| 505183623 | small | Diffusion is only rapid over xxxx distances | |
| 505183624 | hydras, cnidarians, digestion, distribution | xxxx and xxxx are animals that lack a circulatory system, and instead use a central gastrovascular cavity which functions in xxxxx and xxxxx of substances throughout the body | |
| 505210706 | inner, two, outer | In a hydra, only cells of the xxxx layer have direct access to nutrients, but since the body wall is a mere xxxx cells thick, the nutrients diffuse only a short distance to the xxx layer | |
| 505210707 | radial arms, circular canal, Ciliated cells, fluid | Some cnidarians (jellies)-Mouth leads to an elaborate gastrovascular cavity that consists of xxxx xxxx leading to/from xxxx xxxx. xxxx xxxx line canals and circulate xxxx within the cavity as indicated by arrows |  |
| 505210708 | circulatory, gastrovasular cavity, flat, surface area, distances | Flatworms do not a have a xxxxx system. Instead their xxxx xxxx and xxxx body optimizes exchange with the environment. flat bodies optimize diffusion exchange by increasing xxxx xxxx and minimizing diffusion xxxx | |
| 505213217 | circulatory fluid, interconnecting tubes, heart | A circulartory System has 3 basic components:
xxxxxxx xxxxx
xxxxxx xxxxx
xxxxx | |
| 505329237 | metabolic, hydrostatic pressure, vessels | The heart powers circulation by using xxxxxx energy to elevate the xxxxx xxxx of the circulatory fluid, which then flows through a circuit of xxxxx and back to the heart | |
| 505329238 | open, directly | Arthropods and mollusks have a xxxxx circulatory system, in which circulatory fluid bathes the organs xxxx | |
| 505329239 | hemolymph, interstitial | In animals with an open circulatory system, the circulatory fluid is called xxxxx and is also the xxxx fluid | |
| 505329240 | contraction, hemolymph, sinuses, organs, exchange , Relaxation, pores, body movement | In an animal with an open circulatory system, xxxxx of one or more hearts pumps xxxxx through the circulatory vessels into interconnected xxxxxx (spaces surrounding xxxxx) within the sinuses, xxxxx occurs between hemoplymph and body cells. xxxxxxx of the heart draws hemolyph back into the xxxx, and xxxxx xxxx helps circulate the hemolymph by periodically squeezing the sinuses |  |
| 505329241 | blood, vessels, interstitial fluid | In a closed circulatory system, xxxx is confined to xxxxx and is distinct from the xxxxx xxxxx | |
| 505329242 | hearts, blood, vessels, organs | In a closed circulatory system, one or more xxxx pump xxxx into large xxxxx, which branch into smaller ones coursing through the xxxx. materials are exchanged between the smallest vessels and the interstitial fluid of the cells. |  |
| 505329243 | annelids, cephalopods, vertebrates | xxxxxx, xxxx and xxxxx all have closed circulatory systems | |
| 505329244 | hydrostatic pressure, less | [ADVANTAGES OF OPEN CIRCULATORY SYSTEM]
lower xxxxx xxxxx make them xxxx energy exhausting | |
| 505329245 | hydrostatic pressure, open, extend | the xxxx xxxx exerted by an xxxxx circulatory systems also provide spiders the force used to xxxx the animals legs (that's why they shrivel up when they die) | |
| 505329246 | blood pressures, oxygen, nutrients, larger, blood, organs | [ADVANTAGES OF CLOSED CIRCULATORY SYSTEM]
relatively high xxx xxxxx, which enable the effective delivery of xxxxx and xxxxx to cells of xxxx and more active animals
Regulate the distribution of xxxx to different xxxxx | |
| 505329247 | ateries, veins, capillaries | The main three types of vessels are:
xxx
xxxxx
xxxx | |
| 505329248 | arteries, arterioles, blood, capillaries | xxxxx carry blood away from the heart to organs throughout the body. within organs, they branch into xxxxx (small vessels that convey xxxx to the xxxxxx) | |
| 505329249 | capillaries, walls, capillary beds, exchanging, blood, interstitial, venules, veins | xxxxxx are microscopic vessels with very thin, porous xxxx through which diffusion can occur rapidly. networks of these called xxxxx xxxx infiltrate each tissue, xxxxx chemicals between the xxxx and xxxxx fluid. At their downstream end, these converge into xxxxx, which converge into xxxx | |
