AP Psychology Chapter 13 Flashcards
| 9282235770 | Personality | An individual's characteristic pattern of thinking, feeling, and acting. Example: Type A and Type B personality Approach: Psychodynamic |  | 0 |
| 9282235771 | Free Association | In psychoanalysis, a method of exploring the unconscious in which the person relaxes and says whatever comes to mind, no matter how trivial or embarrassing. Example: I'll say a word and you have to say the first word that comes to mind. Approach: Psychodynamic |  | 1 |
| 9282235772 | Psychoanalysis | Freud's theory of personality that attributes thoughts and actions to unconscious motives and conflicts; the techniques used in treating psychological disorders by seeking to expose and interpret unconscious tensions. Example: Id, ego, superego Approach: Psychodynamic |  | 2 |
| 9282235773 | Unconscious | According to Freud, a reservoir of mostly unacceptable thoughts, wishes, feelings, and memories. According to contemporary psychologists, information processing of which we are unaware. Example: Psychoanalysis Approach: Psychodynamic |  | 3 |
| 9282235774 | Id | Contains a reservoir of unconscious psychic energy that, according to Freud, strives to satisfy basic sexual and aggressive drives. The id operates on the pleasure principle, demanding immediate gratification. Example: Immediate desires Approach: Psychodynamic |  | 4 |
| 9282235775 | Ego | The largely conscious, "executive" part of personality that, according to Freud, mediates among the demands of the id, superego, and reality. The ego operates on the reality principle, satisfying the id's desires in ways that will realistically bring pleasure rather than pain. Example: Conscious brain, reality Approach: Psychodynamic |  | 5 |
| 9282235776 | Superego | The part of the personality in Freud's theory that is responsible for making moral choices. Example: Idealism Approach: Psychodynamic |  | 6 |
| 9282235777 | Psychosexual Stages | The childhood stages of development (oral, anal, phallic, latency, genital) during which, according to Freud, the id's pleasure-seeking energies focus on distinct erogenous zones. Example: Oral, anal, phallic, latency, genital Approach: Evolutionary |  | 7 |
| 9282235778 | Oedipus Complex | According to Freud, a boy's sexual desires toward his mother and feelings of jealousy and hatred for the rival father. example: Mother complex Approach: Evolutionary |  | 8 |
| 9282235779 | Identification | The process by which, according to Freud, children incorporate their parents' values into their developing superegos. example: Boy/girl tries to be like father/mother Approach: Sociocultural |  | 9 |
| 9282235780 | Fixation | According to Freud, a lingering focus of pleasure-seeking energies at an earlier psycho sexual stage, in which conflicts were unresolved. Example: Unmovable, doesn't mature. Approach: Psyodynamic |  | 10 |
| 9282235781 | Defense Mechanism | In psychoanalytic theory, the ego's protective methods of reducing anxiety by unconsciously distorting reality. Example: Denies reality Approach: Humanistic | 11 | |
| 9282235782 | Repression | In psychoanalytic theory, the basic defense mechanism that banishes from consciousness anxiety-arousing thoughts, feelings, and memories. Example: Forgetting about a test even if you have known about it for months. Approach: Evolutionary |  | 12 |
| 9282235783 | Regression | Psychoanalytic defense mechanism in which an individual faced with anxiety retreats to a more infantile psycho sexual stage, where some psychic energy remains fixated. Example: Sleeping with your teddy bear when you feel home sick. Approach: Evolutionary |  | 13 |
| 9282235784 | Reaction Formation | Psychoanalytic defense mechanism by which the ego unconsciously switches unacceptable impulses into their opposites. Thus, people may express feelings that are the opposite of their anxiety-arousing unconscious feelings. Example: Denying that you like someone while being beat red. Approach: Evolutionary |  | 14 |
