| 15376791392 | Gastrovascular Cavity | Functions in both digestion and distribution of substances throughout the body | 0 | |
| 15376791393 | Rate of diffusion | Proportional to the square of the distance | 1 | |
| 15376791394 | Heart | Muscular pump | 2 | |
| 15376791395 | Open and Closed Circulatory Systems | Both systems have three basic components: A circulatory fluid (blood or hemolymph) A set of tubes (blood vessels) A muscular pump (the heart) | 3 | |
| 15376791396 | Open Circulatory System | Hemolymph bathes the organs directly. No distinction between blood and interstitial fluid. | 4 | |
| 15376791397 | Closed Circulatory System | Blood is confined to vessels and is distinct from the interstitial fluid. Closed systems are more efficient at transporting circulatory fluids to tissues and cells. | 5 | |
| 15376791398 | Cardiovascular System | 3 main types of blood vessels: arteries, veins, and capillaries. | 6 | |
| 15376791399 | Arteries | Blood from heart to organs | 7 | |
| 15376791400 | Arterioles | Small arteries that connect capillaries to arteries. | 8 | |
| 15376791401 | Venules | Small veins that connect capillaries to veins ( blood back to heart). | 9 | |
| 15376791402 | Capillary beds | Network of capillaries | 10 | |
| 15376791403 | Vertebrate Hearts | Contain 2 or more chambers: Atrium and Ventricle | 11 | |
| 15376791404 | Atrium | Blood enters through the atrium. | 12 | |
| 15376791405 | Ventricle | Blood is pumped out through the ventricle. | 13 | |
| 15376791406 | Single Circulation | Blood leaving the heart passes through two capillary beds before returning. Found in bony fishes, rays and sharks. |  | 14 |
| 15376791407 | Double Circulation | Oxygen-poor and oxygen-rich blood are pumped separately from the right and left sides of the heart. Found in reptiles, amphibians and mammals. |  | 15 |
| 15376791408 | Pulmonary Circuit | Deoxygenated blood leaves the heart, goes to the lungs, and then re-enters the heart. |  | 16 |
| 15376791409 | Pulmocutaneous Circuit | Deoxygenated blood leaves the heart, goes to the lungs and skin and then re-enters the heart. ( pulmonary circuit if only lungs) |  | 17 |
| 15376791410 | Systemic Circuit | Part of the cardiovascular system which carries oxygenated blood away from the heart to the body, and returns deoxygenated blood back to the heart. | 18 | |
| 15376791411 | Amphibian Hearts | 3 Chambered Heart: 2 atria, 1 ventricle | 19 | |
| 15376791412 | Reptile Hearts | Turtles, snakes, and lizards have a 3-chambered heart: 2 atria and 1 ventricle. Crocodilians have an additional septum which divides the ventricle. | 20 | |
| 15376791413 | Mammal and Bird Hearts | Endotherms have a 4-chambered heart with 2 atria and 2 ventricles. | 21 | |
| 15376791483 | Mammalian Circulation |  | 22 | |
| 15376791484 | Mammalian Heart |  | 23 | |
| 15376791414 | Cardiac Cycle | The rhythmic cycle in which the heart contracts and relaxes. |  | 24 |
| 15376791415 | Systole | Phase of the cardiac cycle for contraction or pumping of the heart. |  | 25 |
| 15376791416 | Diastole | Phase of the cardiac cycle for relaxation, or filling of the heart. |  | 26 |
| 15376791417 | Cardiac output | Volume of blood each ventricle pumps per minute | 27 | |
| 15376791418 | Heart rate | Rate of contraction | 28 | |
| 15376791419 | Stroke volume | The volume of blood pumped from a ventricle of the heart in one beat | 29 | |
| 15376791420 | Atrioventricular Valves | Separate each atrium and ventricle to prevent back flow of blood into the heart. | 30 | |
| 15376791421 | Semilunar Valves | Control blood flow to the aorta and the pulmonary artery | 31 | |
| 15376791422 | "lup dup" | "Lup" sound of blood recoiling against AV valves. "Dup" sound of blood recoiling against Semilunar valves. | 32 | |
