| 5833133354 | Scale | the relationship (or ratio) between distance on a map and the corresponding distance on the ground. For example, on a 1:100000 scale map, 1cm on the map equals 1km on the ground. | 0 | |
| 5833142788 | Local Diversity v. Globalization | Local diversity allows unique culture and differentiation of people whereas globalization pulls people together through info. technology and communication | 1 | |
| 5833166080 | Maps/Cartography | a diagrammatic representation of an area of land or sea showing physical features, cities, roads, etc. Cartography is the science or practice of making maps | 2 | |
| 5835581798 | Environmental Determinism | how the physical environment predisposes societies and states towards particular development trajectories | 3 | |
| 5835583522 | Absolute Location | Uses latitudes and longitudes to | 4 | |
| 5835721500 | International date line | The line in the pacific that determines when the next day is | 5 | |
| 5835723680 | Prime Meridian | 0 degree meridian on Greenwich | 6 | |
| 5835724709 | Equator | Centermost parallel on earth. Gets most direct sunlight all year. | 7 | |
| 5835724710 | Tropics | Cancer and Capricorn. | 8 | |
| 5835726433 | What is a place? | Where unique things and culture and people are | 9 | |
| 5835728611 | Map Scale/Map projection | The earth projected by some proportion into 2 dimensions | 10 | |
| 5836375601 | Climate/Biomes | Common weather and landscape patterns of a large mass of land | 11 | |
| 5836376047 | Popluation Distribution | the arrangement or spread of people living in a given area; also, how the population of an area is arranged according to variables such as age, race, or sex | 12 | |
| 5836376048 | LDC | Less developed country. High birth rate and high death rate. Low living conditions. | 13 | |
| 5836376049 | MDC | More developed country. Low to moderate birth rate to low death rate. Better medicine and technology | 14 | |
| 5836376502 | Demography | the study of statistics such as births, deaths, income, or the incidence of disease, which illustrate the changing structure of human populations. | 15 | |
| 5836376503 | Cartogram | a map on which statistical information is shown in diagrammatic form. | 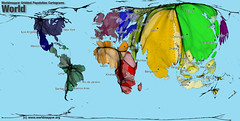 | 16 |
| 5836376944 | Ecumene | inhabited land | 17 | |
| 5836377249 | Arithmetic Density | People per measure of land | 18 | |
| 5836377250 | Agricultural Density | number of farmers per unit area of arable land | 19 | |
| 5836381368 | Earth's Population Clusters | East Asia, South Asia, Europe and Eastern North America | 20 | |
| 5836381783 | CBR | Crude birth rate. | 21 | |
| 5836381784 | CDR | Crude death rate | 22 | |
| 5836383051 | Natural Increase NIR | CBR minus CDR plus immigration and emigration | 23 | |
| 5836383052 | ZPG | Zero population growth | 24 | |
| 5836383053 | Echo Boom (population pyramid) | A small baby boom after the generation of a previous, more major baby boom | 25 | |
| 5836385755 | Doubling Time | the period of time required for a quantity to double in size or value. | 26 | |
| 5836387499 | Areas where there are population issues either overpopulation or negative growth | Ex. Russia has negative population growth at the moment | 27 | |
| 5836388480 | TFR | Total fertility rate- the average number of children born | 28 | |
| 5836388481 | IMR | Infant mortality rate- the average number of infant deaths usually at birth | 29 | |
| 5836388873 | Age-Sex Ratio | The ratio of men to women as well as different ages | 30 | |
| 5836389591 | Analyze the population pyramids | (Rapid, Slow, Negative Growth) why? |  | 31 |
| 5836397182 | Demographic Transition Model | Shows population trends of countries and their correlation with the country's development |  | 32 |
| 5836398215 | Malthus Theory | human populations grow exponentially (i.e., doubling with each cycle) while food production grows at an arithmetic rate | 33 | |
| 5836398216 | Carrying Capacity | Capacity at which a population can be supported | 34 | |
| 5836400547 | Epidemiologic Transition | a phase of development witnessed by a sudden and stark increase in population growth rates brought about by medical innovation in disease or sickness therapy and treatment | 35 | |
| 5836402332 | Chain Migration | the social process by which immigrants from a particular town follow others from that town to a particular city or neighborhood | 36 | |