| 9282235785 | Projection | Psychoanalytic defense mechanism by which people disguise their own threatening impulses by attributing them to others. Example: Hypocrites Approach: Evolutionary |  | 15 |
| 9282235786 | Rationalization | Defense mechanism that offers self-justifying explanations in place of the real, more threatening, unconscious reasons for one's actions. Example: I'll eat this cake and run an extra mile on my workout. Approach: Psychodynamic |  | 16 |
| 9282235787 | Displacement | Psychoanalytic defense mechanism that shifts sexual or aggressive impulses toward a more acceptable or less threatening object or person, as when redirecting anger toward a safer outlet. Example: Punching a pillow when you get in a fight with someone Approach: Behavioral |  | 17 |
| 9282235788 | Denial | The action of declaring something to be untrue. Example: Denying that something happened even if it may be true. Approach: Evolutionary |  | 18 |
| 9282235789 | Collective Unconscious | Carl Jung's concept of a shared, inherited reservoir of memory traces from our species' history. Example: Mother is the nurturing figure Approach: Evolutionary | 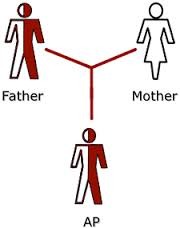 | 19 |
| 9282235790 | Projective Test | A personality test, such as the Rorschach or TAT, that provides ambiguous stimuli to trigger projection of one's inner thoughts and feelings. Example: Rorschach test Approach: Psychodynamic |  | 20 |
| 9282235791 | Thematic Apperception Test (TAT) | A projective test developed by Henry Murray and his colleagues that involves creating stories about ambiguous scene that can be interpreted in a variety of ways. Example: Projective test Approach: Psychodynamic |  | 21 |
| 9282235792 | Rorschach Inkblot Test | A projective psychological test consisting of 10 inkblots printed on cards (five in black and white, five in color) created in 1921 with the publication of Psychodiagnostik by Hermann Rorschach. Example: Colorful or black and white personality test Approach: Psychodynamic |  | 22 |
| 9282235793 | Terror-Management Theory | Proposes that faith in one's worldview and the pursuit of self-esteem provide protection against a deeply rooted fear of death. Example: Managing fear of morality Approach: Psychodynamic |  | 23 |
| 9282235794 | Self-Actualization | According to Maslow, the ultimate psychological need that arises after basic physical and psychological needs are met and self-esteem is achieved; the motivation to fulfill one's potential. Example: Gandi Approach: Humanistic |  | 24 |
| 9282235795 | Unconditional Positive Regard | According to Rogers, an attitude of total acceptance toward another person. Example: Vital to cope with stress Approach: Behavioral |  | 25 |
| 9282235796 | Self-Concept | Central to the person's behavior, consists of a person's beliefs/feelings about himself at any given time. Example: "Who am I" Approach: Cognitive |  | 26 |
| 9282235797 | Trait | A characteristic pattern of behavior or a disposition to feel and act, as assessed by self-report inventories and peer reports. Example: Introvert, optimistic Approach: Behavioral |  | 27 |
| 9282235798 | Personality Inventory | A questionnaire on which people respond to items designed to gauge a wide range of feelings and behaviors. Example: Five- factor model Approach: Cognitive |  | 28 |
| 9282235799 | Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory (MMPI) | The most widely researched and clinically used of all personality tests. Originally used to identify emotional disorders, this test is now used for many other screening purposes. Example: Inventory Approach: Psychodynamic |  | 29 |
| 9282235800 | Empirically Derived Test | A test (such as the MMPI) developed by testing a pool of items and then selecting those that discriminate between groups. Example: Spelling bee words Approach: biological |  | 30 |
