| 8546474455 | cell division | The process in reproduction and growth by which a cell divides to form daughter cells. |  | 0 |
| 8546475781 | genome | all the DNA in one cell of an organism |  | 1 |
| 8546477512 | binary fission | A form of asexual reproduction in single-celled organisms by which one cell divides into two cells of the same size. |  | 2 |
| 8546478469 | somatic cell | Any cell in a multicellular organism except a sperm or egg or their precursors. |  | 3 |
| 8546480209 | germ cell | Reproductive cell that gives rise to sperm and egg | 4 | |
| 8546481907 | chromosome | one long continuous molecule of DNA (consists of numerous genes and regulatory information) |  | 5 |
| 8546485073 | chromatin | The complex of DNA and proteins that makes up eukaryotic chromosomes. |  | 6 |
| 8546490984 | sister chromatids | One half of a duplicated chromosome (identical); full sets of these are created during the S subphase of interphase. |  | 7 |
| 8546493337 | centromere | The region of the chromosome that holds the two sister chromatids together during mitosis. |  | 8 |
| 8546494041 | centriole | In animal cells, a cytoplasmic organelle that organizes the mitotic spindle fibers during cell reproductions. |  | 9 |
| 8546494961 | centrosome | A structure in animal cells containing centrioles from which the spindle fibers develop. |  | 10 |
| 8546495844 | cell cycle | Series of events that cells go through as they grow and divide. |  | 11 |
| 8546496570 | mitosis | Cell division in which the nucleus divides into nuclei containing the same number of chromosomes. |  | 12 |
| 8546497470 | cytokinesis | Division of the cytoplasm to form two separate daughter cells. |  | 13 |
| 8546499140 | S phase | The synthesis phase of the cell cycle; the portion of interphase during which DNA is replicated. |  | 14 |
| 8546499904 | G1 phase | The first gap, or growth phase, of the cell cycle, consisting of the portion of interphase before DNA synthesis begins. |  | 15 |
| 8546500348 | G2 phase | The second growth phase of the cell cycle, consisting of the portion of interphase after DNA synthesis occurs. |  | 16 |
| 8546500883 | interphase | Cell grows, performs its normal functions, and prepares for division; consists of G1, S, and G2 phases. | 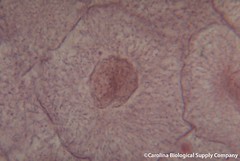 | 17 |
| 8546501485 | mitotic spindle | An assemblage of microtubules and associated proteins that is involved in the movements of chromosomes during mitosis. |  | 18 |
| 8546502682 | kinetochore microtubules | Connects the centrosome with the kinetochore in the centromere region of the chromosome. |  | 19 |
| 8546503213 | kinetochore | proteins that attach to the centromere of a chromosome during mitosis |  | 20 |
| 8546506904 | asters | Microtubules and fibers that radiate out from the centrioles. |  | 21 |
| 8546507348 | metaphase plate | Plane midway between the two poles of the cell where chromosomes line up during metaphase. (aka equator) |  | 22 |
| 8546508042 | cleavage furrow | The first sign of cleavage in an animal cell; a shallow groove in the cell surface near the old metaphase plate. |  | 23 |
| 8546508700 | cell plate | A double membrane across the midline of a dividing plant cell, between which the new cell wall forms during cytokinesis. |  | 24 |
| 8546512092 | density dependent inhibition | dependent inhibition The arrest of cell division that occurs when cells grown in a laboratory dish touch one another. |  | 25 |
| 8546512442 | growth factors | Regulatory proteins that ensure that the events of cell division occur in the proper sequence and at the correct rate. |  | 26 |
| 8546513974 | restriction point | G1 checkpoint; most important checkpoint; a go-ahead here usually leads to completing the cell cycle (through mitosis); a stop leads to the G0 phase |  | 27 |
| 8546514333 | Cdk (cyclin dependent kinases) | an enzyme that activates or inactivates other proteins by phosphorylating them (important at G1 and G2 checkpoints); to be active, these kinases must be joined to cyclin (cyclin fluctuates throughout the cell cycle) |  | 28 |
| 8546514797 | MPF | A cyclin-Cdk complex that causes the cell to move from interphase into mitosis. (think of it as 'mitosis promoting factor') |  | 29 |
| 8546830526 | tumor | a mass of abnormal cells within otherwise normal tissue (may be benign or malignant) |  | 30 |
| 8546515303 | cancer | Any malignant growth or tumor caused by abnormal and uncontrolled cell division. |  | 31 |
| 8546515784 | malignant tumor | mass of cells that is not self-limited in its growth, is capable of invading into adjacent tissues, and may be capable of spreading to distant tissues |  | 32 |
| 8546519129 | benign tumor | mass of cells that does not invade nearby tissue or spread to other parts of the body the way cancer can |  | 33 |
