Flashcards
AP Key Terms Review Flashcards
| 7883459374 | Indentured Servants | The "headright" system enabled Chesapeake tobacco farmers to obtain both land and labor by importing these types of workers from England. | 0 | |
| 7883472383 | Indentured Servants | These Englishmen were the chief source of agricultural labor in Virginia and Maryland before 1675. They accounted for 75% of the 130, English immigrants to Virginia and Maryland during the 17th century. | 1 | |
| 7883491581 | Bacon's Rebellion, 1676 | This rebellion exposed tensions between backcountry farmers and the tidewater gentry. | 2 | |
| 7883496496 | Bacon's Rebellion, 1676 | This rebellion prompted the tidewater gentry to reevaluate their commitment to the system of indentured servants. | 3 | |
| 7883507250 | Slavery | The profitable cultivation of tobacco required this inexpensive form of labor. | 4 | |
| 7883515568 | Slavery | This form of labor in colonial Virginia and Maryland spread rapidly in the last quarter of the 17th century, as Blacks displaced White indentured servants in the tobacco fields. | 5 | |
| 7883583372 | Caribbean | In the 17th and 18th centuries, the vast majority of Africans who survived the transatlantic passage ended up working on plantations in Brazil and the ______. | 6 | |
| 7883600036 | North America | Of all of the slaves transported as part of the slave trade, the fewest slaves were brought into British _______ _________. | 7 | |
| 7883610440 | 1700s | Slavery was legally established in all 13 colonies by the early ______. | 8 | |
| 7883616322 | cultural | Although enslaved, Africans maintained _______ practices brought from Africa. | 9 | |
| 7883629178 | Tobbacco | _______ was the most important cash crop grown in the Chesapeake colonies. | 10 | |
| 7883643488 | Rice | _______ was the most important cash crop grown in South Carolina. | 11 | |
| 7883651825 | indentured servants | Because the supply of _______ _______ from England became insufficient by the late 17th century, slavery began to develop in the Southern colonies. | 12 | |
| 7883664808 | tobacco | Because the spread of _______ cultivation westward created a demand for labor, slavery began to develop in the Southern colonies. | 13 | |
| 7883674001 | morally | Because few 17th and 18th century white colonists view human bondage as _______ unacceptable, slavery began to develop in the Southern colonies. | 14 | |
| 7883686544 | England | Because of it's increase in maritime power, _______ wanted to compete in the profitable slave trad begun by the Portuguese and Dutch, which led to the development of slavery in the Southern colonies. | 15 | |
| 7883703851 | The Stono Rebellion, 1739 | This was one of the earliest known acts of rebellion against slavery in America. | 16 | |
| 7883709331 | The Stono Rebellion, 1739 | This was organized and led by slaves living south of Charleston. They tried unsuccessfully to flee to Spanish Florida, where they hoped to gain their freedom. | 17 | |
| 7883723371 | didn't | The Declaration of Independence _______ call for the abolition of the slave trade. | 18 | |
| 7883729213 | The Northwest Ordinance of 1787 | This excluded slavery north of the Ohio River. | 19 | |
| 7883734736 | The Northwest Ordinance of 1787 | This was the first national document containing a prohibition of slavery. | 20 | |
| 7883743474 | U.S. Constitution | As written in 1787, the _______ explicitly guaranteed the legality of slavery in every state. | 21 | |
| 7883748028 | Three-Fifths Compromise | This was an agreement between the Southern and Northern states. Under the terms of this, 3/5s of the population of slaves would be counted for enumeration purposes regarding both the distribution of taxes and the apportionment of the members of the House of Representatives. | 22 | |
| 7883766803 | 14th Amendment | This invalidated the 3/5s Compromise. It specifically states, "Representatives shall be apportioned... counting the whole number of persons in each state." | 23 | |
| 7883783422 | Haitian Slave Rebellion | This rebellion of the 1790s prompted an increased fear of slave revolts in the South. | 24 | |
| 7883787805 | Toussaint L'Ouverture | He led the Haitian Slave Rebellion. | 25 | |
| 8750943927 | free | The following factors contributed to the growth of the _____ African American population: a) the gradual emancipation laws of individual states, b) manumission granted for Revolutionary War service, c) manumission granted by slaveholders' wills, d) natural increas among free African Americans | 26 | |
| 7883800797 | cotton gin | The invention of this made it possible and profitable to harvest short-staple cotton, contributing to making it the South's most important cash crop. | 27 | |
| 7883811629 | textile | The rise of _______ manufacturing in England created enormous demand for cotton. | 28 | |
| 7883817372 | small | The majority of white adult males were _______ farmers rather than wealthy planters. | 29 | |
| 7883821495 | no | The majority of white families in the antebellum South owned _______ slaves. | 30 | |
| 8750960813 | rose | The cost of slave labor _______ sharply between 1800 and 1860. | 31 | |
| 8750967115 | separations | Despite forced __________, slaves maintained social networks among kindred and friends | 32 | |
| 8750975538 | increase | The dramatic __________ in the South's slave labor force was due to the natural population __________ of American-born slaves. | 33 | |
| 8750983169 | were | During the antebellum period, free African Americans __________ able to accumulate some property in spite of discrimination. | 34 | |
| 8750991680 | slave marriages | Although Southern legal codes did not uniformly provide for the legalization and stability of slave marriage, slaves were generally able to marry, and the institution of marriage was common on Southern plantations. | 35 | |
| 8751002363 | African American culture | The majority of slaves adapted to the oppressive conditions imposed on them by developing a separate ________________________________________. | 36 | |
| 8751008670 | revolts | Slave __________ were infrequent. Most Southern slaves resisted their masters by feigning illness and working as slowly as possible. | 37 | |
| 7883833501 | Missouri Compromise | 1. Maine would enter the Union as a free state. 2. Missouri would enter the Union as a slave state. 3. The remaining territory of the Louisiana Purchase above latitude 36*30' would be closed to slavery. | 38 | |
| 7883849596 | Consequences of the Missouri Compromise | 1. The number of Northerners and Southerners in the Senate remained the same. 2. most of the LA Purchase was closed to slavery. 3. 1st major 19th century conflict over slavery was settled 4. Slavery was temporarily defused as a national political issue. | 39 | |
| 7883875396 | Texas | President Jackson resisted the admission of _______ into the Union in 1836, primarily because he feared that the debate over the admission of it would ignite controversy over slavery. | 40 | |
| 7883888865 | Texas | Following a joint resolution of Congress, _______ joined the Union in December of 1845. | 41 | |
| 7884799644 | The Wilmot Proviso | This specifically provided for the prohibition of slavery in lands acquired from Mexico in the Mexican War. | 42 | |
| 7884820787 | did not | Congress _______ pass the Wilmot Proviso. | 43 | |
| 7884851479 | The Compromise of 1850 | California was admitted to the Union as a free state as part of this. | 44 | |
| 7884860103 | District of Columbia | According to the Compromise of 1850, the slave trade (but not slavery) was abolished in _______. | 45 | |
| 7884868938 | Fugitive Slave Act | As part of the Compromise of 1850 this law was enacted. It proved to be the most controversial and divisive component of the compromise. | 46 | |
| 8751027812 | Ostend Manifesto | This was a proposal to seize Cuba by force. Enraged antislavery Northerners prevented it from beign implemented. | 47 | |
| 8751036280 | Kansas Nebraska Act, 1854 | Provisions include: -proposed territory of Nebraska would be divided into 2 territories -slavery would be settled by popular sovereignty | 48 | |
| 8751066119 | popular sovereignty | the settlers in a given territory would have the sole right to decide wheter or not slavery would be permitted Senator Stephan A. Douglas was the leading proponent of this | 49 | |
| 8751078802 | Stephan A. Douglas | This U.S. senator was a leading proponent of popular sovereignty | 50 | |
| 8751092323 | Missouri Compromise | The Kansas-Nebraska Act repealed the ____________________, thus heightening sectional tensions. | 51 | |
| 8751097759 | Whigs | The Kansas-Nebraska Act led to the demise of the __________. | 52 | |
| 8751102060 | Republican Party | The Kansas-Nebraska Act led to the rise of the ____________________ and Abe Lincoln. | 53 | |
| 8751106130 | Kansas | __________ became the first test of popular sovereignty. | 54 | |
| 8751112531 | The Dred Scott Decision, 1857 | -The Supreme Court ruled that Black people were not citizens of the United States and therefore couldn't petition the Court. -Established the principle that national legislation could not limit the spread of slavery into the territories. -by stating that Congress had no right to prohibit slavery in the territories, this decision repealed the Northwest Ordinance of 1787 and the Missouri Compromise of 1820 -this decision became a contentious issue during the Lincoln-Douglas debates | 55 | |
| 8751137649 | Democratic | The __________ Party was divided on the issue of expanding slavery into the territories. | 56 | |
| 8751140555 | Republican | The __________ Party opposed the extension of slavery into the territories. However, they acknowledged that slavery should be protected in the states where it already existed. | 57 | |
| 8751154599 | The Second Great Awakening | The religious spirit of this time period increased public awareness of the moral outrages perpetuated by slavery. It contributed to the growth of the abolitionist movement. | 58 | |
| 8751163600 | American Colonization Society | -goal was the return of freed slaves to Africa -leaders of this movement were middle-class men and women | 59 | |
| 8751168761 | William Lloyd Garrison | -issued the first call for the "immediate and uncompensated emancipation of the slaves." -"Let Southern oppressors tremble... I will be as harsh as Truth and as uncompromising as Justice... I am in earnest- I will not retreat a single inch- and I WILL BE HEARD!" ~The Liberator | 60 | |
| 8751185933 | Frederick Douglass | -most prominent Black abolitionist during the antebellum period -published his autobiography in 1845 -championed equal rights for women and Native Americans, "I would unite with anybody to do right and with nobody to do wrong." | 61 | |
| 8751196762 | Harriet Beecher Stowe | -wrote Uncle Tom's Cabin, which intensified Northern opposition to slavery (only the Bible sold more copies) | 62 | |
| 8751203467 | Emancipation Proclamation, 1863 | -Lincoln refrained from taking action to emancipate slaves until the Civil War had been in progress for almost 2 years because he wanted to retain the loyalty of the border states. -Union victory at Antietam gave Lincoln the opportunity to issue this -only freed slaves in the rebellious states -did not free slaves in the Border States -immediate effect was to strengthen the moral cause of the Union in the Civil War | 63 | |
| 8751223811 | African Americans at WAr | -for most of the Civil War ____________________ soldiers wer paid less than White soldeirs of equal rank -the South considered ____________________ serving in the Union army as contraband | 64 | |
| 7884878766 | Anne Hutchinson | She challenged Puritan religious authorities in Massachusetts Bay. | 65 | |