| 9282235801 | Social-Cognitive Perspective | Views behavior as influenced by the interaction between persons and their social context. Example: Saying you like something because other people do. Approach: Sociocultural |  | 31 |
| 9282235802 | Reciprocal Determinism | The interacting influences between personality and environmental factors. Example: How a class acts when the teacher is in the room vs. when they leave Approach: Sociocultural |  | 32 |
| 9282235803 | Personal Control | Our sense of controlling our environment rather than feeling helpless. Example: When everything seems manageable Approach: Sociocultural |  | 33 |
| 9282235804 | External Locus of Control | The perception that chance or outside forces beyond one's personal control determine one's fate. Example: It is fate Approach: Psychodynamic |  | 34 |
| 9282235805 | Internal Locus of Control | The perception that one controls one's own fate. Example: I'm in charge Approach: Cognitive |  | 35 |
| 9282235806 | Learned Helplessness | The hopelessness and passive resignation an animal or human learns when unable to avoid repeated aversive events. Example: A lady who blames her never ending shopping on the economy Approach: Cognitive |  | 36 |
| 9282235807 | Positive Psychology | The scientific study of optimal human functioning; aims to discover and promote strengths and virtues that enable individuals and communities to thrive. Example: Similar to unconditional positive regard Approach: Psychodynamic |  | 37 |
| 9282235808 | Self | A person's essential being that distinguishes them from others, especially considered as the object of introspection or reflexive action. Example: This is me Approach: Psychodynamic |  | 38 |
| 9282235809 | Spotlight Effect | Overestimating others' noticing and evaluating our appearance, performance, and blunders. Example: Feeling like you are on stage Approach: Cognitive |  | 39 |
| 9282235810 | Self-Esteem | One's feelings of high or low self-worth. Example: Fourth step in Maslow's Hierarchy of needs Approach: Evolutionary |  | 40 |
| 9282235811 | Self-Serving Bias | A readiness to perceive oneself favorably. Example: Got a good grade on a test, studied hard Approach: Cognitive |  | 41 |
Ap Flashcards
| 13571080876 | Cartography | 0 | ||
| 13571080877 | Contagious Diffusion | 1 | ||
| 13571080878 | Cultural Ecology | 2 | ||
| 13571080879 | cultural landscape | 3 | ||
| 13571080880 | Culture | 4 | ||
| 13571080881 | Density | 5 | ||
| 13571080882 | Diffusion | 6 | ||
| 13571080883 | Distance Decay | 7 | ||
| 13571080884 | Distribution | 8 | ||
| 13571080885 | environmental determinism | 9 | ||
| 13571080886 | Equator | 10 | ||
| 13571080887 | Expansion Diffusion | 11 | ||
| 13571080888 | formal region | 12 | ||
| 13571080889 | Functional Region | 13 | ||
| 13571080890 | GIS | 14 | ||
| 13571080891 | GPS | 15 | ||
| 13571080892 | Hearth | 16 | ||
| 13571080893 | Hierarchical Diffusion | 17 | ||
| 13571080894 | International Date Line | 18 | ||
| 13571080895 | Latitude (parallels) | 19 | ||
| 13571080896 | LDCs | 20 | ||
| 13571080897 | longitudes (meridians) | 21 | ||
| 13571080898 | MDCs | 22 | ||
| 13571080899 | Possibilism | 23 | ||
| 13571080900 | Prime Meridian | 24 | ||
| 13571080901 | Projection | 25 | ||
| 13571080902 | relocation diffusion | 26 | ||
| 13571080903 | remote sensing | 27 | ||
| 13571080904 | Scale | 28 | ||
| 13571080905 | Site | 29 | ||
| 13571080906 | Situation | 30 | ||
| 13571080907 | space-time compression | 31 | ||
| 13571080908 | spatial analysis | 32 | ||
| 13571080909 | Stimulus Diffusion | 33 | ||
| 13571080910 | time zones | 34 | ||
| 13571080911 | Toponym | 35 | ||
| 13571080912 | uneven development | 36 | ||
| 13571080913 | vernacular region | 37 | ||
| 13571080914 | "Why of Where" | 38 |
Flashcards
AP - le logement Flashcards
| 13516715303 | housing | le logement | 0 | |
| 13516715304 | at home | chez soi | 1 | |
| 13516715305 | repairs | les réparations (f.) | 2 | |
| 13516715306 | DIY | le bricolage | 3 | |
