| 5970602395 | Middle Adulthood (40s to 60s) | Generativity vs. stagnation | 0 | |
| 5970667926 | Stagnation | Refers to the failure to find a way to contribute. These individuals may feel disconnected or uninvolved with their community and with society as a whole. Ex: An old man is all alone and has nothing to do but be by himself. | 1 | |
| 5970588458 | Preschool | (3-6yrs) Initiative vs Guilt |  | 2 |
| 5970604813 | Identity | Teens try different things out in order to find out who they are. Ex: May act one way at home but with friends they are a different person. |  | 3 |
| 5970671941 | Guilt | Feeling that you have done wrong ex) A child stealing a toy but later feeling guilty about it. |  | 4 |
| 5970596742 | Formal Operational (Stage 4) | Description: Abstract Reasoning Development: Abstract Thinking (Ages 12 and up) Example: A kid during this stage would laugh at a joke that requires abstract thinking. |  | 5 |
| 5970603852 | Sensorimotor (Birth to 2) | Using five senses: touch, tasting. Developments: Stranger trust and object permanence. Example: Little ones playing peek-a-boo see how things disappear and appear again. |  | 6 |
| 5970675144 | Role Confusion | When a teen feels that they have not found their purpose in life. Ex: Alexander Crisostomo is starting to apply to colleges but he doesn't know what his major is going to be. He hasn't figured out his future yet. |  | 7 |
| 5970669232 | Postconventional morality | third level of Kohlberg's stages of moral development in which the person's behavior is governed by moral principles that have been decided on by the individual and which may be in disagreement with accepted social norms |  | 8 |
| 5970629471 | Generativity | Refers to "making your mark". It is an extension of love into the future and being less selfish. Ex: Person is starting to think of starting a family, raising children, being productive at work, etc. | 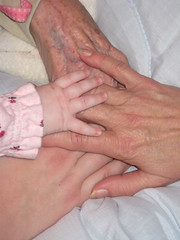 | 9 |
| 5970623950 | Initiative | Initiate independent things ex) A toddler learning to drink from a sippy cup. |  | 10 |
| 5970596405 | Adolescence | Identity vs. Role Confusion |  | 11 |
| 5970619972 | Preconventional morality | First level of Kohlberg's theory of moral reasoning in which control is external and rules are obeyed in order to gain rewards or avoid punishment or out of self-interest. |  | 12 |
| 5970630227 | Inferiority | is the conscious or unconscious feeling that one is not as good as others. EX: The student might feel insecure if everyone in the class gets proficient scores and he does not. |  | 13 |
| 5970628690 | Shame and doubt | When a child doubts their ability. Ex:When a child has the need to use the restroom, but chooses to shy away because he/she is embarrassed. |  | 14 |
| 5970618175 | Intimacy | Intimacy: is the experience of emotional closeness. It occurs when two people are able to be emotionally open with one another, and reveal their true feelings, thoughts, fears and desires. Ex. Being able to be open to a partner in a relationship without any struggle. |  | 15 |
| 5970627180 | Young Adult (20s to early 40s) | Intimacy vs. Isolation | 16 | |
| 5970645615 | Industry | Children learn the pleasure of applying themselves to tasks. Ex. Children become mindful of the tasks that they do and learn the meaning of doing them. |  | 17 |
| 5970644718 | Isolation | Young adults struggle to form close relationships and failure to do so makes them feel isolated (alone). Ex: Having many friends but none which remembered your birthday. |  | 18 |
| 5970630916 | Elementary School | Industry Vs. Inferiority |  | 19 |
| 5970666606 | Despair | The complete loss or absence of hope during the end of your life. |  | 20 |
| 5970658196 | Trust | an issue in the infancy stage Ex. When a one year old, doesn't cry when the mother carries him/her. |  | 21 |
| 5970633783 | Mistrust | The child expresses mistrust to people who they don't interact with everyday. Ex. Johnny cried when I passed him to my husband who's been away for months in the military. | 22 | |
| 5970602606 | Concrete Operational (Piaget's 3rd Stage) | in Piaget's theory, the stage of cognitive development (from about 6 or 7 to 11 years of age) during which children gain the mental operations that enable them to think logically about concrete events. Ex: Children now understand mass and volume |  | 23 |
| 5970665407 | Autonomy | Toddler learns to exercise their will and do things for themselves Ex. I can tie my shoe. |  | 24 |
| 5970661433 | Integrity | The quality of being honest and having strong moral principles; moral uprightness. |  | 25 |
| 5970714260 | Preoperational (2 to 6 or 7 years) | Images, Drawings, and Coloring used as a way of Communication. *Egocentric *Pretend Play Ex: Toddlers learning their alphabet with shapes and songs |  | 26 |
| 5970716607 | Late Adulthood (Late 60's and up) | Integrity vs. Despair |  | 27 |
| 5970651524 | Toddlerhood | Autonomy vs. shame and doubt |  | 28 |
| 5970762852 | Conventional Morality (Early Adolescence) | morality that focuses on caring for other people and upholding laws and social rules Ex. Becoming a cop and following the laws rules |  | 29 |