| 7884889355 | Anne Hutchinson | Puritan authorities banished her because she challenged religious doctrine, gender roles, and clerical authority, and she claimed to have had revelations from God. | 66 | |
| 7884905793 | women | _______ usually lost control of their property when they married. | 67 | |
| 7884912442 | identity | Married women had no separate legal _______ apart from their husband in colonial times. | 68 | |
| 7884915032 | couldn't | Women _______ hold political office, serve as clergy, vote, or serve as jurors during colonial times. | 69 | |
| 7884926222 | single | _______ women and widows did have the legal right to own property. | 70 | |
| 7884928184 | unmarried | Women serving as indentured servants had to remain _______ until the period of their indenture was over. | 71 | |
| 7884934815 | Chesapeake Colonies | In this area, there was a scarcity of women and a high mortality rate among men. This was especially true in the 17th century. | 72 | |
| 7884943315 | higher | As a result of the scarcity of women, the status of women in the Chesapeake colonies was _______ than that of women in the New England colonies. | 73 | |
| 7884952380 | Abigail Adams | An early proponent of women's rights. | 74 | |
| 7884960669 | cult of domesticity | This refers to the idealization of women in their roles as wives and mothers. | 75 | |
| 7884965073 | republican mother | This term suggested that women would be responsible for rearing their children to be virtuous citizens of the new American republic. By emphasizing family and religious values, women could have a positive moral influence on the American political character. | 76 | |
| 7884975525 | Middle | _______-class Americans viewed the home as a refuge from the world rather than a productive economic unit. | 77 | |
| 7884984820 | Catharine Beecher | She supported the cult of domesticity. "...The mother writes the character of the future man; the sister bends the fibers that hereafter are the forest tree; the wife sways the heart, whose energies may turn for good or evil the destinies of a nation. Let the women of a country be virtuous and intelligent, and the men will certainly be the same. | 78 | |
| 7885005684 | Lowell system | This was a plan developed in the early nineteenth century to promote and expand textile manufacturing. | 79 | |
| 7885012016 | Lowell | During the first half of the 19th century, textile mills in _______ relied heavily on a labor force of women and children. | 80 | |
| 7885017043 | rural | During the 1820s and 1830s, the majority of workers in the textile mills of Massachusetts were young, unmarried women from _______ New England who sought to earn money of their own. | 81 | |
| 7885026633 | Irish | Prior to the Civil War, _______ immigrants began to replace New England farm girls in the textile mills. | 82 | |
| 7885039637 | land | Most scholars now believe that the first Native Americans reached North America by traveling across a _______ bridge connecting eastern Siberia and Alaska. | 83 | |
| 7885049356 | Pre-Columbian | _______ peoples developed all of the following: -a mathematically based calendar -irrigation systems -domesticated cereal crops such as maize -multifamily dwellings -herbal medical treatments -large cities such as the Aztec capital | 84 | |
| 7885061870 | Pre-Columbian | _______ peopled did not develop the following: -wheeled vehicles -gunpowder -waterwheels | 85 | |
| 7885081157 | Columbian Exchange | The term refers to the exchange of plants and animals between the New World and Europe following the "discovery" of America in 1492. | 86 | |
| 7885097480 | New | _______ World crops such as corn, tomatoes, and potatoes had a dramatic effect on the European diet. | 87 | |
| 7885102794 | Old | _______ World domesticated animals such as horses, cows, and pigs had a dramatic effect on life for Native Americans. | 88 | |
| 7885108624 | epidemics | Old World diseases caused _______ among the Native American inhabitants of the New World. | 89 | |
| 7885115312 | smallpox | Native Americans suffered severe population declined because they lacked immunity to _______ and other European diseases. | 90 | |
| 7885127455 | agricultural | Both Native Americans and the first English settlers had _______ economies. | 91 | |
| 7885130828 | villiage | Both Native Americans and the first English settlers lived in _______ communities. | 92 | |
| 7885134798 | domesticated | Both Native Americans and the first English settlers _______ corn and other vegetables. | 93 | |
| 7885138681 | spirituality | Both Native Americans and the first English settlers had a strong sense of _______. | 94 | |
| 7885144423 | property | Native Americans and the first English settlers had radically different conceptions of _______. | 95 | |
| 7885154183 | Iroquois Confederacy | This was the most important and powerful Native American alliance. | 96 | |
| 7885161479 | Iroquois Confederacy | The tribes of this formed the most important Native American political organization to confront the colonist. | 97 | |
| 7885166943 | permanent | During the 18th century, the Iroquois lived in _______ settlements. | 98 | |
| 7885174105 | Cherokee | The _______ differed from other Native American tribes in that they tried to mount a court challenge to a removal order. | 99 | |
| 7885181579 | Worchester v. Georgia | In this case, the U.S. Supreme Court upheld the rights of the Cherokee tribe to their tribal lands. | 100 | |
| 7885201279 | Jackson | This president refused to recognize the Court's decision in Worchester v. Gerogia. "John Marshall has made his decision: now let him enforce it." | 101 | |
| 7885210617 | Jackson's | _______'s antipathy toward Native Americans was well know: "I have long viewed treaties with American Indians as an absurdity not to be reconciled to the principles of our government." | 102 | |
| 7885221524 | Trail of Tears | Jackson's Native American policy which resulted in this removal of the Cherokee from their homeland to settlements across the Mississippi River. | 103 | |
| 7885237810 | 1/4 | Approximately _______ of the Cherokee people died on the Trail of Tears. | 104 | |
| 7885248391 | John Marshall | He believed that the U.S. would be best served by concentrating power in a strong central government. | 105 | |
| 7885254670 | business enterprise | Under Chief Justice John Marshall, Supreme Court decisions tended to promote _______ _______. | 106 | |
| 7885260861 | federal | Under John Marshall's leadership, the Supreme Court upheld the supremacy of _______ legislation over state legislation. | 107 | |
| 7885267713 | Marbury v. Madison, 1803 | This case established the principle of judicial review. | 108 | |
| 7885272470 | Judicial review | this gave the Supreme Court the authority to declare acts of Congress unconstitutional. | 109 | |
| 7885280265 | strenghtened | Marbury v. Madison was one of a series of landmark decisions by Chief Justice John Marshall that strengthened the federal government. | 110 | |
| 7885293705 | Dartmouth College v. Woodward, 1819 | The Supreme Court ruled that the Constitution protected contracts from state encroachments. | 111 | |
| 7885298482 | state | The ruling in Dartmouth College v. Woodward safeguarded business enterprise from interference by _______ governments. | 112 | |
| 7885316041 | James Fenimore Cooper | Author of The Last of the Mohicans, 1757. | 113 | |
| 7885325412 | Leatherstocking Tales | The Last of the Mohicans was part of this series of novels. | 114 | |
| 7885331149 | James Fenimore Cooper | He was the first American writer to feature uniquely American characters. | 115 | |
| 7885334726 | Western | Cooper created the first genuine _______ heroes in American literature. | 116 | |
| 7885338399 | "noble savage" | Cooper's novels gave expression to this concept. | 117 | |
| 7885345439 | Common Sense 1776 | This was a pamphlet written by Thomas Paine. | 118 | |
| 7885349573 | independence | Common Sense was a strongly worded call for independence from Great Britain. | 119 | |
| 7885361050 | Republican | in Common Sense, Paine opposed monarchy (he called King George a Pharaoh!) and strongly favored this type of government. | 120 | |
| 7885371425 | biblical | In Common Sense, Paine used _______ analogies and references to illustrate his arguments. | 121 | |
| 7885377781 | The Federalist Papers | These were written by Hamilton, Madison, and Jay to support ratification of the Constitution of 1787. | 122 | |
| 7885386344 | republic | The Federalist Papers challenged the conventional political wisdom of the 18th century when they asserted that a large _______ offered the best protection of minority rights. | 123 | |
| 7885401525 | Navigation Acts, 1651 | These acts put mercantilism into practice. Colonial products that could be shipped only to England were listed. | 124 | |
| 7885407874 | Navigation Acts, 1651 | These were designed to subordinate the colonial economy to that of the mother country. | 125 | |
| 7885414279 | Sugar Act, 1764 | This was the first law passed by Parliament to raise revenue for the British Crown. | 126 | |
| 7885418610 | enforcement | The Sugar Act was designed to tighten _______ of English customs laws in America. | 127 | |
| 7885422706 | lowered | Following bitter protests from the colonists over the Sugar Act, British officials _______ the duties. | 128 | |
| 7885429225 | Stamp Act, 1765 | The primary purpose of this act was to raise revenue to support British troops stationed in America. | 129 | |
| 7885435921 | consent | The Stamp Act raised the issue of Parliament's right to tax the colonies without their _______. | 130 | |
| 7885440651 | boycotts | The Stamp Act was repealed because colonial _______ of English goods were hurting British merchants. | 131 | |
| 7885448379 | British | The Stamp Act is important because it revealed that many colonists believed they were entitled to all the rights and privileges of _______ subjects. | 132 | |
| 7885458010 | violence | The Stamp Act is important because the colonists demonstrated their willingness to use ______ rather than legal means to frustrate British policy. | 133 | |
| 7885471270 | Coercive Acts, 1774 | The British response to the Boston Tea Party, these were widely known in the colonies as the Intolerable Acts. | 134 | |
| 7885476959 | Intolerable Acts | In these, Parliament closed the port of Boston and drastically reduced the power of self-government in the Massachusetts colony. They also provided for the quartering of troops in the colonists' barns and empty houses. | 135 | |
| 7885490802 | Kansas-Nebraska Act, 1854 | Repealed the Missouri Compromise of 1820, heightening the sectional crisis. Applied the principle of popular sovereignty to the territories. Permitted the expansion of slavery beyond the Southern states. sparked the formation of the Republican Party. | 136 | |
| 7885513097 | Puritans | These people immigrated to New England in the 1630s for the following reasons: -a desire to escape political repression -a desire to find new economic opportunities and avoid an economic recession in England -a desire to escape restrictions on their religions practices | 137 | |
| 7885527980 | Great English Migration | The Puritans who immigrated to New England were part of this. It numbered some 70,000 people. It is interesting to note that over twice as many Puritans immigrated to the West Indies as to New England. | 138 | |
| 7885539083 | Proclamation of 1763 | This set a boundary along the crest of the Appalachians beyond which the colonists could not cross. The ban was an ill-considered attempt to prevent costly conflicts with trans-Appalachian Indians. | 139 | |
