AP Exam review Flashcards
| 6834289853 | Chloropleth | Shading to show different levels of data |  | 0 |
| 6834294988 | Graduated Symbol | Sized-Symbol to show frequency or intensity of a variable |  | 1 |
| 6834323467 | Cartogram | Shows size using data other than area | 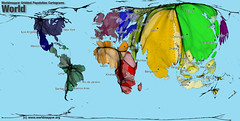 | 2 |
| 6834329162 | Isoline | Connects points of equal value to form lines |  | 3 |
| 6834341142 | Ethnic neighborhood | A place where people of similar origin reside | 4 |
AP Statistics Vocabulary Flashcards
| 9911394334 | 5 number summary | The minumum value, lower quartile, median, upper quartile, and maximum value for a data set. These five values give a summary of the shape of the distribution and are used to make box plots. The five numbers that help describe the center, spread and shape of data |  | 0 |
| 9911394335 | z score | a measure of how many standard deviations you are away from the norm (average or mean) -Number of standard deviations a score is above or below the mean (positive above, negative below |  | 1 |
| 9911394336 | standard deviation | A statistical measure of how far away each value is, on average, from the mean. A measure of spread. Specifically, the typical distance the data points are from the mean. |  | 2 |
| 9911394337 | population | (statistics) the entire aggregation of items from which samples can be drawn What the sample in an experiment or study usually reperesents | 3 | |
| 9911394338 | categorical data | Data that can be placed into categories . For example "gender" is a categorical data and the categories are "male" and "female". Labels or names used to identify categories of like items If you asked people in which month they were born or what their favorite class is, they would answer with names, which would be categorical data. However, if you asked them how many siblings they have, they would answer with numbers, not categories Labels or names used to identify categories of like items |  | 4 |
| 9911394339 | quantitative data | Data associated with mathematical models and statistical techniques used to analyze spatial location and association. numerical information describing how much, how little, how big, how tall, how fast, etc. age is quantitative |  | 5 |
| 9911394340 | bar graph | a type of graph in which the lengths of bars are used to represent and compare data in categories A graph that uses horizontal or vertical bars to represent data. |  | 6 |
| 9911394341 | parameter | (n) a determining or characteristic element; a factor that shapes the total outcome; a limit, boundary a characteristic or constant factor something that determines the limits of certain data values |  | 7 |
| 9911394342 | sample | A relatively small proportion of people who are chosen in a survey so as to be representative of the whole. a small part of a population that represents the whole A survey in star city representing the entire state of arkansas |  | 8 |
| 9911394343 | random | Assigning participants to experimental and control conditions by chance, thus minimizing preexisting differences between those assigned to the different groups. Assigning subjects to expenrimental groups based on chance. pulling names or numbers out of a hat |  | 9 |
| 9911394344 | bias | Any systematic failure of a sampling method to represent its population Any way that tampers with the accuracy of the sample | 10 | |
| 9911394345 | Undercoverage | A sampling scheme that biases the sample in a way that gives a part of the population less representation than it has in the population. When some groups in the population are left out of the process of choosing the sample |  | 11 |
| 9911394346 | nonresponse | bias introduced to a sample when a large fraction of those sampled fails to respond When many people of a sample do not respond |  | 12 |
| 9911394347 | voluntary response bias | Bias introduced to a sample when individuals can choose on their own whether to participate in the sample. |  | 13 |
| 9911394348 | statistic | Application of mathematics to describing and analyzing data |  | 14 |
| 9911394349 | independent | (statistics) a variable whose values are independent of changes in the values of other variables | 15 | |
| 9911394350 | historgram | graphical representation of a frequency distribution using vertical bars but bars touch each other to indicate variables are related | 16 | |
| 9911394351 | box plot | A dsiplay that shows the distribution of values in a data set seperated into four equal-sized groups. A box plot is constructed from the five number summary of the data. |  | 17 |
