chapter 3 voyages textbook: AP world history Flashcards
| 8509605557 | Ashoka | (r.268-232 B.C.E.) The third king of the Mauryan dynasty (ca. 320-185 B.C.E.), the first ruler to support Buddhism. | 0 | |
| 8510022484 | Dharma | A Sanskrit term meaning correct conduct according to law or custom;Buddhists including Ashoka, used this concept to refer to the teachings of the Buddha. | 1 | |
| 8510028355 | Monsoon | A term referring both to seasonal winds in South Asia blowing northeast in spring and early summer and southwest in fall and winter, and to the heavy seasonal rains they bring. | 2 | |
| 8510030711 | Indus River Valley | Site of the earliest complex society on the Indian subcontinent (2600-1700 B.C.E.) characterized by brick cities, drainage systems, open plazas, and broad avenues. | 3 | |
| 8510034493 | Sanskrit | A language, such as Latin, Greek, and English, belonging ti the Indo-European language family and spoken by Indo-Aryan migrants to north India around 1500-1000 B.C.E. | 4 | |
| 8510038175 | Rig Veda | A collection of 1,028 Sanskrit hymns, composed around 1500-1000 B.C.E. but written down around 1000 C.E. One of the most revealing sources about Indo-Europeans who settled in north India. | 5 | |
| 8510044549 | Vedic Religion | Religious belief system of Indo-European migrants to north India; involved animal sacrifice and elaborate ceremonies to ensure that all transitions in the natural world-day to night, or one season to the next-proceeded smoothly. | 6 | |
| 8510049504 | Nomads | A term for the people who migrate seasonally from place to place to find grass for their animals. they do not usually farm but tend their herds full-time. | 7 | |
| 8510052172 | Varna | From the Sanskrit word for "color": the four major social groups of ancient Indian society, ranked in order of purity (not wealth or power): Brahmin priests at the top, then warriors, then farmers and merchants, and finally dependent laborers. | 8 | |
| 8510056141 | Jati | A term, sometimes translated as "sub-caste" for groups of five thousand people in modern day India. Many, but not all, Indians marry someone from the same Jati and share meals on equal footing only with people of the same Jati. | 9 | |
| 8510059969 | Karma | The sum of one's deeds in this and all earlier existences that determines one's rebirth in the next life. | 10 | |
| 8510063494 | Jainism | An Indian religion founded around the same time as Buddhism that emphasizes right faith, right knowledge, and right conduct: a key tenet is not to harm any living beings. | 11 | |
| 8510065776 | Buddha | The founder of the Buddhist religion, Siddhartha Gautama (ca. 600-400 B.C.E.) also called the Buddha or the enlightened one. | 12 | |
| 8510067814 | Nirvana | A Sanskrit word that literally means "extinction," as when the flame on a candle goes out. In Buddhism the term took on a broader meaning: those who followed the eightfold path and understood the Four Noble Truths would gain true understanding. | 13 | |
| 8510071565 | Mauryan Dynasty | (ca.320-185 B.C.E.) A dynasty that unified much of the Indian subcontinent. Relying on trunk roads, it exercised more control in the cities that in the countryside. | 14 | |
| 8511872252 | Chakravartin | Literally "turner of the wheel", a Buddhist term for the ideal ruler who patronized Buddhism but never became a monk. | 15 | |
| 8511876993 | Ceremonial state | State whose ruler sponsored religious observances and construction of religious edifices in the hope that his subjects would willingly acknowledge him as a ruler. Usually contrasted with rulers who depended on sheer force to govern. | 16 | |
| 8511896767 | Lay Buddhist | A Buddhist devotee who observes the five precepts not to kill, steal, commit adultery, lie, or drink alcohol, but continues to live at home and does not join the Buddhist order. | 17 | |
| 8511905507 | Dhows | Small sailboats used in the Indian ocean. | 18 |
AP World History Religions Flashcards
Ap world hosts religions
| 11141567848 | Why did we develop belief systems? | Because humans have always needed to understand natural phenomenon. We want to explain the world around us. | 0 | |
| 11141567849 | Polytheism | Belief in many gods |  | 1 |
| 11141567850 | Monotheism | Belief in one God | 2 | |
| 11141567851 | Animism | -They practice nature worship -They believe that everything has a spirit -They communicated with and showed respect to ancestors. -It is practiced worldwide but mostly in Africa and the Americas. | 3 | |
