AP Euro Renaissance Flashcards
Ethel wood book
| 9560377771 | Brunelleschi, Filippo | (1377 - April 15, 1446) was one of the foremost architects and engineers of the Italian Renaissance. He is perhaps most famous for his studies of linear perspective and engineering the dome of the Florence Cathedral. |  | 0 |
| 9560377772 | Bruni, Leonardo | Florentine who first gave the name humanitas (humanity) to the learning of grammar, rhetoric, poetry, history, politics, and moral philosophy based on the Greek and Latin classics. Wrote about the history of Florence. |  | 1 |
| 9560377773 | Castiglione, Baldassare | In 1528, he published The Book of the Courtier, which many consider to be the most influential work on education of the Renaissance. The idea of the "Renaissance Man" was described by him to be virtuous, refined, and a student of the liberal arts - perfectly well suited to artistic, written and spiritual pursuits. |  | 2 |
| 9560377774 | city-states | these trade rich cities of Italy in the 13th and 14th century expanded to become powerful city-states that dominated the political and economic life of the surrounding countryside.Lacked a central control and became independent states. By the 15th century, five states-Milan, Florence, Venice, the Papal States, and the Kingdom of Naples overshadowed the other smaller states and were in fierce competition with one another for economic and political power. |  | 3 |
| 9560377775 | the Courtier | (1528), by Castiglione, it described the ideal courtier, or attendant at a court, as someone who had mastered the classics and several languages, and who could paint, sing, write poetry, advise and console his prince, as well as run, jump, swim, and wrestle. | 4 | |
| 9560377776 | David | 18 foot sculpture by Michelangelo that stood for many years in the great square of Florence, and it has been one of the most popular sculptures in the world. | 5 | |
| 9560377778 | Durer, Albrecht | Leading northern artist, a German who blended the northern and southern styles. He made two trips to Venice, where he studied the southern styles, but his work clearly re |  | 6 |
| 9560377779 | Erasmus, Desiderius | Dutch scholar. Began writing career with dialogues that he prepared for his students. These dialogues were intended to teach them how to speak and live well, and to exhibit good manners worthy of the gentlemen he wanted them to become. Wrote in Praise of Folly. Was a Catholic but his works were placed on the Index of Forbidden Books. Also, wrote about how Christian princes should rule. |  | 7 |
| 9560377780 | Ferdinand and Isabella | A king and queen of Spain in the late fifteenth and early sixteenth centuries. They united their country and sponsored the exploration of the New World by Christopher Columbus. Reduced the power of the great nobles when they filled the political bureaucracy including the royal council-with hidalgos, lesser aristocrats who owed their positions to the throne. |  | 8 |
| 9560377781 | Gutenberg, Johann | German goldsmith and printer of Mainz, Germany. Developed movable type (although it had been invented in China and Korea) his printing press printed the bible. |  | 9 |
| 9560377782 | Humanism | A Renaissance intellectual movement in which thinkers studied classical texts and focused on human potential and achievements.Most new works by Petrarch and Boccaccio were written in the vernacular and expressed the accomplishments of the individual. |  | 10 |
| 9560377783 | Inquisition | tribunal originally set up to monitor the sincerity of former Muslims and Jews who had converted (often by force) to Christianity. |  | 11 |
| 9560377784 | Italian Renaissance | ..., A period of intense artistic and intellectual activity, said to be a 'rebirth' of Greco-Roman culture. From roughly the mid-fourteenth to mid-fifteenth century followed by this movement spreading into the Northern Europe during 1400-1600 | 12 | |
| 9560377785 | Machiavelli, Niccolo | (1469-1527) Author of The Prince(16th century): emphasized realistic discussions of how to seize and maintain power; one of the most influential authors of the Italian Renaissance |  | 13 |
| 9560377786 | Medici, Cosimo de' | Head of Medici family-supported by a few patrician families who helped to banish prominent members of the most powerful rival clans. Very "magnificent." |  | 14 |
| 9560377787 | Medici Family | A wealthy merchant family that ruled over Florence as uncrowned rulers. Great patrons of the arts. Includes Cosimo and Lorenzo. |  | 15 |
| 9560377788 | Medici, Lorenzo de' | Politician and promoted the family's power with his extravagant patronage of the arts |  | 16 |
| 9560377789 | Mona Lisa | A painting by Leonardo da Vinci of a woman with a mysterious smile. It is now of the most readily recognized paintings in the world. Reflects the humanist interest in individual facial expressions and in painting realistic landscapes as backgrounds |  | 17 |
| 9560377790 | "new monarchs" | The term applied to Louis XI of France, Henry VII of England, and Ferdinand and Isabella of Spain, who strengthened their monarchical authority often by Machiavellian means.Emphasized royal majesty and authority over their subjects, and they suppressed opposition and rebellion. Still continued some middle age practices. | 18 | |