| 9911394352 | scatterplot | A graphed cluster of dots, each of which represents the values of two variables. The slope of the points suggests the direction of the relationship between the two variables. The amount of scatter suggests the strength of the correlation (little scatter indicates high correlation). |  | 18 |
| 9911394353 | correlation | A measure of the extent to which two factors vary together, and thus of how well either factor predicts the other. The correlation coefficient is the mathematical expression of the relationship, ranging from -1 to +1 |  | 19 |
| 9911394354 | skewness | The extent to which cases are clustered more at one or the other end of the distribution of a quantitative variable rather than in a symmetric pattern around its center |  | 20 |
| 9911394355 | varience | commons measure of spread about the mean as center | 21 | |
| 9911394356 | statistical significance | A statistical statement of how likely it is that an obtained result occurred by chance/The condition that exists when the probability that the observed findings are due to chance is very low |  | 22 |
| 9911394357 | P-value | A measure of statistical significance. The lower, the more likely the results of an experiment did not occur simply chance. |  | 23 |
| 9911394358 | empirical rule | The rules gives the approximate % of observations w/in 1 standard deviation (68%), 2 standard deviations (95%) and 3 standard deviations (99.7%) of the mean when the histogram is well approx. by a normal curve |  | 24 |
| 9911394360 | null hypothesis | Hypothesis that predicts NO relationship between variables. The aim of research is to reject this hypothesis | 25 | |
| 9911394361 | alternate hypothesis | , is the hypothesis to be considered as an alternative to the null hypothesis. The null hypothesis will be rejected in favor of the Ha only if the sample data strongly indicate that the null hypothesis is false. |  | 26 |
| 9911394362 | quota sample | A sample deliberately constructed to reflect several of the major characteristics of a given population | 27 | |
| 9911394363 | probability | A number with a value from 0 to 1 that describes the likelihood that an event will occur. example, if a bag contains a red marble, a white marble and a blue marble then the probability of selecting a red marble is 1/3. |  | 28 |
| 9911394364 | descriptive statistics | Mathematical procedures for organizing collections of data, such as determining the mean, the median, the range, the variance, and the correlation coefficient | 29 | |
| 9911394365 | mean | A measure of center in a set of numerical data, computed by adding the values in a list and then dividing by the number of values in the list. | 30 | |
| 9911394366 | median | A measure of center in a set of numerical data. The median of a list of values is the value appearing at the center of a sorted version of the list - or the mean of the two central values if the list contains an even number of values. | 31 | |
| 9911394367 | mode | Measure of central tendency that uses most frequently occurring score. |  | 32 |
| 9911394368 | range | Distance between highest and lowest scores in a set of data. | 33 | |
| 9911394369 | data | Facts and statistics collected together for reference or analysis |  | 34 |
| 9911394370 | Q1 | A location measure of the data such that has one fourth or 25% of the data is smaller than it. Found by dividing the ordered data set in half (excluding the middle observation if n is odd) and finding the median of the lower half of the data. | 35 | |
| 9911394371 | Q3 | A location to measeure when counting data to such as the median where instead of counting 50% it is 75% from the beginning of the sorted data | 36 | |
| 9911394372 | minimum | (n.) the smallest possible amount; (adj.) the lowest permissible or possible | 37 | |
| 9911394373 | outlier | A value much greater or much less than the others in a data set |  | 38 |
| 9911394374 | margin of error | In statistical research, the range of outcomes we expect for a population, given the data revealed by a sample drawn from that population |  | 39 |
| 9911394376 | simple random sample | A sample selected in such a way that every element in the population or sampling frame has an equal probability of being chosen. Equivalently, all samples of size n have an equal chance of being selected. A sample of size n selected from the population in such a way that each possible sample of size n has an equal chance of being selected. |  | 40 |
| 9911394377 | sampling distribution | Distribution of sample proportions from sample to sample. A sampling distribution of a sample statistic for a fixed sample size n is the distribution of that statistic derived from every possible sample of size n for a given population. A distribution of statistics obtained by selecting all the possible samples of a specific size from a population | 41 | |