| 11141567852 | Shinto | A Japanese religion whose followers believe that all things in the natural world are filled with divine spirits -"Way of the Gods" -Founded around the year 500 BCE -The Emperor of Japan was considered to be divine and a direct descendant of the Sun Goddess. | 4 | |
| 11141567853 | Hinduism | A religion and philosophy developed in ancient India, characterized by a belief in reincarnation and a supreme being who takes many forms. -Polytheistic -A result of cultural diffusion between the Aryans and other native people in India. -Practiced in India -The Vedas, Upanishads, etc.. were all significant writings. | 5 | |
| 11141567854 | Brahma | The term for the Supreme God and Universal Soul in Hinduism. | 6 | |
| 11141567855 | Reincarnation | In Hinduism and Buddhism, the process by which a soul is reborn continuously until it achieves perfect understanding Basically Samsara | 7 | |
| 11141567856 | Karma | (Hinduism and Buddhism) the effects of a person's actions that determine his destiny in his next incarnation (life) | 8 | |
| 11141567857 | Dharma | Fulfilling one's duty in life | 9 | |
| 11141567858 | Caste System | A Hindu social class system that controlled every aspect of daily life | 10 | |
| 11141567859 | Judaism | -A religion with a belief in one god (Monotheistic) -It originated with Abraham and the Hebrew people. -Practiced worldwide but most Jews are in Israel. -They have 10 commandments | 11 | |
| 11141567860 | Buddhism | A religion founded in India by Siddhartha Gautama which teaches that the most important thing in life is to reach peace by ending suffering. | 12 | |
| 11141567861 | The Four Noble Truths | The core of the Buddhist teaching. There is suffering. There is a cause to suffering. There is an end to suffering. The is a path out of suffering (the Noble 8-fold path). 1. Life is full of pain and suffering 2. human desire causes this suffering 3. By putting an end to desire, humans can end suffering 4. Humans can end desire by following the Eightfold Path | 13 | |
| 11141567862 | The Eightfold Path | 1. Know that suffering is caused by desire 2. Be selfless and love all life 3. Do not lie, or speak without a cause 4. Do not kill, steal, or commit other unrighteous acts 5. Do not do things which promote evil 6. Take effort to promote righteousness 7. Be aware of your physical actions, state of mind, and emotions. 8. Learn to meditate. | 14 | |
| 11141567863 | Confucianism | A philosophy that adheres to the teachings of the Chinese philosopher Confucius. It shows the way to ensure a stable government and an orderly society in the present world and stresses a moral code of conduct. | 15 | |
| 11141567864 | Five Relationships in Confucianism: | - Ruler to ruled - Father to Son - Older brother to Younger brother - Husband to Wife - Friend to Friend | 16 | |
| 11141567865 | Taoism or Daoism | an ideology whose central theme is the Way, a philosophy teaching that eternal happiness lies in total identification with nature and deploring passion, unnecessary invention; simple life of individuals -Ying and Yang is used to illustrate the natural harmony in the world. |  | 17 |
| 11141567866 | Christianity | A monotheistic system of beliefs and practices based on the Old Testament and the teachings of Jesus as embodied in the New Testament and emphasizing the role of Jesus as savior. -Also has the Ten Commandments -Believe in the Holy Trinity Christians take part in sacraments. | 18 | |
| 11141567867 | Islam | A religion based on the teachings of the prophet Mohammed which stresses belief in one god (Allah), Paradise and Hell, and a body of law written in the Quran. Followers are called Muslims. | 19 | |
| 11141567868 | The Five Pillars of Islam | 1. Confession of Faith 2. Prayer 3. Charity 4. Fasting 5. Pilgrimage | 20 | |
| 11141567869 | Zoroastrianism | - A dualistic faith, this means they believe in two gods representing good and evil -It was very important during the Sassanid Persian Dynasty. | 21 | |
| 11141567870 | Legalism | Chinese philosophy developed by Hanfeizi; taught that humans are naturally evil and therefore need to be ruled by harsh laws | 22 |
AP World history chapters 1-3 Flashcards
| 7522684175 | Norte Chico/Caral | 0 | ||
| 7522684176 | Indus Valley civilization | A Bronze Age civilization mainly in the northwestern regions of South Asia | 1 | |
| 7522697250 | Olmec civilization | Pre-classical meso-america from 1200-400 BCE and is generally considered the forerunner of all subsequent mess-american cultures such as the Myans and Aztecs | 2 | |
