| 14923528319 | Three laws of cells | 1. all organisms are made of cells 2. the cell is the simplest version of matter that can be alive 3. all cells are related by descent of other cells | 0 | |
| 14923538055 | Light Microscope (LM) | lenses refract the light so image is magnified (x1000) | 1 | |
| 14923545353 | Three parameters of microscopy | Magnification, resolution, contrast | 2 | |
| 14923548417 | Organelles | membrane-enclosed compartments | 3 | |
| 14923552385 | Electron microscopes (EM) | used to study subcellular structures | 4 | |
| 14923555849 | Scanning electron microscope (SEM) | produce images that look 3D, some color | 5 | |
| 14923563618 | Transmission electron microscope (TEM) | used to study internal structure of cells, black and white | 6 | |
| 14923571405 | Cell fractionation | breaks up cells and separates components | 7 | |
| 14923577204 | Eukaryotic domains | protists, fungi, animals, plants | 8 | |
| 14923580876 | Prokaryotic domains | bacteria and archaea | 9 | |
| 14923584401 | Features of all cells | plasma membrane, cytosol, chromosomes, ribosomes | 10 | |
| 14923591987 | Characteristics of eukaryotic cells | DNA is in a nucleus with surrounding cytoplasm | 11 | |
| 14923595368 | Characteristics of prokaryotic cells | no nucleus, DNA is in the nucleoid region, no membrane-bound organelles, cytoplasm | 12 | |
| 14923605836 | Plasma membrane | barrier that allows sufficient passage of oxygen and nutrients | 13 | |
| 14923616976 | Difference in eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells |  | 14 | |
| 14923626885 | Ribosomes | use information from DNA to make proteins | 15 | |
| 14923649070 | Nucleus | contains cells genes | 16 | |
| 14923651468 | Nuclear envelope | encloses the nucleus, separating it from the cytoplasm | 17 | |
| 14923657693 | Nuclear pores | regulate the entry and exit of molecules | 18 | |
| 14923659475 | Nuclear lamina | composed of protein, maintains the shape of the nucleus | 19 | |
| 14923663891 | Nucleus diagram |  | 20 | |
| 14923670456 | Chromosomes | discrete units that DNA is organized into | 21 | |
| 14923671762 | Chromation | DNA and proteins of chromosomes together | 22 | |
| 14923678179 | Nucleolus | site of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) | 23 | |
| 14923685279 | Where are ribosomes located? | cytoplasm and rough ER | 24 | |
| 14923693829 | Components of the endomembrane system | nuclear envelope, endoplasmic reticulum, golgi apparatus, lysosomes, vacuoles, and plasma membrane | 25 | |
| 14923701743 | Vesicles | connects endomembrane system components | 26 | |
| 14923712111 | Endoplasmic reticulum is made up of... | smooth ER and rough ER | 27 | |
| 14923713944 | Smooth ER distinction | lacks ribosomes | 28 | |
| 14923718290 | Rough ER distinction | surface is studded with ribosomes | 29 | |
| 14923722858 | Endoplasmic reticulum |  | 30 | |
| 14923732663 | Functions of the smooth ER | synthesizes lipids, metabolizes carbohydrates, detoxifies drugs and poisons, stores calcium ions | 31 | |
| 14923739653 | Functions of the rough ER | has bound ribosomes which secrete glycoproteins, distributes transport vesicles, membrane factory for the cell | 32 | |
| 14923748338 | Functions of the Golgi apparatus | modifies products of the ER, manufactures certain macromolecules, sorts and packages materials into transport vesicles | 33 | |
| 14923754628 | Cisternae | flattened membranous sacs in the golgi apparatus | 34 | |
| 14923760780 | Golgi apparatus |  | 35 | |
| 14923763972 | Lysomsome | membranous sac of hydrolytic enzymes that digest macromolecules | 36 | |
| 14923774317 | Phagocytosis | cell engulfing another cell and forming a food vacuole | 37 | |
| 14923784059 | Lysosomes and phagocytosis |  | 38 | |
| 14923789665 | Vacuoles | large vesicles derived from the ER and Golgi apparatus | 39 | |
| 14923792221 | Food vacuoles | formed by phagocytosis | 40 | |
