| 7857695978 | adenosine triphosphate (ATP) | compound used by cells to store and release energy |  | 0 |
| 7857695979 | aerobic | process that requires oxygen | 1 | |
| 7857695980 | anaerobic | process that does not require oxygen | 2 | |
| 7857695981 | anaphase | phase of mitosis in which the chromosomes separate and move to opposite ends of the cell |  | 3 |
| 7857695982 | apoptosis | process of programmed cell death | 4 | |
| 7857695983 | asexual reproduction | process of reproduction involving a single parent that results in offspring that are genetically identical to the parent |  | 5 |
| 7857695984 | ATP synthase | cluster of proteins that span the cell membrane and allow hydrogen ions (H+) to pass through it | 6 | |
| 7857695985 | Autotroph | organism that is able to capture energy from sunlight or chemicals and use it to produce its own food from inorganic compounds; also called a producer |  | 7 |
| 7857695986 | binary fission | type of asexual reproduction in which an organism replicates its DNA and divides in half, producing two identical daughter cells |  | 8 |
| 7857695987 | Calorie | measure of heat energy in food; equivalent to 1000 calories | 9 | |
| 7857695988 | Calvin cycle | light-independent reactions of photosynthesis in which energy from ATP and NADPH is used to build high-energy compounds such as sugar |  | 10 |
| 7857695989 | Cancer | disorder in which some of the body's cells lose the ability to control growth | 11 | |
| 7857695990 | Cell | basic unit of all forms of life |  | 12 |
| 7857695991 | cell division | by which a cell divides into two new daughter cells |  | 13 |
| 7857695992 | cell membrane | thin, flexible barrier that surrounds all cells; regulates what enters and leaves the cell |  | 14 |
| 7857695993 | cell theory | fundamental concept of biology that states that all living things are composed of cells; that cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things; and that new cells are produced from existing cells | 15 | |
| 7857695994 | cell wall | strong, supporting layer around the cell membrane in some cells |  | 16 |
| 7857695995 | cellular respiration | process that releases energy by breaking down glucose and other food molecules in the presence of oxygen |  | 17 |
| 7857695996 | centriole | structure in an animal cell that helps to organize cell division |  | 18 |
| 7857695997 | centromere | region of a chromosome where the two sister chromatids attach |  | 19 |
| 7857695998 | chlorophyll | principal pigment of plants and other photosynthetic organisms | 20 | |
| 7857695999 | chloroplast | organelle found in cells of plants and some other organisms that captures the energy from sunlight and converts it into chemical energy |  | 21 |
| 7857696000 | chromatid | one of two identical "sister" parts of a duplicated chromosome |  | 22 |
| 7857696001 | chromatin | substance found in eukaryotic chromosomes that consists of DNA tightly coiled around histones |  | 23 |
| 7857696002 | chromosome | threadlike structure within the nucleus that contains genetic information that is passed from one generation to the next |  | 24 |
| 7857696003 | cyclin | a regulatory molecule that induces mitosis when its levels increase | 25 | |
| 7857696004 | cytokinesis | division of the cytoplasm to form two separate daughter cells |  | 26 |
| 7857696005 | cytoplasm | fluid portion of the cell outside the nucleus |  | 27 |
| 7857696006 | cytoskeleton | network of protein filaments in a eukaryotic cell that gives the cell its shape and internal organization and is involved in movement |  | 28 |
| 7857696007 | differentiation | process in which cells become specialized in structure and function |  | 29 |
| 7857696008 | diffusion | process by which particles tend to move from an area where they are more concentrated to an area where they are less concentrated |  | 30 |
| 7857696009 | DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) | the macromolecule containing genetic information |  | 31 |
| 7857696010 | electron transport chain | series of electron carrier proteins that shuttle high-energy electrons during ATP-generating reactions | 32 | |
| 7857696011 | embryo | developing stage of a multicellular organism |  | 33 |
| 7857696012 | endergonic reaction | a chemical reaction that requires an input of energy |  | 34 |
| 7857696013 | endoplasmic reticulum | internal membrane system found in eukaryotic cells; place where lipid components of the cell membrane are assembled |  | 35 |
| 7857696014 | eukaryote | organism whose cells contain a nucleus | 36 | |
| 7857696015 | exergonic reaction | a chemical reaction that releases energy |  | 37 |
| 7857696016 | facilitated diffusion | process of diffusion in which molecules pass across the membrane through cell membrane channels |  | 38 |
| 7857696017 | FAD | small energy carrier molecule | 39 | |
| 7857696018 | Fermentation | process by which cells release energy in the absence of oxygen |  | 40 |
| 7857696019 | G0 phase | resting phase during which the cell does not prepare to divide | 41 | |
| 7857696020 | G1 phase | phase of the cell cycle in which the cell carries out normal functions and prepares to replicate its DNA | 42 | |
| 7857696021 | G2 phase | phase of the cell cycle in which the cell prepares to begin mitosis | 43 | |
| 7857696022 | Gene | sequence of DNA that codes for a protein and thus determines a trait; factor that is passed from parent to offspring | 44 | |
| 7857696023 | genetic information | set of genes that code for all the proteins needed by an organism | 45 | |
| 7857696024 | glycolysis | first set of reactions in cellular respiration in which a molecule of glucose is broken into two molecules of pyruvic acid |  | 46 |
| 7857696025 | Golgi apparatus | organelle in cells that modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and other materials from the endoplasmic reticulum for storage in the cell or release outside the cell |  | 47 |
| 7857696026 | growth factor | a regulatory molecule that stimulates or inhibits the rate of cell division |  | 48 |