| 9911394378 | stratified random sample | A method of sampling that involves dividing your population into homogeneous subgroups and taking a simple random sample in each subgroup. a sampling design in which the population is divided into several groups, and random samples are then drawn from each stratum |  | 42 |
| 9911394379 | systematic sample | A sample drawn by selecting individuals systematically from a sampling frame A sample drawn by selecting individuals systematically from a sampling frame. When there is no relationship between the order of the sampling frame and the variables of interest, a systematic sample can be representative. |  | 43 |
| 9911394380 | cluster sample | Is obtained by selecting all individuals within a randomly selected collection or group of individuals. | 44 | |
| 9911394381 | 10% rule | a sample has to be lass than 10% of the whole population | 45 | |
| 9911394382 | Interpolation | The estimation of an unknown number between known numbers. Interpolation is a way of approximating price or yield using bond tables that do not give the net yield on every amount invested at every rate of interest and for every maturity. | 46 | |
| 9911394383 | Qualitative | Data in the form of recorded descriptions rather than numerical measurements. | 47 | |
| 9911394384 | theoretical probability | A probability obtained by analyzing a situation. If all of the outcomes are equally likely, you can find the theoretical probability of an event by listing all of the possible outcomes and then finding the ratio of the number of outcomes producing the desired event to the total number of outcomes. For example, there are 36 possible equally likely outcomes (number pairs) when two fair number cubes are rolled. of these six have a sum of 7, so the probability of rolling a sum of 7 is 6/36 or 1/6 | 48 | |
| 9911394440 | experimental probability | 49 | ||
| 9911394385 | block design | The subjects in an experiment are first divided into groups (called 'blocks') based on some common characteristic (such as gender) that is hypothesised to have an effect on the response. Randomization of treatments then happens within each block (each block is like its own mini-experiment)." | 50 | |
| 9911394386 | blinding | The practice of concealing group assignment from study subjects, investigators, and/or those who assess subject outcomes, typically in the context of a randomized controlled trial. For ex, study subjects may receive capsules with identical appearance and taste; however, the treatment group receives the active drug, whereas the control group receives the placebo. | 51 | |
| 9911394387 | double blind | An experiment in which neither the subjects nor the people who work with them know which treatment each subject is receiving Neither the subjects nor the people who have contact with them know which treatment a subject received | 52 | |
| 9911394388 | placebo | A fake treatment. A chemically inert substance that produces real medical benefits because the patient believes it will help her |  | 53 |
| 9911394389 | least squares regression line | the line with the smallest sum of squared residuals |  | 54 |
| 9911394390 | type I error | An error that occurs when a researcher concludes that the independent variable had an effect on the dependent variable, when no such relation exists; a "false positive | 55 | |
| 9911394391 | type II error | An error that occurs when a researcher concludes that the independent variable had no effect on the dependent variable, when in truth it did; a "false negative | 56 | |
| 9911394392 | matched pairs | an observational technique that involves matching each participant in the experimental group with a specific participant in the control group in order to eliminate the possibility that a third variable (and not the independent variable) caused changes in the dependent variable |  | 57 |
| 9911394393 | conditional prabability | probability given that something else has already occurred | 58 | |
| 9911394394 | sample space | Set of all possible outcomes of an experiment |  | 59 |
| 9911394395 | confounded variable | A variable whose effect on the response variable cannot be separated from the effect of the explanatory variable on the response variable. (Note: Usually confounded variables are lurking variables but only a few lurking variables are also confounded.) | 60 | |
| 9911394396 | marginal frequency | A set of intervals, usually adjacent and of equal width, into which the range of a statistical distribution is divided, each associated with a frequency indicating the number of measurements in that interval. | 61 | |