| 9560377791 | Papal States | ruled by the pope and formed another important power during Renaissance Italy |  | 19 |
| 9560377793 | Petrarch | (1304- 1374) He was the first great humanist thinker and a scholar of Latin. He used writing to consider the ebb and flow of his life and the human condition itself. He is known as the "Father of Humanism". Instrumental in standardizing the Florentine vernacular. Admired Cicero and valued St. Augustine. Also famous for his Italian verse, short sonnets. |  | 20 |
| 9560377794 | The Prince | A short political treatise about political power how the ruler should gain, maintain, and increase it. Machiavelli explores the problems of human nature and concludes that human beings are selfish and out to advance their own interests. He believed it was better to be feared than loved. | 21 | |
| 9560377795 | Raphael | (1483-1520) Italian Renaissance painter; he painted frescos, his most famous being The School of Athens. famous for his madonnas. Died young |  | 22 |
| 9560377796 | Reconquista | Beginning in the eleventh century, military campaigns by various Iberian Christian states to recapture territory taken by Muslims. In 1492 the last Muslim ruler was defeated, and Spain and Portugal emerged as united kingdoms. |  | 23 |
| 9560377797 | Renaissance | 1. the time period which Europe flourished and the rebirth the love of the classics 2. The great period of rebirth in art, literature, and learning in the 14th-16th centuries, which marked the transition into the modern periods of European history began in Italy |  | 24 |
| 9560377798 | "Renaissance Man" | multi-talented, skilled in many areas: Arts, Math/Science, Music, Architecture. Example: Leonardo Da Vinci | 25 | |
| 9560377799 | republics | in Italy during the Renaissance Italian states were divided into two categories. these were base on the old medieval communes. or associations with free men who sought complete political and economic independence from local nobles |  | 26 |
| 9560377801 | The School of Athens | Raphael - Italian Renaissance fresco wall painting of Greek philosophers drawn to scale in accordance with the vantage point of the viewer. The placement, in the center of the archway, of Plato and Aristotle emphasizes the importance of these two central figures. Raphael shows his style of basic one-point perspective converging in a single vanishing point just behind Plato and Aristotle. The exception is the cube in the foreground which gives a two-point perspective. It easy to see, that with the removal of the figures, the building is symmetrically balanced. | 27 | |
| 9560377802 | scholasticism and neoplatonism | attempt to reconcile the beliefs and values of Christianity with the logical reasoning of Greek philosophy. |  | 28 |
| 9560377803 | secularism | An indifference to religion and a belief that religion should be excluded from civic affairs and public education |  | 29 |
| 9560377805 | Tudors | The House of Lancaster and the House of York feuded over the throne for more than twenty years, until finally a compromis was reached when a new royal house-------emerged in 1485 by intermarriage between two warring families. Henry VII, the first of this dynasty. This dynasty would dominate England throughout the 16th century |  | 30 |
| 9560377806 | Van Eyck, Jan | An important painter of the Northern Renaissance. He is credited with the first use of the oil glazing technique of painting. He is also known for the great detail in his work. His most famous work was the Arnolfini Wedding. |  | 31 |
| 9560377807 | Vernacular | Everyday language of ordinary people. |  | 32 |
| 9560377808 | Vinci, Leonardo da | "Renaissance Man"- great artist, engineer, scientist, and inventor. He created the Mona Lisa. |  | 33 |
| 9560377809 | War of the Roses | 1455-1485; A war between the York family and Lancaster family of England for the crown. This struggle was ended when Henry Tudor, who was on the Lancaster side, won. He became Henry VII, the first Tudor king. |  | 34 |
| 9560377810 | Lorenzo Valla | Proved the Donation of Constantine to be a fake by using his expert Latin knowledge. | 35 | |
| 9560377811 | Civic Humanism | Renaissance movement/idea that emphasized that the duty of an intellectual was to live an active life for one's state. | 36 | |
| 9560377812 | Neoplatonism | started my Marsilio Ficino, an attempt to synthesize Christianity and Plato's philosophy | 37 | |
| 9560377813 | Pico della Mirandolo | wrote the Oration of the dignity of man which discussed the unlimited potential of man and became the manifesto of the Renaissance. | 38 | |
| 9560377817 | Botticelli | He painted this |  | 39 |
AP World: Chapter 22 Flashcards
| 9654777334 | Ottoman dynasty | dynasty founded by Turkic-speaking people who advanced into Asia Minor during the 14th century; the most powerful Islamic empire in history; lasted until the early twentieth century. | 0 | |