| 13516715307 | hardware store | la quincaillerie | 4 | |
| 13516715308 | hammer | le marteau | 5 | |
| 13516715309 | nail | le clou | 6 | |
| 13516715310 | screwdriver | le tournevis | 7 | |
| 13516715311 | roof | le toit | 8 | |
| 13516715312 | kitchen | la cuisine | 9 | |
| 13516715313 | bathroom | la salle de bains | 10 | |
| 13516715314 | toilet | les toilettes (f.) | 11 | |
| 13516715315 | sink | le lavabo | 12 | |
| 13516715316 | living room | le salon | 13 | |
| 13516715317 | dining room | la salle à manger | 14 | |
| 13516715318 | bedroom | la chambre (à coucher) | 15 | |
| 13516715319 | patio/balcony | la terrasse | 16 | |
| 13516715320 | yard | le jardin | 17 | |
| 13516715321 | garden | le potager | 18 | |
| 13516715322 | yard work | le jardinage | 19 | |
| 13516715323 | real estate agency | l'agence immobilière | 20 | |
| 13516715324 | neighborhood | le quartier | 21 | |
| 13516715325 | zip code | le code postal | 22 | |
| 13516715326 | building | le bâtiment | 23 | |
| 13516715327 | bills | les factures (f.) | 24 | |
| 13516715328 | mortgage | le prêt immobilier | 25 | |
| 13516715329 | rent | le loyer | 26 | |
| 13516715330 | to rent | louer | 27 | |
| 13516715331 | heat | le chauffage | 28 | |
| 13516715332 | electricity | l'électricité (f.) | 29 | |
| 13516715333 | gas | le gaz | 30 | |
| 13516715334 | floor (level) | l'étage (m.) | 31 | |
| 13516715335 | ground floor | le rez-de-chaussée | 32 | |
| 13516715336 | furnished | meublé | 33 | |
| 13516715337 | furniture | les meubles (m.) | 34 | |
| 13516715338 | lease | le bail | 35 | |
| 13516715339 | loft bed | la mezzanine | 36 | |
| 13516715340 | loft apartment | le loft | 37 | |
| 13516715341 | studio apartment | le studio | 38 | |
| 13516715342 | efficiency apartment | un T1/F1 | 39 | |
| 13516715343 | 1-bedroom apartment | un T2/F2 | 40 | |
| 13516715344 | 2-bedroom apartment | un T3/F3 | 41 | |
| 13516715345 | roommate | le/la colocataire | 42 | |
| 13516715346 | Social welfare office for housing/families | la CAF | 43 |
Chapters 19 and 20 Ap world history Flashcards
| 11626071489 | What was going on during the age of enlightenment | reformation; Luther; people were scared to go against the church | 0 | |
| 11626089083 | The scientific revolution | A major change in European thought, starting in the mid-1500s, in which the study of the natural world began to be characterized by careful observation and the questioning of accepted beliefs. | 1 | |
| 11626095607 | Hellocentric theory | the idea that the earth and the other planets revolve around the sun. Scientists include: Nicolas Copernicus Tycho Brahe Johanne Kepler Galileo Galileil | 2 | |
| 11626098223 | Geocentric Theory | Earth is the center of the Universe | 3 | |
| 11626153085 | Issac Newton | British scientist who defined the laws of motion, discovered gravity, experimented with optics, invented differential calculus and wrote "Principia" insisted upon empirical rationalization to check rational explanation. Encouraged nature philosophy | 4 | |
| 11626198659 | Francis Bacon | (1561-1626) English politician, writer. Formalized the empirical method. (proving) Inductive reasoning. Empiricism | 5 | |
| 11626255369 | Rene Descartes | I think therefore I am. research going beyond empiricism | 6 | |
| 11626283446 | French Royal Academy of Sciences | society funded by Louis XIV, which was thought to benefit the king and state and emphasized practical science for new tools and machines. people: Newton Darwin Einstein | 7 | |
| 11626310622 | British Royal Society | 1750-1914 : Association of scientists established in England in 1660 that was dedicated to the promotion of "useful knowledge". Charles II | 8 | |
| 11626326898 | Royal society of sciences in Uppsala | People: Linneaus | 9 | |
| 11626336052 | Royal swedish society | Noble prize | 10 | |
| 11626347413 | how did the age of exploration impact the study of science? | Sciences were needed for fame and money (like arts) | 11 | |
