell lacking a membrane-enclosed nucleus and membrane-enclosed organelles. Organisms with prokaryotic cells (bacteria and archaea) are called prokaryotes. |  | 77 |
| 3010499344 | central vacuole (3.2) | large "holding container" in plant cells for water; helps maintain turgor pressure in plants. |  | 78 |
| 3010561252 | vesicle transport (3.3) | type of active transport in which substances are carried across the cell membrane by vesicles |  | 79 |
Cells Flashcards
Primary tabs
Need Help?
We hope your visit has been a productive one. If you're having any problems, or would like to give some feedback, we'd love to hear from you.
For general help, questions, and suggestions, try our dedicated support forums.
If you need to contact the Course-Notes.Org web experience team, please use our contact form.
Need Notes?
While we strive to provide the most comprehensive notes for as many high school textbooks as possible, there are certainly going to be some that we miss. Drop us a note and let us know which textbooks you need. Be sure to include which edition of the textbook you are using! If we see enough demand, we'll do whatever we can to get those notes up on the site for you!