| 5989403300 | Midlife Transition | Entering their forties people go through a crisis, a time of great struggle, regret, or even feeling struck down by life. Ex: An early-forties man who forsakes his family for a younger girlfriend and a hot sports car. |  | 30 |
| 5989421222 | Divorce | Most common among those in their twenties, suicide among those in their seventies and eighties. |  | 31 |
| 5989385288 | Fetus | an unborn offspring of a mammal, in particular an unborn human baby more than eight weeks after conception. |  | 32 |
| 5989385787 | Teratogens | an agent or factor that causes malformation of an embryo. |  | 33 |
| 5989387170 | Imprinting | when animals form attachments in their early life |  | 34 |
| 5989394046 | Puberty | Developmental stage at which a person becomes capable of reproduction. |  | 35 |
| 5989424977 | menopause | Cessation of menstrual periods owing to a lack of ovarian hormones |  | 36 |
| 5989419778 | Chance Events | lasting significance because they often deflect us down one road rather than another. Example: "winning the lottery was a happy accident" | 37 | |
| 5989412572 | Secondary sex characteristics | a sex-differentiating characteristic that doesn't relate directly to reproduction, such as breast enlargement in women and deepening voices in men |  | 38 |
| 5989397265 | Primary sex characteristics | the body structures (ovaries, testes, and external genitalia) that make sexual reproduction possible |  | 39 |
| 5989387035 | Fetal Alcohol Syndrome (FAS) | physical and cognitive abnormalities in children caused by a pregnant woman's heavy drinking |  | 40 |
| 5989431610 | Prenatal Development | The process of growth and development within the womb, in which a single-cell zygote (the cell formed by the combination of a sperm and an egg) becomes an embryo, a fetus, and then a baby. |  | 41 |
| 5989423166 | Cohort Sequential | A research method in which a cross-section of the population is chosen and then each cohort is followed for a short period of time. Much less susceptible to bias, therefore yields more accurate data than a cross sectional study. | 42 | |
| 5989399270 | Formal Operational | Ages 12- Adulthood Abstract reasoning -Abstract logic -Potential for mature moral reasoning |  | 43 |
| 5989405592 | Object Permanence | The awareness that things still exist even when they are not perceived. Ex: if you place a toy under a blanket, the child who has achieved object permanence knows it is there. |  | 44 |
| 5989414366 | Rooting | Neonates response of turning his or her head when touched | 45 | |
| 5989411671 | Neonates | a newborn child or mammal (less then 4 weeks old) |  | 46 |
| 5989384904 | Developmental psychology | examines how people are continually developing- physically, cognitively, and socially- from infancy through old age. |  | 47 |
| 5989389803 | Sensorimotor Stage | The first Piaget stage, its when Infants use the there five senses in order to learn. Ex: hearing, looking, touching, mouthing, gasping |  | 48 |
| 5989416671 | Cognition | all the mental activities associated with thinking, knowing, remembering, and communicating. |  | 49 |
| 5989408597 | Self-concept | understanding who we are our thoughts and feelings define your "self" |  | 50 |
| 5989430162 | Adolescence | transition period from childhood to adulthood puberty to independence |  | 51 |
| 5989392246 | Social Clock | aka "The right time" for marriage, parenthood, and retirement. It is different from culture to culture. |  | 52 |
| 5989392247 | Emerging Adulthood | 53 | ||
| 5989409133 | Maturation | Biology growth processes that enable orderly changes in behavior, relatively uninfluenced by experience. |  | 54 |
| 5989388639 | Concrete Operational | Ages 7-11 Thinking logically about concrete event; grasping concrete analogies and preforming arithmetical operations. -Conservation -Mathematical Transformations |  | 55 |
| 5989436952 | continuity versus discontinuity | question whether development is gradual, or sequence of distinct stages |  | 56 |
| 5989441845 | Longitudinal | study that follows the same group of people over a period of time |  | 57 |
| 5989392747 | Primary Sex Characteristics | Men and women both have have hair on our heads, our face, etc. However, primary sex characteristics are body structures that are specific to sex. Females have ovaries whereas men have testes. ex: Sex | 58 | |
| 5989390766 | Schemas | concepts or mental molds into we we pour our experiences ex. By adulthood we have built countless schemas, such as cats and dogs to our concept of love. |  | 59 |
| 5989387502 | Pre-Operational | Age Range : 2 - 6 or 7 years old. Description: Representing things with words and images; using intuitive rather than logical reasoning. Developmental Phenomena: Pretend Play and Egocentrism. |  | 60 |
| 5989424338 | Stability Versus Change | issue of whether or not personality traits present during infancy endure through the life span. |  | 61 |
| 5989388809 | Puberty | when a child's body begins to develop and change as they become an adult. Girls develop breasts and start their periods, and boys develop a deeper voice and start to look like men. ex: jimmy started getting a beard at 16 |  | 62 |
