| 5047573248 | disaccharide | A double sugar, consisting of two monosaccharides joined by dehydration synthesis. |  | 0 |
| 5047573249 | alpha-helix | the coiled structural arrangement of many proteins consisting of a single chain of amino acids stabilized by hydrogen bonds. |  | 1 |
| 5047573250 | biurets | used to test solutions for protein; if it is a positive, the color changes from blue to purple; (stays the same for a negative test) | 2 | |
| 5047573251 | glucose | A sugar that's the major source of energy for the body's cells. It is produced during photosynthesis and can be used to make carbohydrates. |  | 3 |
| 5047573252 | nucleotide | A building block of DNA, consisting of a five-carbon sugar covalently bonded to a nitrogenous base and a phosphate group. |  | 4 |
| 5047573253 | cellulose | A large polysaccharide -provides structural support in plant cell walls. | 5 | |
| 5047573254 | glycogen | An extensively branched glucose storage polysaccharide found in the liver and muscle of animals; the animal equivalent of starch. | 6 | |
| 5047573255 | keratin | A fiber protein that is the principal component of hair, skin, and nails | 7 | |
| 5047573256 | structural | The physical shape of a molecule as a result of atoms bonding. | 8 | |
| 5047573257 | 1-2-1 ratio | Carbohydrates are composed of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen in a consistent ratio. | 9 | |
| 5047573258 | central carbon | the carbon atom of an amino acid that the other amino acid groups (corboxyl group, amino group, etc.) all connect to |  | 10 |
| 5047573259 | inhibition | something that interferes with enzymatic activity | 11 | |
| 5047573260 | benedicts | Indicator used to test for simple sugars and most disaccharides (not sucrose), changes from blue to orange in the presence of sugars, when heated | 12 | |
| 5047573261 | phospholipid | A lipid made up of a glyerol joined to two fatty acids and a phosphate group; has two hydrophobic tails and a polar, hydrophilic head | 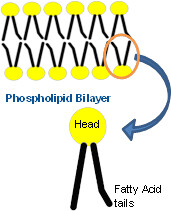 | 13 |
| 5047573262 | R-group | used to represent one of 20 possible side chains found in amino acids of living systems |  | 14 |
| 5047573263 | glycerol backbone | it is the molecule that the fatty acids connect to to form a lipid such as a triglyceride (as well as the phosphate group in a phospholipid) |  | 15 |
| 5047573264 | unsaturated | is a fat or fatty acid in which there is at least one double bond |  | 16 |
| 5047573265 | phosphate group | -this molecule forms the hydrophilic head on a phospholipid - also one of the 3 parts of a nucleotide |  | 17 |
| 5047573266 | sucrose | A disaccharide made of glucose + fructose; Table sugar | 18 | |
| 5047573267 | transparency test | the "paper bag" test used in the lab to test for lipids | 19 | |
| 5047573268 | starch | A storage polysaccharide in plants consisting entirely of glucose. | 20 | |
| 5047573269 | monosaccharide | A single sugar molecule such as glucose or fructose, All monosaccharides have the same chemical formula |  | 21 |
| 5047573270 | iodine | used to test for polysaccharides in the lab. It turns purplish black when positive | 22 | |
| 5047573271 | cholesterol | a type of lipid. | 23 | |
| 5047573272 | enzymes | Functional proteins; their names usually end in - ase Catalyze Reactions (speed it up) | 24 | |
| 5047573273 | nitrogen base | one of the 3 parts of a nucleotide |  | 25 |
| 5047573274 | polysaccharide | Carbohydrates that are made up of more than two monosaccharides | 26 | |
| 5047573275 | dehydration synthesis | A chemical reaction in which two molecules covalently bond to each other with the removal of a water molecule. | 27 | |
| 5047573276 | fatty acids | A building block of lipids, it is a long carbon skeleton, with usually 16-18 carbons, at the end has a carboxyl group attached to a hydrocarbon. |  | 28 |
| 5047573277 | saturated | Fats with the maximum number of hydrogens. Usually animal fats and solid at room temperature |  | 29 |
