| 6194538334 | Histology or Microscopic Anatomy | -the study of tissues and how they are arranged into organs | 0 | |
| 6194538335 | Tissue | -similar cells and cell products (matrix) | 1 | |
| 6194538336 | Matrix | -ground substance and fibers | 2 | |
| 6194538337 | Primary germ layers | -the three layers (ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm) of the late gastrulation, which develop into all parts of an animal. | 3 | |
| 6194538338 | Ectoderm | -outermost germ layer -the germ layer that gives rise to the skin and nervous system | 4 | |
| 6194538339 | Endoderm | -innermost germ layer -develops into the linings (mucous membrane) of the digestive tract and much of the respiratory system | 5 | |
| 6194538340 | Mesoderm | -middle germ layer -the germ layer that gives rise to the blood, bones and muscles | 6 | |
| 6194538341 | Mesenchyme | -embryonic connective tissue that arises from mesoderm and produces all types of connective tissues | 7 | |
| 6194538342 | Histological sections | -tissue preparations mounted on microscope slides. -artificially colored to bring out detail | 8 | |
| 6194538343 | Fixative | -preservative for cells | 9 | |
| 6194538344 | Stains | -artificial color that enhances details | 10 | |
| 6194538345 | Longitudinal Section | | | 11 | |
| 6194538346 | Cross Section | _ | 12 | |
| 6194538347 | Transverse Section | _ | 13 | |
| 6194538348 | Oblique Section | / | 14 | |
| 6194538349 | Smears | -tissue is rubbed or spread across the slide rather than sliced | 15 | |
| 6194538350 | Spreads | -tissue is laid out on the slide | 16 | |
| 6194538351 | Sections | -tissue is sliced | 17 | |
| 6194538352 | Epithelial Tissue | -a body tissue that covers the interior and exterior surfaces of the body | 18 | |
| 6194538353 | 6 Functions of Epithelial Tissue | Functions: Protection, Secretion, Excretion, Absorption, Filtration, Sensation | 19 | |
| 6194538354 | Basement Membrane | -cells at the base (basal cells) of an epithelial layer are attached to this -regulates the exchange of materials between the epithelium and the underlying tissues | 20 | |
| 6194538355 | Simple Epithelium | -has only one layer of cells | 21 | |
| 6194538356 | Simple Squamous | -has only one layer of cells, with a scale like shape | 22 | |
| 6194538357 | Simple Cuboidal | -has only one layer of cells, with a cube like shape | 23 | |
| 6194538358 | Simple Columnar | -has only one layer of cells, with a colum like shape | 24 | |
| 6194538359 | Pseudostratified Columnar | -has only one layer of cells, but appears to be stratified columnar | 25 | |
| 6194538360 | Goblet Cells | -secrete a glycoprotein called mucin | 26 | |
| 6194538361 | Stratified Epithelia | -has more than one layer of cells | 27 | |
| 6194538362 | Stratified Squamous | -has more than one layer of cells, with a scale like shape | 28 | |
| 6194538363 | Stratified Cuboidal | -has more than one layer of cells, with a cube like shape | 29 | |
| 6194538364 | Stratified Columnar | -has more than one layer of cells, with a colum like shape | 30 | |
| 6194538365 | Transitional Epithelium | -somewhat resembles stratified squamous epithelium, but surface cells are rounded, not flattened, and often bulge at surface | 31 | |
| 6194538366 | Exfoliation or Desquamation | -epithelium dies and flakes off of the surface | 32 | |
| 6194538367 | Nonkeratinized | -lacks the surface layer of dead cells -moist and slippery | 33 | |
| 6194538368 | Keratinized | -epithelium, found in the epidermis, is covered with a layer of compact, dead squamous cells -packed with the durable protein keratin -dry and water resistant | 34 | |
| 6194538369 | Connective Tissues | -cells that occupy less space than the extracellular matrix | 35 | |
