Flashcards
Flashcards
Flashcards
Flashcards
Flashcards
AP World History (Summer Vocabulary) Flashcards
| 13638650512 | Empire | an extensive group of states or countries under a single supreme authority, formerly especially an emperor or empress. | 0 | |
| 13638652395 | nation-state | a sovereign state whose citizens or subjects are relatively homogeneous in factors such as language or common descent. | 1 | |
| 13693990856 | Domestication | the taming of animals for human use, such as work or as food | 2 | |
| 13694000858 | Agricultural Revolution | The time when human beings first domesticated plants and animals and no longer relied entirely on hunting and gathering | 3 | |
| 13694003977 | Aristocracy | A government in which power is in the hands of a hereditary ruling class or nobility | 4 | |
| 13694011429 | Hinduism | A religion and philosophy developed in ancient India, characterized by a belief in reincarnation and a supreme being who takes many forms | 5 | |
| 13694015828 | Darma | doing one's moral duty in this life so that the soul can advance in the next life | 6 | |
| 13694313694 | cultural diffusion | The spread of ideas, customs, and technologies from one people to another | 7 | |
| 13694322397 | Syncretism | The unification or blending of opposing people, ideas, or practices, frequently in the realm of religion. | 8 | |
| 13694331703 | Dynastic Cycle | rise and fall of Chinese dynasties according to the Mandate of Heaven | 9 | |
| 13694335395 | eglitarian | Believing in the equality of all peoples | 10 | |
| 13694339564 | patriarchy | Assumes that society should be male-dominated society and doesn't allow women to hold upper-tier jobs. | 11 | |
| 13694356732 | irrigation | Supplying land with water through a network of canals | 12 | |
| 13694367607 | Specialization of Labor | Focusing work effort on a particular product or a single task | 13 | |
| 13694380945 | monogamy/polygamy | Marriage to one person/ marriage to several people at once | 14 | |
| 13694396109 | Theocracy | A government controlled by religious leaders | 15 | |
| 13694400474 | ancestor worship | honoring ancestors through rituals, such as offering food and wine to the dead | 16 | |
| 13694426199 | Bodhisattva | a person who has attained enlightenment but who has postponed nirvana in order to help others achieve enlightenment | 17 | |
| 13694429924 | Siddhartha Gautama | Founder of Buddhism | 18 | |
| 13694433548 | Four Noble Truths | 1) All life is full of suffering, pain, and sorrow. 2) The cause of suffering is nonvirtue, or negative deeds and mindsets such as hated and desire. 3) The only cure for suffering is to overcome nonvirture. 4) The way to overcome nonvirtue is to follow the Eightfold Path | 19 | |
| 13694441170 | Castes System | A complex social group system in India into which people are born and from they cannot change. | 20 | |
| 13694465560 | Confucianism | A philosophy that adheres to the teachings of the Chinese philosopher Confucius. It shows the way to ensure a stable government and an orderly society in the present world and stresses a moral code of conduct. | 21 | |
| 13694474356 | Dao (Tao) | Mean "the way" of nature. Let it take its course in the world. Inaction. | 22 | |
| 13694483153 | Diaspora | A dispersion of people from their homeland | 23 | |
| 13694487203 | Filal Piety | respect shown by children for their parents and elders | 24 | |
| 13694490863 | Hellenistic Culture | Greek culture blended with Egyptian, Persian and Indian ideas, as a result of Alexander the Great's Empire. | 25 | |
| 13694508362 | Silk Road | An ancient trade route between China and the Mediterranean Sea extending some 6,440 km (4,000 mi) and linking China with the Roman Empire. | 26 | |
| 13694520928 | Missionary | An individual who helps to diffuse a universalizing religion. | 27 | |
| 13694529065 | monastery | A place where communities of monks live lives of devotion to God in isolation from the outside world | 28 | |
| 13694539647 | Reincarnation | In Hinduism and Buddhism, the process by which a soul is reborn continuously until it achieves perfect understanding | 29 | |
| 13694547339 | Republic | A form of government in which citizens choose their leaders by voting | 30 | |
| 13694556552 | Universalizing Religion | A religion that attempts to appeal to all people, not just those living in a particular location. | 31 | |