| 9911394397 | coefficient of determination | The statistic or number determined by squaring the correlation coefficient. Represents the amount of variance accounted for by that correlation. Statistic that represents amount of variance accounted for by a correlation. | 62 | |
| 9911394398 | binomial | A two-name naming system. |  | 63 |
| 9911394399 | unimodal | having one mode; this is a useful term for describing the shape of a histogram when it's generally mound-shaped a data set with one mode such a normal distribution usually has only one mode | 64 | |
| 9911394400 | bimodal | A type of distribution, where there is two or more categories with an equal count or cases and with more cases than the other categories. A distribution with two modes | 65 | |
| 9911394401 | experiment | A kind of research in which the researcher controls all the conditions and directly manipulates the conditions, including the independent variable. Testing the hypothesis | 66 | |
| 9911394402 | law of large numbers | (statistics) law stating that a large number of items taken at random from a population will (on the average) have the population statistics | 67 | |
| 9911394403 | extrapolation | calculation of the value of a function outside the range of known values | 68 | |
| 9911394405 | IQR | A measure of variability, based on dividing a data set into quartiles Difference between upper and lower quartile of a boxplot | 69 | |
| 9911394406 | Confidence interval | A range of values for a variable of interest; the specified probability is called the confidence level and the end points of the confidence interval are called the confidence limits A range of numbers in which most of the data values are likely to fall. we are 95% confident that etc. | 70 | |
| 9911394407 | Standard Error | A statistic providing an estimate of the possible magnitude to error. The larger the standard error of measurement, the less reliable the score. Standard deviation of sampling distribution |  | 71 |
| 9911394442 | Residual | 72 | ||
| 9911394408 | Convenience sample | Whenever a sample is taken it gives an improper results because the sample was taken from a very convenient area instead of representing a population | 73 | |
| 9911394409 | simulation | A representation of a situation or problem with a similar but simpler model or a more easily manipulated model in order to determine experimental results. | 74 | |
| 9911394410 | degrees of freedom | The number of individual scores that can vary without changing the sample mean. Statistically written as 'N-1' where N represents the number of subjects. | 75 | |
| 9911394411 | two way table | A table containing counts for two categorical variables. It has r rows and c columns. describes to categorical variables with row variable and column variable | 76 | |
| 9911394412 | spread | The visible variation in a sample distribution | 77 | |
| 9911394413 | center | The measure of the distance the mode is from the center of a distribution | 78 | |
| 9911394444 | discrete random variable | a random variable that may assume either a finite number of values or an infinite sequence of values | 79 | |
| 9911394445 | central limit theorem | the sampling distribution of the mean approaches a normal curve as N gets larger | 80 | |
| 9911394447 | mutually exclusive | Events that cannot occur at the same time. | 81 | |
| 9911394414 | wording bias | Whenever a bias is created in a sample by the way the survey is worded to favor one question | 82 | |
| 9911394448 | causation | 83 | ||
| 9911394449 | z test | 84 | ||
| 9911394450 | t test | 85 | ||
| 9911394415 | chi squared goodness of fit | tests how well close the observes data is to what would be expected under the model. If a sign diff is found b/w the two then ob. data has not been generated by chance. nominal data Determine if scores from one variable match expectations for that distribution a gambler placed $1,000 into a game of greed in which he lost. He hopes to catch his opponent and bust him for loading the dice. He does this by choosing one dice to roll 36 times. He knows that the each side has an equal chance of landing face up. He hopes to get an outcome abnormal to this. Given the data below, can we prove that the dice are loaded |  | 86 |
| 9911394416 | frequency table | A grouping of qualitative data into mutually exclusive classes showing the number of observations in each class. A chart showing the number of times a specific event happens. |  | 87 |