| 505329250 | veins, capillaries | xxxxxx are vessels that carry blood back to the heart from xxxxxx | |
| 505329251 | capillaries | The portal vein is the only vein that carries blood to xxxxx | |
| 505329252 | atria, ventricles | The heart of all vertebrates contain 2 or more chambers. The chambers that receive blood entering the heart are called xxxx. the chambers responsible for pumping blood out of the heart are called xxxxx | |
| 505329253 | once | the heart of fish, rays, and sharks consists of 2 chambers (atrium and ventricle). the blood passes through the heart xxxx in each circuit | |
| 505329254 | fish, rays, sharks | the heart of xxxx xxxx and xxxx exhibits single circulation | |
| 505329255 | 1 | Single circulation is when only xxxx circuit of blood passing through the heart is needed | |
| 505350415 | atrium, ventricle, contraction, ventricle, gills, oxygen, carbon dioxide, oxygen, heart | In Single Circulation, blood entering the heart collects in the xxxx before transfer to the xxxxx. xxxx of the xxxx pumps blood to the xxxx, where diffusion of xxxxx into the blood and xxxx xxxx out of the blood occurs. As blood leaves the gills, the capillaries converge into a vessel that carries xxxxx rich blood (Red in picture) to capillary beds throughout the body. de-oxiginated Blood (Blue in picture) then returns to the xxxx (atrium first) |  |
| 505446707 | 2, gill, systemic, blood pressure, blood, contraction, relaxation, muscles, accelerates | In single circulation, blood that leaves the heart passes through xxxxx capillary beds (xxxx and xxxxx). When blood flows through a capillary bed, xxxxx xxxx substantially drops, which limits the rate of xxxx flow throughout the body. However, excessive swimming allows stimulates the xxxxx and xxxxx of its xxxx, which xxxxx the rate of blood flow throughout the body |  |
| 505446708 | amphibians, reptiles, mammals | xxxx, xxxx, and xxxx exhibit double circulation | |
| 505446709 | right, poor, gas exchange, oxygen, carbon dioxide, rich, left, contraction, organs, tissues, oxygen, nutrients, poor, heart | In double circulation, the xxxx side of the heart delivers oxygen-xxxx blood to the capillary beds of the xxxxx xxxxx tissues, where xxxxx diffuses into the blood and xxxx xxxx diffuses out. (This can occur in the lungs or the lungs AND skin) As oxygen-xxxxx blood leaves from gas exchange, it enters the xxxx side of the heart. From here, xxxx of the heart propels the this blood to capillary beds in xxxx and xxxx throughout the body. At these areas, the blood diffuses xxxx and xxxx out of the blood to places of need. And finally, oxygen-xxxx blood returns to the xxxx | |
| 505446710 | mammals, reptiles, lungs, gas exchange | [PART OF DOUBLE CIRCULATION]
The pulmonary circuit is exhibited by xxxx and xxxx. The pulmonary circuit is the delivery of blood to the xxxx, where xxxx xxx that occurs. | |
| 505446711 | amphibians, lungs, skin, gas exchange | [PART OF DOUBLE CIRCULATION]
The pulmocutaneous circuit is exhibited by xxxx. The pulmocutaneous circuit is the delivery of blood to the xxxx AND xxxx, where xxxxx xxxx that occurs. | |
| 505446712 | decreases, heart, high, repressurizing, gas exchange, high, low | Remember, gas exchange significantly xxxxx blood pressure.The flow of blood in double circulation is driven by the xxxx, which maintains xxxx blood pressure by xxxxxx blood after it undergoes xxxx xxxxx. this makes the blood pressure xxxx after gas exchange occurs. In single circulation, blood pressure remains relatively xxxx after gas exchange and therefore progresses slowly to the rest of the body. |  |
| 505446713 | 3, 2, 1, ventricle, poor, right, pulmocutaneous, rich, left, systemic, lungs, skin | [HEART OF AMPHIBIAN]
Amphibians have a heart with xxx chambers (xxx atria, xxx ventricle). The xxxx pumps blood into a forked artery that splits oxygen-xxxxx blood from the xxxx atrium into the xxxxxx circuit & oxygen-xxxxx blood from the xxxx atrium into the xxxxx circuit. when the amphibian goes underwater, blood flow to the xxxx shuts off, and gas exchange in the xxxx initiates. |  |
| 505446714 | ... | [HEART OF A REPTILE]