| 7885552224 | defeated | As American Indians were _______, Scotch-Irish, German, and English immigrants moved into Appalachia. | 140 | |
| 7885559349 | land | British colonists were principally motivated to settle west of the Appalachians by the low price and easy availability of this. | 141 | |
| 7885569069 | Ireland | This country supplied the largest number of immigrants to the U.S. during the first half of the 19th century. | 142 | |
| 7885574852 | Potato famine | The Irish immigrants fled the devastating effects of this. | 143 | |
| 7885579499 | urban | Most Irish immigrants settled in ______ cities along the Eastern Seaboard. | 144 | |
| 7885584933 | canal | Many Irish immigrants worked on ______ and railroad construction projects. | 145 |
AP World History Vocab: Chapter four Flashcards
| 10385299385 | Plebeians | A commoner in Ancient Rome |  | 0 |
| 10385313645 | Patricians | an aristocrat or nobleman. |  | 1 |
| 10385317102 | checks and balances | counterbalancing influences by which an organization or system is regulated, typically those ensuring that political power is not concentrated in the hands of individuals or groups |  | 2 |
| 10385320585 | Law of Twelve Tables | a set of laws inscribed on 12 bronze tablets created in ancient Rome |  | 3 |
| 10385329691 | Consuls | an official appointed by a government to live in a foreign city and protect and promote the government's citizens and interests there. |  | 4 |
| 10391001852 | Roman Senate | a political institution in the ancient Roman kingdom |  | 5 |
| 10391006263 | tribunes | an official in ancient Rome chosen by the plebeians to protect their interests. |  | 6 |
| 10391010518 | Cicero | An orator, writer, and statesman of ancient Rome |  | 7 |
| 10391013552 | Spartacus Rebellion | a Thracian gladiator who, along with the Gauls Crixus, Gannicus, Castus, and Oenomaus, was one of the escaped slave leaders in the Third Servile War |  | 8 |
| 10391016485 | Julius Caesar | the general and dictator Julius Caesar. |  | 9 |
| 10391026371 | Octavian | Octavian was the name used commonly for Emperor Augustus. |  | 10 |
| 10391031829 | Pax Romana | the peace that existed between nationalities within the Roman Empire. |  | 11 |
| 10391035609 | Edict of Milan | a letter signed by the Roman emperors Constantine and Licinius, that proclaimed religious toleration in the Roman Empire. |  | 12 |
| 10391039169 | Constantine | Constantine the Great, the Christian emperor who made Christianity the official religion of the Roman Empire. |  | 13 |
| 10391041619 | Virgil | used for the Roman poet Publius Vergilius Maro |  | 14 |
| 10391049849 | the Aeneid | a Latin epic poem, written by Virgil between 29 and 19 BC, that tells the legendary story of Aeneas |  | 15 |
| 10391053634 | Stoicism | an ancient Greek school of philosophy founded at Athens by Zeno of Citium. |  | 16 |
| 10391072357 | Paul and Peter` | phrases meaning to take from one person or thing to give to another |  | 17 |
| 10391080411 | St Augustine | one of the great Fathers of the early Christian church |  | 18 |
| 10391134145 | martyrdom | the death or suffering of a martyr. | 19 |
Amsco Chapter 7 Ap World History Terms Flashcards
| 11245228427 | Hagia Sophia | Most famous example of Byzantine architecture, it was built under Justinian I and is considered one of the most perfect buildings in the world. | 0 | |
| 11245228428 | theocracy | A government ruled by or subject to religious authority. | 1 | |
| 11245228429 | patriarch | the male head of a family or tribe | 2 | |
| 11245228430 | monasteries | Religious community where Christians called monks gave up their possessions and devoted their lives to serving God. | 3 | |
| 11245228431 | Cyrillic | relating to the Slavic alphabet derived from the Greek and traditionally attributed to St. Cyril; in modified form still used in modern Slavic languages | 4 | |
| 11245228432 | schism | (n.) a formal split within a religious organization; any division or separation of a group or organization into hostile factions | 5 | |
| 11245228433 | Eastern Orthodox Church | Christian followers in the Eastern Roman Empire (Byzantine Empire); split from Roman Catholic Church and shaped life in eastern Europe and western Asia | 6 | |
| 11245228434 | theme system | System of administration and defense perfected by Byzantine king Leo III that organized the empire into provinces, each under the command of a military governor | 7 | |
| 11245228435 | illuminated manuscripts | a handwritten book decorated with bright colors and precious metals | 8 | |
| 11245228436 | Bulgars | Asiatic people who migrated to the Balkans and conquered large parts of Eastern empire along the Danube | 9 | |
| 11245228437 | University of Constantinople | Established in AD 85, this was one of the earliest institutions of higher learning in the Western World | 10 | |
| 11245228438 | Hippodrome | Built by Justinian; A huge stadium; Held athletic events and games, especially chariot races. Seated 60,000 people located in Constantinople. Site of Nika Revolt. | 11 | |
| 11245228439 | Oleg | First Viking to settle in Kiev and the founder of the Russian state Kievan Rus | 12 | |
| 11245228440 | Dnieper River | river between the Black and Baltic Seas that was part of a Byzantine trade route | 13 | |
| 11245228441 | Kievan Rus | A monarchy established in present day Russia in the 6th and 7th centuries. It was ruled through loosely organized alliances with regional aristocrats from. The Scandinavians coined the term "Russia". It was greatly influenced by Byzantine | 14 | |
| 11245228442 | boyars | Russian landholding aristocrats; possessed less political power than their western European counterparts | 15 | |
| 11245228443 | Prince Vladimir | the prince of Kiev who made the entire city convert to Christianity in 988 AD | 16 | |
| 11245228444 | Yaroslav the Wise | He ruled Kiev (1019-1054), forged trading alliances with western Europe, and created a legal code | 17 | |
| 11245228445 | Russkaya Pravda | It was the "Russian Truth (justice or law)". It was their own law code. It showed signs of an advanced society, more so than Europe. There were crimes against property as well as interest rates implemented which was very sophisticated. It, like everything, was based off of Byzantium law. But was much more mild. | 18 | |
| 11245228446 | Byzantium | the civilization that developed from the eastern Roman Empire following the death of the emperor Justinian (C.E. 565) until the fall of Constantinople in 1453. | 19 | |
| 11245228447 | Corpus Juris Civilis | New code of the Roman Law decided by Justinian I in 529 CE that made Orthodox Christianity the law of the land. It means the "body of civil law". | 20 | |
| 11245228448 | Heraclius | Emperor who defeated the Persians and the Slavs and created the position of "theme" | 21 | |
| 11245228449 | Basil II | Macedonian emperor who campaigned against the Bulgars and annexed Bulgaria, Crete, Cyprus, and Syria, expanding the empire to the Euphrates | 22 | |
| 11245228450 | Battle of Kleidion | Bulgars vs. Byzantium. Byzantium wins. | 23 | |
| 11245228451 | Byzantine Empire | Historians' name for the eastern portion of the Roman Empire from the fourth century until its downfall to the Ottomans in 1453. Famous for being a center of Orthodox Christianity and Greek-based culture. | 24 | |
| 11245228452 | Justinian | Byzantine emperor in the 6th century A.D. who reconquered much of the territory previously ruler by Rome, initiated an ambitious building program , including Hagia Sofia, as well as a new legal code | 25 | |
| 11245228453 | Battle of Manzikert | Battle between the Byzantines and Seljuk Turks; Byzantines destroyed and way paved for the Seljuk Turk invasion into present day Turkey | 26 | |
| 11245228454 | Crusades | A series of holy wars from 1096-1270 AD undertaken by European Christians to free the Holy Land from Muslim rule. | 27 | |
| 11245228455 | Fourth Crusade | Crusade called for by Pope Innocent III in 1204 in which crusaders went rogue and sacked Constantinople. The Byzantine Empire was eventually restored in 1261 | 28 | |
| 11245228456 | Normans | A member of a Viking people who raided and then settled in the French province later known as Normandy, and who invaded England in 1066 | 29 | |
| 11245228457 | Slavs | The ancestors of the Czechs, Slovaks, Croatians, Serbians, Bulgarians, Poles, and Russians | 30 | |
| 11245228458 | Vikings | Invaders of Europe that came from Scandinavia | 31 | |
| 11245228459 | Rus | This kingdom expanded its territory thousands of miles Eastward during the 19th century and also sought to take advantage of a weakened Ottoman Empire. | 32 |
AP World History - Period 2 Flashcards
| 10112856949 | Alexander the Great | Alexander III of Macedon (356-323 B.C.E.), conqueror of the Persian Empire and part of northwest India. |  | 0 |
| 10112856950 | Aryans | Indo-European pastoralists who moved into India about the time of the collapse of the Indus Valley civilization; their role in causing this collapse is still debated by historians. |  | 1 |
| 10112856951 | Ashoka | The most famous ruler of the Mauryan Empire (r. 268-232 B.C.E.), who converted to Buddhism and tried to rule peacefully and with tolerance. |  | 2 |
| 10112856952 | Caesar Augustus | The great-nephew and adopted son of Julius Caesar who emerged as sole ruler of the Roman state at the end of an extended period of civil war (r. 31 B.C.E.-14 C.E.). |  | 3 |
| 10112856953 | Cyrus (the Great) | Founder of the Persian Empire (r. 557-530 B.C.E.); a ruler noted for his conquests, religious tolerance, and political moderation. |  | 4 |
| 10112856954 | Darius I | Great king of Persia (r. 522-486 B.C.E.) following the upheavals after Cyrus's death; completed the establishment of the Persian Empire. |  | 5 |
| 10112856955 | Greco-Persian Wars | Two major Persian invasions of Greece, in 490 B.C.E. and 480 B.C.E., in which the Persians were defeated on both land and sea. |  | 6 |
| 10112856956 | Gupta Empire | An empire of India (320-550 C.E.). |  | 7 |
| 10112856957 | Han dynasty | Chinese dynasty that restored unity in China softened legalist policies. Begun in 202 B.C. by Liu Bang, the dynasty ruled China for more than 400 years. |  | 8 |
| 10112856958 | Hellenistic era | The period from 323 to 30 B.C.E. in which Greek culture spread widely in Eurasia in the kingdoms ruled by Alexander's political successors. |  | 9 |
| 10112856959 | Herodotus | Greek historian known as the "father of history" (ca. 484-ca. 425 B.C.E.). His Histories enunciated the Greek view of a fundamental divide between East and West, culminating in the Greco-Persian Wars of 490-480 B.C.E. | 10 | |
| 10112856962 | Mandate of Heaven | The ideological underpinning of Chinese emperors, this was the belief that a ruler held authority by command of divine force as long as he ruled morally and benevolently. | 11 | |
| 10112856963 | Battle of Marathon | Athenian victory over a Persian invasion in 490 B.C.E. | 12 | |
| 10112856964 | Mauryan Empire | A major empire (322-185 B.C.E.) that encompassed most of India. | 13 | |
| 10112856965 | Patricians | Wealthy, privileged Romans who dominated early Roman society. | 14 | |
| 10112856966 | Pax Romana | The "Roman peace," a term typically used to denote the stability and prosperity of the early Roman Empire, especially in the first and second centuries C.E. | 15 | |
| 10112856967 | Peloponnesian War | Great war between Athens (and allies) and Sparta (and allies), lasting from 431 to 404 B.C.E. The conflict ended in the defeat of Athens and the closing of Athens's Golden Age. |  | 16 |
| 10112856968 | Persepolis | The capital and greatest palace-city of the Persian Empire, destroyed by Alexander the Great. |  | 17 |