| 9911394417 | area principle | the area occupied by a part of the graph should correspond to the magnitude of the value it represents | 88 | |
| 9911394418 | contingency table | displays counts, and, sometimes, percentages of individuals falling into named categories on two or more variables. The table categorizes the individuals on all variables at once, to reveal possible patterns in one variable that may be contingent on the category of the other. A two-variable table with cross-tabulated data. | 89 | |
| 9911394419 | stem and leaf display | A multiple column table depicting the individual digits of the scores. A score of 95 would have a stem of 9 and a leaf of 5, a score of 62 would have a stem of 6 and a leaf of 2. If a particular stem has more than one leaf, such as the scores 54, 58, and 51, the stem of 5 has three leaves, in this case 458. . It shows the range of values of the variable |  | 90 |
| 9911394420 | multimodal | Describes a graph of quantitative data with more than two clear peaks. A distribution with more than two modes |  | 91 |
| 9911394421 | uniform | A histogram doesn't appear to have any mode and in which all the bars are approximately the same height Evenly spaced |  | 92 |
| 9911394422 | symetric | When in a normal distribution both sides are identical |  | 93 |
| 9911394423 | time plot | Displays data that change over time. Often, successive values are connected with lines to show trends more clearly. Sometimes a smooth curve is added to the plot to help show long-term patterns and trends. Displays data that change over time. |  | 94 |
| 9911394424 | se | standard deviation of residuals | 95 | |
| 9911394425 | r2 | overall measure of how successful the regression is in linearlly relating to y and x | 96 | |
| 9911394426 | influential point | a point when omitted will give very different results | 97 | |
| 9911394427 | census | When a survey has no sample but instead test or surveys the entire population | 98 | |
| 9911394428 | pilot | small trial run of a survey to see if questions are clear | 99 | |
| 9911394429 | convenience sample | Choosing a sample because it is convenient. failing to get a proper representation of the population because If you survey everyone on your soccer team who attends tonight's practice, you are surveying a convenience sample. |  | 100 |
| 9911394430 | response bias | Anything in a survey design that influences responses falls under the heading of response bias. One typical response bias arises from the wording of questions, which may suggest a favored response. Voters, for example, are more likely to express support of "the president" than support of the particular person holding that office at the moment. Anything that changes the response in a survey A police officer asking teenagers about drug use |  | 101 |
| 9911394431 | observational study | A study based on data in which no manipulation of factors has been employed. A study that observes characteristics of an existing population. usually a survey | 102 | |
| 9911394432 | retrospective study | What study examines whether a past association exists between an exposure of interest and development of a present condition? data are collected from the past by going back in time | 103 | |
| 9911394433 | prospective study | an observational study in which subjects are followed to observe future outcomes |  | 104 |
| 9911394434 | statistic factor | A multifactor model in which statistical methods are applied ot a set of historical returns to determine portfolios that best explain either historical return covariances or variances. | 105 | |
| 9911394435 | control group | In an experiment, the group that is not exposed to the treatment; contrasts with the experimental group and serves as a comparison for evaluating the effect of the treatment. |  | 106 |
| 9911394436 | blinding | The practice of concealing group assignment from study subjects, investigators, and/or those who assess subject outcomes, typically in the context of a randomized controlled trial. For ex, study subjects may receive capsules with identical appearance and taste; however, the treatment group receives the active drug, whereas the control group receives the placebo. | 107 | |
| 9911394437 | placebo effect | Experimental results caused by expectations alone; any effect on behavior caused by the administration of an inert substance or condition, which is assumed to be an active agent. |  | 108 |
| 9911394438 | trial | A performed experiment based upon the hypothesis you made. |  | 109 |
| 9911394439 | maximum | (n.) the greatest possible amount or degree in a data sample the largest value in a set of data | 110 |
AP World History- Chapters 23-25 Flashcards