| 11626367837 | John Locke | argued against the belief that human beings are born with certain ideas already in their minds "tabula rasa" experiences shape character rejected that sin permanently flawed humans humans can take charge of their own destiny government should protect property governments are needed | 12 | |
| 11626457607 | Utopia | perfect society | 13 | |
| 11626465543 | Enlightenment thinking | Emphasized natural law and de-emphasized God's role in the world. France= no freedom of speech England and netherlands = most freedom of speech | 14 | |
| 11626485061 | where did many enlightenment thinkers do their work? | Coffee houses, and salons | 15 | |
| 11626500614 | Where did enlightenment ideas present the largest challenge? | France and Spain because people were afraid to go against the church | 16 | |
| 11626516595 | What invention was pivotal once again during the age of enlightenment? | Printing press because it spread ideas faster | 17 | |
| 11626526811 | The philosophers | People who favored change, championed reform and advocated tolerance. would most likely be found at university's or coffee houses. were usually for expansion of trade, improvement of agriculture and transportation, invention of new industries. No preaching No god However they varied views on specific government forms: some like constitutional monarchy; some like a republic. | 18 | |
| 11626577953 | Deism is the belief that | God created the universe but does not actively run it. very tolerant, reasonable, capable of encouraging virtuous living. | 19 | |
| 11626600854 | The enlightenment and Religion | The enlightenment challenges the church and its concepts of "original sin" Also challenged for its practices: Not paying taxes being rulers and religious leaders literary censorship The enlightenment did not like that the church was separate from its people NO THROCRACY | 20 | |
| 11626804640 | Voltaire | French philosopher and writer whose works epitomize the Age of Enlightenment, imprisoned at bastille for offending louis XIV. Preached tolerance Published works: Letter on the English Emelments on the philosophy of newton Candide | 21 | |
| 11626876393 | The Encyclopedia | Edited by Denis Diderot and Joan Le Rond d'Alembert. aimed to secularize learning and take religion out of learning | 22 | |
| 11626921771 | Beccaria and Reform of Criminal law | Wrote On Crimes and Punishment (1764) Spoke put against torture and capital punishment. wanted speedy trails severity of punishment should be based on the severity of the crime The purpose of laws was to guarantee happiness for as many people as possible. believed draconian laws were a thing of the past | 23 | |
| 11627054227 | Adam Smith | wrote the Inquiry into the nature and causes of the wealth of nations. Argued best way to create economic growth was for propel to pursue thrown selfish self interests. Founder of laissez faire economic thought | 24 | |
| 11627108117 | laws of supply and demand | when supplies of goods and services become plentiful, prices tend to drop. When supplies become scarcer, prices tend to rise. | 25 | |
| 11627117045 | Laissez-faire economics | Theory that opposes governmental interference in economic affairs beyond what is necessary to protect life and property. (wartime economy) | 26 | |
| 11627153394 | Montesquieu | (1689-1755) wrote 'Spirit of the Laws', said that no single set of political laws was applicable to all - depended on relationship and variables, supported division of government. Believed in separation of powers | 27 | |
| 11627171976 | Jean-Jacques Rousseau | Wrote "Social Contract" he explained an ideal society where each community member would vote on issues and majority would become one law. Discourse on the moral effects of the arts and sciences Discourse on the origin of inequality If majority get their way=Tierany | 28 | |