| 14923795440 | Contractile vacuoles | found in freshwater protists, pump excess water out of cells | 41 | |
| 14923797842 | Central vacuoles | found in many mature plant cells, hold organic compounds and water | 42 | |
| 14923805184 | Endomembrane system structure |  | 43 | |
| 14923809428 | Mitochondria | sites of cellular respiration, generates ATP | 44 | |
| 14923812579 | Chloroplasts | found in plants and algae, sites of photosynthesis | 45 | |
| 14923819883 | Endosymbiont theory | explains that eukaryotic cells may have evolved from prokaryotic cells | 46 | |
| 14923829393 | Endosymbiont theory process |  | 47 | |
| 14923843540 | Cristae | smooth outer membrane and inner membrane folded in mitochondria | 48 | |
| 14923847117 | Mitochondrial matrix | inner membrane of mitochondria | 49 | |
| 14923853336 | Mitochondria structure |  | 50 | |
| 14923865076 | Where are chloroplasts found? | leaves, other green organs of plants and in algae | 51 | |
| 14923870324 | Thylakoids | membranous sacs stacked to form in a granum in chloroplasts | 52 | |
| 14923873813 | Stroma | internal fluid of chloroplast | 53 | |
| 14923878198 | Chloroplasts belongs in a group of plant organelles called... | plastids | 54 | |
| 14923878199 | chloroplasts structure |  | 55 | |
| 14925471054 | peroxisomes | specialized metabolic compartments bounded by a single membrane | 56 | |
| 14925474754 | Peroxisome function | produce hydrogen peroxide and then convert it to water | 57 | |
| 14958588862 | cytoskeleton | a network of fibers extending through the cytoplasm that organizes the cell's structure and activity | 58 | |
| 14958607756 | Motor protein and cytoskeleton relationship |  | 59 | |
| 14958637474 | 3 main types of fibers | microtubules, microfilaments, intermediate filaments | 60 | |
| 14958637475 | Microtubules | Thickest, made of protein tubulin, shape and support cell, cilia and flagella, separate chromosomes during cell division | 61 | |
| 14958643531 | Microfilaments | Long thin fibers, made from actin, in bundles, absorb nutrients in intestines from food, small intestine | 62 | |
| 14958646072 | Intermediate filaments | size in between microfilaments and microtubules, support shape of cell, more permanent than the other 2 | 63 | |
| 14958653607 | Structure and function of cytoskeleton |  | 64 | |
| 14958736642 | Layers of cell wall | primary cell wall, middle lamella, secondary cell wall | 65 | |
| 14958739732 | Primary cell wall | relatively thin and flexible | 66 | |
| 14958742919 | Middle lamella | thin layer between primary walls of adjacent cells | 67 | |
| 14958746377 | Secondary cell wall | added between the plasma membrane and the primary cell wall | 68 | |
| 14958755967 | Plasmodesmata | channels between adjacent plant cells | 69 | |
| 14958758754 | Plant cell wall and plasmodesmata | 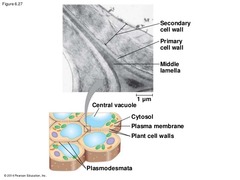 | 70 | |
| 14958777156 | Extracellular Matrix (ECM) | made of collagen, proteoglycans, fibronectin, bind to receptor proteins in the plasma membrane called integrins | 71 | |
| 14958790892 | ECM structure |  | 72 | |
| 14958827580 | Cell junctions |  | 73 |
AP Biology - Test 2 Flashcards
Primary tabs
Need Help?
We hope your visit has been a productive one. If you're having any problems, or would like to give some feedback, we'd love to hear from you.
For general help, questions, and suggestions, try our dedicated support forums.
If you need to contact the Course-Notes.Org web experience team, please use our contact form.
Need Notes?
While we strive to provide the most comprehensive notes for as many high school textbooks as possible, there are certainly going to be some that we miss. Drop us a note and let us know which textbooks you need. Be sure to include which edition of the textbook you are using! If we see enough demand, we'll do whatever we can to get those notes up on the site for you!