| 8169419859 | What are the three motives for exploration? | search for basic resources and lands suitable fir the cultivation of cash crops establish new trade routes to Asian markets expand influence of Christianity | 0 | |
| 8169439555 | Why did Portugal originally start to explore? | to supplement meager resources of Portugal | 1 | |
| 8169453814 | Portugal discovered ______and ______ Islands which were developed into _____ plantations | Azores Madieras sugar | 2 | |
| 8169463225 | The silk roads became more dangerous since the fall of _____ | Mongol empires | 3 | |
| 8169474057 | ________ and _______ missionaries were sent to India, central Asia, and China | Franciscan Dominican | 4 | |
| 8169483725 | What was used on ships because they worked better with cross winds? | square sails triangular lateen sails | 5 | |
| 8169497338 | What is the knowledge of winds and the currents of the ocean known as "return though the sea"? | The Volta do Mar | 6 | |
| 8169509128 | Who promoted exploration of the west African coast after seizing the Strait of Gibraltar? | Prince Henry of Portugal | 7 | |
| 8169520933 | Who rounded the Cape of Good Hope and entered the Indian Ocean basin? | Bartolommeo Dias | 8 | |
| 8169528126 | Who reached India through the route of Dias? | Vasco de Gama | 9 | |
| 8169538324 | Christopher Columbus believed that the ______ route to Asia would be quicker | western | 10 | |
| 8169548215 | Christopher Columbus estimated Japan to be _______ miles west of the Canaries | 2,500 | 11 | |
| 8169557162 | Who underwrites Christopher's voyage when Portugal refuses? | Fernando and Isabel of Spain | 12 | |
| 8169566651 | Christopher Columbus discovers _____ and _____ | Bahamas Cuba | 13 | |
| 8169578749 | ______ finds the Pacific Ocean while searching for gold in ______ | Vasco de Balboa Panama | 14 | |
| 8169585885 | ________ uses Spanish support to circumnavigate the globe | Ferdinand Magellan | 15 | |
| 8169601784 | Magellan sails through the Strait of ______ at the southern tip of South America | Magellan | 16 | |
| 8169606123 | How was Magellan killed? | in local political dispute in Philippine Islands | 17 | |
| 8169618024 | _____ build Philippines | Spanish | 18 | |
| 8169623487 | _____ and _____ look for a NW passage to Asia | English Russians | 19 | |
| 8169631261 | _________ from Russia sails through the Bering Strait | Vitus Bering | 20 | |
| 8169641130 | ______ from England explores the west coast of North America | Sir Frances Drake | 21 | |
| 8169648885 | ______ from England explores southern Pacific | James Cook | 22 | |
| 8169659513 | ______ is the first to set up trading posts in order to _____ duties to pass safely | Portuguese charge | 23 | |
| 8169674869 | English concentrate on _____ trade in the rival between the English and Dutch | Indian | 24 | |
| 8169684586 | The Dutch concentrate on trade in _____, _____, and ______ in the rival between the English and Dutch | Cape Town Colombo southern Pacific | 25 | |
| 8179039261 | Were joint stock companies government supported? | yes | 26 | |
| 8179039262 | Joint stock companies and powered the right to engage _____, build post ,and even make ______ | trade war | 27 | |
| 8179039263 | Europe had little control and Asia except for these two countries? | Philippines Indonesia | 28 | |
| 8179039264 | The Spanish conqueror the Philippines and name it after ______ | King Phillip II | 29 | |
| 8179039265 | What becomes the major port city for the Philippines? | Manila | 30 | |
| 8179039266 | Dutch concentrate on _____ trade in Indonesia | spice | 31 | |
| 8179039267 | The Dutch establish ______ and leave the rest of Indonesia to the locals and uproot spice plants on _______ to monopolize | Batavia neighboring islands | 32 | |
| 8179039268 | Russians built _____ empire while Europeans built _____ empire | land maritime | 33 | |
| 8179039269 | Russians take over _______ | Mongol khanates | 34 | |
| 8179039270 | Who led the Siberian expansions for Russia? | Yermak | 35 | |
| 8179039271 | Who was exiled to Siberia by Russia? | criminals prisoners of war | 36 | |
| 8179160331 | What causes the Seven Years' War? | a fight for domination among commercial rivalries between empires at seas | 37 | |
| 8179160332 | What are the two sides in Europe during the 7 Years' War? | Britain, Prussia vs. France, Austria, Russia | 38 | |
| 8179160333 | What are the two sides in India during the 7 Years' War? | British vs. French | 39 | |
| 8179160334 | What are the two sides in the Caribbean during the 7 Years' War? | Spanish, French vs. British expansion | 40 | |
| 8179160335 | What are the two sides in North America during the 7 Years' War? | English vs. French (French and Indian War) | 41 | |