| 7522720033 | Uruk | An ancient city of Sumer situated in the east of the present bed of the Euphrates river | 3 | |
| 7522728105 | Epic of Gilgamesh | A written piece from ancient Mesopotamia that is often regarded as the earliest forms of literature | 4 | |
| 7522744715 | Harappa | An archaeological site in Punjab, Pakistan | 5 | |
| 7522748843 | Mohenjo-Daro | An archaeological site in Sindh, Pakistan built around 2500 BCE | 6 | |
| 7522762060 | Rise of the state/Empire | A central government that includes people of all different regions, cultures, and languages | 7 | |
| 7522771701 | Ancient Egypt | Civilization of northeast Africa concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile river | 8 | |
| 7522776380 | Sumer | The first Urban civilization in the historical region of southern Mesopotamia | 9 | |
| 7522778689 | Paneb | A villian, someone who stole, a criminal | 10 | |
| 7522785575 | Nubia | A region along the Nile river encompassing the areas between what is today central Sudan and southern Egypt | 11 | |
| 7522796674 | Persian Empire | Cryus, Darius, and Xerxes | 12 | |
| 7522796675 | Athenian Democracy | Women not included, male and land owners could vote, direct democracy | 13 | |
| 7532333425 | Battle of Salamis | 480 BC, second assult on Greece, naval battle, Perisans loose | 14 | |
| 7532333426 | Dark ages | 1,500-800 BC, econmic collapse | 15 | |
| 7522804726 | Centeral Asia/ Oxus civilization | 16 | ||
| 7522816883 | Greco-Persian Wars | Series of conflicts between the Achaemenid Empire of Persia and Greek city-states that started and ended in 449 BC | 17 | |
| 7522816884 | Alexander the Great | A- Conqures Persia B- Spreads greek culture- hellenism C- Names 26 cities Alexandria | 18 | |
| 7522819559 | Hellenistic Era | The time between the death of Alexander the Great and the rise of the Roman domination, spreads great culture | 19 | |
| 7522819560 | Augustus | Founder of the Roman Principate and the first Roman emperor from 27 BC-14 AD | 20 | |
| 7522819561 | Pax Romana | Long period of relative peacefulness | 21 | |
| 7522825020 | Qin Shihuangdi | The founder of the Qin Dynasty and the first emperor of unified China | 22 | |
| 7522833373 | Han Dynasty | 23 | ||
| 7522833374 | Trung Trac | Leader of the first Vietnamese independent movement | 24 | |
| 7522837297 | Kushan Empire | Syncretic empire, formed by Yuezhi in the bacterial territories, first century | 25 | |
| 7522839854 | Mauryan Empire | A geographically extensive Iron Age historical power founded by Chandragupta Maurya which dominated ancient India between c. 322 and 187 BCE. | 26 | |
| 7532333427 | Mycenaean civilization | 2,000 BCE, mainland Greece, warlike- desifer their language | 27 | |
| 7532333428 | Minoan civilization | 2,000 BCE, Crete, large city, Knossos, peaceful | 28 | |
| 7522839855 | Ashoka | Indian emperor of the Mauryan Dynasty who ruled all of the India subcontinent from 268-232 BCE | 29 | |
| 7522843787 | Iliad and the Odyssey | 30 | ||
| 7522843788 | Shang Dynasty | 1750-1027 BC, the first major Chinese empire centered around the Yellow and Yangze rivers | 31 | |
| 7522843789 | Hitties | The first major military culture that developed iron weapons and conquered Anatolia | 32 | |
| 7522847290 | Neo-Assyrian Empire | 911-612 BC, the largest state empire in Anatolia that also constructed the first known library of Ashurbinapol | 33 | |
| 7522847291 | Phoenician Empire | Immerse sea-going empire which established colonies around the Mediterranean, also developed our 26 letter alphabet | 34 | |
| 7522849937 | Diaspora | 35 | ||
| 7522852545 | Library at Ashurbinapol | 36 | ||
| 7536565644 | Persepolis | A- Capital of the Persian empire B- Alexander the Great conquered this city |  | 37 |
| 7536593659 | Rosetta Stone | A- Hieroglyphs, coptic, and greek B- Français Champollion |  | 38 |
| 7536620683 | Egyptian burial portrait | A- Found in the pyramid of manure B- Shows a positive view of the afterlife | 39 | |
| 7536628893 | Egyptian burial statue | A- Pharaoh and his wife in the burial chamber B- First culture that created statues of women |  | 40 |
| 7536639594 | The great pyramids of Giza | 2,500 BC 40-50 years to build A- Tombs for Pharaohs B- Biggest structures in the world until the Eiffel tower |  | 41 |
| 7536657324 | The Sphinx | 2,500 BC 65 feet tall, 250 long A- Pharaoh and a lion B- Symbolic protector of the tomb |  | 42 |