| 10112856969 | Persian Empire | A major empire that expanded from the Iranian plateau to incorporate the Middle East from Egypt to India; flourished from around 550 to 330 B.C.E. | 18 | |
| 10112856971 | Punic Wars | Three major wars between Rome and Carthage in North Africa, fought between 264 and 146 B.C.E., that culminated in Roman victory and control of the western Mediterranean. | 19 | |
| 10112856972 | Qin Dynasty | A short-lived (221-206 B.C.E.) but highly influential Chinese dynasty that succeeded in reuniting China at the end of the Warring States period. |  | 20 |
| 10112856973 | Qin Shihuangdi | Literally "first emperor" (r. 221-210 B.C.E.) forcibly reunited China and established a strong and repressive state. | 21 | |
| 10112856975 | Wudi | Han emperor (r. 141-86 B.C.E.) who began the Chinese civil service system by establishing an academy to train imperial bureaucrats. | 22 | |
| 10112856976 | Xiongnu | Nomadic peoples to the north of the Great Wall of China who were a frequent threat to the stability of the Chinese state. | 23 | |
| 10112856977 | Aristotle | A Greek polymath philosopher (384-322 B.C.E.); student of Plato and teacher of Alexander the Great. | 24 | |
| 10112856979 | Brahman | The "World Soul" or final reality in upanishadic Hindu belief. | 25 | |
| 10112856980 | Brahmins | The priestly caste of India. | 26 | |
| 10112856981 | Buddhism | The cultural/religious tradition first enunciated by Siddhartha Gautama | 27 | |
| 10112856982 | Confucianism | The Chinese philosophy first enunciated by Confucius, advocating the moral example of superiors as the key element of social order. | 28 | |
| 10112856983 | Confucius | The founder of Confucianism (551-479 B.C.E.); an aristocrat of northern China who proved to be the greatest influence on Chinese culture in its history. | 29 | |
| 10112856984 | Constantine | Roman emperor (r. 306-337 C.E.) whose conversion to Christianity paved the way for the triumph of Christianity in Europe. |  | 30 |
| 10112856985 | Daoism | A Chinese philosophy/popular religion that advocates simplicity and understanding of the world of nature, founded by the legendary figure Laozi. | 31 | |
| 10112856986 | Filial piety | The honoring of one's ancestors and parents, a key element of Confucianism. | 32 | |
| 10112856988 | Hinduism | A word derived from outsiders to describe the vast diversity of indigenous Indian religious traditions. | 33 | |
| 10112856989 | Hippocrates | A very influential Greek medical theorist (ca. 460-ca. 370 B.C.E.); regarded as the father of medicine. | 34 | |
| 10112856992 | Karma | In Hinduism, the determining factor of the level at which the individual is reincarnated, based on purity of action and fulfillment of duty in the prior existence. |  | 35 |
| 10112856994 | Legalism | A Chinese philosophy distinguished by an adherence to clear laws with vigorous punishments. | 36 | |
| 10112856995 | Moksha | In Hindu belief, liberation from separate existence and union with Brahman. | 37 | |
| 10112856996 | Nirvana | The end goal of Buddhism, in which individual identity is "extinguished" into a state of serenity and great compassion. | 38 | |
| 10112856999 | Siddhartha Gautama (the Buddha) | The Indian prince (ca. 566-ca. 486 B.C.E.) who founded Buddhism. | 39 | |
| 10112857000 | Socrates | The first great Greek philosopher to turn rationalism toward questions of human existence (469-399 B.C.E.). | 40 | |
| 10112857002 | Vedas | The earliest religious texts of India, a collection of ancient poems, hymns, and rituals that were transmitted orally before being written down ca. 600 B.C.E. | 41 | |
| 10112857003 | Warring States Period | Period in China from 403 to 221 B.C.E. that was typified by disorder and political chaos. | 42 | |
| 10112857004 | Yin and Yang | Expression of the Chinese belief in the unity of opposites. | 43 | |
| 10112857006 | caste as varna and jati | The system of social organization in India that has evolved over millennia; it is based on an original division of the populace into four inherited classes, with the addition of thousands of social distinctions based on occupation, which became the main cell of social life in India. | 44 | |
| 10112857007 | dharma | In Indian belief, performance of the duties appropriate to an individual's caste; good performance will lead to rebirth in a higher caste. | 45 | |
| 10112857009 | Kshatriya | The Indian social class of warriors and rulers. | 46 | |
| 10112857010 | latifundia | Huge estates operated by slave labor that flourished in parts of the Roman Empire | 47 | |
| 10112857011 | Pericles | A prominent and influential statesman of ancient Athens (ca. 495-429 B.C.E.); presided over Athens's Golden Age. | 48 | |
| 10112857012 | Sudra | The lowest Indian social class of varna; regarded as servants of their social betters; eventually included peasant farmers | 49 | |
| 10112857013 | the "three submissions" | In Chinese Confucian thought, the notion that a woman is permanently subordinate to male control: first that of her father, then of her husband, and finally of her son. | 50 | |
| 10112857014 | Untouchables | An Indian social class that emerged below the Sudras and whose members performed the most unclean and polluting work. | 51 | |
| 10112857015 | Vaisya | The Indian social class that was originally defined as farmers but eventually comprised merchants. | 52 | |
| 10112857016 | Silk Road | Trade route stretching from China into Europe. | 53 |
AP World History Unit 5 Exam Flashcards
| 6342038572 | Louis XVI | King during the French Revolution; married to Marie Antoinette; called in the Estates General; When Louis and his wife were kill, traditionalists were shocked and it marked a new stage of revolutionary violence; |  | 0 |
| 6342040790 | Declaration of the Rights of Man | Made up by the National Assembly (the third estate in the Estates General); declared that "men are born and remian free and equal in rights"; drew upon ideas of the Enlightenment and the Declaration of Independence; these actions launched the French Revolution and radicalized many of the National Assembly's participants; | 1 | |
| 6342041730 | Napoleon | Leader of French; spread French influence after the French Revolution through conquest, contrasting with the United States; seized power in 1799; credited with taming the revolution in the ace of growing disenchantment with its more radical features; Preserved modern elements like civil equality, religious freedom, secular law code, while reconciling with the Catholic Church and suppressing the revolution's more democratic elements in a military dictatorship; he was able to subdue most of Europe, thus creating the continent's largest empire since the Romans; imposed revolutionary practices; further seeds of changed were planted; end of French Revolution when brought down; |  | 2 |
| 6342043848 | Toussaint L'Ouverture | Led Haitian slaves in a successful revolt | 3 | |
| 6342044882 | Declaration of Independence | Written in 1776; declared U.S. independence from Britain; Enlightenment ideas (equality, freedom, property) inspired this declaration and many others |  | 4 |
| 6342044883 | Simon Bolivar | Creole leader with roots in Enlightenment values. Explained better forms of government and hopes for Creole independence in a letter. Wanted to create United States of Latin America, but only succeeded in declaring Brazil's independence. | 5 | |
| 6342046230 | Abolition | Abolition of slavery; ideas against antislavery were partially caused by the Enlightenment and the natural rights of man; Slavery was no longer beneficial to the economically powerful states; the actions of slaves themselves likewise hastened the end of slavery; secular, religious, economic, and political ideas came together in abolitionist movements brought governments growing pressure to abolish slavery; British was first; end of Atlantic slavery was a major turn in the world's social history; economic lives of freed slaves did not improve dramatically; Haiti exception; did not achieve anything close to political freedom; however, the abolitionist movement was won because it is simply the act of abolishing slavery, which was accomplished; |  | 6 |
| 6342046231 | Cottage Industry | 7 | ||
| 6342047778 | Capital | Wealth in the form of money or other assets owned by a person or organization or available or contributed for a particular purpose such as starting a company or investing; European investors found it more profitable to invest their money abroad than at home-capital reason; In United States during the industrial revolution, 1/3 of their capital investment was financed by British, French, and German capitalists; capital = money; lots of capital from industrial revolution; | 8 | |
| 6342047779 | Steam Engine | Ground-breaking invention during the industrial revolution using natural energy from gas; The coal-fired engine, which provided an inanimate and almost limitless source of power beyond that of wind, water, or muscle and could be used to drive any number of machines as well as locomotives and oceangoing ships; this technology helped Europe and especially forge ahead of its competitors; | 9 | |
| 6342049036 | Factory System | New organization of work; human impact of factory labor was a central feature in the debate about this massive transformation of economic life; lots of more jobs; major and negative impact on environment; biggest problem with the factory system was the treatment of workers; social issues; helped with urbanization with cities; desperate people looking for jobs, but conditions sucked; |  | 10 |
| 6342049037 | Stock Market | Complex corporate structures, stock markets, and insurance developed from finiancial institutions / financiers to allow businessmen to raise capital or expand production | 11 | |
| 6342050505 | Corporation | New corporations often spanned several countries or continents, such as the United Fruit Company in North, Central, and South America | 12 | |
| 6342050506 | Transnational Business | 13 | ||
| 6342052353 | Laissez-Faire | Economic system without the interference of the government | 14 | |
| 6342052354 | Adam Smith | Wrote a book on Capitalism; believed capitalism was the best and that the problems within it during the Industrial Revolution would work itself out and it eventually did; |  | 15 |
| 6342053521 | Infrastructure | New canals, railroads, etc. were built to facilitate trade and transportation; infrastructure was built upon because the industrial revolution and factories; | 16 | |
| 6342054652 | Self-strengthening movement | Chinese authorities were not passive in the face of their country's mounting crises, about internal and external; policies to make China great again; Overall program for China's modernization was inhibited by the fears of conservative leaders that urban, industrial, or commercial development would erode the power and privileges of the landlord class; Furthermore, the new industries remained largely dependent on foreigners for machinery, materials, and expertise; they served to strengthen local authorities who largely controlled them, rather than the central Chinese state; failure of the "self-strengthening movement" came to an end with the Boxer movement; | 17 | |
| 6342054653 | Suffrage | The movement for women to gain the right to vote; the feminist movement was mainly focused on this; the only place that grants women the right to vote during this time period is New Zealand; | 18 | |