| 15376791423 | Heart Murmur | Caused by back flow of blood through a defective valve. | 33 | |
| 15376791424 | Sinoatrial Node | Pacemaker; sets the rate and timing at which cardiac muscle cells contract. |  | 34 |
| 15376791425 | Atrioventricular Node | Impulses are delayed and then travel to the Purkinje fibers that make the ventricles contract. |  | 35 |
| 15376791426 | Electrocardiogram | Records impulses that travel during the cardiac cycle. (ECG or EKG) |  | 36 |
| 15376791427 | Endothelium | The epithelial layer that lines blood vessels. Capillaries have endothelium and a basement membrane. Arteries and veins have an endothelium, smooth muscle, and connective tissue | 37 | |
| 15376791428 | Basal lamina | Extra cellular layer surrounding capillaries | 38 | |
| 15376791485 | Arteries and Veins |  | 39 | |
| 15376791429 | Systolic Pressure | The pressure in the arteries during ventricular systole. | 40 | |
| 15376791430 | Diastolic Pressure | The pressure in the arteries during diastole. | 41 | |
| 15376791431 | Pulse | The rhythmic bulging of artery walls with each heartbeat. | 42 | |
| 15376791432 | Vasoconstriction | The contraction of smooth muscle in arteriole walls. | 43 | |
| 15376791433 | Vasodilation | The relaxation of smooth muscles in the arterioles. | 44 | |
| 15376791434 | Blood Pressure | Generally measured using an artery in the arm at the same height as the heart. (120/80). Systole/ diastole | 45 | |
| 15376791435 | precapillary sphincters | smooth muscle cells that guard the entrance to capillaries | 46 | |
| 15376791436 | Lymphatic System | Returns fluid that leaks out in the capillary beds. The lymphatic system drains into veins in the neck | 47 | |
| 15376791437 | Lymph | Fluid lost by capillaries, similar to interstitial fluid | 48 | |
| 15376791438 | Lymph Nodes | Organs that filter lymph and play an important role in the body's defense. | 49 | |
| 15376791439 | Plasma | Liquid matrix of blood. 45% of the blood volume. Blood plasma is 90% water. | 50 | |
| 15376791440 | Erythrocytes | Red blood cells. Erythrocytes transport oxygen. Contains hemoglobin. | 51 | |
| 15376791441 | Leukocytes | White blood cells. Monocytes, neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils, and lymphocytes. | 52 | |
| 15376791442 | Leukocytes in Defense | Phagocytizing bacteria and debris or by producing antibodies. | 53 | |
| 15376791443 | Platelets | Fragments of cells that are involved in clotting. | 54 | |
| 15376791444 | Hemoglobin | An iron-containing protein in red blood cells that reversibly binds oxygen. | 55 | |
| 15376791445 | Sickle cell disease | Abnormal form of hemoglobin polymerizes into aggregates | 56 | |
| 15376791446 | Blood Clotting | Fibrinogen converts into fibrin forming the clot. | 57 | |
| 15376791447 | Erythropoietin | stimulates generation of more erythrocytes | 58 | |
| 15376791448 | Anemia | a lower than normal number of erythrocytes in the blood | 59 | |
| 15376791449 | Thrombus | Blood clot formed within a blood vessel. | 60 | |
| 15376791450 | Cardiovascular Disease | Accounts for more than half the deaths in the United States. | 61 | |
| 15376791451 | Atherosclerosis | The buildup of plaque deposits within arteries. |  | 62 |
| 15376791452 | Heart Attack | The death of cardiac muscle tissue resulting from blockage of one or more coronary arteries. Myocardial infarction |  | 63 |
| 15376791453 | Stroke | The death of nervous tissue in the brain, usually resulting from rupture or blockage of arteries in the head. | 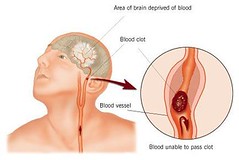 | 64 |
| 15376791454 | Low-density Lipoproteins | Associated with plaque formation; "bad cholesterol". | 65 | |
| 15376791455 | High-density Lipoproteins | Reduce the deposition of cholesterol; "good cholesterol". | 66 | |