| 7536672037 | Death mask of King Tut | A- The best preserved object from ancient Egypt B- The curse of the mummy |  | 43 |
| 7536691977 | Greek theater at Epidauris | 350 BC A- Seats about 25,000 people B- Acustically perfect | 44 | |
| 7536703877 | The Parthenon | 450 BC A- Temple to the goddess of wisdom B- Entasis- visually beautiful |  | 45 |
| 7536721472 | Greek discabolas (disk player) | 500 BC A- More anatomically correct B- Admired nudity | 46 |
AP World History Review Test Monday/27 Flashcards
| 6450189575 | SPICE | Social, political, human-environment interaction, cultural, economic | 0 | |
| 6450189576 | Historical thinking skills | Argumentation, analyzing evidence, causation, continuity and change over time, comparison, contextualization, synthesis, interpretation, periodization | 1 | |
| 6450189577 | 8000 BCE-600 BCE | Agricultural/Neolithic revolution-Buddhism/Confucianism/Taoism DARTH Domestication, agriculture, river valleys, trans-regional trade, Hittites and Iron | 2 | |
| 6450189578 | 600 BCE-600 CE | B/C/T-Islam begins Quiet People Make Great Human Resources Qin, Persia, Mauryan and Maya, Gupta and Greece, Han, Rome | 3 | |
| 6450189579 | 600 CE-1450 CE | Islam-the age of exploration TIMBER Tang-Song, Islam and Incas, Mongols and Mali, Byzantine, Europe Regionalized | 4 | |
| 6450189580 | 1450 CE-1750 CE | Byzantine decline/rise of Ottoman-Industrial Revolution GERMS Gunpowder empires, exchange and exploration, Renaissance and reformation, silver-sugar-slavery | 5 | |
| 6450189581 | 1750 CE-1900 CE | Industrial Revolution-tensions leading to WWI RAISING Revolutions, Abolition, industrialization, social Darwinism and spheres of influence, imperialism, nationalism, global migrations, ING=Qing | 6 | |
| 6450189582 | 1900 CE-present | DICE Decolonization, innovations and integration, conflicts and communism, environmental issues and economic integration | 7 | |
| 6450189583 | Chinese dynasty song | Shang, Zhou, Qin, Han, Sui, Tang, Song, Yuan, Ming, Qing, Republic, Mao, Deng | 8 | |
| 6452309113 | 4 parts of the AP exam | multiple choice, short answer, document based, long essay | 9 | |
| 6452309623 | multiple choice | 55 questions | 10 | |
| 6452312050 | short answer | 4 questions | 11 | |
| 6452312413 | document based | 1 question | 12 | |
| 6452312984 | long essay | 1 question | 13 |
AP World History - Strayer Chapter 18 Flashcards
| 8960469003 | steam engine | steam engine Mechanical device in which the steam from heated water builds up pressure to drive a piston, rather than relying on human or animal muscle power; the introduction of the steam engine allowed a increase in productivity and made the Industrial Revolution possible; Invented by James Watt |  | 0 |
| 8960469004 | Indian Cotton Textiles | well-made and inexpensive cotton textiles from India; competition stimulated the British textile industry to industrialize, led to the eventual destruction of the Indian textile market in Europe and India |  | 1 |
| 8960469005 | Middle class Values | middle-class values Belief system typical of the middle class that developed in Britain in the nineteenth century; it emphasized thrift, hard work, rigid moral behavior, cleanliness, and "respectability" |  | 2 |
| 8960469006 | lower middle class | Developed in nineteenth century that consisted of people employed in the service sector as clerks, salespeople, secretaries, police officers, and the like; by 1900, about 20 percent of Britain's population |  | 3 |
| 8960469007 | Karl Marx | Karl Marx a philosopher and economist famous for his ideas about capitalism and communism |  | 4 |
| 8960469008 | Labour Party | Working-class political party in the 1890s and dedicated to reforms and a peaceful transition to socialism, viable alternative to the emphasis of Marxism |  | 5 |
| 8960469009 | Latin American export boom | Large-scale increase in Latin American exports (mostly raw materials and foodstuffs) to industrializing countries in the second half of the nineteenth century, made possible by major improvements in shipping; the boom mostly benefited the upper and middle classes |  | 6 |
| 8960469010 | Proletariat | the industrial working class; originally used in ancient Rome to describe the poorest part of the urban population |  | 7 |
| 8960469011 | Bourgeoisie | owners of industrial capital; originally meant "townspeople" |  | 8 |
| 8960469012 | Socialism in the US | minor political movement in the United States | 9 | |
| 8960469013 | Progressives | advocated reform measures to correct the ills of industrialization |  | 10 |