| 6342054658 | Feminism | The French Revolution raised the possibility of re-creating human societies on new foundations; within growing middle classes of industrializing societies, more women found both educational opportunities and some freedom from household drudgery; some took part in organizations; working-class sisters became active trade unionists; the first organized expression of this new feminism took place at a women's rights conference in Seneca Falls, New York; feminism was a transatlantic movement; growing access to schools and professions; feminist movements in the West were focusing primarily on the issue of suffrage; National American Woman Suffrage Association had 2 million members; became a mass movement; women's literacy rates grew, and more rights like being able to own property were granted; Progress was slower in a political domain; provoked bitter opposition; Like nationalism, it spread; however, unlike abolition of slavery, the feminist movement overall was unsuccessful during this time period; this is because more people were less opposed to slavery than the rights of women; | 19 | |
| 6342056354 | Mary Wollstonecraft | In neighboring England, the French Revolution stimulated he writer Mary Wollstonecraft to pen her famous, Vindication of the Rights of Women, one of the earliest expressions of a feminist consciousness; advocated for women's education; | 20 | |
| 6342056355 | Seneca Falls | The first organized expression of this new feminism took place at a women's rights conference in Seneca Falls, New York, in 1848; At that meeting Elizabeth Cady Stanton drafted a statement that began by paraphrasing the Declaration of Independence: "We hold these truths to be self-evident, that all men and women are created equal" | 21 | |
| 6342057551 | Karl Marx | Wrote the Communist Manifesto; believed in scientific socialism/communism; against capitalist ideas and Adam smith; influenced socialism in the future (Russia and China); German by birth, but lived in England where he witnessed the brutal conditions of Britain's Industrial Revolution and wrote voluminously about history and economics; believed capitalism was unstable ;"scientific socialism"; Marxism; |  | 22 |
| 6342057552 | Robert Owens | A wealthy British cotton textile manufacturer, urged the creation of small industrial communities where workers and their families would be well treated; he established on such commuinty, with ten-hour workday, spacious housing, decent wages, and education for children, at his mill in New Lanark in Scotland; Socialist | 23 | |
| 6342058880 | Bourgeoisie | the middle class, typically with reference to its perceived materialistic values or conventional attitudes; in Marxist contexts, the capitalist class who own most of society's wealth and means of production. | 24 | |
| 6342058881 | Proletariat | Workers or working-class people, regarded collectively-often used with reference to Marxism; Marx had expected industrial capitalist societies to polarize into small wealthy class and a huge and increasingly impoverished proletariat; | 25 | |
| 6342060022 | Settler Colony | Colonies that are settled in by foreigners; ex: Algeria, Kenya, Zimbabwe, South Africa; in these particular settler colonies European communities, with he help of colonial governments, obtained huge tracts of land, much of which had previously been home to African society; Europe had many settler colonies; | 26 | |
| 6342060023 | Formal vs. Informal colony | 27 | ||
| 6342061432 | Economic Imperialism | This form of imperialism allowed the area to operate as its own nation, but the imperialist nation almost completely controlled its trade and other business. For example, it may impose regulations that forbid trade with other nations, or imperialist companies may own or have exclusive rights to its natural resources. During this era, China and most of Latin America were subjected to economic imperialism. | 28 | |
| 6342061433 | Opium Wars | China vs. Britain; Britain had a lot of expensive Opium, a highly addictive drug, that they sold to China. When China tried to cut off the inflow of Opium into their country, Britain would not let them because it was a primary source for their trade profits; there were several wars, but Britain surpassed in their war technology; Britain won and forced the Chinese to accept the unequal treaties given to them; defining point in history because symbolic of the global changing: Europe taking lead and China losing the lead; |  | 29 |
| 6342062951 | Treaty of Nanjing | The treaty that ended the Opium Wars in 1842; largely on British terms, imposed numerous restrictions on Chinese sovereignty and opened five ports to European traders; Its provisions reflected the changed balance of global power that had emerged with Britain's Industrial Revolution; To the Chinese, that agreement represented the first of the "unequal treaties" that seriously eroded China's independence by the end of the century; | 30 | |
| 6342062952 | Nationalism | Nationalism was developed during this time; | 31 | |
| 6342064160 | Rousseau | Jean-Jacques Rousseau minimized the importance of book learning for the education of children and prescribed instead an immersion in nature, which taught self-reliance and generosity rather than the greed and envy fostered by "civilization"; Enlightenment thinker; | 32 | |
| 6342064161 | Locke | The English philosopher offered principles for constructing a constitutional government, a contract between rulers and ruled that was created by human ingenuity rather than divinely prescribed; influenced the Declaration of Independence; argued, the "social contract" between ruler and ruled should last only as long as it served the people well; Enlightenment thinker; | 33 | |
| 6342065455 | Voltaire | Enlightenment thinker; Deist; believed in a rather abstract and remote Deity, sometimes compared to a clockmaker, who had created the world, but not in a personal God who intervened in history or tampered with natural law; French writer; wrote satire; cared about his freedom of speech; | 34 | |
| 6342067108 | Montesquieu | 35 | ||
| 6342067109 | Social Contract | The relationship between the kings/ government and the people? | 36 | |
| 6342069053 | Popular Sovereignty | New ideas--Politically, the core notion was "popular sovereignty" which meant that the authority to govern derived from the people rather than from God or from established tradition; | 37 | |
| 6342069054 | Meiji | Japan was very secluded and blocked off from the war until the U.S. came "knocking at their door"; War was avoided, but aware of what had happened to China in resisting European demands, Japan agreed to a series of unequal treaties with various Western powers; that humiliating capitulation to the demands of the "foreign devils" further eroded support for the shogunate, triggered by a brief civil war, and by 1868 led to a political takeover by a group of young samurai from southern Japan; this decisive turning point in Japan's history was known as the Meiji restoration, for the country's new rulers claimed that they were restoring to power the young emperor; | 38 | |
| 6342070522 | Communist Manifesto | Written by Karl Marx; written during the worst parts of Industrial Revolution; beliefs in scientific socialism; took hold in some parts like Russia; influences the future; |  | 39 |
| 6342070523 | Liberal | The liberal emphasis is on reason, education, secular values and personal liberty during the Enlightenment. Liberals would likely benefit from proposed changes. | 40 | |
| 6342070524 | Conservative | The conservative emphasis is on tradition, established order and ritual. Conservatives would not likely benefit from proposed changes they opposed. | 41 | |
| 6342072787 | Caudillos | Strong military men; achieved power as defenders of order and property, although they too succeeded on each other with great frequency; they were used in Latin America after the states claimed Independence and their was political turbulence between the countries; | 42 | |
| 6342072788 | 1905 Revolution | Russia found socialism very desirable in the conditions they were in; Russian Social-Democratic Labor Party was formed; By 1905, they reached their bursting point and Russia erupted in spontaneous insurrection; Workers in Moscow and St. Petersburg went on strike and created their own representative councils, called soviets; Peasant uprising, student demonstrations, revolts of non-Russian nationalities, and mutinies in the military all continued to the upheaval; forced the tsar to make some political reforms; | 43 | |
| 6342074093 | Duma | National assembly in Russia; made because the tsar's regime was forced to make more substantial reforms after 1905 Revolution; duma refused to work with the tsar's new political system between 1906-07 and Tsar Nicholas II twice dissolved that elected body and finally changed the electoral laws to favor the landed nobility; | 44 | |
| 6342074094 | Mexican Revolution | Lower classes in South America had it the worst with exporting goods because they lost jobs and land; protests and violence were frequent but only revolution was in Mexico; over throw dictatorship but failed because disorganized | 45 | |
| 6342076048 | Indian Revolt of 1857 | Sepoy Rebellion of 1857: The Sepoys were Indian Muslims and Hindus who served the British as soldiers in the army that defended the subcontinent. The rebellion took the British by surprise, but they found out that the Indian fury could be traced to a new training technique that the soldiers refused to follow. It required them to put a bullet shell in their mouths that had been greased in either pork or beef fat, with the pork fat being highly offensive to the Muslims and the beef to the Hindu. The British changed the practice, but it was too late because nationalism had reached India, too, and a movement for a country based on Indian identity was beginning. The leaders of the movement would have to wait about 90 years, though, to fulfill their dreams. | 46 | |
| 6342077560 | Taiping Rebellion | The Qing Dynasty was significantly weakened by the Taiping Rebellion, a revolt led by Hong Xiuquan. Hong was an unusual leader, believing that he was the younger brother of Jesus, and advocating abolition of private property and equality for women. The Chinese government finally ended the civil war, with a great deal of help from the Europeans, but the cost to the country was about 20-30 million killed in this 14-year struggle. | 47 | |
| 6342078451 | Boxer Rebellion | Chinese nationalism was more apparent in the 1900 Boxer Rebellion, in which a group called the Boxers led an army against the Qing with the express purpose of recovering "China for the Chinese." The group fed on their efforts to rid the country of European interests, and even though the rebellion was unsuccessful, the Boxers laid the foundations for the 1911 Chinese Revolution that finally ended the Qing Dynasty. A series of unequal treaties with British merchants contributed to the Boxer Rebellion, which attempted to expel all foreigners from China | 48 | |
| 6342079577 | Tanzimat | reorganization of the Ottoman empire; far-reaching reformist measures; modernization and westernization; | 49 | |
| 6342079578 | Young Turks | While the Ottoman empire attempted to reform itself along European lines (including following a French legal system), many groups opposed these reforms, and a group of Young Turks overthrew the sultan in 1908 | 50 | |
| 6342080866 | Commodore Matthew Perry | 51 | ||
| 6342080867 | Zaibatsu | Japanese monopolies; | 52 | |
| 6342082182 | "Scramble for Africa" | Though Europeans had little presence in Africa at the start of the period, the scramble for Africa between 1875 and 1900 led to the occupation and exploitation of nearly the entire continent. The highly competitive states of European competed and made treaties with each other to obtain resourceful land in Africa; | 53 | |