| 9654777335 | Safavid dynasty | founded by a Turkic nomad family with Shi'a Islamic beliefs; established a kingdom in Iran and ruled until 1722. | 1 | |
| 9654777336 | Mughal empire | established by Turkic invaders in 1526; endured until the mid-19th century. | 2 | |
| 9654777337 | Ottomans | Turkic-speaking people who advanced into Asia Minor during the 14th century; established an empire in the Middle East, north Africa, and eastern Europe that lasted until after Word War I. | 3 | |
| 9654777338 | Mehmed II | "the Conqueror"; Ottoman sultan; captured Constantinople, 1453, and destroyed the Byzantine Empire. | 4 | |
| 9654777339 | Janissaries | conscripted youths from conquered regions who were trained as Ottoman infantry divisions; became an important political influence after the 15th century. | 5 | |
| 9654777340 | vizier | head of the Ottoman bureaucracy; after the 15th century often more powerful than the sultan. | 6 | |
| 9654777341 | Sail al-Din | eponymous founder of the Safavids, Sufi mystic; leader of the Red Heads. | 7 | |
| 9654777342 | Red Heads | name given to Safavid followers because of their distinctive red headgear. | 8 | |
| 9654777343 | Ismâ'il | Safavid leader; conquered the city of Tabriz in 1501 and was proclaimed shah. | 9 | |
| 9654777344 | Chaldiran | an important battle between the Safavids and Ottomans in 1514; Ottoman victory demonstrated the importance of firearms and checked the western advance of the Safavid Shi'a state. | 10 | |
| 9654777345 | Abbas I, the Great | Safavid shah (1587-1629); extended the empire to its greatest extent; used Western military technology. | 11 | |
| 9654777346 | imams | Shi'a religious leaders who traced their descent to Ali's successors. | 12 | |
| 9654777347 | mullahs | religious leaders under the Safavids; worked to convert all subjects to Shi'ism. | 13 | |
| 9654777348 | Isfahan | Safavid capital under Abbas the Great; planned city exemplifying Safavid architecture. | 14 | |
| 9654777349 | Nadir Khan Afshar | emerged following fall of Safavids; proclaims himself shah, 1736. | 15 | |
| 9654777350 | Babur | Turkic leader who founded the Mughal dynasty; died in 1530. | 16 | |
| 9654777351 | Humayn | son and successor of Babur; expelled from India in 1540 but returned to restore the dynasty in 1556. | 17 | |
| 9654777352 | Akbar | son and successor of Humayn; built up the military and administrative structure of the dynasty; followed policies of cooperation and toleration with the Hindu majority. | 18 | |
| 9654777353 | Din-i-Ilahi | religion initiated by Akbar that blended elements of Islam and Hinduism; did not survive his death. | 19 | |
| 9654777354 | Aurangzeb | son and successor of Shah Jahan; pushed extent of Mughal control in India; reversed previous policies to purify Islam of Hindu influences; incessant warfare depleted the empire's resources; died in 1707. | 20 | |
| 9654777355 | Taj Mahal | mausoleum for Mumtaz Mahal, built by her husband Shah Jahan; most famous architectural achievement of Mughal India. | 21 | |
| 9654777356 | Nur Jahan | wife of ruler Jahangir who amassed power at the Mughal court and created a faction ruling the empire during the later years of his reign. | 22 | |
| 9654777357 | Mumtaz Mahal | wife of Shah Jahan; took an active political role in Mughal court; entombed in Taj Mahal. | 23 | |
| 9654777358 | Marattas | people of western India; challenged Mughal rule under Aurangzeb. | 24 | |
| 9654777359 | Sikhs | Indian sect, beginning as a synthesis of Hindu and Muslim faiths; pushed to opposition to Muslim and Mughul rule. | 25 |
AP World - Period 3 Flashcards
| 5434418063 | Trans -Saharan Trade | Trade of goods through the Sahara dessert Goods: Salt, gold, animal hides, slaves Important points: Timbuktu, Goa,Djenne |  | 0 |
| 5434418064 | Islam | Monotheistic religion created in the 7th century by Arabic merchant, Muhammed |  | 1 |
| 5434418065 | Caliphate | A regional state unified by Islam |  | 2 |
| 5434418066 | Crusades | A series of Christian vs Muslim military campaigns for the "holy land" |  | 3 |
| 5434418067 | Dar-al-Islam | territory of Islam |  | 4 |
| 5434418068 | Byzantine Empire | Eastern Roman empire extending to the Eastern Mediterranean and Southwest Asia |  | 5 |
| 5434418070 | Mongols | nomadic invaders that conquered Eurasia with force and diplomacy |  | 6 |
| 5434418071 | Black Death | Plague that killed 1/3 of European population |  | 7 |
| 5434418072 | Maya | MesoAmerican civilization that had pyramids, large cities, a written system, and complex society |  | 8 |
| 5434418073 | Coerced labor | slavery, serfdom, corvee (government-recquired labor on public works projects), and indentured servitude |  | 9 |
| 5434418074 | Feudalism | Agricultural workers serving landowners or lords (knights and samurai) |  | 10 |
| 5434418075 | Zheng He | Ming explorer that crossed the Indian Ocean |  | 11 |
| 5434418076 | Silk | highly-priced luxury commodity mainly exported from China |  | 12 |
| 5434418077 | Chinese Inventions | gunpowder, compass, paper, astrolabe |  | 13 |