| 8546521904 | cleavage | The process of cytokinesis in animal cells, characterized by pinching of the plasma membrane |  | 34 |
| 8546523374 | allele | One of the alternative forms of a gene that governs a characteristic, such as hair color. |  | 35 |
| 8546523799 | alteration of generations | The alteration of two or more different forms in the life cycle of a plant or animal (e.g. gametophyte and sporophyte) |  | 36 |
| 8546528877 | gametophyte | Haploid, or gamete-producing, phase of an organism; makes haploid gametes by mitosis |  | 37 |
| 8546529601 | sporophyte | Diploid, or spore-producing, phase of an organism; Makes haploid spores by meiosis. |  | 38 |
| 8546532542 | haploid | an organism or cell having only one complete set of chromosomes (1n) |  | 39 |
| 8546533235 | diploid | an organism or cell having two sets of chromosomes or twice the haploid number (2n) |  | 40 |
| 8546533824 | triploid | A chromosomal mutation where an organism has three sets of chromosomes (3n) instead of two (2n) |  | 41 |
| 8546534244 | trisomy | 3 copies of a chromosome |  | 42 |
| 8546535488 | asexual reproduction | One parent produces a genetically identical offspring by mitosis or binary fission |  | 43 |
| 8546535968 | sexual reproduction | process by which cells from two different parents unite to produce the first cell of a new organism (offspring are diverse) |  | 44 |
| 8546537286 | autosomes | Chromosomes that are not directly involved in determining the sex of an individual. |  | 45 |
| 8546537926 | sex chromosomes | X and Y chromosomes (for people) | 46 | |
| 8546538421 | chiasmata | X-shaped regions where crossing over occurred. |  | 47 |
| 8546538714 | clone | An organism that is genetically identical to the organism from which it was produced |  | 48 |
| 8546541309 | crossing over | Nonsister chromatids exchanging DNA segments. (increases genetic variation) |  | 49 |
| 8546542412 | independent assortment | random distribution of homologous chromosomes during meiosis |  | 50 |
| 8546543272 | fertilization | Union of gametes. |  | 51 |
| 8546543273 | zygote | fertilized egg |  | 52 |
| 8546545166 | gamete | A haploid cell such as an egg or sperm that unite during sexual reproduction to produce a diploid zygote. |  | 53 |
| 8546546973 | gene | A segment of DNA on a chromosome that codes for a specific trait |  | 54 |
| 8546548115 | homologous chromosomes | Pair of chromosomes that are the same size/appearance and have the same genes (but have different variations or alleles for many genes); you get one of each from mom, the other from dad. |  | 55 |
| 8546552811 | karyotype | Photograph of chromosomes grouped in order and in pairs. |  | 56 |
| 8546552812 | life cycle | the sequence of stages leading from the adults of one generation to the adults of the next |  | 57 |
| 8546554831 | locus | The specific site of a particular gene on its chromosome. |  | 58 |
| 8546555590 | nonsister chromatids | the chromatids of the homologous chromosome (they may contain different alleles). |  | 59 |
| 8546568622 | recombinant chromosome | A chromosome that carries genes from each parent (crossing over has occurred). |  | 60 |
| 8546573451 | spore | in plants/algae - a haploid cell that can grow into a multi-cellular haploid individual (gametophyte); in fungi - a haploid cell that produces a mycelium |  | 61 |
| 8546595041 | synapsis | Homologous chromosomes pair up, aligned gene by gene; allows matching-up of homologous pairs prior to their segregation, and possible chromosomal crossover between them. |  | 62 |
| 8546596961 | tetrad | structure containing 4 chromatids (homologous chromosome pair) that forms during meiosis |  | 63 |
| 8546600290 | variation | Any difference between individuals of the same species. |  | 64 |
| 8546674568 | G0 phase (the '0' should be a subscript) | a nondividing state (not really in the cell cycle anymore) | 65 | |
| 8546793786 | metastasis | the spread of cancer cells to locations distant from their original site |  | 66 |
10 Cell Division (AP Biology) Flashcards
Primary tabs
Need Help?
We hope your visit has been a productive one. If you're having any problems, or would like to give some feedback, we'd love to hear from you.
For general help, questions, and suggestions, try our dedicated support forums.
If you need to contact the Course-Notes.Org web experience team, please use our contact form.
Need Notes?
While we strive to provide the most comprehensive notes for as many high school textbooks as possible, there are certainly going to be some that we miss. Drop us a note and let us know which textbooks you need. Be sure to include which edition of the textbook you are using! If we see enough demand, we'll do whatever we can to get those notes up on the site for you!