| 13694566563 | Sanskrit | an Indo-European, Indic language, in use since c1200 b.c. as the religious and classical literary language of India. | 32 | |
| 13694602473 | Black Death | The common name for a major outbreak of plague that spread across Asia, North Africa, and Europe in the mid-fourteenth century, carrying off vast numbers of persons. | 33 | |
| 13694605949 | Mongols | A people of this name is mentioned as early as the records of the Tang Empire, living as nomads in northern Eurasia. After 1206 they established an enormous empire under Genghis Khan, linking western and eastern Eurasia. | 34 | |
| 13694610540 | Bushido | The Feudal Japanese code of honor among the warrior class. | 35 | |
| 13694615012 | Caliphate | Islamic empire ruled by those believed to be the successors to the Prophet Muhammad. | 36 | |
| 13694618455 | Muhammad | Founder of Islam | 37 | |
| 13694623542 | Constantine | Emperor of Rome who adopted the Christian faith and stopped the persecution of Christians (280-337). Later became the emperor of the Byzantine Empire. | 38 | |
| 13694637001 | Chinampas | Raised fields constructed along lake shores in Mesoamerica to increase agricultural yields. | 39 | |
| 13694647695 | Civil Service Exam | In Imperial China starting in the Han dynasty, it was based on Confucian teachings that was used to select people for various government service jobs in the nationwide administrative bureaucracy. | 40 | |
| 13694654495 | Dar al-Islam | an Arabic term that means the "house of Islam" and that refers to lands under Islamic rule | 41 | |
| 13694660891 | Gunpowder | The formula, brought to China in the 400s or 500s, was first used to make fumigators to keep away insect pests and evil spirits. In later centuries it was used to make explosives and grenades and to propel cannonballs, shot, and bullets. | 42 | |
| 13694663266 | Feudalism | A political system in which nobles are granted the use of lands that legally belong to their king, in exchange for their loyalty, military service, and protection of the people who live on the land | 43 | |
| 13694681428 | Fiefs | pieces of land given to vassals by their lord | 44 | |
| 13694683771 | gentry | A general term for a class of prosperous families, sometimes including but often ranked below the rural aristocrats. | 45 | |
| 13694691341 | Griots | Professional oral historians who served as keepers of traditions and advisors to kings within the Mali Empire | 46 | |
| 13694693897 | Gold-Salt Trade | Gold and salt made up trade and wealth in the African kingdoms because the Europeans wanted gold, and the Africans needed salt | 47 | |
| 13694700076 | Hajj | A pilgrimage to Mecca, performed as a duty by Muslims | 48 | |
| 13694703653 | kowtow | a former Chinese custom of touching the ground with the forehead as a sign of respect or submission | 49 | |
| 13694707654 | Manorialism | Economic system during the Middle Ages that revolved around self-sufficient farming estates where lords and peasants shared the land. | 50 | |
| 13694713882 | Neoconfucianism | term that describes the resurgence of Confucianism and the influence of Confucian scholars during the T'ang Dynasty; a unification of Daoist or Buddhist metaphysics with Confucian pragmatism | 51 | |
| 13694719604 | Papcy | The pope of the Catholic and Western Roman church. The papacy was viewed as the leader of the bishops and was more like a pyramid, with the pope at the top | 52 | |
| 13694722650 | Great Schism of 1054 | The separation between the Roman Catholic Church and the Eastern Orthodox Church | 53 | |
| 13694729923 | Christendom | The Church's sphere of power and authority, both politically and spiritually, during the Middle Ages. | 54 | |
| 13694734121 | Quipu | An arrangement of knotted strings on a cord, used by the Inca to record numerical information. | 55 | |
| 13694738139 | Samurai | Class of warriors in feudal Japan who pledged loyalty to a noble in return for land. | 56 | |
| 13694740874 | Serfs/Peasants | * Lowest class of Feudalism * The people who "worked" the lands but had to give the Lords the majority of the profits from the land | 57 | |
| 13694755761 | Shia Islam | minority branch of Islam; belief that only a descendant of Muhammad can be caliph. | 58 | |