| 11627218456 | Enlightened Absolutism | a system in which rulers tried to govern by Enlightenment principles while maintaining their full royal powers (tricky but possible) | 29 | |
| 11627229268 | Frederick the Great of Prussia | *Promotion through Merit- work and education rather than birth would decide who would run prussia *religious tolerance- for christian, muslim, and jew Reforms included- Abolishing torte and limiting the number of capital crimes Enlightened Absolutist | 30 | |
| 11627267177 | Prussia | NOT RUSSIA!!!!!!!! military driven, growing power | 31 | |
| 11627294314 | Joesph II of Austria | Centralization of Authority- aimed to extend Austro-Hungarian empire at the expense of the ottoman empir, poland and bolivia ecclesiastical polices- religious toleration, and bringing the Roman Catholic church under royal control Economic reform Attempts to abolish serfdom improves transportation and trade | 32 | |
| 11627360292 | Austro-Hungarian Empire | Dual Monarchy established by hapsburgs | 33 | |
| 11627371083 | Junkers | Germany Nobility | 34 | |
| 11627379962 | Catherine the Great | Ruled for 30 years, married into the Romanov dynasty. 2nd sovereign female 3 major goals: 1) continue the work of westernization started under the rule pf peter the great 2) Domestic reforms: improve eduction, allow limited religious toleration, prepare a new legal code (successful) Forbid torture (mildly successful) eliminate the institution of serfdom and limit the power of boyars (not successful) 3)Territorial expansion: achieved through acquisition of parts of poland, the ukraine and Crimea |  | 35 |
| 11627800238 | Enclosure Acts | a series of United Kingdom Acts of Parliament which enclosed open fields and common land in the country, creating legal property rights to land that was previously considered common. | 36 | |
| 11627804068 | cottage industry | Manufacturing based in homes rather than in a factory, commonly found before the Industrial Revolution. | 37 | |
| 11627810014 | Indentured Servitude | A worker bound by a voluntary agreement to work for a specified period of years often in return for free passage to an overseas destination. Before 1800 most were Europeans | 38 | |
| 11627872141 | Slave colonies | British- Jamaica Spanish- Santo Domingo and Cuba Portuguese- Brazil French- Saint Domingue | 39 | |
| 11627903878 | Creoles | In colonial Spanish America, term used to describe someone of European descent born in the New World. upperclass and believed n enlightenment | 40 | |
| 11627934318 | sugar | catalyst to slave trade | 41 | |
| 11627944052 | Abolishment of Slavery | french 1st to abolish Brazil and cuba last | 42 | |
| 11627964995 | Tasman voyages | australians were barbaric so he didn't claim australia for the dutch | 43 | |
| 11627982350 | people native to australia | Aborigines | 44 | |
| 11627997511 | Cooks voyages | viewed australian people as hospitable. however viewed native peoples of new zealand as barbaric. Killed in hawaii | 45 | |
| 11628025379 | Maori | indigenous people of New Zealand | 46 | |
| 11628034307 | how did enlightenment ideas get to the Americas | Trade and exploration | 47 | |
| 11628045636 | how did the enlightenment ideas impact the history of the Americas? | Fueled revolutions, made people realize they didn't have representation in parliament. People began to push back from their mother nations. | 48 | |
| 11635130362 | West Africa | Senegambia and Benin | 49 | |
| 11635165682 | stateless societies | African societies organized around kinship or other forms of obligation and lacking the concentration of political power and authority associated with states. No borders | 50 | |
| 11635174749 | Agriculture in west Africa | Limited farming because of titzi flys. Grew yams and beans | 51 | |
| 11635191994 | Benin Kingdom | dominated a large region around the Nigeria delta. Slave kingdom | 52 | |
| 11635208015 | Trade in West Africa | slaves and was in the middle of the salt gold trade from north and south Africa | 53 | |