| 15376791456 | Hypertension | High blood pressure, promotes atherosclerosis and increases the risk of heart attack and stroke. | 67 | |
| 15376791457 | Gas Exchange | Supplies oxygen for cellular respiration and disposes of carbon dioxide. | 68 | |
| 15376791458 | Partial Pressure | Pressure exerted by a particular gas in a mixture of gases. | 69 | |
| 15376791459 | Respiratory Media | In a given volume, there is less oxygen available in water than in air. | 70 | |
| 15376791460 | Respiratory Surfaces | Gas exchange across respiratory surfaces takes place by diffusion. Respiratory surfaces may include: the outer surface, skin, gills, trachea, and lungs. | 71 | |
| 15376791461 | Ventilation | Moves the respiratory medium over the respiratory surface. | 72 | |
| 15376791462 | Countercurrent Exchange | Used by fish; blood flows in the opposite direction to water passing over the gills |  | 73 |
| 15376791463 | Tracheal System | Used by insects; consists of tiny branching tubes that penetrate the body. Tracheal tubes supply oxygen directly to the cells. |  | 74 |
| 15376791464 | Lungs | respiratory organs | 75 | |
| 15376791465 | Larynx | upper part of the respiratory tract | 76 | |
| 15376791466 | Trachea | windpipe | 77 | |
| 15376791467 | Bronchi | two short branches located at the lower end of the trachea that carry air into the lungs. | 78 | |
| 15376791468 | Bronchioles | smallest branches of the bronchi | 79 | |
| 15376791469 | Alveoli | Terminal air sacs that constitute the gas exchange surface of the lungs. | 80 | |
| 15376791470 | Surfacants | Secretions that cover alveoli. Keeps alveoli from collapsing in on themselves. | 81 | |
| 15376791471 | Positive Pressure Breathing | Used by amphibians; Gulping of air forces air down the trachea. | 82 | |
| 15376791472 | Negative Pressure Breathing | Used by mammals; pulls air into the lungs via diaphragm | 83 | |
| 15376791473 | Tidal Volume | The volume of air inhaled with each breath. | 84 | |
| 15376791474 | vital capacity | tidal volume during maximal inhalation and exhalation | 85 | |
| 15376791475 | residual volume | Amount of air remaining in the lungs after a forced exhalation | 86 | |
| 15376791476 | Respiration in Birds | Air passes through the lungs in one direction only. Every exhalation completely renews the air in the lungs. | 87 | |
| 15376791477 | Respiratory Pigments | Proteins that transport oxygen, greatly increase the amount of oxygen that blood can carry. | 88 | |
| 15376791478 | Hemocyanin | Used by arthropods and some mollusks; respiratory pigments utilizing copper as the oxygen-binding component. | 89 | |
| 15376791479 | Hemoglobin | Respiratory pigment utilizing iron as the oxygen-binding component. A single hemoglobin molecule can carry four molecules of O2. Hemoglobin also helps transport CO2 and assists in buffering |  | 90 |
| 15376791480 | Bohr shift | CO2 produced during cellular respiration lowers blood pH and decreases the affinity of hemoglobin for O2. |  | 91 |
| 15376791481 | breathing control centers | Medulla oblongata | 92 | |
| 15376791482 | Myglobin | Oxygen storing protein | 93 |
Campbell Biology Chapter 42 Flashcards
Primary tabs
Need Help?
We hope your visit has been a productive one. If you're having any problems, or would like to give some feedback, we'd love to hear from you.
For general help, questions, and suggestions, try our dedicated support forums.
If you need to contact the Course-Notes.Org web experience team, please use our contact form.
Need Notes?
While we strive to provide the most comprehensive notes for as many high school textbooks as possible, there are certainly going to be some that we miss. Drop us a note and let us know which textbooks you need. Be sure to include which edition of the textbook you are using! If we see enough demand, we'll do whatever we can to get those notes up on the site for you!