| 13694768477 | Sunni Muslims | Majority of the Muslims; believe successor of Muhammad can be an elected caliph. | 59 | |
| 13694772906 | Sufi | The branch of Islam that believes in a more mystical connection with Allah. | 60 | |
| 13694778757 | Swahili city-states | Waring states that were always competing for control of trade routes and each other. Many of these city-states were Muslim and very cosmopolitan. | 61 | |
| 13694792498 | terrace | a raised, flat mound of earth (dirt) that looks like a platform with sloping sides | 62 | |
| 13694797775 | tribute system | Chinese method of dealing with foreign lands and peoples that assumed the subordination of all non-Chinese authorities and required the payment of tribute—produce of value from their countries—to the Chinese emperor (although the Chinese gifts given in return were often much more valuable). | 63 | |
| 13694824242 | 32 CE | Beginnings of Christianity | 64 | |
| 13694831357 | 333 CE | Roman capital moved to Constantinople | 65 | |
| 13694835109 | 4th century CE | Beginning of Trans-Saharan Trade Routes | 66 | |
| 13694854857 | 476 CE | Fall of Rome | 67 | |
| 13694862220 | 527 CE | Justinian rule of Byzantine Empire | 68 | |
| 13694880870 | 622 CE | Founding of Islam | 69 | |
| 13694885068 | 730 CE | Printing invented in China | 70 | |
| 13694896176 | 900 CE | Decline of classical Maya | 71 | |
| 13694909857 | 1066 CE | Norman conquest of England | 72 | |
| 13694909858 | 1095 CE | 1st Crusade | 73 | |
| 13694919381 | 1206 CE | Chinggis Khan begins Mongol conquests | 74 | |
| 13694944366 | 1054 CE | East-West Great Schism in Christian Church | 75 | |
| 13694948458 | Excommunication | Banishment from the church | 76 | |
| 13694958477 | 1258 CE | Mongols sack Baghdad | 77 | |
| 13694965500 | 1271-1295 | Marco Polo's travels | 78 | |
| 13694968612 | 1279-1368 | Yuan (Mongol) Dynasty in China | 79 |
Terminology for AP Language and Composition Flashcards
| 10060955576 | Alliteration | The repetition of the same sound or letter at the beginning of consecutive words or syllables. |  | 0 |
| 10060959988 | Allusion | An indirect reference, often to another text or an historic event. |  | 1 |
| 10060981438 | Analogy | An extended comparison between two seemingly dissimilar things. |  | 2 |
| 10060987302 | Anaphora | The repetition of words at the beginning of successive clauses. |  | 3 |
| 10061030676 | Anecdote | A short account of an interesting event. |  | 4 |
| 10061049341 | Annotation | Explanatory or critical notes added to a text. |  | 5 |
| 10061051561 | Antecedent | The noun to which a later pronoun refers. |  | 6 |
| 10061089481 | Antimetabole | The repetition of words in an inverted order to sharpen a contrast. |  | 7 |
| 10061108608 | Antithesis | Parallel structure that juxtaposes contrasting ideas. |  | 8 |
| 10061110140 | Aphorism | A short, astute statement of a general truth. |  | 9 |
| 10061115206 | Appositive | A word or phrase that renames a nearby noun or pronoun. |  | 10 |
| 10061117113 | Archaic diction | The use of words common to an earlier time period; antiquated language. |  | 11 |
| 10061125155 | Argument | A statement put forth and supported by evidence. |  | 12 |
| 10061132066 | Aristotelian triangle | A diagram that represents a rhetorical situation as the relationship among the speaker, the subject, and the audience. |  | 13 |
| 10061135787 | Assertion | An emphatic statement; declaration. An assertion supported by evidence becomes an argument. |  | 14 |
| 10061142833 | Assumption | A belief or statement taken for granted without proof. |  | 15 |
| 10061146234 | Asyndeton | Leaving out conjunctions between words, phrases, clauses. |  | 16 |
| 10061156969 | Attitude | The speaker's position on a subject as revealed through his or her tone. |  | 17 |
| 10061159182 | Audience | One's listener or readership; those to whom a speech or piece of writing is addressed. |  | 18 |
| 10061161445 | Authority | A reliable, respected source—someone with knowledge. |  | 19 |
| 10061163505 | Bias | Prejudice or predisposition toward one side of a subject or issue. |  | 20 |
| 10061166874 | Cite | Identifying a part of a piece of writing as being derived from a source. |  | 21 |
| 10061171280 | Claim | An assertion, usually supported by evidence. |  | 22 |