| 7857696027 | heterotroph | organism that obtains food by consuming other living things; also called a consumer |  | 49 |
| 7857696028 | histone | protein that associates with DNA to form chromosomes | 50 | |
| 7857696029 | homeostasis | relatively constant internal physical and chemical conditions that organisms maintain |  | 51 |
| 7857696030 | hypertonic | when comparing two solutions, the solution with the greater concentration of solutes |  | 52 |
| 7857696031 | hypotonic | when comparing two solutions, the solution with the lesser concentration of solutes |  | 53 |
| 7857696032 | interphase | period of the cell cycle between cell divisions | 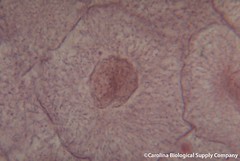 | 54 |
| 7857696033 | isotonic | the concentration of two solutions is the same |  | 55 |
| 7857696034 | Krebs cycle | second stage of cellular respiration in which pyruvic acid is broken down into carbon dioxide in a series of energy-extracting reactions |  | 56 |
| 7857696035 | light-dependent reactions | set of reactions in photosynthesis that use energy from light to produce ATP and NADPH |  | 57 |
| 7857696036 | light-independent reactions | set of reactions in photosynthesis that do not require light; energy from ATP and NADPH is used to build high-energy compounds such as sugar; also called the Calvin cycle |  | 58 |
| 7857696037 | lipid bilayer | flexible double-layered sheet that makes up the cell membrane and forms a barrier between the cell and its surroundings |  | 59 |
| 7857696038 | lysosome | cell organelle that breaks down lipids, carbohydrates, and proteins into small molecules that can used by the rest of the cell |  | 60 |
| 7857696039 | Metaphase | phase of mitosis where the chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell | 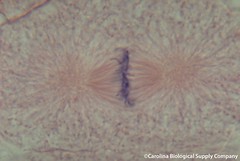 | 61 |
| 7857696040 | Mitochondria | cell organelles that convert the chemical energy stored in food into compounds that are more convenient for the cell to use |  | 62 |
| 7857696041 | Mitosis | part of eukaryotic cell division during which the cell nucleus divides |  | 63 |
| 7857696042 | Multicellular | consisting of many cells |  | 64 |
| 7857696043 | Multipotent | with limited potential to develop into many types of differentiated cells |  | 65 |
| 7857696044 | NAD (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) | electron carrier involved in glycolysis | 66 | |
| 7857696045 | NADPH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate) | carrier molecule that transfers high-energy electrons from chlorophyll to other molecules | 67 | |
| 7857696046 | nuclear envelope | membrane around the nucleus |  | 68 |
| 7857696047 | nuclear pores | holes in the membrane of the nucleus through which substances enter and exit |  | 69 |
| 7857696048 | nucleolus | small structure found in the cell nucleus containing protein and nucleic acids |  | 70 |
| 7857696049 | nucleus | in cells, structure that contains the cell's genetic material in the form of DNA | 71 | |
| 7857696050 | organelle | specialized structure that performs important cellular functions within a eukaryotic cell |  | 72 |
| 7857696051 | osmosis | diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane |  | 73 |
| 7857696052 | osmotic pressure | pressure that must be applied to prevent osmotic movement across a selectively permeable membrane | 74 | |
| 7857696053 | photosynthesis | process used by plants and other autotrophs to capture light energy and use it to power chemical reactions that convert carbon dioxide and water into oxygen | 75 | |
| 7857696054 | photosystem | cluster of chlorophyll and proteins found in thylakoids | 76 | |
| 7857696055 | pigment | light-absorbing molecule used by plants to gather the sun's energy | 77 | |
| 7857696056 | pluripotent | cells that are capable of developing into most, but not all, of the body's cell types |  | 78 |
| 7857696057 | prokaryote | unicellular organism that lacks a nucleus |  | 79 |
| 7857696058 | prophase | first and longest phase of mitosis in which the genetic material inside the nucleus condenses and the chromosomes become visible |  | 80 |
| 7857696059 | ribosome | cell organelle consisting of RNA and protein found throughout the cytoplasm in a cell; the site of protein synthesis |  | 81 |
| 7857696060 | S phase | phase of the cell cycle during which DNA is replicated | 82 | |
| 7857696061 | selectively permeable | property of biological membranes that allows some substances to pass across the membrane while others cannot |  | 83 |
| 7857696062 | stem cell | unspecialized cell that can give rise to one or more types of specialized cells |  | 84 |
| 7857696063 | stroma | fluid portion of the chloroplast; outside the thylakoids |  | 85 |
| 7857696064 | telophase | phase of mitosis in which the distinct individual chromosomes begin to spread out into a tangle of chromatin |  | 86 |
| 7857696065 | thylakoid | saclike photosynthetic membranes found in chloroplasts |  | 87 |
| 7857696066 | tissue | group of similar cells that perform a particular function | 88 | |
| 7857696067 | totipotent | cells that are able to develop into any type of cell found in the body |  | 89 |
| 7857696068 | tumor | mass of rapidly dividing cells that can damage surrounding tissue |  | 90 |
| 7857696069 | unicellular | consisting of one cell |  | 91 |
| 7857696070 | vacuole | cell organelle that stores materials such as water, salts, proteins, and carbohydrates |  | 92 |
Cells Flashcards
Primary tabs
Need Help?
We hope your visit has been a productive one. If you're having any problems, or would like to give some feedback, we'd love to hear from you.
For general help, questions, and suggestions, try our dedicated support forums.
If you need to contact the Course-Notes.Org web experience team, please use our contact form.
Need Notes?
While we strive to provide the most comprehensive notes for as many high school textbooks as possible, there are certainly going to be some that we miss. Drop us a note and let us know which textbooks you need. Be sure to include which edition of the textbook you are using! If we see enough demand, we'll do whatever we can to get those notes up on the site for you!