| 5434418078 | Tang Dynasty | (618-907 CE) The Chinese dynasty that was much like the Han, who used Confucianism. This dynasty had the equal-field system, a bureaucracy based on merit, and a Confucian education system. | 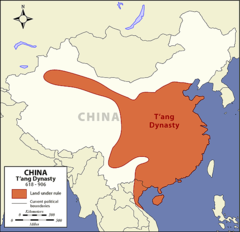 | 14 |
| 5434418079 | Song Dynasty | (960 - 1279 AD); started by Tai Zu; by 1000, a million people were living there; started feet binding; had a magnetic compass, navy, traded with india and persia (brought pepper and cotton), first to have paper money, explosive gun powder |  | 15 |
| 5434418080 | Central Asia | A region that includes the republics of Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan |  | 16 |
| 5434418081 | Indian Ocean trade | trade between Arab, Persian, Turkish, Indian, African, Chinese, and Europe merchants |  | 17 |
| 5434418082 | Ming Dynasty | Succeeded Mongol Yuan dynasty in China in 1368; lasted until 1644; initially mounted huge trade expeditions to southern Asia and elsewhere, but later concentrated efforts on internal development within China. |  | 18 |
| 5434418083 | Grand Canal | an inland waterway 1000 miles long in eastern China |  | 19 |
| 5434418084 | Pax Mongolica | Mongol peace from mid-1200's through mid-1300's imposed stability and law and order across Eurasia. Guaranteed safe passage for trade caravans, travelers, and missionaries from one end of empire to other. |  | 20 |
| 5434418085 | Vikings | A nomadic group that conquered ex: Normans |  | 21 |
| 5434418086 | Syncretism | A blending of two or more religious traditions |  | 22 |
| 5434418087 | Marco Polo | Italian explorer and author who made numerous trips to China and returned to Europe to write of his journeys, responsible for much of the knowledge exchanged between Europe and China during this time period. |  | 23 |
| 5434418088 | Ibn Battuta | (1304-1369) Morrocan Muslim scholar, the most widely traveled individual of his time. He wrote a detailed account of his visits to Islamic lands from China to Spain and the western Sudan. His writings gave a glimpse into the world of that time period. |  | 24 |
| 5434418089 | Mansa Musa | Emperor of the kingdom of Mali in Africa. He made a famous pilgrimage to Mecca and established trade routes to the Middle East. |  | 25 |
| 5434418091 | Secular | Non-religious |  | 26 |
| 5434418092 | Missionary | A person who spreads his or her religious beliefs to others |  | 27 |
| 5434418094 | Charlemagne | 768-843; reunited western Europe for the first time since the Roman Empire. |  | 28 |
| 5434418095 | Justinian | 6th century Byzantine emperor; failed to reconquer the western portions of the empire; rebuilt Constatinople; codified Roman law |  | 29 |
| 5434418096 | hajj | A pilgrimage to Mecca, performed as a duty by Muslims |  | 30 |
| 5434418097 | Zakat | part of 4th Pillar, charitable giving of 2.5% of your net worth to community treasury |  | 31 |
| 5434418098 | jihad | A holy struggle or striving by a Muslim for a moral or spiritual or political goal |  | 32 |
| 5434418099 | Umayyad Caliphate | First hereditary dynasty of Muslim caliphs (661 to 750). From their capital at Damascus, the Umayyads ruled one of the largest empires in history that extended from Spain to India. Overthrown by the Abbasid Caliphate. |  | 33 |
| 5434418100 | Abbasid Caliphate | (750-1258 CE) The caliphate, after the Umayyads, who focused more on administration than conquering. Had a bureaucracy that any Mulim could be a part of |  | 34 |
| 5434418101 | Baghdad | Abbasid capital |  | 35 |
| 5434418103 | Sudanic States | Songhay Ghana and Mali. often led by patriarch or council of elders from a family or lineage |  | 36 |
| 5434418104 | Chinampas | Aztec floating gardens |  | 37 |
APES Chapter 9 Flashcards
| 8530243899 | Aquifers | Permeable layers of rock and sediment that contain groundwater in many small spaces. |  | 0 |
| 8530243900 | Unconfined Aquifer | Water can flow easily in and out of the aquifer. Porous rock covered by soil |  | 1 |
| 8530243901 | Confined Aquifer | Aquifers covered by an impermeable and confining layer impeding water flow in or out. |  | 2 |
| 8530243902 | Water Table | Uppermost aquifer layer where water fully saturates the rock or soil. |  | 3 |
| 8530243903 | Groundwater Recharge | Water from precipitation percolates through soil and into aquifer. If confined, can't recharge. |  | 4 |
| 8530243904 | Springs | Water from some aquifers naturally comes up, natural source of freshwater |  | 5 |
| 8530243905 | Artesian Wells | Drilled hole in a confined aquifer releases pressure and pushes water up. |  | 6 |
| 8530243906 | Cone of Depression | Area where there's no longer any groundwater, caused by well overuse, eventually will go dry. |  | 7 |
| 8530243907 | Saltwater intrusion | Lessened pressure from over-pumping so salt water infiltrates and makes well water salty. |  | 8 |
| 8530243908 | Floodplain | Land adjacent to river where excess water spreads onto. |  | 9 |
| 8530243909 | Oligotrophic | Lakes with low productivity because of little nutrients such as phosphorus and nitrogen. |  | 10 |
| 8530243910 | Mesotrophic | Lakes with moderate levels of productivity |  | 11 |
| 8530243911 | Eutrophic | Lakes with high levels of productivity |  | 12 |