| 10061173910 | Close reading | A careful reading that is attentive to organization, figurative language, sentence structure, vocabulary, and other literary and structural elements of a text. |  | 23 |
| 10061178334 | Colloquialism | An informal or conversational use of language. |  | 24 |
| 10061180576 | Common ground | Shared beliefs, values, or positions. |  | 25 |
| 10061182197 | Complex sentence | A sentence that includes one independent clause and at least one dependent clause. |  | 26 |
| 10061185154 | Concession | A reluctant acknowledgment or yielding. |  | 27 |
| 10061186920 | Connotation | That which is implied by a word, as opposed to the word's literal meaning. |  | 28 |
| 10061189480 | Context | Words, events, or circumstances that help determine meaning. |  | 29 |
| 10061191603 | Coordination | Grammatical equivalence between parts of a sentence, often through a coordinating conjunction such as and, or but. |  | 30 |
| 10061201671 | Counterarugment | A challenge to a position; an opposing argument. Ex: almost like an argument of an issue from the other side/perspective. | 31 | |
| 10061203171 | Cumulative sentence | An independent clause followed by subordinate clauses or phrases that supply additional detail. |  | 32 |
| 10061207873 | Declarative sentence | A sentence that makes a statement. |  | 33 |
| 10061211067 | Deduction | Reasoning from general to specific. |  | 34 |
| 10061212838 | Denotation | The literal meaning of a word; its dictionary definition. |  | 35 |
| 10061220232 | Diction | Word choice. |  | 36 |
| 10061221685 | Documentation | Bibliographic information about the sources used in a piece of writing. |  | 37 |
| 10061224027 | Elegiac | Mournful over what has passed or been lost; often used to describe tone. |  | 38 |
| 10061233506 | Epigram | A brief witty statement. |  | 39 |
| 10061233507 | Ethos | A Greek term referring to the character of a person; one of Aristotle's three rhetorical appeals (see logos and pathos). |  | 40 |
| 10061262888 | Figuative language | The use of tropes or figures of speech; going beyond literal meaning to achieve literary effect. Ex: The grass looks like spiky green hair | 41 | |
| 10061269011 | Figure of speech | An expression that strives for literary effect rather than conveying a literal meaning. |  | 42 |
| 10061269012 | Hyperbole | Exaggeration for the purpose of emphasis. |  | 43 |
| 10061279041 | Imagery | Vivid use of language that evokes a reader's senses (sight, smell, taste, touch, hearing). |  | 44 |
| 10061282941 | Imperative sentence | A sentence that requests or commands. |  | 45 |
| 10061288235 | Induction | Reasoning from specific to general. |  | 46 |
| 10061292120 | Inversion | A sentence in which the verb precedes the subject. Ex: Where in the world were you? | 47 | |
| 10061296385 | Irony | A contradiction between what is said and what is meant; incongruity between action and result. |  | 48 |
| 10061300359 | Juxtaposition | Placement of two things side by side for emphasis. |  | 49 |
| 10061311420 | Logos | A Greek term that means "word"; an appeal to logic; one of Aristotle's three rhetorical appeals (see ethos and pathos) . |  | 50 |
| 10061312941 | Metaphor | A figure of speech or trope through which one thing is spoken of as though it were something else, thus making an implicit comparison. |  | 51 |
| 10061227447 | Metonymy | Use of an aspect of something to represent the whole. Ex: The pen is mightier than the sword. | 52 | |
| 10061227448 | Occasion | An aspect of context; the cause or reason for writing. Ex: Whether or not you like it, I am going to eat the cake. | 53 | |
| 10061317989 | Oxymoron | A figure of speech that combines two contradictory terms. |  | 54 |
| 10061320068 | Paradox | A statement that seems contradictory but is actually true. |  | 55 |
| 10061322813 | Parallelism | The repetition of similar grammatical or syntactical patterns. Ex: I Have a Dream speech by Dr. Luther King Jr. | 56 | |
| 10061325603 | Parody | A piece that imitates and exaggerates the prominent features of another; used for comic effect or ridicule. |  | 57 |
| 10061328632 | Pathos | A Greek term that refers to suffering but has come to be associated with broader appeals to emotion; one of Aristotle's three rhetorical appeals (see ethos and logos). |  | 58 |
| 10061330994 | Persona | The speaker, voice, or character assumed by the author of a piece of writing. |  | 59 |