| 8960469014 | Russian Revolution of 1905 | Russia's defeat at the hands of Japan in 1905; the revolution was suppressed, but it forced the government to make substantial reforms |  | 11 |
| 8960469015 | Mexican Revolution | Mexican reformers from the middle class joined with workers and peasants to overthrow the dictator Porfirio Díaz and create a new democratic order |  | 12 |
| 8960469016 | Caudillos | strongman who seized control of a government in nineteenth-century Latin America |  | 13 |
| 8960469017 | Dependent development | Latin America's economic growth financed by foreign capital, dependent on European and North American |  | 14 |
ap world history vocab Flashcards
| 10502060010 | Paleothic Age | Old Stone Age, ending in 12.000 A.C. ; typified by he use of crude stone tools and hunting and gathering for subsistence | 0 | |
| 10502060011 | Homo sapiens | The humanoid species that emerged as most successful at the end of the Paleolithic period. | 1 | |
| 10502060012 | Neolithic Age | The New Stone Age between 8000 and 5000 B.C.E.; period in which adaptation of sedentary agriculture occurred; domestication of plants and animals accomplished | 2 | |
| 10502060013 | Neolithic Revolution | The succession of technological innovations and changes in human organization that led to the development of agriculture, 8500-3500 B.C.E. | 3 | |
| 10502060014 | hunting and gathering | The original human economy, ultimately eclipsed by agriculture; groups hunt for meat and forage for grains, nuts, and berries. | 4 | |
| 10502060015 | Catal Huyuk | Early urban culture based on sedentary agriculture; located in modern southern Turkey; was larger in population than Jericho, had greater degree of social stratification. | 5 | |
| 10502060016 | Bronze Age | From about 4000 B.C.E., when bronze tools were first introduced in the Middle East, to about 1500 B.C.E., when iron began to replace it. | 6 | |
| 10502060017 | Nomads | Cattle- and sheep-herding societies normally found on the fringes of civilized societies; commonly referred to as "barbarian" by civilized societies | 7 | |
| 10502060018 | civilization | Societies distinguished by reliance on sedentary agriculture, ability to produce food surpluses, and existence of non-farming elites, as well as merchant and manufacturing groups. | 8 | |
| 10502060019 | Mesopotamia | Literally "between the rivers"; the civilizations that arose in the alluvial plain of the Tigris and Euphrates river valleys | 9 | |
| 10502060020 | Sumerians | People who migrated into Mesopotamia c. 4000 B.C.E.; created first civilization within region; organized area into city-states. | 10 | |
| 10502060021 | Cuneiform | A form of writing developed by the Sumerians using a wedge shaped stylus and clay tablets. | 11 | |
| 10502060022 | Ziggurats | Massive towers usually associated with Mesopotamian temple complexes. | 12 | |
| 10502060023 | Babylonians | Unified all of Mesopotamia c. 1800 B.C.E.; empire collapsed due to foreign invasion c. 1600 B.C.E. | 13 | |
| 10502060024 | Hammurabi | The most important ruler of the Babylonian empire; responsible for codification of law.(1792-1750 b.c.e) | 14 | |
| 10502060025 | Pyramids | monumental architecture typical of Old Kingdom Egypt; used as burial sites for pharaohs. | 15 | |
| 10502060026 | Kush | An African state that developed along the upper reaches of the Nile c. 100 B.C.E.; conquered Egypt and ruled it for several centuries. | 16 | |
| 10502060027 | Indus River | River sources in Himalayas to mouth in Arabian Sea; location of Harappan civilization. | 17 | |
| 10502060028 | Harappa | Along with Mohenjodaro, major urban complex of the Harappan civilization; laid out on planned grid pattern. | 18 | |
| 10502060029 | Aryans | Indo-European nomadic pastoralists who replaced Harappan civilization; militarized society | 19 | |
| 10502060030 | Vedas | Aryan hymns originally transmitted orally but written down in sacred books from the 6th century B.C.E. | 20 | |
| 10502060031 | Mahabharata | Indian epic of war, princely honor, love, and social duty; written down in the last centuries BCE; previously handed down in oral form | 21 | |
| 10502060032 | Ramayana | One of the great epic tales from classical India; traces adventures of King Rama and his wife, Sita; written 4th to 2nd centuries B.C.E. | 22 | |
| 10502060033 | Upanishads | Later books of the Vedas; contained sophisticated and sublime philosophical ideas; utilized by Brahmans to restore religious authority | 23 | |