| 8530243912 | Impermeable Surfaces | Pavement, buildings, etc. Doesn't allow water penetration, water then runs into sewers and streams. Excess water causes floods. |  | 13 |
| 8530243913 | Levee | Enlarged bank on each side of river to prevent flooding |  | 14 |
| 8530243914 | Dikes | Similar to levees but to prevent ocean waters from flooding coasts that are under sea level. |  | 15 |
| 8530243915 | Dam | Barrier that runs across a river/stream to control water flow |  | 16 |
| 8530243916 | Reservoir | Large body of water stored behind a dam. Held for consumption, generating electricity, flood control, or recreation. |  | 17 |
| 8530243917 | Fish Ladders | Sets of stairs with water flowing over them to have fish migrate despite dams. |  | 18 |
| 8530243918 | Aqueducts | Canals or ditches used to carry water between locations. Transports water to dry areas. |  | 19 |
| 8530243919 | Desalination | Removes salt from salt water to make fresh water. |  | 20 |
| 8530243920 | Distillation | Desalination method. Seawater flows in, heated to create steam, cool seawater in condensing coil causes steam to condense. Brine and fresh water then flows out. |  | 21 |
| 8530243921 | Reverse Osmosis | Desalination method. Seawater flows in, pressure applied, water goes through semipermeable membrane, salt can't. Water and brine flows out. |  | 22 |
| 8530243922 | Hydroponic Agriculture | Cultivation under greenhouse conditions with roots in nutrient rich solution, and not soil. |  | 23 |
AP Human Geography Agriculture Flashcards
| 9843374341 | Animal Husbandry | An agricultural activity associated with the raising of domesticated animals, such as cattle, horses, sheep, and goats. | 0 | |
| 9843374342 | Cash Cropping | Planting large amounts of profitable crops for mass production and sell. | 1 | |
| 9843374343 | Corporate Agriculture (Agribusiness) | System of food production involving everything from the development of the seeds to the marketing and sale of food products at the market. | 2 | |
| 9843374344 | Commercial Crops | A crop grown for direct sale rather than for livestock feed. | 3 | |
| 9843374345 | Domestication of Plants | Domesticating plants for human use, one of the first steps to a full fledged agricultural economy. | 4 | |
| 9843374346 | Double Cropping | Planting and harvesting a crop on a field more than once a year. | 5 | |
| 9843374347 | Fallow | When farmers grow crops in a clear field for only a few years until the soil nutrients are depleted. The farmers then have the soul empty for a few years so the nutrients in the soil can be restored; uncropped land. | 6 | |
| 9843374348 | GMOs | Foods that are mostly products or organisms that have their genes altered in a laboratory for specific purposes, such as disease resistant, increased productivity, or nutrients value; Genetically Modified Organisms. | 7 | |
| 9843374349 | Intensive Farming | Subsistence agriculture in which farmers must expend a relative large amount of effort to produce the maximum feasible yield from a pared of land. | 8 | |
| 9843374350 | Labor-intensive Crops | Includes fruits, garden vegetables, herbs, and anything requiring constant tending or wielding. | 9 | |
| 9843374351 | Labor-intensive Animals | Animals that require constant tending, includes dairy cow and poultry for eggs. | 10 | |
| 9843374352 | Monoculture | Dependence on a single agricultural commodity. | 11 | |
| 9843374353 | Mechanization | In agriculture, the replacement of human labor with technology or machines. | 12 | |
| 9843374354 | Market Gardens | Small scale production of fruits, vegetables, and flowers as cash crops sold directly to local consumers, Distinguishable by the large diversity of crops grown on a small area of land, during a single growing season. Labor is done manually. | 13 | |
| 9843374355 | Primary Economy | Any economic activity pertaining to the collecting, harvesting, and obtaining of raw materials. | 14 | |
| 9843374356 | Plantation Agriculture | Raising a large amount of a 'cash crop' for local sale or export. | 15 | |
| 9843374357 | Suitcase Farmers | A suitcase farm is a farm in which no one reside permanently, they go against the grain of traditional farming. In the US migrant workers provide a cheap, abundant labor source; they work on the farm during the day and leave at night. There is no residence on the site. | 16 | |
| 9843374358 | Spring Wheat | Wheat planted in the spring and harvested in the late summer. | 17 | |
| 9843374359 | Sustainable Yield | Rate of crop production that can be maintained over time. | 18 | |
| 9843374360 | Transhumance | Movement of animal herd to cooler highland areas in the summer to warmer lowland areas in the winter. | 19 | |
| 9843374361 | Winter Wheat | Wheat plated in the fall and harvested in the early summer. | 20 | |
| 9843374362 | Von Thunen Model | Theory that a commercial farmer will decide which crops to grow and which livestock to raise depending on the proximity to market. |  | 21 |
| 9843374363 | Green Revolution | An outgrowth of the 3rd agricultural revolution, this effort began in the 1940s and developed new strains of hybrid seeds and fertilizers that dramatically increased the crop output possible from each farm. | 22 | |