| 10061333053 | Personification | Assigning lifelike characteristics to inanimate objects. |  | 60 |
| 10061334453 | Polemic | An argument against an idea, usually regarding philosophy, politics, or religion. |  | 61 |
| 10061337336 | Polysyndeton | The deliberate use of a series of conjunctions. |  | 62 |
| 10061339203 | Premise | major, minor two parts of a syllogism. The concluding sentence of a syllogism takes its predicate from the major premise and its subject from the minor premise. Major premise: All mammals are warm-blooded. Minor premise: All horses are mammals. |  | 63 |
| 10061344489 | Conclusion | All horses are warm-blooded (see syllogism). |  | 64 |
| 10061346618 | Propaganda | A negative term for writing designed to sway opinion rather than present information. |  | 65 |
| 10061354575 | Purpose | One's intention or objective in a speech or piece of writing. |  | 66 |
| 10061356975 | Refute | To discredit an argument, particularly a counterargument. |  | 67 |
| 10061359455 | Rhetoric | The study of effective, persuasive language use; according to Aristotle, use of the "available means of persuasion." |  | 68 |
| 10061362389 | Rhetorical modes | Patterns of organization developed to achieve a specific purpose; modes include but are not limited to narration, description, comparison and contrast, cause and effect, definition, exemplification, classification and division, process analysis, and argumentation. |  | 69 |
| 10061364472 | Rhetorical question | A question asked more to produce an effect than to summon an answer. |  | 70 |
| 10061366509 | Rhetorical triangle | A diagram that represents a rhetorical situation as the relationship among the speaker, the subject, and the audience |  | 71 |
| 10061369177 | Satire | An ironic, sarcastic, or witty composition that claims to argue for something, but actually argues against it. |  | 72 |
| 10061371083 | Scheme | A pattern of words or sentence construction used for rhetorical effect. |  | 73 |
| 10061372994 | Scheme patterns | The arrangement of independent and dependent clauses into known sentence constructions—such as simple, compound, complex, or compound-complex. |  | 74 |
| 10061379517 | Sentence variety | Using a variety of sentence patterns to create a desired effect. |  | 75 |
| 10061382265 | Simile | A figure of speech that uses "like" or "as" to compare two things. |  | 76 |
| 10061388331 | Simple sentence | A statement containing a subject and predicate; an independent clause. |  | 77 |
| 10061395000 | Source | A book, article, person, or other resource consulted for information. |  | 78 |
| 10061397122 | Speaker | A term used for the author, speaker, or the person whose perspective (real or imagined) is being advanced in a speech or piece of writing. |  | 79 |
| 10061399569 | Straw man | A logical fallacy that involves the creation of an easily refutable position; misrepresenting, then attacking an opponent's position. |  | 80 |
| 10061402366 | Style | The distinctive quality of speech or writing created by the selection and arrangement of words and figures of speech. Ex: argumentative, narrative, persuasive, descriptive styles | 81 | |
| 10061404027 | Subject | In rhetoric, the topic addressed in a piece of writing. |  | 82 |
| 10061406914 | Subordinate clause | Created by a subordinating conjunction, a clause that modifies an independent clause. |  | 83 |
| 10061409139 | Subordination | The dependence of one syntactical element on another in a sentence. |  | 84 |
| 10061411161 | Syllogism | A form of deductive reasoning in which the conclusion is supported by a major and minor premise (see premise; major, and minor). Ex: Major- All women like to shop. | 85 | |
| 10061412913 | Synthesize | Combining or bringing together two or more elements to produce something more complex. |  | 86 |
| 10061412914 | Thesis | The central idea in a work to which all parts of the work refer. |  | 87 |
| 10061414687 | Thesis statement | A statement of the central idea in a work, may be explicit or implicit. |  | 88 |
| 10061417261 | Tone | The speaker's attitude toward the subject or audience. |  | 89 |
| 10061419400 | Topic sentence | A sentence, most often appearing at the beginning of a paragraph, that announces the paragraph's idea and often unites it with the work's thesis. |  | 90 |
