| 7259575443 | Bio | life | 0 | |
| 7259577068 | chemistry | chemicals | 1 | |
| 7259578127 | Neutral | PH7 | 2 | |
| 7259579121 | Polar | water molecules are attracted to other water molecules due to opposite changes | 3 | |
| 7259583055 | Cohesion | Same substances are attracted to water | 4 | |
| 7259583996 | Adhesion | different substances are attracted to water | 5 | |
| 7259585700 | mixture | water that is not pure | 6 | |
| 7259587036 | solutions | all parts evenly disturbed ex; sweet tea | 7 | |
| 7259588068 | solute | what is being dissolved ex; sugar and tea | 8 | |
| 7259591167 | solvent | what is doing the dissolving, water is a universal solvent | 9 | |
| 7259593659 | cation/ anion | +/- H2O H+ OH- | 10 | |
| 7259596154 | ion | molecule that takes positive or negative charge | 11 | |
| 7259599706 | Ph scale | 1-6 acid, 7 neutral 8-14 base | 12 | |
| 7259602061 | Buffers | weak acids or bases that react with strong acids or bases to prevent sudden Ph changes | 13 | |
| 7259604722 | Reactant | what is used to complete the reaction | 14 | |
| 7259605216 | product | what is made after the reaction | 15 | |
| 7259606879 | structural formula | picture of the molecule | 16 | |
| 7259608728 | Empirical formula | numbers of the reaction | 17 | |
| 7259628537 | carbon compounds | organic compounds | 18 | |
| 7259629129 | large molecules | polymers are formed by small molecules, monomers | 19 | |
| 7259632633 | dehydration synthesis | water is removed from monomers to make polymers | 20 | |
| 7259637066 | carbohydrates | Source of energy; contains carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen; sugars and starches | 21 | |
| 7259642781 | monosaccharide | A simple sugar that is the basic subunit of a carbohydrate One sugar C6 H12 O6 | 22 | |
| 7259646289 | disaccharide | A double sugar, consisting of two monosaccharides joined by dehydration synthesis. C6 H22 O11 | 23 | |
| 7259652975 | formula | C6 H12 O6 + C6 H12 O6 = C12 H24 O12 - H2 O1 = C6 H22 O11 | 24 | |
| 7259660792 | isomer | have the same empirical formula but different structural formula | 25 | |
| 7259664240 | Polysaccharides | complex sugars Carbohydrates that are made up of more than two monosaccharides | 26 | |
| 7259669656 | Lactose, Sucrose and Maltose | Disaccharide | 27 | |
| 7259671739 | Starches, Glycogen, Cellulose | polysaccharides | 28 | |
| 7259674040 | lipids | A fatty substance that does not dissolve in water store energy fats, oils, and waxes glycerol and 3 fatty acids 2 times as much energy stored than carbohydrates greater than a 2:1 ratio | 29 | |
| 7259680121 | saturated fats | All single bonds between carbons | 30 | |
| 7259681892 | unsaturated fats | double bonds liquid at room temperature | 31 | |
| 7259684236 | Proteins | amino acids nutrients that help build and maintain body cells and tissues 20 different amino acids | 32 | |
| 7259688932 | amino acid bonds | AA + AA+AA=Protein + water | 33 | |
| 7259691609 | peptide | short chain of amino acids linked by peptide bonds that make protein | 34 | |
| 7259693672 | dipetide | 2 amino acids linked together | 35 | |
| 7259695299 | polypeptide | long chain of amino acids that makes proteins | 36 | |
| 7284588925 | enzymes | proteins that act as biological catalysts Proteins that speed up chemical reactions or slow down chemical reactions in cells | 37 | |
| 7284598536 | lower activation energy | Faster reaction the amount of energy needed to start the reaction | 38 | |
| 7284631699 | lock and key hypothesis | Substrates fit into enzymes like a key fits into a lock There is ONE ENZYME for ONE SUBSTRATE | 39 | |
| 7284636025 | substrate | The reactant on which an enzyme works. | 40 | |
| 7284643574 | enzyme and substrate | they fit together until the reaction is over, when it is over a product is released and the product starts over again | 41 | |
| 7284656762 | nucleic acids | DNA and RNA nucleotide is what they are built with macromolecules containing hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, carbon, and phosphorus Complex macromolecules that store and transmit genetic information helps makes proteins | 42 | |
| 7284671193 | enzyme concentration | The more enzymes, the greater the rate of chemical reactions more enzymes = more they will collide | 43 | |
| 7284679608 | substrate concentration | "Enzyme activity increases as substrate concentration increases" More substrate means more chance encounters between substrate molecules and the enzyme | 44 | |
| 7284793081 | optimum temperature | temperature at which organisms grow best. the temperature at which the enzyme has the highest rate of catalysis. human enzymes = 35* - 40* c body temp 37*c | 45 | |
| 7284809851 | raise temperature | denature protein, unfold= lose shape | 46 | |
| 7284816290 | lower temp. | molecules move slower and decrease collisions | 47 | |
| 7284824278 | pH changes | protein shape | 48 | |
| 7284829729 | pH 6-8 | most human enzymes | 49 | |
| 7284833087 | pH 3 | stomach | 50 | |
| 7284835850 | pH 8 | small intestines | 51 | |
| 7301515422 | monosaccaride molecule |  | 52 | |
| 7301516164 | lipid molecule |  | 53 | |
| 7301517230 | amino acid molecule |  | 54 | |
| 7301518216 | glycerol molecule | 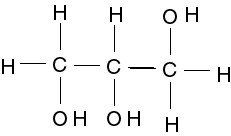 | 55 | |
| 7301519544 | water molecule |  | 56 | |
| 7308543736 | starch | iodine, positive- blue, black color | 57 | |
| 7308546809 | simple sugar | Benedict, positive- orange, blue | 58 | |
| 7308551105 | protein lab | Biuret, positive - light purple | 59 | |
| 7308554964 | lipids lab | brown paper, positive- translucent | 60 |
Biochemistry Flashcards
Primary tabs
Need Help?
We hope your visit has been a productive one. If you're having any problems, or would like to give some feedback, we'd love to hear from you.
For general help, questions, and suggestions, try our dedicated support forums.
If you need to contact the Course-Notes.Org web experience team, please use our contact form.
Need Notes?
While we strive to provide the most comprehensive notes for as many high school textbooks as possible, there are certainly going to be some that we miss. Drop us a note and let us know which textbooks you need. Be sure to include which edition of the textbook you are using! If we see enough demand, we'll do whatever we can to get those notes up on the site for you!