| 5989407482 | Animism | The belief that objects have feelings, thoughts, and have the mental characteristics and qualities of living things. Example: Children caring for their toys such as hugging them, putting them clothes, fear if they are left outside in the cold, etc. | 63 | |
| 5989414505 | Stranger Anxiety | fear of unfamiliar people. Happens around 8 months old. |  | 64 |
| 5989413622 | menarche | Is the first menstrual cycle, or first menstrual bleeding, in female humans. From both social and medical perspectives, it is often considered the central event of female puberty, as it signals the possibility of fertility. Ex: Yoda one |  | 65 |
| 5989393348 | Authoritarian | Strict parents. They want their child to follow exactly as they say. |  | 66 |
| 5989401553 | assimilation | new experiences we interpret them in terms of our understanding ex. For cow, a toddler may call it a four-legged animal. |  | 67 |
| 5989409282 | Gender | The state of being male or female |  | 68 |
| 5989394129 | Permissive | These parents let their kids do whatever they want. Ex: You can go out until 4 am. | 69 | |
| 5989394130 | Temperament | 70 | ||
| 5989393359 | Authoritative | Make rules but they explain them to their kids. |  | 71 |
| 5989411926 | accommodate | adapting our schemas to incorporate new information |  | 72 |
| 5989431889 | Gender role stereotypes | are broad categories that reflect our impressions and beliefs about male and females |  | 73 |
| 5989410148 | Maturation | biological growth processes that enable orderly changes in behavior, relatively uninfluenced by experience |  | 74 |
| 5989393006 | Habituation | learning process wherein there is a decrease in response to a stimulus after being repeatedly exposed to it. |  | 75 |
| 5989395335 | Basic Trust | the world is predictable and trustworthy; formed during infancy because of experiences with caregivers |  | 76 |
| 5989403963 | Secondary sex characteristics | SSC: These are the physical features other than reproductive orgrans that distinguish men from women. Unlike primary sex characteristics which are the main sex-specific reproductive organs, testicals, and breast. ex; Harold has a lot of facial hair and Samantha got her period. |  | 77 |
| 5989403368 | Nature versus nurture controversy | A debate surrounding the relative importance of heredity (nature) and environment (nurture) in determining behavior |  | 78 |
| 5989385644 | Embryo | an unborn or unhatched offspring in the process of development, in particular a human offspring during the period from approximately the second to the eighth week after fertilization |  | 79 |
| 5989418312 | Androgyny | the presence of desirable masculine and feminine characteristics in the same individual |  | 80 |
| 5989396488 | Biological Perspective | A way of looking at psychological topics by studying the physical basis for animal and human behavior |  | 81 |
| 5989398315 | Self-awareness | Consciousness of oneself as a person. | 82 | |
| 5989421131 | Identity | describe personal identity, or the idiosyncratic things that make a person unique. Meanwhile, sociologists often use the term to describe social identity, or the collection of group memberships that define the individual. ex; FBI agent identify the criminal |  | 83 |
| 5989398360 | Social Referencing | Observing the behavior consciousness of others in social situations to obtain information or guidance. | 84 | |
| 5989410318 | Egocentric | preschoolers having trouble of perceiving things from another point of view |  | 85 |
| 5989403959 | Secure Attachment | 86 | ||
| 5989413250 | Evolutionary Perspective | behavioral tendencies prepare us to survive and reproduce |  | 87 |
| 5989403960 | Insecure Attachment | 88 | ||
| 5989402913 | Attachment | The formation of an infant's close emotional relationship to their mother. |  | 89 |
| 5989431665 | Gender Roles | The role or behavior learned by a person as appropriate to their gender, determined by the prevailing cultural norms |  | 90 |
| 5989384905 | Zygote | a diploid cell resulting from the fusion of two haploid gametes; a fertilized ovum. |  | 91 |
| 5989435127 | social identity | the "we" aspect of our self-concept; the part of our answer to "who am i" that comes from our group memberships. | 92 |
Developing through the life span Flashcards
Primary tabs
Need Help?
We hope your visit has been a productive one. If you're having any problems, or would like to give some feedback, we'd love to hear from you.
For general help, questions, and suggestions, try our dedicated support forums.
If you need to contact the Course-Notes.Org web experience team, please use our contact form.
Need Notes?
While we strive to provide the most comprehensive notes for as many high school textbooks as possible, there are certainly going to be some that we miss. Drop us a note and let us know which textbooks you need. Be sure to include which edition of the textbook you are using! If we see enough demand, we'll do whatever we can to get those notes up on the site for you!