| 11635216395 | Type of society in west Africa | Matriarchal because many of the men were taken for slave trade. | 54 | |
| 11635228279 | Age grade power system in Western Africa | Older you are the more power you have | 55 | |
| 11635237990 | Oba | king in Western Africa | 56 | |
| 11635255014 | Songhai slave economy | was a muslim kingdom | 57 | |
| 11644637662 | the sudan | songhai, Kanem-Bornu, and Hausaland | 58 | |
| 11644644735 | The west coast | Senegambia and Benin | 59 | |
| 11644665624 | Sudan: internal problems | religious division | 60 | |
| 11644684152 | Kanem-Bornu | Had military strength and lots of warfare. | 61 | |
| 11644688285 | Hausa trade | Slave merchants | 62 | |
| 11644756284 | Polygamy | multiple spouses. Societies were poliginy (multiple wives) | 63 | |
| 11644773493 | Agriculture | Western african farmers struggle because of the titzi flies | 64 | |
| 11644794077 | Western Africa | Disease and Drought | 65 | |
| 11644843613 | Trade among African Societies | Trade routes: Sand roads Products: West -> Shara gold and slaves Shara-> west salt | 66 | |
| 11644915708 | Who dominated slave trade and trade. | Portuguese for a while. | 67 | |
| 11644942539 | The East African Coast | Ethiopia: Jesuit influences | 68 | |
| 11645004824 | Christanity in Nigeria | less than muslim and islam | 69 | |
| 11645037230 | Pastor John | Legend. Wealthy guy | 70 | |
| 11645050016 | Swahili city states | Vasco de game - sailed around them and discovered. | 71 | |
| 11645140848 | Noncooperation | Swahili city states stopped trading with the portuguese so they would leave them alone | 72 | |
| 11645167479 | Benin and angola | Places people took the slaves from | 73 | |
| 11645306833 | Portuguese | First explore to eastern africa | 74 | |
| 11645309911 | Kingdom of Axume | In Ethiopia | 75 | |
| 11645325783 | King Ezana and Frumentius | Create coptic christianity | 76 | |
| 11645376422 | noteworthy trade cities | Mogadishu Kilwa Malindini sophala mumbali | 77 | |
| 11645441109 | Impact Portuguese on Swahili states | trade goods; cause evacuation of cities eventually | 78 | |
| 11645460779 | slave trade | Started in Spanish Americas. Many slaves landed in the Caribbean islands | 79 | |
| 11645471833 | Asiento System | System that took slaves to the New World to work for the Spanish. Required that a tax be paid to the Spanish ruler for each slave brought over. | 80 | |
| 11645483223 | where were slaves taken from? | transported from the heart of africa to west Africa and finally to the Americas | 81 | |
| 11645511013 | what was shoreline trading? | Method of obtaining slaves and making slave trade more efficient | 82 | |
| 11645588000 | How did they capture and ship slaves? | shore trading | 83 | |
| 11645597719 | Middle Passage | A voyage that brought enslaved Africans across the Atlantic Ocean to North America and the West Indies. Awful journey | 84 | |
| 11645604877 | Slavery Gender Imbalance | Men were in high demand . Created polygamous societies | 85 | |
| 11645623001 | Africas slave supplying states | The asante Oyo and kongo states | 86 | |
| 11645637691 | What class rose in sub saharan africa | Warrior class | 87 |
Flashcards
Flashcards
Flashcards
Flashcards
Pages
Need Help?
We hope your visit has been a productive one. If you're having any problems, or would like to give some feedback, we'd love to hear from you.
For general help, questions, and suggestions, try our dedicated support forums.
If you need to contact the Course-Notes.Org web experience team, please use our contact form.
Need Notes?
While we strive to provide the most comprehensive notes for as many high school textbooks as possible, there are certainly going to be some that we miss. Drop us a note and let us know which textbooks you need. Be sure to include which edition of the textbook you are using! If we see enough demand, we'll do whatever we can to get those notes up on the site for you!