| 9843374364 | Communes | A group of people living together and sharing processions. | 23 | |
| 9843374365 | SE Asia domesticated what? | Yams, Taro Root, Bananas, palm oil, cattle, sheep, goats | 24 | |
| 9843374366 | Western Africa domesticated what? | Millet(China), Sorghum | 25 | |
| 9843374367 | S. Mexico domesticated what? | squash, beans, cotton, Maize(Corn), | 26 | |
| 9843374368 | SW Asia domesticated what? | Wheat, Barley, Rice(India) | 27 | |
| 9843374369 | 1st Agric Revo Location | Nile River Valley/Fertile Crescent | 28 | |
| 9843374370 | 1st Agric Revo Change | Nomadic herders to sedentary lifestyle and intentional farming | 29 | |
| 9843374371 | 1st Agric Revo Impact | Birth of civilization Birth of urban areas Birth of government Birth of class structures(social stratified) Before this egalitarian Created irrigation Created farmers,slaves, government officials, merchants Surplus of food Led to writing Began trading which led to system of defense Towns located on high ground(acropolis) and water | 30 | |
| 9843374372 | 2nd Agric Revo Location | England, Denmark, Netherlands | 31 | |
| 9843374373 | 2nd Agric Revo Sustained by... | Mechanical reaper Combustible engine Seed drill Railroad Refrigeration Artificial feed New banking practices | 32 | |
| 9843374374 | 2nd Agric Revo Before I.R | Improved methods Improved plows and draft-animals (Leesdale and ox) New crops Potato and Corn since both can be grown in marginalized land(Not-so fertile land) Government policies British Enclosure Act Crop rotation and consolidated/fenced off land In same year and plot, rotate crops to maintain soil fertility Improved soil fertility Canals | 33 | |
| 9843374375 | 3rd Agric Revo Defintion | new strains with higher yields through genetic manipulation to increase yield through the use of herbicides and fertilizers | 34 | |
| 9843374376 | How to increase GMOs | 1. Purchase artificial fertilizer Chemicals 2. Irrigation system 3. Purchase herbicides/pesticides 4. Purchase machines to keep up with production 5. Need a receptive environment 6. Need receptive commodity markets 7. Barriers to implementation Poor, unreceptive environment river water | 35 | |
| 9843374377 | Shifting Cultivation Location | Subtropics and Tropics | 36 | |
| 9843374378 | Shifting Cultivation Steps and Characteristics | Steps: Clear land Plant land Fallow(not planting anything so soil can replenish itself) Come back to land when it is full of nutrients Characteristics: Low quality land Low population density | 37 | |
| 9843374379 | Slash-and-Burn is also know as | Patch agriculture Milpa(Yucatan peninsula) Swidden(Indonesia) Chitemene (Nambia) Ladang(Old english meaning to farm) | 38 | |
| 9843374380 | Nomadism | Dry Areas Same climate as livestock ranching(commercial farms in MDCs) Marginalized land | 39 | |
| 9843374381 | Commercial Farming Positives | Increase yield Keeps food costs low | 40 | |
| 9843374382 | Commercial Farming Negatives | Use of chemicals Human health Younger age of puberty Cancer increase Environment Rainforest destruction Desertification Rise in sustainably sourced farming Local and organic Blue zone where business collaborate to show thi | 41 | |
| 9843374383 | Livestock Ranching | Raising of domesticated animals for food or items like leather Climate: Dry Growing industry As countries develop, meat eating increases Standard of living increases Not near market Bulk-reducing industry | 42 | |
| 9843374384 | Dairying | Climate: Cold Perishable Area surrounding dairying is milk shed Closer to market North Latitude Bulk-gaining Bottling fluid | 43 | |
| 9843374385 | Mixed livestock and grain | Raise domesticated animals and growing feed | 44 | |
| 9843374386 | Commercial Grain Farming | Wheat belt Bread-basket US Corn belt | 45 | |
| 9843374387 | Market Gardening | Items people garden Near market since items are perishable Suitcase farms Rely on migrant labor | 46 | |
| 9843374388 | Mediterranean | Dry summers High rainfall needed France, Spain, Greece, North Africa, Australia, Chile, California Produce grapes, citrus, etc. Wine production | 47 | |
| 9843374389 | Plantation farming | Tropics In LDCs Owned by MDCs Cash crops | 48 | |
| 9843374390 | Cash Crop Examples | Worldwide Cotton Rubber Amazon Rice India Sugar from Caribbean | 49 | |
| 9843374391 | Coffee | Ethiopian Origin US #1 consumer Central America and Africa produce it | 50 | |
| 9843374392 | Tea | Most production in Asia China British own most tea plantations | 51 | |
| 9843374393 | Illegal Drugs | Marijuana, Poppy seeds Core are demanders Periphery grows them Takes processing | 52 | |
| 9843374394 | What two factors influenced Von Thunen model? | Perishability and Transport Costs | 53 | |
| 9843374395 | Von Thunen ring outside city(1) | Market gardening/dairying/feedlot Feedlots fatten livestock before slaughter Skinny before sent near market | 54 | |
| 9843374396 | Von Thunen ring (2) | Forestry and growing feed grains Wood: Fuel and building materials Feed: Food for livestock | 55 | |
| 9843374397 | Von Thunen ring (3) | Food grains and cash crops | 56 | |