| 6194538370 | 8 Functions of Connective Tissue | Functions: Binding of organs, Support, Physical protection, Immune protection, Movement, Storage, Heat production, Transport | 36 | |
| 6194538371 | The cells of fibrous connective tissue | Common Cells: Fibroblasts, Macrophages, Leukocytes, Plasma cells, Mast cells, Adipocytes | 37 | |
| 6194538372 | Fibroblasts | -produce fibers and ground substance | 38 | |
| 6194538373 | Macrophages | -cells that wander through the connective tissues, where they engulf and destroy bacteria, other foreign particles, and dead or dying cells of our own body. | 39 | |
| 6194538374 | Leukocytes | -react against bacteria, toxins and other foreign substances | 40 | |
| 6194538375 | Plasma cells | -synthesize disease-fighting proteins called antibodies | 41 | |
| 6194538376 | Mast cells | -secrete heparin (inhibits blood clotting) and histamine (dilates blood vessels) | 42 | |
| 6194538377 | Adipocytes | -specialized fat cells whose cytoplasm contains nothing but triglycerides | 43 | |
| 6194538378 | 3 types of fibers | -Collagenous Fibers, Reticular fibers, Elastic fibers | 44 | |
| 6194538379 | Collagenous Fibers | -fibers made of collagen, that are tough, flexible and resist stretching | 45 | |
| 6194538380 | Reticular fibers | -thin collagen fibers coated with glycoprotein that form a spongelike framework | 46 | |
| 6194538381 | Elastic fibers | -fibers made of a protein called elastin | 47 | |
| 6194538382 | Elastin | -a protein whose coiled structure allows it to stretch and recoil like a rubber band. | 48 | |
| 6194538383 | Ground Substance | -a gelatinous substance that is made of 3 large molecules glycosaminoglycans, proteoglycans, and adhesive glycoproteins | 49 | |
| 6194538384 | Glycosaminoglycan | -long polysaccharide composed of unusual disaccharides called amino sugars -it includes chondroitin sulfate, heparin (an anticoagulant) and hyaluronic (lubricant in the joints) -good at attracting and holding water. | 50 | |
| 6194538385 | Chondroitin Sulfate | -the most abundant type of glycosaminoglycan that makes cartilage stiff | 51 | |
| 6194538386 | Proteoglycan | -gigantic molecule that forms thick colloids which slows the spread of pathogenic organisms through the tissues -also bind the cell to the matrix | 52 | |
| 6194538387 | Adhesive Glycoproteins | -bind plasma membrane proteins to collagen and proteoglycans outside the cell | 53 | |
| 6194538388 | Loose Connective Tissue | -ground substane occupies more space than the cells and fibers | 54 | |
| 6194538389 | Dense Connective Tissue | -fiber occupies more space than the cells and ground substance | 55 | |
| 6194538390 | Areolar Tissue | -Fibers: mostly collagenous fibers -Cells: all of the 6 cells found in connective tissues -found in almost every part of the body -has an abundance of blood vessels | 56 | |
| 6194538391 | Reticular Tissue | -Fibers: reticular fibers -Cells: fibroblasts -forms the structural framework (spongy) for some viscera | 57 | |
| 6194538392 | Dense Regular Connective Tissue | -very little space between parallel collagen fibers | 58 | |
| 6194538393 | Elastic Tissue | -a type of dense regular tissue with added elastic fibers -has more fibroblasts (larger nuclei) than normal dense regular tissue | 59 | |
| 6194538394 | Dense Irregular Connective Tissue | -very little space between collagen fibers that run in random directions | 60 | |
| 6194538395 | Adipose tissue | -Fibers: areolar tissue and reticular tissue -Cells: adipocytes | 61 | |
| 6194538396 | White Fat | -is the only significant adipose tissue of the adult body | 62 | |
| 6194538397 | Brown fat | -abundance of blood vessels and mitochondria -mitochondria don't produce ATP only energy as heat only in children and under. | 63 | |
| 6194538398 | Cartilage | -a strong connective tissue that is more flexible than bone | 64 | |