Reptiles have 3 chambered hearts, with a septum partially dividing the ventricle into separate left and right chambers. However, alligators crocodiles and caimans have 4 chambered hearts |  |
| 505667546 | 4, completely, septum, rich, poor, oxygen | [HEART OF MAMMAL AND BIRDS]
Mammals and birds have a xxx chambered heart with a ventricle that is xxxx divided by a xxxxx, (making both a left and right ventricle and aorta) The left side of the heart receives and pumps only oxygen-xxxx blood, while the right side receives and pumps only oxygen-xxxx blood. Since mammals are endotherms, the larger heart helps them circulate more quantities of xxxxx for metabolic tasks |  |
| 505667547 | contraction, ventricle, lungs, pulmonary arteries, oxygen, carbon dioxide, rich, pulmonary veins, atrium, ventricle, aorta, coronary arteries, heart, forelimbs, abdominal organs, hind limbs, oxygen, carbon dioxide, poor, atrium, vein, superior vena cava, inferior vena cava, ventricle | [MAMMALIAN CIRCULATION]
Mammalian circulation begins when xxxx of the right xxxx pumps blood to the xxxx via the xxxxx xxxxx. as blood flows through capillary beds in the left and right lungs, it loads xxxxx and discharges xxxxx xxxx. oxygen-xxxx blood returns from the lungs via the xxxxxx xxxxx to the left xxxxx of the heart. Then, oxygen rich blood proceeds to the left xxxx. From there, the oxygen rich blood leaves via the xxxx. From here, the blood leaves the aorta via the xxxxx xxxx, which supplies the xxxx muscle with blood. From here the aorta sends blood to the capillary beds of the xxxx, then descends to the abdomen, supplying oxygen-rich blood to the capillary beds of xxxxxx xxxxx and xxxx xxxx. Within the capillaries, there is a net diffusion of xxxxx out of the blood and xxxxx xxxx into the blood. After diffusion, oxygen-xxxx blood from the forelimbs returns to right xxxx through a type of xxxx called the xxxx xxxx xxxx. oxygen-poor blood from the hindlimbs return to the right atrium of the heart via the xxxx xxxx xxx. Once at the right atrium, the blood returns to the right xxxxx and the process starts over |  |
| 505667548 | thin, returning, relaxes, thick, atria, left, right, equal | [DETAILED LOOK AT MAMMALIAN HEART]
The 2 atria of the human heart have relatively xxxx walls and serve as collection chambers for blood xxxx to the heart. Blood flows into the ventricles from the atria when the heart xxxxx. Ventricles have xxxx walls and contract more violently than the xxxx. The xxx ventricle contracts more than the xxxx because it must pump blood to the entire body. However both ventricles still pump xxxx amounts of blood. |  |
| 505667549 | ... | [RHYTHMIC BEATS OF HEART]
When a heart contracts, it pumps blood. When a heart relaxes, it takes in blood. | |
| 505667550 | ... | [RHYTHMIC BEATS OF HEART]
a cardiac cycle is one rhythmic cycle of heart contracting & relaxing. The contraction phase is known as the systole, and the relaxation phase is called the diastole. | |
| 505667551 | ... | Two factors determine cardiac output:
the rate of contraction (heart rate)
the amount of blood pumped by a ventricle in a single contraction (stroke volume) (average volume for human is 70ml) | |
| 505667552 | 4 | xxxx valves of tissue prevent backflow and keep blood moving in the correct direction. Each are made of flaps of connective tissue. The atrioventricular valve lies between each atrium and ventricle. These open when the atriums conctract, (pumping blood into the ventricles) and close when the ventricles contract,(preventing back flow of blood into atrium. The semilunar valve is located where blood leaves the heart (aorta of left ventricle, pulmonary artery of right ventricle) |  |
| 505667553 | backward, valve | A Heart murmor is the result of blood squirting xxxxx through a defective xxxx | |
| 506042305 | 72, .8, veins, AV valves, atrial, ventricles, ventricular, arteries, semilunar | [CARDIAC CYCLE]
A typical human heart has a rate of xxx beats per minutes and one complete cycle taking xxxx seconds. During a relaxation phase, blood returning from the large xxxx flows into the atria and ventricle through the xxxx xxx. Then a brief period of xxxxx contraction then forces all blood remaining in the atria into the xxxxx. During the remainder of the cycle, xxxxx contraction pumps blood into the large xxxx through xxxxx valves | |