| 10502060034 | yellow river | Also known as the Huanghe; site of development of sedentary agriculture in China. | 24 | |
| 10502060035 | Shang | First Chinese dynasty for which archeological evidence exists; capital located in Ordos bulge of the Huanghe; flourished 1600 to 1046 B.C.E. | 25 | |
| 10502060036 | Olmecs | People of a cultural tradition that arose at San Lorenzo and La Venta in Mexico c. 1200 B.C.E.; featured irrigated agriculture, urbanism, elaborate religion, beginnings of calendrical and writing systems. | 26 | |
| 10502060037 | Chavin de Huantar | Chavin culture appeared in highlands of Andes between 1800 and 1200 B.C.E.; typified by ceremonial centers with large stone buildings; greatest ceremonial center was Chavin de Huantar; characterized by artistic motifs. | 27 | |
| 10502060038 | Phoenicians | Seafaring civilization located on the shores of the eastern Mediterranean; established colonies throughout the Mediterranean | 28 | |
| 10502060039 | Monotheism | The exclusive worship of a single god; introduced by the Jews into Western civilization. | 29 | |
| 10502060040 | afro-eurasia | A super continent that comprises Africa and Eurasia | 30 | |
| 10502060041 | agrarian | relating to land; relating to the management or farming of land | 31 | |
| 10502060042 | Animism | the doctrine that all natural objects and the universe itself have souls | 32 | |
| 10502060043 | Before Common Era (BCE) | of the period prior to Christian Era. Previously BC | 33 | |
| 10502060044 | circa | When noting dates the letter "c." before a date represents what? (example: Jesus was born c. 5 BCE). It means approximately. | 34 | |
| 10502060045 | Common Era (CE) | refers to period of time began after the birth of jesus christ | 35 | |
| 10502060046 | Culture | the arts and other manifestations of human intellectual achievement regarded collectively. | 36 | |
| 10502060047 | divine | of, from, or like God or a god. | 37 | |
| 10502060048 | eglitarian | of, relating to, or believing in the principle that all people are equal and deserve equal rights and opportunities. | 38 | |
| 10502060049 | Eurasia | the combined continent of Europe and Asia | 39 | |
| 10502060050 | hierarchy | a system or organization in which people or groups are ranked one above the other according to status or authority. | 40 | |
| 10502060051 | indigenous | originating or occurring naturally in a particular place; native. | 41 | |
| 10502060052 | kin | relatives | 42 | |
| 10502060053 | lineage | lineal descent from an ancestor; ancestry or pedigree. | 43 | |
| 10502060054 | matriarchy | a system of society or government ruled by a woman or women. | 44 | |
| 10502060055 | Metallurgy | the branch of science and technology concerned with the properties of metals and their production and purification. | 45 | |
| 10502060056 | Migration | movement of people from one place to another | 46 | |
| 10502060057 | Monotheistic | relating to or characterized by the belief that there is only one God. | 47 | |
| 10502060058 | patriarchy | a system of society or government in which the father or eldest male is head of the family and descent is traced through the male line | 48 | |
| 10502060059 | Periodization | an act or instance of dividing a subject into historical eras for purposes of analysis and study. | 49 | |
| 10502060060 | Polytheistic | the doctrine that there is more than one god or many gods | 50 | |
| 10502060061 | Revolution | a forcible overthrow of a government or social order in favor of a new system. | 51 | |
| 10502060062 | Secular | denoting attitudes, activities, or other things that have no religious or spiritual basis. | 52 | |
| 10502060063 | Shaman | a person regarded as having access to, and influence in, the world of good and evil spirits, especially among some peoples of northern Asia and North America. Typically such people enter a trance state during a ritual, and practice divination and healing. | 53 | |
| 10502060064 | ascetic | a person who practices severe self-discipline and abstention | 54 | |
| 10502060065 | Alms | money or food given to poor people | 55 | |
| 10502060066 | archaic | ancient; old-fashioned | 56 | |
| 10502060067 | austerity | sternness or severity of manner or attitude | 57 | |
| 10502060068 | Autocracy | a system of government by one person with absolute power. | 58 | |
| 10502060069 | Aristocracy | the highest class in certain societies, especially those holding hereditary titles or offices. | 59 | |
