World History Pre - AP | Chapter 22 Sec. 4 Flashcards
| 13769179056 | Constitutional Monarchy | Glorious Revolution of 1688 had given England a this system of government, various laws limited the power of the English king. | 0 | |
| 13769202904 | George III of England | Became king of Great Britain in 1760, |  | 1 |
| 13769209221 | North American Colonies | Combined population soared from about 250,000 in 1700 to 2,150,000 in 1770, they thrived on trade with the nations of Europe, a new sense of identity was growing in the colonists' minds for nearly 150 years. |  | 2 |
| 13769256344 | Navigation Act of 1651 | Prevented colonists from selling their most valuable products to any country except Britain, colonists had to pay high taxes on imported French and Dutch goods. |  | 3 |
| 13769292046 | French and Indian War (1754-1763) | War between the English and the French, the French enlisted numerous Native American tribes to fight on their side, Britain emerged victorious—and seized nearly all French land in North America. It led to huge debt. |  | 4 |
| 13769325184 | Stamp Act of 1765 | Colonists had to pay a tax to have an official stamp put on wills, deeds, newspapers, and other printed material. |  | 5 |
| 13769347413 | Boston Tea Party (1773) | In protest an import tax on tea, a group of colonists dumped a large load of British tea into Boston Harbor, George III ordered the British navy to close the port of Boston. |  | 6 |
| 13769366669 | First and Second Continental Congress | On September 1774, representatives from every colony except Georgia gathered in Philadelphia to protested the treatment of Boston, since the king paid little attention to their complaints, the colonies decided to form the next one to debate their next move. |  | 7 |
| 13769398531 | Battles of Lexington and Concord (April 19, 1775) | British soldiers and American militiamen exchanged gunfire on the village green in Lexington, Massachusetts, it spread to nearby Concord, The American Revolution had begun. | 8 | |
| 13769489791 | Declaration of Independence (1776) | Written by Thomas Jefferson, firmly based on the ideas of John Locke and the Enlightenment, included a long list of George III's abuses and it ended by declaring the colonies' separation from Britain. |  | 9 |
| 13769501975 | Thomas Jefferson | Political leader, who wrote the Declaration of Independence |  | 10 |
| 13769548643 | Reasons for American Success | 1. Americans' motivation for fighting was much stronger than that of the British, since their army was defending their homeland, 2. Overconfident British generals made several mistakes. 3. Time itself was on the side of the Americans. 4. Fighting an overseas war, 3,000 miles from London, was expensive. 5. Americans did not fight alone. | 11 | |
| 13769594765 | Lord Cornwallis | British general who surrendered at Yorktown, Virginia (1781). Combined forces of about 9,500 Americans and 7,800 French trapped his army. |  | 12 |
| 13769632491 | Articles of Confederation | Ratified in 1781, established the United States as a republic, a government in which citizens rule through elected representatives, states held most of the power, and no executive or judicial branches, only the Congress. Each state, regardless of size, had one vote in Congress. Congress could declare war, enter into treaties, and coin money, it had no power, however, to collect taxes or regulate trade. Passing new laws needed the approval of 9 of the 13 states. |  | 13 |
| 13769707948 | Constitutional Convention (1787) | 55 delegates were experienced statesmen who were familiar with political theories using the political ideas of the Enlightenment, the delegates created a new system of government. | 14 | |
| 13769727693 | Checks and Balances | Each branch checks the actions of the other two, the president received the power to veto legislation passed by Congress, however, the Congress could override a presidential veto with the approval of two-thirds of its members |  | 15 |
| 13769744147 | Federal System | Power was divided between national and state governments. |  | 16 |
| 13769764822 | Federalists | Supporters of the Constitution. | 17 | |
| 13769771291 | Federalist Papers | Argued that the new government would provide a better balance between national and state powers. |  | 18 |
| 13769782986 | Anti-Federalists | Opposed the Constitution, feared that the Constitution gave the central government too much power, wanted a bill of rights to protect the rights of individual citizens. | 19 | |
| 13769817428 | Bill of Rights | Ten amendments to the Constitution, protected basic rights like freedom of speech, press, assembly, and religion. |  | 20 |
Flashcards
Flashcards
Flashcards
Flashcards
Flashcards
Flashcards
AP Human Geography: World Regions Flashcards
| 10611307589 | Central America | Countries from Mexico south to Panama |  | 0 |
| 10611307590 | North America | Canada and the United States |  | 1 |
| 10611307591 | Caribbean | Islands near North America |  | 2 |
| 10611307592 | Latin America | Portuguese and Spanish speaking countries of the Americas |  | 3 |
| 10611307593 | Brazil | Large Portugese speaking country in Latin America |  | 4 |
| 10611307594 | Europe | Countries west of the Ural Mountains and North of Dardanelle Strait |  | 5 |
| 10611307595 | Russian Federation | Largest country in the world |  | 6 |
| 10611307596 | Western Europe | Consisting mostly the countries of Latin and Germanic ethnicity |  | 7 |