| 9843374398 | Von Thunen ring (4) | Livestock ranching Low land cost and marginalized land | 57 | |
| 9843374399 | Von Thunen assumptions | Flat terrain---Similar climate/soil---no barriers to transportation | 58 | |
| 9843374400 | Von Thunen factors that decrease the model | Refrigeration Food preservation Global markets/corporate decision making New alternatives for fuel New ways grains are used | 59 | |
| 9843374401 | Horizontal integration | Companies buy out companies Allows for them to set prices No quality for consumers Aka Monopoly Laws created in 1900s that makes monopoly illegal Multiple like industries | 60 | |
| 9843374402 | Vertical integration | One industry that eliminates the middleman Control supply chain Food is homogenous Farm production becomes aggregated Create more commercial agricultural No more small farms Harmful effects on people and environment | 61 | |
| 9843374403 | Double cropping | Harvesting twice in one year Employ crop rotation | 62 | |
| 9843374404 | Triple cropping | Harvesting 3 times in one year Employ crop rotation | 63 | |
| 9843374405 | Vertical farming | Urban, crowded, squatter areas Takes up less space | 64 | |
| 9843374406 | Agrarian-based society | Based on agriculture Mesopotamian, River valley, Primary sectors | 65 | |
| 9843374407 | Animal husbandry | Care of domesticated animals | 66 | |
| 9843374408 | Open-lot farming | Type of subsistence farming Village farms the land Ejiado | 67 | |
| 9843374409 | Subsistence crop | Food crops used only by family or local market trading | 68 | |
| 9843374410 | Organic Farming | o extracts farmers from big corporations o environmental=reduce synthetic chemicals in soil/water farming and ranching without the use of herbicides, pesticides, growth hormones, and other synthetic inputs. o sold in 54% of US grocery store | 69 | |
| 9843374411 | Truck Farms | Farm where farmers produce fruits for the market Use mechanization to produce large quantities of fruits and veggies | 70 | |
| 9843374412 | Staple Grains | wheat, barley, rye, maize, or rice; potatoes, yams, taro, arrowroot, or cassava | 71 | |
| 9843399352 | agribusiness | commercial agriculture characterized by the integration of different steps in the food-processing industry, usually through ownership of large corporations. | 72 | |
| 9843425294 | Agriculture | the deliberate effort to modify a portion of the Earth's surface through the cultivation of crops and the raising of livestock for sustenance or economic gain. | 73 | |
| 9843438176 | Aquaculture | The cultivation of seafood under controlled conditions. | 74 | |
| 9843442688 | Biotechnology | the branch of engineering science in which biological science is used to study the relation between workers and their environments | 75 | |
| 9843453667 | Boserup hypothesis | Population growth compels subsistence farmers to consider new farming approaches that produce enough food to take care of the additional people. | 76 | |
| 9843460220 | Carl Sauer | Geographer from the University of California at Berkeley who defined the concept of cultural landscape as the fundamental unit of graphical analysis. This landscape results from interaction between and the physical environment. Sauer argued that virtually no land escaped alteration by human activities. | 77 | |
| 9843467011 | Commodity Chain | series of links connecting the many places of production and distribution and resulting in a commodity that is on world market | 78 | |
| 9843476666 | Crop Rotation | The practice of rotating use of different fields from crop to crop each year, to avoid exhausting the soil. | 79 | |
| 9843739882 | Domestication | the process of changing plants or animals to make them more useful to humans | 80 | |
| 9843746368 | Feedlot | a building where livestock are fattened for market | 81 | |
| 9843748434 | Horticulture | the cultivation of plants | 82 | |
| 9843750659 | Intertillage | the clearing of rows in the field through the use of hoes, rakes, & other manual equipment | 83 | |
| 9843755186 | Thomas Malthus | an English economist who argued that increases in population would outgrow increases in the means of subsistence (1766-1834) | 84 | |
| 9843757285 | "Tragedy Of The Commons" | situation in which people acting individually and in their own interest use up commonly available but limited resources, creating disaster for the entire community | 85 | |
| 9843764675 | Sustainable Agriculture | Farming methods that preserve long-term productivity of land and minimize pollution, typically by rotating soil- restoring crops with cash crops and reducing in-puts of fertilizer and pesticides. | 86 | |
| 9843766705 | Subsidy | a government payment that supports a business or market | 87 | |
| 9843770846 | Slash-And-Burn (Swidden) | farmers clear land for planting by slashing vegetation and burning the debris. Swidden is the cleared area that is known by a variety of names in different regions (swidden is the name in one specific region). | 88 |
AP Los Desafios Mundiales Flashcards
| 10177242130 | agotarse | to run out, exhaust |  | 0 |