| 5047573278 | amylase | An enzyme that digests starch into disaccharides. It is secreted by salivary glands and by the pancreas. | 30 | |
| 5047573279 | carboxyl group | A functional group present in organic acids and consisting of a single carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom and also bonded to a hydroxyl group. |  | 31 |
| 5047573280 | peptide bond | The covalent bond between two amino acids, joining them into a peptide or protein. | 32 | |
| 5047573281 | dipeptide | Two amino acids bonded together | 33 | |
| 5047573282 | polypeptide | A polymer (chain) of many amino acids linked together by peptide bonds. | 34 | |
| 5047573283 | primary (protein) | -first level of protein structure - linear sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide chain. -held together by covalent bonds such as peptide bonds |  | 35 |
| 5047573284 | secondary (protein) | Level of protein structure that is formed by the hydrogen bonds between the polar side groups of the main chain. Can be alpha helix or beta pleat sheet |  | 36 |
| 5047573285 | tertiary (protein) | third level of protein structure; the 3-D shape the molecule assumes, as a result of twisting, bending, and folding caused by various types of bonding between R groups (H bonds, ionic bonds, covalent bonds) in large proteins |  | 37 |
| 5047573286 | quaternary (protein) | Relationship among multiple polypeptides of a protein. |  | 38 |
| 5047573287 | maltose | A disaccharide made of glucose + glucose. | 39 | |
| 5047573288 | beta-pleated sheet | polypeptide chain folds back and forth; stabilized by hydrogen bonding |  | 40 |
| 5047573289 | fructose | A 6-carbon monosaccharide in the form of a ring structure. The sweetest of all natural sugars. | 41 | |
| 5047573290 | functional protein | -Proteins that cause chemical changes in the molecules, -control cell activities | 42 | |
| 5047573291 | triglyceride | A molecule made up of three fatty acids covalently bonded to glycerol; Does energy storage, thermal insulation, binds and cushions organs, fills space |  | 43 |
| 5047573292 | amino group | A functional group that consists of a nitrogen atom bonded to two hydrogen atoms |  | 44 |
| 5047573293 | collagen | Fibrous protein that gives the skin form and strength | 45 | |
| 5047573294 | photosynthesis | Plants use the sun's energy to convert water and carbon dioxide into sugars | 46 | |
| 5047573295 | insulation | a material that reduces or prevents the transmission of heat | 47 | |
| 5047573296 | enzyme-substrate complex | A temporary complex formed when an enzyme binds to its substrate molecule(s). |  | 48 |
| 5047573297 | hydrolysis | A chemical reaction that breaks bonds between two molecules by the addition of water; functions in disassembly of polymers to monomers. | 49 | |
| 5047573298 | activation energy | Energy needed to get a reaction started | 50 | |
| 5047573299 | lactase | A digestive enzyme that breaks lactose into glucose and galactose. | 51 | |
| 5047573300 | reusable | able to be used again | 52 | |
| 5047573301 | denature | A change in the shape of a protein (such as an enzyme) that can be caused by changes in temperature or pH (among other things). | 53 | |
| 5047573302 | catalyst | A substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction. | 54 |
Biochemistry Flashcards
Primary tabs
Need Help?
We hope your visit has been a productive one. If you're having any problems, or would like to give some feedback, we'd love to hear from you.
For general help, questions, and suggestions, try our dedicated support forums.
If you need to contact the Course-Notes.Org web experience team, please use our contact form.
Need Notes?
While we strive to provide the most comprehensive notes for as many high school textbooks as possible, there are certainly going to be some that we miss. Drop us a note and let us know which textbooks you need. Be sure to include which edition of the textbook you are using! If we see enough demand, we'll do whatever we can to get those notes up on the site for you!