| 6194538399 | Chondroblasts | -cartilage producing cell that secrete matrix until surrounded | 65 | |
| 6194538400 | Chondrocytes | -cartilage producing cell enclosed in a lacunae | 66 | |
| 6194538401 | Lacunae | -a little cavity that a cell becomes enclosed in | 67 | |
| 6194538402 | Hyaline Cartilage | -fine collagen fibers that appear glassy | 68 | |
| 6194538403 | Elastic Cartilage | -cartilage with abundant elastic fibers; more flexible than hyaline cartilage. | 69 | |
| 6194538404 | Fibrocartilage | -tough form of cartilage, made of thick bundles of collagen fibers embedded in chondroitin sulfate ground substance | 70 | |
| 6194538405 | Perichondrium | -a sheath of dense irregular connective tissue surrounding most hyaline and elastic cartilage | 71 | |
| 6194538406 | Osseous Tissue | -is a hard, calcified connective tissue that composes the skeleton | 72 | |
| 6194538407 | Spongy Bone | -fills the heads of the long bones and forms the middle layer of flat bones -always covered by a shell of compact bone | 73 | |
| 6194538408 | Compact Bone | -is a denser calcified tissue with no spaces visible to the naked eye | 74 | |
| 6194538409 | Central Canals | 1 |  | 75 |
| 6194538410 | Concentric Lamellae | 3 |  | 76 |
| 6194538411 | Osteon |  | 77 | |
| 6194538412 | Lacunae of Osseous Tissue | 4 |  | 78 |
| 6194538413 | Canaliculi | 2 |  | 79 |
| 6194538414 | Periosteum | -a sheath of dense irregular connective tissue covering the bone | 80 | |
| 6194538415 | Blood | -Fibers: none -Cells: erythrocytes, leukocytes and platelets -GS: blood plasma (more abundant in GS than anything) | 81 | |
| 6194538416 | Blood Plasma | -the ground substance in blood | 82 | |
| 6194538417 | Formed Elements | -collective of cells inside blood (erythrocytes, leukocytes, and platelets) | 83 | |
| 6194538418 | Erythrocytes | -transport O2 and CO2 | 84 | |
| 6194538419 | Platelets | -small cell fragments that are involved in clotting and secreting growth factors that promote blood vessel growth and maintenance | 85 | |
| 6194538420 | Excitable Tissues | -tissues such as neurons or muscles that are capable of producing membrane potential | 86 | |
| 6194538421 | Membrane Potential | -the voltage across a cell's plasma membrane. | 87 | |
| 6194538422 | Nervous tissue | -is specialized for communication by means of electrical and chemical signals -Cells: neurons and glial cells (which are more abundant) | 88 | |
| 6194538423 | Neurons | -detect stimuli, respond quickly, and transmit coded information rapidly to other cells | 89 | |
| 6194538424 | Glial Cell | -protect and assist the neurons | 90 | |
| 6194538425 | Neurosoma | -cell body of a neuron that houses the nucleus and most other organelles | 91 | |
| 6194538426 | Dendrites | -branch out of the neurosoma -receive signals from other cells and conduct messages to the neurosoma | 92 | |
| 6194538427 | Axon (Nerve Fiber) | -sends outgoing signals to other cells | 93 | |
| 6194538428 | Muscular Tissue | -contract moving various parts of the body when stimulated | 94 | |
| 6194538429 | Skeletal Muscle | -striated and voluntary | 95 | |
| 6194538430 | Muscle Fibers | -long, slender cells that make up (skeletal) muscles | 96 | |
| 6194538431 | Sphincter | -muscular rings or cuffs that open and close body passages | 97 | |
| 6194538432 | Striations | -alternating vertical light and dark bands |  | 98 |
| 6194538433 | Cardiac Muscle | -striated and involuntary -only located on the heart | 99 | |
| 6194538434 | Cardiocytes | -short muscle cells of the heart | 100 | |
| 6194538435 | Myocytes | -short muscle cells (smooth or cardiac muscle) | 101 | |
| 6194538436 | Intercalated Discs | -junctions that join cardiocytes together end to end | 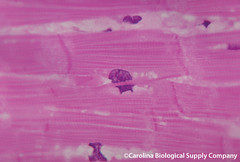 | 102 |