| 506042306 | signal, nervous, the superior vena cava, right ventricle, sinoatrial node, rate, contract | cardiac contraction is autorhythmic, meaning they contract and relax repeatedly without any xxxx from the xxxxx system. A cluster of cells located where xxxx xxxxx xxxx meets the xxxxx xxxx called the xxxxxx xxxx, sets the xxxx and timing at which all cardiac muscle cells xxxx | |
| 506042307 | impulses, cardiac, gap junctions, heart, atria, contract, atrium, atrioventicular node, .1, atrias, ventricles, bundle branches, purkinje fibers | The sinoatrial node (SA) generates electrical xxxxx that act on xxxxx muscle cells. Since all cells are interconnected by xxxx xxxx, impulses given off by the SA node spread rapidly through xxxx tissue. First, the SA impulses causes both xxxx to xxxx in unison. Then the impulses reach another cluster of autorhythmic cells located between the left and right xxxxx called the xxxxx xxxx (AV). The AV node waits xxxx second so that the xxxxx can fully empty blood into the xxxxx and then conducts signals throughout the ventricular walls by specialized muscle fibers called xxxxxx xxxx and xxxxx xxxxx | |
| 506042308 | sinoatrial, 2, sympathetic, parasympathetic, hormones, temperature | Physiological cues alter heart tempo by regulating the xxxxx node. xxxx nerves are responsible for this. the xxxxx nerve increases heart rate. the xxxxx nerve decreases heart rate. heart rate can also be affected by secretions of xxxxx and body xxxx | |
| 506042309 | edothelium, single, epithelial, | Blood vessels contain a central lumen lined with an xxxxx (xxxx layer of flattened xxxxx cells) | |
| 506042310 | small, 2, diffusion | Capillaries have a very xxxx diamter and only consists of xxx layers (which facilitates the rate of xxxxx of substances between the blood and interstitial fluid) | |
| 506042311 | connective, elastic, stretch, smooth, elastic | Arteries and Veins have an endothelium that have the 2 layers of tissue surrounding it. (an outer layer of xxxxx tissue containing xxxx fibers which allow the vessel to xxxx and recoil, and a middle layer of xxxx muscle also made of xxxx fibers | |
| 506042312 | larger, pressures, velocity, blood pressure, nervous, hormones | Arteries have a xxxx diameter than veins because they must pump blood at high xxxxx and xxxxx. the elastic recoil of arteries help maintain xxxxx xxxx when heart relaxes. Blood flow of arteries is controlled by signals in the xxxx system and xxxx secreted into the blood stream |  |
| 506042313 | smaller, pressure, velocity | Veins have a xxxx diameter than arteries because they convey blood back to the heart at a low xxxx and xxxxx |  |
| 506042314 | smaller, increase, decreases, pressure, velocity, diffusion | capillaries (where gas exchange occurs) have a xxxxx diameter than arteries, so one would expect the pressure in this area to xxxxx when blood coming from an artery reaches the capillaries. However, the pressure in capillaries xxxx because there are so many capillaries that the blood is distributed out to where the xxxx and xxxxx of the blood flow decreases. The decrease in velocity allows adequate xxxx of substances into the blood stream. | |
| 506042315 | capillaries | diffusion and transfer of substances in the blood only occurs in the xxxxx | |
| 506042316 | high, low | blood flows from areas of xxx pressure to areas of xxxx pressure | |
| 506042317 | ventricular, ventricular, decrease, pressure | Arterial blood pressure is highest when the heart contracts during xxxxxx contraction (systolic pressure). The huge rush of blood into the arteries causes the arteries to xxxxx in diameter to facilitate the flow of blood without bursting. When the heart relaxes, arteries xxxx in diameter to maintain significant xxxxx to pump blood to the capillary beds | |
| 506042318 | increases, decreasing | Vasoconstriction xxxxx blood pressure by xxxx the diameter of the arteries. can occur as the result of hormonal secretion | |