| 6342082183 | Congo Free State | King Leopold II of Belgium began the major scramble for Africa when he established a brutal rubber plantation colony in the Congo Free State. | 54 | |
| 6342083465 | Indian National Congress | The Indian National Congress was formed in 1885, with the goals of promoting political unity and appointing more Indians into higher positions in the British Civil Service. The Congress was controlled by Hindus, and in 1906 another nationalist group was established for Muslims called the All-India Muslim League. Despite tensions between them, by 1914 both groups were demanding Indian independence from the British | 55 | |
| 6342083466 | Congress of Vienna | The allies that had defeated Napoleon met at Vienna in 1815 to reach a peace settlement that would make further revolutions impossible. The Congress of Vienna reached an agreement based on restoring the balance of power in Europe, or the principle that no one country should ever dominate the others. Rather, the power should be balanced among all the major countries | 56 |
Flashcards
AP World History - Summer Assignment Terms & Concepts Flashcards
| 10457969393 | Originally a vassal family of Shang China. The Zhou overthrew the Shang and established second historical Chinese dynasty. The Dynasty then Flourished from------------(1122 B.C.E to 256 B.C.E). First leader was King Wu Zhou. | Zhou (Dynasty) 1122 B.C.E to 256 B.C.E |  | 0 |
| 10445337586 | concerning farms, farmers, or the use of land | agrarian |  | 1 |
| 10445337587 | an alliance of nations joining together to fight a common enemy | allies |  | 2 |
| 10445337588 | a group of many islands in a large body of water | archipelago |  | 3 |
| 10445337591 | Characteristic of absolute rule or absolute ruler | autocratic / autocracy |  | 4 |
| 10445337590 | New name for the Western Pacific Rim where a significant regional realignment is now taking place. Includes rapidly-developing countries & parts of countries lining the Pacific from Japan's Hokkaido in the north to New Zealand in the South ________________________________________________________________________ | Austrasia |  | 5 |
| 10445337589 | How a minority group gradually adopts the customs and attitudes of the dominant/prevailing culture and becomes accepted. ________________________________________________________________________ | assimilation |  | 6 |
| 10445337592 | The number of births in a population in a certain amount of time | birth rate | 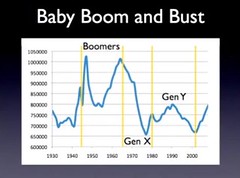 | 7 |
| 10445337593 | A world religion or philosophy based on the teaching of the Buddha and holding that a state of enlightenment can be attained by suppressing worldly desire ________________________________________________________________________ | Buddhism |  | 8 |
| 10445337594 | an economic system based on private ownership of capital | Capitalism |  | 9 |
| 10445337595 | farm crop grown to be sold or traded rather than used by the farm family | cash crop |  | 10 |
| 10445337596 | a social structure in which classes are determined by heredity | Caste system |  | 11 |
| 10445337597 | A monotheistic system of beliefs and practices based on the Old Testament and the teachings of Jesus as embodied in the New Testament and emphasizing the role of Jesus as savior ________________________________________________________________________ | Christianity |  | 12 |
| 10445337599 | A political system characterized by a centrally planned economy with all economic and political power resting in the hands of the central government. ________________________________________________________________________ | Communism |  | 13 |
| 10445337598 | The average weather a place has over a long period of time (usually 20 to 30 years) ________________________________________________________________________ | climate |  | 14 |
| 10445337600 | The largest main land masses of the globe | continent |  | 15 |
| 10445337601 | The ideas, beliefs, and customs that are shared and accepted by people in a society. ________________________________________________________________________ | culture |  | 16 |
| 10445337602 | something done by people in a particular society because it is traditional | custom |  | 17 |
| 10445337603 | the number of deaths per 1,000 people in an area | death rate |  | 18 |
| 10445337604 | a low triangular area where a river divides before entering a larger body of water | delta |  | 19 |
| 10445337605 | A political system in which the supreme power lies in a body of citizens who can elect people to represent them. ________________________________________________________________________ | democracy |  | 20 |
| 10445337606 | statistical characteristics of human populations, such as gender, age, income level, etc. | demographics |  | 21 |
| 10445337607 | Degradation of land, especially in semiarid areas, primarily because of human actions like excessive crop planting, animal grazing, and tree cutting. ________________________________________________________________________ | desertification |  | 22 |
| 10445337608 | the movement of customs or ideas from one place to another | diffusion |  | 23 |
| 10445337609 | height above (or below) sea level | elevation |  | 24 |
| 10445337610 | a distinct region or community enclosed within a larger territory | enclave |  | 25 |
| 10445337611 | An imaginary circle around the middle of the earth, halfway between the North Pole and the South Pole. ________________________________________________________________________ | Equator |  | 26 |
| 10445337612 | a social division based on national origin, religion, language, and often race | ethnicity |  | 27 |
| 10445337613 | Thinking about things based only on what your own culture/ethnicity does. Not valuing the culture, traditions, etc. of others. Belief your own ethnic group is superior. | ethnocentrism |  | 28 |
| 10445337614 | To ship out (merchandise, resources, workers, ideas, etc.) to other countries for sale, exchange, etc. ________________________________________________________________________ | export |  | 29 |
| 10445337615 | A geographical area of fertile land in the Middle East stretching in a broad semicircle from the Nile to the Tigris and Euphrates ________________________________________________________________________ | Fertile Crescent |  | 30 |
| 10445337616 | A political and social system that developed during the Middle Ages; nobles offered protection and land in return for service ________________________________________________________________________ | feudalism |  | 31 |
| 10445337617 | A low plain adjacent to a river that is formed chiefly of river sediment and is subject to flooding and overflow. Perfect for agricultural needs. ________________________________________________________________________ | flood plain |  | 32 |
| 10445337618 | the study of where people, places, and things are located and how they relate to each other | geography |  | 33 |
| 10445337619 | A poor densely populated city district occupied by a minority ethnic group linked together by economic hardship and social restrictions ________________________________________________________________________ | ghetto |  | 34 |
| 10445337620 | half of the earth | hemisphere |  | 35 |
| 10445337621 | A religion and philosophy developed in ancient India, characterized by a belief in reincarnation and a supreme being who takes many forms. ________________________________________________________________________ | Hinduism |  | 36 |
| 10445337622 | a person who comes to a country where they were not born in order to settle there | immigrant/emigrant |  | 37 |
| 10445337623 | The policy of extending authority over several foreign countries to form an empire. Imperialism takes colonialism to the next level by holding many colonies, not just one. ________________________________________________________________________ | imperialism |  | 38 |
| 10445337624 | To bring in (merchandise, resources, ideas, workers, etc.) from a foreign country for use, trade, sale, and processing. ________________________________________________________________________ | import |  | 39 |
| 10445337625 | Something that is originally from an area: Native. | indigenous |  | 40 |
| 10445337626 | French colony made up of Cambodia, Laos, and Vietnam | Indochina |  | 41 |
| 10445337627 | When a country organizes factories, technology, and workers to manufacture (in order to mass-produce) things for sale. ________________________________________________________________________ | industrialization |  | 42 |
| 10445337628 | the system of public works of a country, state, or region, such as roads, electricity, sewers, running water, etc. | infrastructure |  | 43 |
| 10445337629 | The dependence of countries on goods, resources, and knowledge from other parts of the world. ________________________________________________________________________ | interdependence |  | 44 |
| 10445337630 | supplying dry land with water by means of ditches | irrigation |  | 45 |
| 10445337631 | a relatively narrow strip of land (with water on both sides) connecting two larger land areas | isthmus |  | 46 |
| 10445337632 | the monotheistic religion founded by Abraham and whose followers are called Jews | Judaism |  | 47 |
| 10445337633 | The way that the first people may have arrived in the Americas; connected Siberia and Alaska around 40,000 years ago. ________________________________________________________________________ | land bridge |  | 48 |
| 10445337634 | natural features of the earth's surface | landforms |  | 49 |
| 10445337635 | surrounded by land; cut off from the sea | landlocked |  | 50 |
| 10445337636 | The set of imaginary parallel lines that circle the earth parallel to the Equator and measure the distance north and south of the equator in degrees. ________________________________________________________________________ | latitude |  | 51 |
| 10445337637 | distance east or west of the Prime Meridian, measured in degrees | longitude |  | 52 |
| 10445337638 | A society in which the mother is the supreme authority in the family, clan or tribe and children belong to the mother's family or tribe; women have the governing authority. ________________________________________________________________________ | matriarchy | 53 | |
| 10445337639 | relating to or situated in or extending toward the middle | median |  | 54 |
| 10445337640 | a very large urban complex (usually involving several cities and towns) | megalopolis |  | 55 |
| 10445337641 | a person of mixed Spanish and Native American ancestry | mestizo |  | 56 |
| 10445337642 | the transformation of traditional societies into industrial societies | modernization |  | 57 |
| 10445337643 | The term used in Spanish and Portuguese colonies to describe someone of mixed African and European descent ________________________________________________________________________ | mulatto |  | 58 |
| 10445337644 | an independent geopolitical unit of people having a common culture and identity | nation-state |  | 59 |
| 10445337645 | The natural wealth of a country, consisting of land, forests, mineral deposits, water, etc.; natural resources 1) make a country wealth, 2) have a limit 3) are not man-made | natural resources |  | 60 |
| 10445337646 | west; denoting or characteristic of countries of Europe and the Western Hemisphere | occidental |  | 61 |
| 10445337647 | a political system governed by a small group of people | oligarchy |  | 62 |
| 10445337648 | east; denoting or characteristic of the biogeographic region including southern Asia and the Malay Archipelago as far as the Philippines and Borneo and Java. ________________________________________________________________________ | oriental |  | 63 |