| 6194538437 | Smooth Muscle | -fusiform and involuntary | 103 | |
| 6194538438 | Visceral Muscle | -muscles of the viscera (internal organs) -usually smooth muscle | 104 | |
| 6194538439 | Cell Junctions | -The connections between one cell and another | 105 | |
| 6194538440 | Tight Junction | -completely encircles an epithelial cell near its apical surface creating a seal -linked by transmembrane cell-adhesion proteins | 106 | |
| 6194538441 | Desmosome | -doesn't completely encircles an epithelial cell -enables a tissue to resist mechanical stress | 107 | |
| 6194538442 | Hemidesmosomes | -half desmosomes that attach the basal cells to the basement membrane | 108 | |
| 6194538443 | Gap Junction | -a channel that connects cells together -allows ions, glucose, amino acids, and other small solutes to pass directly from one cell to it's neighbor | 109 | |
| 6194538444 | Gland | -a cell or organ that secretes substances for use elsewhere in the body or for elimination as waste | 110 | |
| 6194538445 | Secretion | -a product useful to the body that is released | 111 | |
| 6194538446 | Excretion | -a waste product that is released | 112 | |
| 6194538447 | Exocrine Glands | -secrete chemical substances into ducts that lead either to other organs or out of the body | 113 | |
| 6194538448 | Duct | -an epithelial tube that moves secretion to the surface | 114 | |
| 6194538449 | Endocrine Glands | -lost contact with the surface and have no ducts -secrete their products directly into the blood | 115 | |
| 6194538450 | Unicellular glands | -secretory cells found in an epithelium that is predominantly nonsecretory -ex: goblet cells | 116 | |
| 6194538451 | Capsule | -encloses gland | 117 | |
| 6194538452 | Septa or Trabeculae | -extensions of the capsule that divide the interior of glands | 118 | |
| 6194538453 | Lobes | -the compartments made by septa | 119 | |
| 6194538454 | Lobules | -created by fine septa further dividing lobes | 120 | |
| 6194538455 | Stroma | -connective tissue framework of the gland i.e. capsule and septa | 121 | |
| 6194538456 | Parenchyma | -cells that perform the tasks of synthesis and secretion | 122 | |
| 6194538457 | Simple | -a single unbranched duct |  | 123 |
| 6194538458 | Compound | -branched ducts |  | 124 |
| 6194538459 | Tubular | -duct and secretory portion are of uniform diameter | 125 | |
| 6194538460 | Acinar | -secretory gland form a dilated sac | 126 | |
| 6194538461 | Acinus or Alveolus | -secretory cells form a dilated sac | 127 | |
| 6194538462 | Tubuloacinar Gland | -secretory cells in both the tubular and acinar portions | 128 | |
| 6194538463 | Serous Glands | -produce relatively thin, watery fluids | 129 | |
| 6194538464 | Mucous Glands | -has cells that secrete a glycoprotein called mucin (mucin absorbs water and forms the sticky product mucus) | 130 | |
| 6194538465 | Mixed Glands | -contain both serous and mucous cells | 131 | |
| 6194538466 | Cytogenic Glands | -release whole cells (testes and ovaries) | 132 | |
| 6194538467 | Eccrine Glands or Merocrine Glands | -have vesicles that release their secretion by exocytosis | 133 | |
| 6194538468 | Holocrine Glands | -cells accumulate a product and then the entire cell disintegrates | 134 | |
| 6194538469 | Apocrine Glands | -same as merocrine with the exception of larger lumen | 135 | |
| 6194538470 | Cutaneous Membrane | -the skin -dry | 136 | |
| 6194538471 | muscularis mucosae | -a layer of smooth muscle in mucous membrane | 137 | |
| 6194538472 | lamina propria | -an areolar connective tissue layer of mucous membrane | 138 | |
| 6194538473 | Mucous Membrane | -lines passages that open to the exterior environment -layers; (1) an epithelium (2) lamina propria (3) muscularis mucosae | 139 | |