| 5836404289 | Interregional migration | Migration within a country or general region | 37 | |
| 5836405435 | International Migration | Migration across countries | 38 | |
| 5836406984 | Rust Belt | The American Eastern Midwest | 39 | |
| 5836407370 | Cotton Belt | The American "South" | 40 | |
| 5836407371 | Hollow Core | 41 | ||
| 5836407652 | Sun Belt | The American Southwest | 42 | |
| 5836408205 | Counterurbanization | a demographic and social process whereby people move from urban areas to rural areas | 43 | |
| 5836409633 | In a LDC, what direction does migration move and why? | Outward so people can live better lives | 44 | |
| 5836410160 | EG Ravenstein | German English geographer photographer | 45 | |
| 5836410561 | Short Term Migration | When a migrant moves to another country for at least three months but less than a year | 46 | |
| 5836410852 | Emigration vs. Immigration | Emigration is the act of leaving one's own country, whereas immigration is the articulate of migrants | 47 | |
| 5836411150 | Push Factors | Factors that drive a person away from a place | 48 | |
| 5836411151 | Pull Factors | Factors that attract people to a place | 49 | |
| 5836411758 | Economic or Place Utility | A place's "usefulness" that makes it attractive | 50 | |
| 5836411759 | Refugee | A person forced to leave their own country in order to escape conflict | 51 | |
| 5836411987 | Asylum Seeker | A person who has left their home a political refugee and is seeking asylum in another | 52 | |
| 5836412594 | Intervening obstacle/ Intervening opportunity | Obstacles are factors that make it more difficult to migrate/ opportunities are factors that make a closer place seem more attractive than the previous choice | 53 | |
| 5836413101 | Voluntary vs. Forced Migration | Voluntary migration is a choice whereas forced is when a person doesn't have a choice but to leave | 54 | |
| 5836414158 | According to Ravenstein, who are most of the long distance migrants? Why has it changed? | 55 | ||
| 5836417318 | Wilbur Zelinsky migration transition concepts | 56 | ||
| 5836417907 | Undocumented Workers | Workers without legal documentation to live and/or work in another country | 57 | |
| 5836417908 | Cultural Ecology | The study of human adaptations to social and physical environments | 58 | |
| 5836419514 | Core-Domain-Sphere model | The area outside of the core of a culture region is still dominant but less intense | 59 | |
| 5836419835 | Cultural Transition Zone | Area where two different cultures come together | 60 | |
| 5836420652 | Folk Culture v. Popular Culture | Isolated, traditional, unique, and less prevalent v. Placeless, dynamic, and common | 61 | |
| 5836421312 | Different types of diffusion | Hierarchal- VIPs spread innovations and ideas Relocation- people bring ideas and innovations from other places Contagious- an idea or innovation spreads through people-people contact | 62 | |
| 5836421629 | Western culture's impact | Cars, music, fashion, technology, language, military strength, government | 63 | |
| 5836422578 | Values associated with American culture | Constitutional, fundamental human rights, diversity and expressionism | 64 | |
| 5836422921 | Cultural hearth | Place where culture originates | 65 | |
| 5836422922 | Cultural Realm | The general language, religion, economic development, and artistry of general region | 66 | |
| 5836423419 | Cultural Trait | A certain aspect of culture unique to a people or place | 67 | |
| 5836423420 | Cultural Landscape | a geographic area, including both cultural and natural resources and the wildlife or domestic animals therein, associated with a historic event, activity, or person or exhibiting other cultural or aesthetic values | 68 | |
| 5836423826 | Functional and nodal region | Functional- consist of a central place and the surrounding areas that are dependent upon that place, such as a metropolitan area. Nodal- an area organized around a node, or focal point, and is defined by interactions or connections | 69 | |
| 5836423827 | Syncretism | The amalgamation of different cultures or schools of thought | 70 | |
| 5836424681 | Acculturation | The adaptation of a more dominant culture to a less dominant one | 71 | |
| 5836424682 | Assimilation | The almost indistinguishable merging of two different cultures into one or the complete domination of a more dominant one | 72 | |