| 10061419401 | Trope | Artful diction; the use of language in a nonliteral way; also called a figure of speech. |  | 91 |
| 10061421886 | Understatement | Lack of emphasis in a statement or point; restraint in language often used for ironic effect. |  | 92 |
| 10061423715 | Voice | In grammar, a term for the relationship between a verb and a noun (active or passive voice). In rhetoric, a distinctive quality in the style and tone of writing. |  | 93 |
| 10061425335 | Zeugma | A construction in which one word (usually a verb) modifies or governs—often in different, sometimes incongruent ways—two or more words in a sentence. |  | 94 |
| 10062399431 | Syntax | Sentence structure. |  | 95 |
AP Psych: Module 12 Flashcards
| 15302791974 | cerebral cortex | The intricate fabric of interconnected neural cells covering the cerebral hemispheres; the body's ultimate control and information-processing center. | 0 | |
| 15302791975 | 4 lobes of cerebral cortex | Frontal, parietal, occipital, temporal | 1 | |
| 15302791976 | Frontal lobe | Lying just behind the forehead; involved in speaking and muscle movements and in making plans and judgments | 2 | |
| 15302791977 | parietal lobe | Lying at the top of the head and toward the rear; receives sensory input for touch and body position | 3 | |
| 15302810366 | occipital lobe | A region of the cerebral cortex that processes visual information | 4 | |
| 15302836710 | temporal lobe | A region of the cerebral cortex responsible for hearing and language. | 5 | |
| 15302848811 | motor cortex | area at the rear of the frontal lobes that controls voluntary movements | 6 | |
| 15302857179 | somatosensory cortex | area at the front of the parietal lobes that registers and processes body touch and movement sensations | 7 | |
| 15302887751 | glial cells | support, nourish, and protect neurons (has a role in learning and thinking) | 8 | |
| 15302932004 | body parts that require precise control or those that are particularly sensitive... | occupy the greatest amount of space in the motor cortex and somatosensory cortex, respectively. | 9 | |
| 15302947808 | association areas | make up 85% of the brain. Integrates information involved in learning, remembering, thinking, and other higher-level functions. | 10 | |
| 15303016642 | Our mental experiences arise from... | coordinated brain activity | 11 | |
| 15303023109 | brain plasticity | The capacity for the brain to alter its structure and function. | 12 | |
| 15303033686 | if one hemisphere is damaged early in life... | the other will pick up many of its functions by reorganizing or building new pathways. | 13 | |
| 15303049026 | neurogensesis | the formation of new neurons | 14 | |
| 15303057566 | cognitive neural prosthetics | those with paralyzed limbs or amputation may be able to use their brain signals to control computers and robotic limbs | 15 |
AP World History Geographical Regions Flashcards
| 14794848158 | North America |  | 0 | |
| 14794848159 | Caribbean |  | 1 | |
| 14794848160 | Latin America |  | 2 | |
| 14794848161 | Mexico |  | 3 | |
| 14794848162 | North Africa | 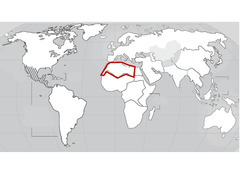 | 4 | |
| 14794848163 | West africa |  | 5 | |
| 14794848164 | East Africa |  | 6 | |
| 14794848165 | Central Africa |  | 7 | |
| 14794848166 | Southern Africa |  | 8 | |
| 14794848167 | Central Asia |  | 9 | |
| 14794848168 | Middle East |  | 10 | |
| 14794848169 | South Asia |  | 11 | |
| 14794848170 | East Asia |  | 12 | |
| 14794848171 | Europe |  | 13 | |
| 14794848172 | Oceania |  | 14 | |
| 14794848173 | Southeast Asia |  | 15 |
Pages
Need Help?
We hope your visit has been a productive one. If you're having any problems, or would like to give some feedback, we'd love to hear from you.
For general help, questions, and suggestions, try our dedicated support forums.
If you need to contact the Course-Notes.Org web experience team, please use our contact form.
Need Notes?
While we strive to provide the most comprehensive notes for as many high school textbooks as possible, there are certainly going to be some that we miss. Drop us a note and let us know which textbooks you need. Be sure to include which edition of the textbook you are using! If we see enough demand, we'll do whatever we can to get those notes up on the site for you!