| 10177242131 | el medio ambiente | environment |  | 1 |
| 10177242132 | la atmósfera | atmosphere |  | 2 |
| 10177242133 | bastante | enough or rather |  | 3 |
| 10177242134 | el dióxido de carbono | carbon dioxide |  | 4 |
| 10177242135 | el calentamiento global | global warming |  | 5 |
| 10177242136 | el cambio climático | climate change |  | 6 |
| 10177242137 | la capa de ozono | ozone layer |  | 7 |
| 10177242138 | los combustibles | fuels |  | 8 |
| 10177242139 | de bajo consumo | energy efficient |  | 9 |
| 10177242140 | derramar | to spill |  | 10 |
| 10177242141 | el derretimiento | melting |  | 11 |
| 10177242142 | los desperdicios, los desechos | garbage, waste |  | 12 |
| 10177242143 | deteriorarse | to deteriorate |  | 13 |
| 10177242144 | disminuir/reducirse | to diminish; to reduce |  | 14 |
| 10177242145 | el efecto invernadero | greenhouse effect |  | 15 |
| 10177242146 | el albergue | housing; shelter |  | 16 |
| 10177242147 | el alfabetismo | literacy |  | 17 |
| 10177242148 | el comercio | trade |  | 18 |
| 10177242149 | el crecimiento | growth |  | 19 |
| 10177242150 | el derrame | the spill |  | 20 |
| 10177242151 | el ecosistema | ecosystem |  | 21 |
| 10177242152 | el envejecimiento | aging |  | 22 |
| 10177242153 | el foco de atención | focus |  | 23 |
| 10177242154 | el gobierno | the government |  | 24 |
| 10177242155 | el medio ambiente | the environment |  | 25 |
| 10177242156 | el petróleo | petroleum |  | 26 |
| 10177242157 | el racismo | racism |  | 27 |
| 10177242158 | el refugiado | refugee |  | 28 |
| 10177242159 | el terremoto; el sismo | earthquake | 29 | |
| 10177242160 | el terrorismo | terrorism |  | 30 |
| 10177242161 | el tráfico | traffic | 31 | |
| 10177242162 | empeorar | to worsen |  | 32 |
| 10177242163 | la energia eólica | wind energy |  | 33 |
| 10177242164 | el entorno | surroundings |  | 34 |
| 10177242165 | las especies en peligro de extinción | endangered species |  | 35 |
| 10177242166 | extinguirse | to go extinct |  | 36 |
| 10177242167 | el glaciar | glacier |  | 37 |
| 10177242168 | la huella ecológica | carbon footprint | 38 | |
| 10177242169 | la biodiversidad | biodiversity |  | 39 |
| 10177242170 | la contaminación | contamination |  | 40 |
| 10177242171 | la deforestación | deforestation |  | 41 |
| 10177242172 | la enfermedad | illness |  | 42 |
| 10177242173 | la escasez | shortage/ scarcity |  | 43 |
| 10177242174 | la especie | species |  | 44 |
| 10177242175 | la extinción | extinction |  | 45 |
| 10177242176 | la falta de recursos | lack of resources |  | 46 |
| 10177242177 | la inundación | flood |  | 47 |
| 10177242178 | la pobreza | poverty |  | 48 |
| 10177242179 | la segregación | segregation |  | 49 |
| 10177242180 | la tasa de analfabetismo | illiteracy rate |  | 50 |
| 10177242181 | la tasa de natalidad | birth rate |  | 51 |
| 10177242182 | a largo plazo | long term |  | 52 |
| 10177242183 | las armas | weapons |  | 53 |
| 10177242184 | los derechos humanos | human rights |  | 54 |
| 10177242185 | la masa polar | polar |  | 55 |
| 10177242186 | mejorar | to improve |  | 56 |
| 10177242187 | de bajo consumo | energy efficient | 57 | |
| 10177242188 | el reciclaje | recycling |  | 58 |
| 10177242189 | reciclar | to recycle |  | 59 |
| 10177242190 | los recursos naturales | natural resources |  | 60 |
| 10177242191 | los residuos tóxicos | toxic waste |  | 61 |
| 10177242192 | los recursos | resources |  | 62 |
| 10177242193 | la sobrepoblación | overpopulation |  | 63 |
| 10177242194 | sostenible | sustainable |  | 64 |
| 10177242195 | suficiente | sufficient |  | 65 |
| 10177242196 | la sostenibilidad | sustainability | 66 | |
| 10177242197 | vincular | to link | 67 |
AP Psychology Chapter 1 Flashcards
| 10393040273 | cognitive perspective | thinking, perceiving, interpretations | 0 | |
| 10393041976 | Biological Perspective | a branch of psychology concerned with the links between biology and behavior (brain chemistry) | 1 | |
| 10393043724 | socio-cultural perspective | How behavior and thinking vary across situations and cultures (family, religion, social norms) | 2 | |
| 10393046664 | Psychodynamic Perspective | Unconscious drives, motives, conflicts, and childhood experiences | 3 | |
| 10393047678 | Humanistic Perspective | Growth potential | 4 | |
| 10393054281 | evolutionary perspective | how the natural selection of traits has promoted the survival of genes | 5 |
Flashcards
Flashcards
Pages
Need Help?
We hope your visit has been a productive one. If you're having any problems, or would like to give some feedback, we'd love to hear from you.
For general help, questions, and suggestions, try our dedicated support forums.
If you need to contact the Course-Notes.Org web experience team, please use our contact form.
Need Notes?
While we strive to provide the most comprehensive notes for as many high school textbooks as possible, there are certainly going to be some that we miss. Drop us a note and let us know which textbooks you need. Be sure to include which edition of the textbook you are using! If we see enough demand, we'll do whatever we can to get those notes up on the site for you!