| 506042319 | decreases, increasing | vasodialation xxxx blood pressure by xxxxx the diameter of the arteries | |
| 506042320 | increase, oxygen, high, increase | physical exertion causes an xxxxxxx in the diameter of arteries to facilitate the diffusion of xxxxx to muscles, however xxxx pressure is maintained by an xxxx in heart rate | |
| 506042321 | 120, 70 | the normal blood pressure for a human is xxx mmhg at contraction and xxxx mmhg at relaxation | |
| 506042322 | smooth, skeletal, upward, inhalation, veins, increase, | blood returning to the heart from the legs must combat not only low pressure but gravity. factors that combat this are contraction of xxxx muscles, xxxxx muscles (moves blood xxxx) and xxxxx(which causes xxxxx to xxxxx in diameter to fill with blood) | |
| 506042323 | brain, heart, kidney, liver | The organs that capillaries must supply with blood at all times are the xxxxx, xxxx, xxxxx, and xxxx | |
| 506042324 | temperature, increases | Blood flow to skin is variable and regulated to control xxxxx. Blood flow to the digestive tract xxxx after a meal | |
| 506042325 | smooth, decreases, increases, sphincters | Capillaries do not have xxxx muscles so must be aided in altering the flow of blood. contraction of the smooth muscle in the wall of arteriole xxxxx the amount of blood flow into the capillary beds. dialation of smooth muscle in the wall of arteriole xxxxx the amount of blood flow into the capillary beds. Another tactic involves precapillary xxxxxx, which open and close in response to signals | 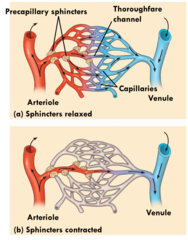 |
| 506042326 | nerve, hormones, chemicals | Signals that regulate blood flow include xzxxxx impulses, xxxxx in the blood stream, and xxxxx produced locally. | |
| 506042327 | histimine, relaxation, increasing | the chemical xxxxx is released by cells at a wound site, causing smooth muscle xxxx, xxxxx blood flow | |
| 506431810 | won't, will | [DIFFUSION OF CAPILLARIES]
When the blood pressure of the capillaries is higher than the osmotic pressure of the interstitial fluid then diffusion into the capillaries xxxx occur. When the blood pressure of the capillaries is lower than the osmotic pressure of the interstitial fluid then diffusion into the capillaries xxxx occur. |  |
| 506431811 | lymphatic, lymph, contractions, walls, skeletal, veins, circulatory, valves | Lost fluid and proteins return to the blood via the xxxx system. Fluid and proteins from the capillaries diffuse into the lymphatic system as a kind of fluid called xxxxx. The lymphatic system moves lymph with the help of rhythmic xxxx of vessel xxxxx and xxxxx muscles and then proceed to drain the lymph into large xxxxx of the xxxxx system at the base of the neck. lymph vessels have specialized xxxx to ensure no backflow of fluid into the lymphatic vessels | |
| 506431812 | organ, immunity, filtering, viruses, bacteria | lymph nodes are a type of xxxxx that play a big role in the body's xxxxx by xxxxx lymph and housing cells that attack xxxx and xxxx | |
| 506431813 | connective, liquid, plasma | Vertebrate blood is actually a type of xxxxx tissue of cells suspended in a xxxxx matrix called xxxxx | |
| 506863347 | salts, ions, electrolytes, buffers, osmotic | Blood plasma contains many inorganic xxxx in the form of dissolved xxxx referred to as blood xxxx. these act as pH xxxxx to maintain the blood pH of 7.4. Salts are also important in maintaining xxxxx balance of the blood. | |
| 506863348 | buffers, osmotic, lipids, clotting, viscosity | Blood plasma contains many proteins that act as pH xxxx, help maintain xxxxx balance, help provide passage for xxxx, help plug leaks in injured vessels by acting as xxxx factors, and contribute to blood's xxxxx | |
| 506863349 | protein, viruses | Antibodies are a type of blood plasma xxxxx that help combat xxxx and other foreign agents that invade the body | |
| 506863350 | erythrocytes, oxygen, hemoglobin, oxygen, nuclei, mitochondria, anaerobically | xxxxxx (Red blood cells) transport xxxxx. contain xxxxx (iron containing compound that transfers xxxxx ), lack xxxxx and a xxxx and generate ATP xxxxx | |
| 506863351 | defense | Leukocytes (white blood cells) function in xxxx | |
