| 5725065733 | G1 Phase | First stage of interphase in which cell grows and performs its normal functions. Cell is diploid. | 0 | |
| 5725065734 | G0 Phase | Cell is performing its normal functions, but has left the cell cycle and is not dividing. | 1 | |
| 5725065735 | S Phase | The synthesis phase of the cell cycle; the portion of interphase during which DNA is replicated. | 2 | |
| 5725065736 | G2 Phase | Last stage of interphase in which cell grows and performs its normal functions. Cell is tetraploid. | 3 | |
| 5725065737 | Interphase | Cell grows, performs its normal functions, and prepares for division; consists of G1, S, and G2 phases |  | 4 |
| 5725065738 | Prophase | Phase of mitosis in which chromosomes condense, nuclear membrane disappears, nucleolus disappears, and spindle fibers begin to form. |  | 5 |
| 5725065739 | Metaphase | Phase of mitosis in which spindle fibers help chromosomes line up on the midline of the cell. | 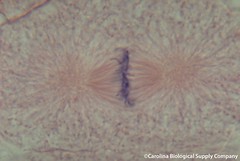 | 6 |
| 5725065740 | Anaphase | Phase of mitosis in which the chromosomes separate and move to opposite ends of the cell. |  | 7 |
| 5725065741 | Telophase | Phase of mitosis during which chromosomes uncoil, a nuclear envelope returns around the chromatin, and a nucleolus becomes visible in each daughter cell" |  | 8 |
| 5725065742 | Cytokinesis | At the end of telophase, actin fibers form an equator around the cell and contract, separating the cytoplasm into two daughter cells. |  | 9 |
| 5725065743 | Centriole | A paired cluster of microtubules near the nucleus in animal cells. This organelle organizes spindle fibers during mitosis. | 10 | |
| 5725065744 | Centromere | Region of a chromosome where the two sister chromatids attach to one another. Contains the kinetochore. | 11 | |
| 5725065745 | Kinetochore | A specialized region on the centromere that links each sister chromatid to the mitotic spindle. | 12 | |
| 5725065746 | Spindle Fibers | Made of microtubules that connect centrioles to kinetochores of chromosomes and that separate sister (mitosis) or homologous (meiosis) chromosomes during cell division | 13 | |
| 5725065747 | Chromosome | A threadlike, gene-carrying structure found in the nucleus. Each chromosome consists of one very long DNA molecule and associated proteins. | 14 | |
| 5725065748 | Chromatid | One of two identical "sister" parts of a duplicated chromosome. | 15 | |
| 5725065749 | Haploid | A cell with only one copy of each chromosome. | 16 | |
| 5725065750 | Diploid | A cell with two copies of each chromosome. | 17 | |
| 5725065753 | Cyclin-Dependent Kinase (CDK) | A group of protein kinases that are activated by the formation of a complex with a cyclin and are involved in the regulation of the cell cycle. Only active when bound to a cyclin. | 18 | |
| 5725065754 | Cyclin | A cellular protein that occurs in a cyclically fluctuating concentration and that plays an important role in regulating the cell cycle. | 19 | |
| 5725065758 | Proto-oncogene | A normal cellular gene corresponding to an oncogene; a gene with a potential to cause cancer but that requires some alteration to become an oncogene. | 20 |
Mitosis - AP Biology Flashcards
Primary tabs
Need Help?
We hope your visit has been a productive one. If you're having any problems, or would like to give some feedback, we'd love to hear from you.
For general help, questions, and suggestions, try our dedicated support forums.
If you need to contact the Course-Notes.Org web experience team, please use our contact form.
Need Notes?
While we strive to provide the most comprehensive notes for as many high school textbooks as possible, there are certainly going to be some that we miss. Drop us a note and let us know which textbooks you need. Be sure to include which edition of the textbook you are using! If we see enough demand, we'll do whatever we can to get those notes up on the site for you!