| 10502060070 | barbarian | a member of a community or tribe not belonging to one of the great civilizations | 60 | |
| 10502060071 | Bureaucracy | a system of government in which most of the important decisions are made by state officials rather than by elected representatives. | 61 | |
| 10502060072 | Caste | the system of dividing society into hereditary classes | 62 | |
| 10502060073 | city-state | a city that with its surrounding territory forms an independent state.(athens and sparta of greece) | 63 | |
| 10502060074 | Clergy | the body of all people ordained for religious duties, especially in the Christian Church. | 64 | |
| 10502060075 | concubine | a woman who lives with a man but has lower status than his wife or wives(polygamous societies) | 65 | |
| 10502060076 | cultural diffusion | the spreading out of culture, culture traits, or a cultural pattern from a central point. | 66 | |
| 10502060077 | deity | a god or goddess (in a polytheistic religion). | 67 | |
| 10502060078 | Democracy | a system of government by the whole population or all the eligible members of a state, typically through elected representatives. | 68 | |
| 10502060079 | domestic | relating to the running of a home or to family relations;existing or occurring inside a particular country,not foreign or international | 69 | |
| 10502060080 | Dowry | property or money brought by a bride to her husband on their marriage | 70 | |
| 10502060081 | Dynasty | a line of hereditary rulers of a country. | 71 | |
| 10502060082 | Eunuch | a man who has been castrated, especially (in the past) one employed to guard the women's living areas at an oriental court. | 72 | |
| 10502060083 | filial | of or due from a son or daughter | 73 | |
| 10502060084 | mandate | an official order or commission to do something. | 74 | |
| 10502060085 | maritime | connected with the sea, especially in relation to seafaring commercial or military activity. | 75 | |
| 10502060086 | merchant | a person or company involved in wholesale trade, especially one dealing with foreign countries or supplying merchandise to a particular trade. | 76 | |
| 10502060087 | monastic | Relating to or resembling a monastery (where monks or nuns live), esp. by being quiet, secluded, contemplative, strict, and/or lacking luxuries | 77 | |
| 10502060088 | orthodox | conforming to what is generally or traditionally accepted as right or true; established and approved. | 78 | |
| 10502060089 | Pagan | a person holding religious beliefs other than those of the main world religions | 79 | |
| 10502060090 | paternal | of or like a father | 80 | |
| 10502060091 | peasant | a poor farmer of low social status who owns or rents a small piece of land for cultivation | 81 | |
| 10502060092 | Syncretic | the attempted reconciliation or union of different or opposing principles, practices, or parties. | 82 | |
| 10502060093 | Tariff | a tax or duty to be paid on a particular class of imports and exports | 83 |
Flashcards
AP World History Strayer Chapter 8 Vocabulary Flashcards
Unit Three Part Three
| 11330566218 | Sui Dynasty | *Definition:* Short dynasty between Han and Tang. *Significance:* Built Grand Canal, strengthened government, and introduced Buddhism to China. |  | 0 |
| 11330566219 | Tang Dynasty | *Definition:* Dynasty often referred to as "China's Golden Age". (618 CE - 907 CE) *Significance:* China expands to Vietnam, Imperial examination perfected. New technologies (paper money, gunpowder, junks, etc...) through silk road. | 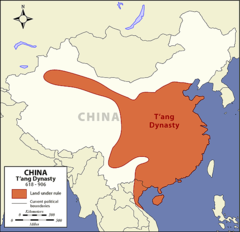 | 1 |
| 11330566220 | Song Dynasty | *Definition:* (960 CE - 1279 CE) Started by Tai Zu. *Significance:* Million people there. Foot binding, magnetic compass, navy, and traded with India and Persia. |  | 2 |
| 11330566221 | Hangzhou | *Definition:* Capital of later Song Dynasty. *Significance:* Permitted overseas trading with population exceeding 1 million. |  | 3 |
| 11330566222 | Economic Revolution | *Definition:* Rapid population growth, economic speculation, increase in industrial production and innovations (Song dynasty). *Significance:* Made China "by far the richest, most skilled, and most populous country on Earth." |  | 4 |
| 11330566223 | Foot Binding | *Definition:* Practice in Chinese society to mutilate women's feet to make them smaller. *Significance:* It was associated with images of female beauty and eroticism. |  | 5 |
| 11330566224 | Tribute System | *Definition:* Chinese method of dealing with foreign lands and people that assumed subordination of all non-chinese authorities. They required all foreigners wanting access to China to pay tribute. *Significance:* System the attempted to regulate their relationships with Northern Nomads. |  | 6 |