| 5836426459 | Universalizing v. Ethnic Religion | Universalizing try to get people to join whereas ethnic keep to there own people or place | 73 | |
| 5836427873 | Popular Religious Concepts | Afterlife, deity, nature is sacred, certain way of life | 74 | |
| 5836427874 | Diaspora | The the scattering of the Jewish population from the Levant area | 75 | |
| 5836429565 | Which languages have been globally diffused? | English, German, French, Chinese, | 76 | |
| 5836430462 | Latin based languages | Spanish, French, Italian, Portuguese, Romanian | 77 | |
| 5836431183 | French-speaking North American city | Montreal, Quebec | 78 | |
| 5836431829 | Half of world's citizens speak from what language family? | Indo-European | 79 | |
| 5836432404 | Components of a dialect | Grammar, speech, and sound | 80 | |
| 5836432639 | Isogloss | A line in a dialect map marking the boundary between linguistic features | 81 | |
| 5836433580 | Language that uses ideographic writing and why it is a problem to learn | Chinese. There is a different character(s) for every word | 82 | |
| 5836434708 | Language no longer used | Dead language | 83 | |
| 5836435756 | Why would a country have an official language? | To make it easier to organize legal documentation | 84 | |
| 5836437090 | American English has adopted vocab from what other languages? | French, | 85 | |
| 5836438297 | Lingua franca | A language that is adopted as a common language between speakers whose native languages are different | 86 | |
| 5836438841 | Does U.S have official language? | No | 87 | |
| 5836440161 | Why is french the official language in places like Senegal? | They were under French rule during the imperialist era | 88 | |
| 5836440162 | Pidgin language | A grammatically simplified means of communication with elements from multiple languages | 89 | |
| 5836440529 | Creole | A pidgin language with elements of French, Spanish, African, and Native-American roots | 90 | |
| 5836440862 | Why is English used globally | Western culture became highly influential after the Great War | 91 | |
| 5836441979 | Why is Basque unusual? | Its language is not of the Indo-European family yet it is in the middle of two European countries | 92 | |
| 5836442903 | Cultural Diffusion | The spread of ideas and innovation | 93 | |
| 5836443246 | How is culture spread? | Through diffusion and immigration | 94 | |
| 5836443247 | Ethnicity | the fact or state of belonging to a social group that has a common national or cultural tradition | 95 | |
| 5836443618 | Ethnocentrism | The judgement of another ethnicity based on the traits and mindset of one's own | 96 | |
| 5836443949 | Subsistence Agriculture | Farming to only sustain one household | 97 | |
| 5836444971 | Hispanic population focused where in U.S? African-Americans? | Southwest. Midwest and South | 98 | |
| 5836447407 | Ethnic enclaves | A neighborhood with a high density of a certain ethnicity | 99 | |
| 5836447934 | Apartheid | Segregation of government by race or ethnicity. Ex. South Africa in the 20th century | 100 | |
| 5836447940 | Ethnic Conflict | Conflict of interests or morals due to the difference in way of life or territorial claims by two different peoples | 101 | |
| 5836448452 | Cultural hearths | Origins of culture (ideas and innovation) | 102 | |
| 5836449135 | Chain migration and ethnic enclave connection | As certain people move to a neighborhood,it causes a chain of migration to a certain neighborhood, causing that neighborhood to become an ethnic enclave | 103 |
AP Human Geography Midterms Flashcards
Primary tabs
Need Help?
We hope your visit has been a productive one. If you're having any problems, or would like to give some feedback, we'd love to hear from you.
For general help, questions, and suggestions, try our dedicated support forums.
If you need to contact the Course-Notes.Org web experience team, please use our contact form.
Need Notes?
While we strive to provide the most comprehensive notes for as many high school textbooks as possible, there are certainly going to be some that we miss. Drop us a note and let us know which textbooks you need. Be sure to include which edition of the textbook you are using! If we see enough demand, we'll do whatever we can to get those notes up on the site for you!