| 10445337649 | Disease that occurs over a wide geographic area and affects a very high proportion of the population. ________________________________________________________________________ | pandemic |  | 64 |
| 10445337650 | the super continent where all the continents were once joined | Pangaea |  | 65 |
| 10445337651 | a society in which the father is the supreme authority in the family, clan or tribe and children belong to the fathers family or tribe; men have authority over woman and children. | patriarchy |  | 66 |
| 10445337652 | body of land jutting into a lake or ocean, surrounded on three sides by water | peninsula |  | 67 |
| 10445337653 | a map that shows mountains, hills, plains, rivers, lakes, oceans, etc. | physical map |  | 68 |
| 10445337654 | an extensive area of level and rolling, treeless country, often covered by rich, fertile soil | plains |  | 69 |
| 10445337655 | an estate where cash crops are grown on a large scale (especially in tropical areas) | plantation |  | 70 |
| 10445337656 | a large area of flat land elevated high above sea | plateau |  | 71 |
| 10445337657 | a map showing units such as countries, states, provinces, districts, etc.l each is normally a different color | political map |  | 72 |
| 10445337658 | worshipping or believing in more than one god | polytheistic |  | 73 |
| 10445337659 | number of individuals per unit area | population density |  | 74 |
| 10445337660 | a line that runs north to south through Greenwich England; other meridians are measured from this | prime meridian |  | 75 |
| 10445337661 | the leader of the executive branch of a parliamentary government | prime minister | 76 | |
| 10445337662 | people who are believed to belong to the same genetic stock | race |  | 77 |
| 10445337663 | People who are forced to migrate from their home country and cannot return for fear of persecution because of their race, religion, nationality, membership in a social group, or political opinion ________________________________________________________________________ | refugees |  | 78 |
| 10445337664 | A ritual performed in some cultures at times when a individual changes his status (as from adolescence to adulthood) ________________________________________________________________________ | rite of passage |  | 79 |
| 10445337665 | another name for ceremonies or rites | rituals |  | 80 |
| 10445337666 | of, pertaining to, or characteristic of the country, country life, or country people; of or pertaining to agriculture: rural economy ________________________________________________________________________ | rural |  | 81 |
| 10445337667 | grassland with scattered trees; found in tropical regions of Africa, Australia, and South America | savanna |  | 82 |
| 10445337668 | not spiritual or religious; worldly | secular |  | 83 |
| 10445337669 | not migratory; settled | sedentary |  | 84 |
| 10445337670 | a usually poor town or section of a town consisting mostly of small wooden shacks | shantytown |  | 85 |
| 10445337671 | system in which landowners leased a few acres of land to farm workers in return for a portion of their crops ________________________________________________________________________ | sharecropping |  | 86 |
| 10445337672 | group of people who hold similar positions in society, share similar wealth, and receive similar respect from other members of society ________________________________________________________________________ | social classes |  | 87 |
| 10445337673 | the level of material comfort as measured by the goods, services, and luxuries available to an individual, group, or nation ________________________________________________________________________ | standard of living |  | 88 |
| 10445337674 | farming that provides for the basic needs of the farmer without surpluses for marketing | subsistence farming |  | 89 |
| 10445337675 | a noble title for the ruler of a Muslim country (especially of the former Ottoman Empire) | sultan |  | 90 |
| 10445337676 | a government tax on imports or exports | tariff |  | 91 |
| 10445337677 | a government controlled by religious leaders | theocracy |  | 92 |
| 10445337678 | the business of buying and selling or exchanging items | trade |  | 93 |
| 10445337679 | a stream or river that flows into a larger river | tributary |  | 94 |
| 10445337680 | sameness; monotony; (adj.) uniform: the same all over | uniformity |  | 95 |
| 10445337681 | of, relating to, or located in a city; characteristic of the city or city life | urban |  | 96 |
| 10445337682 | the growth of cities and the migration of people into them | urbanization |  | 97 |
| 10445337683 | the temperature and humidity of a place at a specific time | weather |  | 98 |
| 10445337684 | The adoption of Western culture, government, food, clothing, and religion | Westernization |  | 99 |
| 10457906298 | The Old Stone Age ending in 12,000 B.C.E.; typified by use of crude stone tools and hunting and gathering for subsistence. ________________________________________________________________________ | Paleolithic Age Until~ 12,000 B.C.E |  | 100 |
| 10457907308 | The New Stone Age between 8000 and 5000 B.C.E.; period in which adaptation of sedentary agriculture occurred; domestication of plants and animals accomplished. ________________________________________________________________________ | Neolithic Age ~8,000 B.C.E to 5,000 B.C.E |  | 101 |
| 10457910901 | From about 4000 B.C.E.; when bronze tools were first introduced in the Middle East, to about 1500 B.C.E., when iron began to replace it. ________________________________________________________________________ | Bronze Age ~4,000 B.C.E to 1,500 B.C.E |  | 102 |
| 10457913810 | A level of social organization normally consisting of 20-30 people; nomadic hunters and gatherers; labor divided on a gender basis. ________________________________________________________________________ | Band |  | 103 |
| 10457918878 | Societies distinguished by reliance on sedentary agriculture, ability to produce food surpluses, and existence of non-farming elites, as well as merchant and manufacturing groups. ________________________________________________________________________ | Civilization ~3,200 B.C.E to Current period |  | 104 |
| 10457923095 | A form of writing developed by the Sumerians using a wedge-shaped stylus and clay tablets. ________________________________________________________________________ | Cuneiform 3,500 B.C.E to 100 B.C.E |  | 105 |
| 10457924953 | Cattle- and sheep-herding societies normally founded on the fringes of civilized societies; commonly referred to as "barbarian' by civilized societies. ________________________________________________________________________ | Nomads |  | 106 |
| 10457926658 | Literally "between the rivers"; the civilizations that arose in the alluvial plain of the Tigris and Euphrates river valleys. ________________________________________________________________________ | Mesopotamia ~5000 B.C.E to ~3500 B.C.E |  | 107 |
| 10457928058 | People who migrated in to Mesopotamia c. 4000 B.C.; created first civilization within region; organized area into city-states. ________________________________________________________________________ | Sumerians ~4000 B.C.E to 2200 B.C.E |  | 108 |
| 10457941517 | Massive towers usually associated with Mesopotamian temple complexes. | Ziggurauts |  | 109 |
| 10457942836 | A form of political organization typical of Mesopotamian civilizations; consisted of agricultural hinterlands ruled by an urban-based king. ________________________________________________________________________ | city-state |  | 110 |
| 10457944331 | Unified all of Mesopotamia c. 1800 B.C.E.; collapsed due to foreign invasion c. 1600 B.C.E ________________________________________________________________________ | Babylonian Empire 1792 B.C.E to 539 B.C.E |  | 111 |
| 10457946195 | (r. 1792-1750 B.C.E.) The most important ruler of the Babylonian empire; responsible for codification of the law. ________________________________________________________________________ | Hammurabi 1640 B.C.E to 1750 B.C.E |  | 112 |
| 10457947973 | Monumental architecture typical of Old Kingdom Egypt; used as burial sites for pharaohs. | pyramids |  | 113 |
| 10457948719 | An African state that developed along the upper reaches of the Nile c. 1000 B.C.E; conquered Egypt and ruled it for several centuries. ________________________________________________________________________ | Kush civilization |  | 114 |
| 10457950646 | River sources in Himalayas to mouth in Arabian Sea; location of Harappan civilization. | Indus River Valley ~2600 B.C.E to 1900 B.C.E |  | 115 |
| 10457951565 | Along with Mohenjo daro, major urban complex of the Harappan civilization; laid out on planned grid pattern. ________________________________________________________________________ | Harappa ~2500 B.C.E to ~2000 B.C.E |  | 116 |
| 10457953578 | Also known as the Huanghe; site of development of sedentary agriculture in China. | Yellow River |  | 117 |
| 10457955938 | First Chinese dynasty for which archeological evidence exists; capital located in Ordos bulge of the Huanghe; flourished 1600 to 1046 B.C.E. ________________________________________________________________________ | Shang ~1600 B.C.E to ~1000 B.C.E |  | 118 |
| 10457958312 | Pictographic characters grouped together to create new concepts; typical of Chinese writing. | ideographs |  | 119 |
| 10457959442 | Seafaring civilization located on the shores of the eastern Mediterranean; established colonies throughout the Mediterranean. ________________________________________________________________________ | Phoenicians ~1500 B.C.E to ~300 B.C.E |  | 120 |
| 10457962221 | The exclusive worship of a single god; introduced by the Jews into Western civilization. | monotheism |  | 121 |
| 10457963297 | Founder of the brief Qin dynasty in 221 B.C.E. | Shi Huangdi 259 B.C.E to 210 B.C.E |  | 122 |
| 10457964811 | Established in 221 B.C.E. at the end of the Warring States period following the decline of the Zhou dynasty; fell in 207 B.C.E ________________________________________________________________________ | Qin dynasty 221 B.C.E to 207 B.C.E |  | 123 |
| 10457967039 | Chinese dynasty that succeeded the Qin in 202 B.C.E.; rules for next 400 years. | Han dynasty 206 B.C.E to 220 C.E |  | 124 |
| 10457971782 | Also known as Kung Fuzi; major Chinese philosopher born in 6th century B.C.E. Philosophy based on need for restoration of order through advice of superior men. ________________________________________________________________________ | Confucius 551 B.C.E to 479 B.C.E |  | 125 |
| 10457977305 | Chinese defensive fortification in tended to keep out the nomadic invaders from the north; initiated during Qin dynasty and reign of Qin Shi Huangdi. ________________________________________________________________________ | The Great Wall Built from: 220 B.C.E to 206 B.C.E |  | 126 |
| 10457981188 | Creator of a major Indian and Asian religion; born in 6th century B.C.E. as son of local ruler among Aryan tribes. Found enlightenment;taught enlightenment could be achieved only by abandoning desires for all earthly things. | Buddha |  | 127 |
| 10457981189 | Indo-European nomadic pastoralists who replaced Harappan civilization; militarized society. | Aryans |  | 128 |
| 10457986236 | The sacred and classical Indian language. | Sanskrit Created: ~1500 B.C.E |  | 129 |
| 10457986975 | Aryan hymns originally transmitted orally but written down in sacred books. | Vedas Written: ~1200 B.C.E |  | 130 |
| 10457988637 | Clusters of caste group in Aryan society; four social castes - Brahmans (priests) warriors, merchants, and peasants; beneath four Aryan castes was group of socially untouchable Dasas. ________________________________________________________________________ | Varnas |  | 131 |