| 11330566225 | Khitan/Jurchen People | *Definition:* Nomadic people who established a state that included parts of Northern China. *Significance:* Was a nomadic group who "picked up the pieces" after collapse of Tang Dynasty. |  | 7 |
| 11330566226 | Silla Dynasty (Korea) | *Definition:* First ruling dynasty to bring a measure of political unity to Korean Peninsula. *Significance:* Allied with China to bring political unity to the peninsula for the first time. |  | 8 |
| 11330566227 | Hangul | *Definition:* Phonetic alphabet in Korea (14th century). *Significance:* Helped Korea move toward greater cultural independence. | 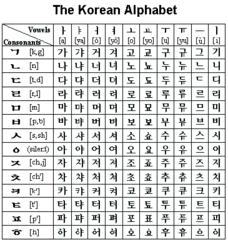 | 9 |
| 11330566228 | Shotoku Taishi | *Definition:* Japanese statesman who launched the drive to make Japan into centralized bureaucratic state modeled on China. *Significance:* Launched a series of large-scale missions to China. |  | 10 |
| 11330566229 | Bushido | *Definition:* "Way of the Warrior". *Significance:* A distinct set of values for Samurais. |  | 11 |
| 11330566230 | Chinese Buddhism | *Definition:* Entered China through cultural accommodations. *Significance:* Useful to helping nomadic rulers govern northern China because it was foreign. |  | 12 |
| 11330566231 | Emperor Wendi | *Definition:* Sui Emperor who patronized Buddhism. *Significance:* He was responsible for the monasteries constructed at the base of China's 5 sacred mountains. |  | 13 |
| 11330566232 | Trung Sisters | *Definition:* Two sisters who began the Vietnam revolution against China *Significance:* They became a symbol for Vietnam to look towards during Chinese rule |  | 14 |
| 11330566233 | Chu nom | *Definition:* The writing system of Vietnam *Significance:* United Vietnam even during times of civil war |  | 15 |
AP Stat Formula Sheets Flashcards
More detailed discussions of each formula available at: http://stattrek.com/ap-statistics/formulas.aspx
| 5798159655 | Sample mean |  | 0 | |
| 5798164797 | Sample Standard Deviation |  | 1 | |
| 5798165321 | Pooled sample standard error |  | 2 | |
| 5798166302 | Simple linear regression line |  | 3 | |
| 5798206454 | Regression Coefficient |  | 4 | |
| 5798209286 | Regression Slope intercept |  | 5 | |
| 5798210007 | Sample Correlation Coefficient |  | 6 | |
| 5798210759 | Regression Coefficient |  | 7 | |
| 5798211695 | Standard Error of regression slope |  | 8 | |
| 5798212552 | Probability Rule of Addition |  | 9 | |
| 5798212553 | Probability Rule of Multiplication P(A given B) |  | 10 | |
| 5798212999 | Expected Value of X (probability distribution) |  | 11 | |
| 5798213000 | Variance of X (probability distribution) |  | 12 | |
| 5798213767 | Binomial Formula |  | 13 | |
| 5798213768 | Mean of Binomial Distribution |  | 14 | |
| 5798214179 | Standard Deviation of Binomial Distribution |  | 15 | |
| 5798214390 | Mean of sampling distribution of the Proportion |  | 16 | |
| 5798215379 | Standard Deviation of sampling distribution of the proportion |  | 17 | |
| 5798215914 | Mean of sampling distribution of the mean |  | 18 | |
| 5798216232 | Standard deviation of the sampling distribution of the mean |  | 19 | |
| 5798217033 | Inferential Statistics: Standardized Test Statistifc | 20 | ||
| 5798217602 | Inferential Statistics: Confidence Interval | 21 | ||
| 5798218181 | Standard Deviation of sample mean |  | 22 | |
| 5798218182 | Standard Deviation of a proportion |  | 23 | |
| 5798218510 | Standard Deviation of the difference of sample means |  | 24 | |
| 5798218883 | Standard Deviation of the difference of sample proportions |  | 25 | |
| 5798219668 | chi-square test statistic. | 26 |
Pages
Need Help?
We hope your visit has been a productive one. If you're having any problems, or would like to give some feedback, we'd love to hear from you.
For general help, questions, and suggestions, try our dedicated support forums.
If you need to contact the Course-Notes.Org web experience team, please use our contact form.
Need Notes?
While we strive to provide the most comprehensive notes for as many high school textbooks as possible, there are certainly going to be some that we miss. Drop us a note and let us know which textbooks you need. Be sure to include which edition of the textbook you are using! If we see enough demand, we'll do whatever we can to get those notes up on the site for you!