| 10611307597 | Eastern Europe | Countries east of Germany, normally associated with Slavic, Balkan, and Baltic States |  | 8 |
| 10611307598 | East Asia | The Korean Peninsula, China, Mongolia, Taiwan, and Japan |  | 9 |
| 10611307599 | Central Asia | Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan and Tajikistan |  | 10 |
| 10611307600 | South Asia | India, Bhutan, Nepal, Bangladesh and Sri Lanka |  | 11 |
| 10611307601 | Southeast Asia | Asian Countries and Islands located east of India and south of China |  | 12 |
| 10611307602 | Asia | Continent bounded by the Pacific, Arctic, and Indian Oceans and Mediterranean Sea |  | 13 |
| 10611307603 | West Africa | Sub-Saharan Countries west of (but not including) Chad and Cameroon |  | 14 |
| 10611307604 | North Africa | African countries North of the Saharan Desert but south of the Mediterranean Sea | 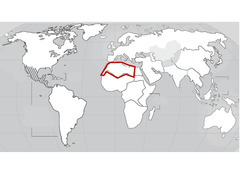 | 15 |
| 10611307605 | Southern Africa | Countries to the south of (but not including) the Democratic Republic of the Congo and Tanzania (Including Madagascar) |  | 16 |
| 10611307606 | East Africa | All countries bordering Kenya and Ethiopia |  | 17 |
| 10611307607 | Antarctica | Uninhabited southernmost continent |  | 18 |
| 10611307608 | Southwest Asia | AKA The middle east |  | 19 |
| 10611307609 | Sub-Saharan Africa | Countries that lie within and below the Saharan Desert |  | 20 |
| 10611307610 | Melanesia | New Guinea, others in the Pacific Area shaded blue in picture |  | 21 |
| 10611307611 | Micronesia | Small islands in Pacific Area pink in the picture |  | 22 |
| 10611307612 | Polynesia | Hawaii, New Zealand, others in Pacific Area purple in picture |  | 23 |
| 10611307613 | Oceania | Area that includes Australia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia |  | 24 |
| 10611307614 | Australia | Largest island in Pacific and Oceania |  | 25 |
| 10611307615 | Pacific Ocean | Largest world ocean, body of water between western sides of North/South America and eastern side of Asia and all of Oceania |  | 26 |
| 10611307616 | Atlantic Ocean | Body of water between eastern North/South America and western side of Europe and Africa |  | 27 |
| 10611307617 | Indian Ocean | Body of water between eastern Africa, southern South Asia, and west of Australia |  | 28 |
| 10611307618 | Southern Ocean | Body of water just north of Antarctica |  | 29 |
| 10611307619 | Arctic Ocean | Body of water north of North America, Asia, and Europe |  | 30 |
| 10611307620 | Africa | Continent surrounded by Atlantic and Indian Oceans |  | 31 |
AP Literature & Composition Character Types Flashcards
| 11615427373 | Direct Characterization | The process by which a character is revealed through direct exposition: narrative description, adjectives, or epithets. The narrative voice tells the reader how to feel about the character. | 0 | |
| 11615429557 | Indirect Characterization | The process by which a character is revealed through the character's speech, actions, or appearance. The reader is invited to draw her own conclusions about the character by using her own judgment. | 1 | |
| 11615435319 | Round Character | A character who is complex, nuanced, multi-faceted. Round characters generally are dynamic and have unexpected facets to their personality. | 2 | |
| 11615437374 | Flat Character | A stereotypical, stock, or one-dimensional character. Usually static, shallow. | 3 | |
| 11615491870 | Stock Character | An easily recognizable character "type," a frequently used character in literature traditions, flat and generally static, cliché. (Ex: "the villain in the black hat," "the ditsy cheerleader," "the hooker with a heart of gold"). | 4 | |
| 11615495142 | Protagonist | The story's central character, of primary focus or interest. | 5 | |
| 11615498174 | Antagonist | The character that opposes the Protagonist and often produces the primary conflict in the narrative. | 6 | |
| 11615511398 | Antihero | A protagonist who has traits that are the opposite of a traditional hero. This character may be confused, misguided, or ineffectual. Antiheroes usually change little in the narrative, and often only to learn that the world is isolating or indifferent to individuals. | 7 | |
| 11615514291 | Foil Character | A character whose attributes contrast with a main character (protagonist or antagonist) in order to accentuate or emphasize the main character's traits. | 8 | |
| 11615517154 | Static Character | A character who does not undergo growth or change, stays the same in his or her essential characteristics. | 9 | |
| 11615517196 | Dynamic Character | A character who undergoes growth or change in the course of the narrative. | 10 |
Pages
Need Help?
We hope your visit has been a productive one. If you're having any problems, or would like to give some feedback, we'd love to hear from you.
For general help, questions, and suggestions, try our dedicated support forums.
If you need to contact the Course-Notes.Org web experience team, please use our contact form.
Need Notes?
While we strive to provide the most comprehensive notes for as many high school textbooks as possible, there are certainly going to be some that we miss. Drop us a note and let us know which textbooks you need. Be sure to include which edition of the textbook you are using! If we see enough demand, we'll do whatever we can to get those notes up on the site for you!