| 6194538474 | Serous Membrane | -a simple squamous epithelium resting on a thin layer of areolar connective tissue -produces watery fluid | 140 | |
| 6194538475 | Serous Fluid | -watery product of serous membrane | 141 | |
| 6194538476 | Mesothelium | -the epithelium found in serous membranes lining the ventral body cavity and covering its organs | 142 | |
| 6194538477 | Endothelium | -layer of simple squamous epithelium lining cavities of heart, blood & lymphatic vessels | 143 | |
| 6194538478 | Synovial Membranes | -lines some joints -made only of connective tissue | 144 | |
| 6194538479 | Hyperplasia | -tissue growth through cell multiplication | 145 | |
| 6194538480 | Hypertrophy | -the enlargement of preexisting cells | 146 | |
| 6194538481 | Neoplasia | -the development of a tumor | 147 | |
| 6194538482 | Differentiation | -process in which cells become specialized in structure and function | 148 | |
| 6194538483 | Metaplasia | -a change from one type of mature tissue to another | 149 | |
| 6194538484 | Stem Cells | -undifferentiated cells that are not yet performing any specialized function | 150 | |
| 6194538485 | Developmental Plasticity | -range of mature cell types that a stem cell can become | 151 | |
| 6194538486 | Embryonic Stem Cells | -compose the early human embryo | 152 | |
| 6194538487 | Totipotent | -have the potential to develop into any type of fully differentiated human cell | 153 | |
| 6194538488 | Pluripotent | -cells of the inner cell mass -can still develop into any cell type of the embryo, but not into the accessory organs of pregnancy | 154 | |
| 6194538489 | Adult Stem Cells | -undifferentiated cells found among differentiated cells in a tissue or organ | 155 | |
| 6194538490 | Multipotent | -able to develop into two or more different cell lines, but not just any type of body cell. | 156 | |
| 6194538491 | Unipotent | -able to develop into only one cell type | 157 | |
| 6194538492 | Regeneration | -replacement of dead or damaged cells by the same type of cells as before | 158 | |
| 6194538493 | Fibrosis | -replacement of damaged tissue with scar tissue, composed mainly of collagen produced by fibroblasts | 159 | |
| 6194538494 | Granulation Tissue | -deeper portions of the clot become infiltrated by capillaries and fibroblasts and transform into a soft mass | 160 | |
| 6194538495 | Atrophy | -the shrinkage of a tissue through a loss in cell size or number | 161 | |
| 6194538496 | Necrosis | -premature tissue death | 162 | |
| 6194538497 | Infarction | -the sudden death of tissue, such as cardiac muscle or brain tissue -occurs when its blood supply is cut off | 163 | |
| 6194538498 | Gangrene | -any tissue necrosis resulting from an insufficient blood supply, usually involving infection | 164 | |
| 6194538499 | Decubitus Ulcer | -a form of dry gangrene that occurs when an immobilized person, have continual pressure on the skin cutting off blood flow to the area | 165 | |
| 6194538500 | Apoptosis | -is the normal death of cells that have completed their function and best serve the body by dying | 166 |
CHAPTER 5: Histology Flashcards
Primary tabs
Need Help?
We hope your visit has been a productive one. If you're having any problems, or would like to give some feedback, we'd love to hear from you.
For general help, questions, and suggestions, try our dedicated support forums.
If you need to contact the Course-Notes.Org web experience team, please use our contact form.
Need Notes?
While we strive to provide the most comprehensive notes for as many high school textbooks as possible, there are certainly going to be some that we miss. Drop us a note and let us know which textbooks you need. Be sure to include which edition of the textbook you are using! If we see enough demand, we'll do whatever we can to get those notes up on the site for you!