| 10457990882 | Low social caste in Hindu culture; performed tasks that were considered polluting - street sweeping, removal of human waste, and tanning ________________________________________________________________________ | untouchables |  | 132 |
| 10457994990 | Dynasty established in Indian subcontinent in 4th century B.C.E. following invasion by Alexander the Great. ________________________________________________________________________ | Mauryan ~320 B.C.E to ~180 B.C.E |  | 133 |
| 10457997353 | Grandson of Chandragupta Maurya; completed conquests of Indian subcontinent; converted to Buddhism and sponsored spread of new religion though his empire. ________________________________________________________________________ | Ashoka 340 B.C.E to 232 B.C.E (r. 273 - 232 B.C.E.) |  | 134 |
| 10458000331 | The caste position and career determined by a person's birth; Hindu culture required that one accept one's social position and perform occupation to the best of one's ability in order to have a better situation in the next life. | Dharma |  | 135 |
| 10458002426 | Dynasty that succeeded the Kushans in the 3rd century B.C.E.; built empire that extended to all but the southern regions of Indian sub-continent; less centralized that Mauryan Empire. ________________________________________________________________________ | Guptas 240 C.E to 590 C.E |  | 136 |
| 10458005772 | Animist religion that saw material existence as battle between forces of good and evil; stressed the importance of moral choice; righteous lived on or after death in "house of Song"; chief religion of Persian Empire. | Zoroastrianism Created: ~600 B.C.E |  | 137 |
| 10458010171 | Athenian political leader during the 5th century B.C.E.; guided development of Athenian empire; died during early stages of Peloponnesian War. ________________________________________________________________________ | Pericles 494 B.C.E to 429 B.C.E |  | 138 |
| 10458013220 | That culture associated with the spread of Greek influence as a result of Macedonian conquests; often seen as the combination of Green culture with eastern political forms. ________________________________________________________________________ | Hellenistic Period ~320 B.C.E to ~30 B.C.E |  | 139 |
| 10458015617 | The balanced constitution of Rome from c. 510 to 47 B.C.E.; featured an aristocratic Senate, a pane of magistrates, and several popular assemblies. ________________________________________________________________________ | Roman republic ~800 B.C.E to ~470C.E |  | 140 |
| 10458017733 | Roman general responsible for conquest of Gaul; brought back to Rome and overthrew republic; assassinated in 44 B.C.E. by conservative senators. ________________________________________________________________________ | Julius Caesar 100 B.C.E to 44 B.C.E |  | 141 |
| 10458020963 | Roman emperor from 312 to 337 C.E.; established second capital at Constantinople; attempted to use religious force of Christianity to unify empire spiritually. ________________________________________________________________________ | Constantine 272 C.E to 337 C.E |  | 142 |
| 10458025412 | Where people participate directly in assemblies that make laws and select leaders, rather than electing representatives. ________________________________________________________________________ | Direct Democracy Created: ~500 B.C.E |  | 143 |
| 10458027751 | Assembly of Roman aristocrats; advised on policy within the republic; one of the early elements of the Roman constitution. ________________________________________________________________________ | Senate |  | 144 |
| 10458030778 | Two chief executives or magistrates of the Roman republic; elected by an annual assembly dominated by aristocracy ________________________________________________________________________ | consuls |  | 145 |
| 10458032906 | (384-322 B.C.E.) Greek philosopher; teacher of Alexander the Great; knowledge based on observation of phenomena in material world. ________________________________________________________________________ | Aristotle 384 B.C.E to 322 B.C.E |  | 146 |
| 10458036388 | Athenian philosopher of later 5th century B.C.E.; tutor of Plato; urged rational reflection of moral decisions; contemned to death of corrupting minds of Athenian young. ________________________________________________________________________ | Socrates 470 B.C.E to 399 B.C.E |  | 147 |
| 10458040058 | Greek epic poem attributed to Homer but possibly he work of many authors; defined gods and human nature that shaped Greek mythos. ________________________________________________________________________ | Iliad |  | 148 |
| 10458043220 | Greek epic poem attributed to Homer but possibly he work of many authors; defined gods and human nature that shaped Greek mythos ________________________________________________________________________ | Odysssey |  | 149 |
| 10458045028 | Kingdom located in Ethiopian highlands; replaced Meroë in 1st century C.E.; received strong influence from Arabian peninsula; eventually converted to Christianity. ________________________________________________________________________ | Axum |  | 150 |
| 10458050151 | A Christian kingdom that developed int eh highlands of eastern Africa under the dynasty of King Lalaibela; retained Christianity in the face of Muslim expansion elsewhere in Africa. ________________________________________________________________________ | Ethiopia ~980 B.C.E to Present |  | 151 |
| 10458051687 | Religion of early Japanese culture; deveotees worshipped numerous gods and spirits associated with the natural world; offers of food and prayers made to gods and nature spirits. ________________________________________________________________________ | Shinto 800 B.C.E to 1945 C.E |  | 152 |
| 10458053570 | Cultural tradition that arose at San Lorenzo and La Venta in Mexico c. 1200 B.C.E.; featured irrigated agriculture, urbanism, elaborate religion, beginnings of calendrical and writing systems. | Olmec culture 1200 B.C.E to 400 B.C.E |  | 153 |
| 10458057844 | Site of classic culture in central Mexico; urban center with important religious functions; supported by intensive agriculture in surrounding regions; population of as much as 200,000. ________________________________________________________________________ | Teotihuacan Built: 100 B.C.E |  | 154 |
| 10458059671 | Classic culture in southern Mexico and Central America contemporary with Teotihuacan; extended over broad region; featured monumental architecture, written language, and highly developed: Math, Calendrical and religion systems. | Maya 1800 B.C.E to 250 C.E |  | 155 |
| 10458061082 | Group of clans centered at Cuzco that were able to create empire incorporating various Andean cultures; term also used for leader of empire. ________________________________________________________________________ | Inca ~1400 C.E to ~1500 C.E |  | 156 |
| 10458063893 | Islands contained in a rough triangle whose points lie inHawaii, New Zealand, and Easter Island. | Polynesia |  | 157 |
| 10458065076 | Chinese Daoists who launched a revolt in 184 C.E. in China promising a golden age to be brought about by divine magic. ________________________________________________________________________ | Yellow Turbans 184 C.E to 205 C.E |  | 158 |
| 10458074247 | Dynasty that succeeded the Han in China; emerged from strong rulers in northern China; united all of northern China and reconquered southern China. ________________________________________________________________________ | Sui (Dynasty) 581 C.E to 610 C.E |  | 159 |
| 10458077570 | Dynasty that succeedd the Sui in 618 C.E.; more stable than previous dynasty. | Tang (Dynasty) 618 C.E to 918 C.E |  | 160 |
| 10458078737 | Major world religion having its origins in 610 c.e. in the Arabian peninsula; meaning literally submission; based on prophecy of Muhammad. ________________________________________________________________________ | Islam Created: 700 C.E |  | 161 |
| 10458080386 | Eastern half of Roman Empire following collapse of western half of old empire; retained Mediterranean culture, particularly Greek; later lost Palestine, Syria, and Egypt to Islam; capital at Constantinople. | Byzantine Empire 330 C.E to 1453 C.E |  | 162 |
| 10458083810 | Christian sect in Egypt, later tolerated after Islamic takeover. | Coptic Created: 42 C.E |  | 163 |
| 10458084538 | A religious outlook that sees gods in many aspects of nature and propitiates them to help control and explain nature; typical of Mesopotamian religions. ________________________________________________________________________ | animism |  | 164 |
| 10458095059 | Name given to Octavian following his defeat of Mark Anthony and Cleopatra; first emperor of Rome. ________________________________________________________________________ | Augustus Caesar 63 B.C.E. to 14 C.E. |  | 165 |
Ap world history Flashcards
China: Dynasties
| 10858937138 | Zhou Dynasty | human sacrifice | 0 | |
| 10858937139 | Zhou Dynasty | unified language- Mandarin Chinese | 1 | |
| 10858937140 | Zhou Dynasty | Start of Confucianism, Daoism, and Legalism | 2 | |
| 10858937141 | Era of Warring States | 256 BCE- 221 BCE | 3 | |
| 10858937142 | Qin Dynasty | Political- •increased centralized power •Bureaucracy •killed critics •scholars buried alive | 4 | |
| 10858937143 | Qin Dynasty | Interaction- Great Wall | 5 | |
| 10858937144 | Qin Dynasty | Cultures- • China is derived from Ch`in | 6 | |
| 10858937145 | Qin Dynasty | Decline- •Peasants revolted and overthrew and eventually the dynasty ended. | 7 | |
| 10858937146 | Han Dynasty | Social- •Patriarchal •Classic of Filial Piety -subordination to elder males | 8 | |
| 10858937147 | Han Dynasty | Political- • increased taxes • bureaucracy • Mandate of Heaven | 9 | |
| 10858937148 | Han Dynasty | Interaction- • invaded vietnam and korea • produce spoiled because they had so much • Yellow Turban uprising | 10 | |
| 10858937149 | Han Dynasty | Cultures- • established a university • adopted Confucianism as official course of study | 11 | |
| 10858937150 | Han Dynasty | Economic- • improved silk and cotton • Development of paper | 12 | |
| 10858937151 | Han Dynasty | Decline- • weakened Han Dynasty collapses by 220 CE | 13 | |
| 10858937152 | Chinese Philosophies | Confucianism- moral order in society | 14 | |
| 10858937153 | Confucianism | • Filial piety • Respect for elders • Kindness • status, age, and gender | 15 | |
| 10858937154 | Legalism | rule by harsh law and order | 16 | |
| 10858937155 | Legalism | •humans are selfish • the ruler must rule with a strong, punishing hand | 17 | |
| 10858937156 | Daoism | freedom for individuals and less govt. to avoid uniformity and comformity | 18 | |
| 10858937157 | Daoism | founder: Laozi • The Dao (" The Way of nature") • reject education • discover nature •Yin and Yang | 19 | |
| 10858937158 | 20 |
Pages
Need Help?
We hope your visit has been a productive one. If you're having any problems, or would like to give some feedback, we'd love to hear from you.
For general help, questions, and suggestions, try our dedicated support forums.
If you need to contact the Course-Notes.Org web experience team, please use our contact form.
Need Notes?
While we strive to provide the most comprehensive notes for as many high school textbooks as possible, there are certainly going to be some that we miss. Drop us a note and let us know which textbooks you need. Be sure to include which edition of the textbook you are using! If we see enough demand, we'll do whatever we can to get those notes up on the site for you!