| 506863352 | bone marow, clotting, nuclei | Platelets are a fragments of xxxx xxxx cells part of blood that function in xxxx. lack a xxxxx | |
| 506863353 | 250, 4 | 1 red blood cell houses xxxx million hemoglobin, and each hemoglobin carries xxxx oxygen molecules | |
| 506863354 | endothelium, connective, blood, platelets, collagen, prothrombin, thrombin, enzyme, fibrinogen, fibrin | [BLOOD CLOTTING]
Blood clotting initiates when xxxxxx of a vessel is damaged, exposing xxxx tissue in the vessel wall to xxxx. xxxx adhere to the xxxxx and form a seal to prevent leaking. Clotting converts a plasma protein called xxxxx to its active form, xxxx. Thrombin is an xxxx that converts the sealant (xxxx) to xxxx |  |
| 506863355 | clot | Hemophillia is a genetic mutation that is characterized by excessive bleeding and bruising from inability of blood to effectively xxxxx. | |
| 506863356 | clot, blood | A thrombus is the formation of a xxxx within a blood vessel, blocking the flow of xxxx | |
| 506863357 | erythrocytes, leukocytes, platelets | xxxxxx, xxxxx and xxxx all develop from stem cells | |
| 506863358 | Negative, erythrocyte, oxygen, Kidneys, erythropoietin, erythrocyte | xxxxx feed-back system controls xxxxx production based on the amount of xxxxxx reaching body tissues
If oxygen levels are low, the xxxxx secrete the hormone xxxxxx (EPO) that stimulates xxxxx production | |
| 506863359 | hemoglobin, erythropoietin | Anemia is a condition that is characterized by xxxxxx deficiency. This can be treated by injecting the hormone xxxxx (EPO) into the persons blood | |
| 506863360 | cardiovascular, plaque, arteries | Atherosclerosis is a xxxxxx disease caused by a buildup of xxxxx within xxxx |  |
| 506863361 | cardiac muscle, coronary arteries | A heart attack is the damage of death of xxxxx xxxx resulting from blockage of one or more xxxxxx xxxxx | |
| 506863362 | nervous, brain, oxygen, arteries, head | A stroke is the death of xxxx tissue in the xxxx due to lack of xxxx. result from the rupture or blockage of xxxxxx in the xxxx | |
| 506863363 | cholesterol, increases, decreases, statin | A major contributor to atherosclerosis is xxxxxx. low-density lipoproteins xxxxx the amount of plaque in arterial walls. high-density lipoproteins xxxxx the amount of plaque in arterial walls. The drug xxxx lowers LDL levels. | |
| 506863364 | high, heart attack, stroke, plaque, endothelium, 140, 90 | hypertension (xxxx blood pressure) is another contributor to xxxx xxx and xxxxx by promoting xxxxx formation in arteries by damaging the xxxxx that lines the arteries. increases systolic pressure above xxxxx mmHg and increases diastolic pressure above xxxx mmHg | |
| 506863365 | atherosclerosis, thrombus, aspirin, CRP | Inflammation is a contributor to xxxxxx and xxxx formation. can be combated with the drug xxxx. the protein xxxx also lowers the amount of inflammation | |
| 506863366 | air | Partial pressure of gas in solution equals the partial pressure of gas in xxxx. The concentration of a gas in the solution is not the same as the amount in the air however | |
| 506863367 | high, low | Gas diffuses from a region of xxxx partial pressure to a region of xxxx partial pressure | |
| 506863368 | parapoida, gills | many polychaetes have a pair of flattened appendages called xxxxxx. the parapoida function as xxxxx |  |
| 506863369 | ... | Crayfish have long feathery gills covered by the exoskeleton. specialized body appendages drive water over the surface of the gills |  |
| 506863370 | skin, feet | the gills of a sea star are tubular projections of the xxxx. its tube xxxx also function in gas exchange |  |
| 506863371 | mouth, 2, gill, lamellae, blood, lamellae, oxygen | Fish pumps water across its gills by opening its xxxx. each gill possesses xxxx rows of xxxxx filaments, composed of flattened plates called xxxxx. xxxx flowing through capillaries within the the xxxxx picks up xxxxx from the water | |
| 506863372 | oxygen, opposite | The countercurrent flow allows aquatic fish to maximize diffusion of xxxx into the blood by having water flow across the fish's gills in the xxxxx direction in which the blood of the fish is |  |