| 8179160336 | French power ousted from _____ and _____ after the 7 Years' War | India North American | 42 | |
| 8179160337 | Spain retains ____, but loses ______ to England after the 7 Years' War | Cuba Florida | 43 | |
| 8179160338 | _____ dominates world trade after the 7 Years' War | Britain | 44 | |
| 8179160339 | What was the Columbian exchange name for? | Christopher Columbus | 45 | |
| 8179160340 | What was the global diffusion of plants, crops, animals, human populations, and disease pathogens after explorations? | columbian exchange | 46 | |
| 8179160341 | The Columbian exchange permanently alters what two things? | human geography natural environment | 47 | |
| 8179160342 | The Columbian exchange links between previously _____ and very ____ regions | independent different | 48 | |
| 8179160343 | What knocks out 90% of the Aztec empire? | smallpox | 49 | |
| 8179160344 | Does the Columbian exchange increase population? | yes | 50 | |
| 8179160345 | The Columbian exchange introduces European ____ to Americas | animals (horses, cattle, pigs, chickens) | 51 | |
| 8179160346 | The Columbian exchange introduces American _____ to Europe, Asia, and Africa | food (maize, potatoes, beans) | 52 | |
| 8210906913 | Where did enslaved Africans go due to the Columbian Exchange? | South America North America Caribbean | 53 | |
| 8210925324 | Within transoceanic trade in the Atlantic Ocean basin, ______ goods were sent from Europe and _____ goods were exported from the Americas | manufactured raw | 54 | |
| 8210931782 | What dominated the Pacific Ocean trade? | Spanish galleons | 55 | |
| 8210963448 | What type animals of were hunted to extinction or near-extinction? | fur-bearing whales catfish other animals with industrial uses | 56 | |
| 8210970779 | __________ attacks the Roman Catholic Church | Martin Luther | 57 | |
| 8210980780 | What are preferential pardons for charitable donors? | indulgences | 58 | |
| 8210996793 | Martin Luther was excommunicated by _______ in 1521 | Pope Leo X | 59 | |
| 8211002839 | What did Martin Luther write? | 95 Theses | 60 | |
| 8211023424 | Martin Luther issued the closure of _______, translations of Bible into _____, and the end of _____ authority | monasteries common languages priestly | 61 | |
| 8211035815 | Who was interested in Martin Luther's new ideals? | German princes | 62 | |
| 8211046141 | In England, ______ has a conflict with the pope over requested divorce | Henry VIII | 63 | |
| 8211060316 | In France, _____ codifies Protestant teachings while in exile in Genava | John Calvin | 64 | |
| 8232075996 | How does the Catholic church reform? | refine doctrine missionary activities to Protestants attempt to renew spiritual activity | 65 | |
| 8232075997 | What is the name of the council that met to discuss the reform of the Catholic church? | Council of Trent | 66 | |
| 8232075998 | Who founded the Society of Jesus? | St. Ignatius | 67 | |
| 8232075999 | The Society of Jesus was based on rigorous relics and classical ______ | education | 68 | |
| 8232076000 | Did the Society of Jesus have effective missionaries? | yes | 69 | |
| 8232076001 | Witch hunts were common where there was tensions between _____ and _____ | Catholics Protestants | 70 | |
| 8232076002 | Who were the vast majority of those charged for witch craft? | single females | 71 | |
| 8232076003 | Width hunters were also blamed for _____ and _____ | crop failures miscarriages | 72 | |
| 8232076004 | ______ attacks England to force the return of Catholicism, but English destroy ______ by sending flaming unmanned ships into the fleet | Philip II of Spain Spanish ships | 73 | |
| 8258017014 | Within the 30 Years' War, the Holy Roman emperor attempts to force ______ to return to the Roman Catholic Church | Bohemians | 74 | |
| 8258024721 | Who is the principal background in the 30 Years' War? | Germany | 75 | |
| 8258039460 | Who tries to revive the Holy Roman Empire as a strong center of Europe? | Charles V | 76 | |
| 8258056268 | Who creates new fines and fees for royal services and confiscate3s monastic holdings in England? | Henry VIII | 77 | |
| 8258065111 | Who places new taxes on sales and salt trade in France? | Louis XI, Francis I | 78 | |
| 8258072732 | Who founded the Spanish Inquisition? | Fernando and Isabel | 79 | |
| 8258086048 | The original task of the Spanish Inquisition was to search for practitioners of ____ or _____ | Judaism Islam | 80 | |
| 8258098102 | What type of government does England develop? | constitutional monarchy | 81 | |
| 8258108323 | What type of government does the Netherlands develop? | republic | 82 | |
| 8258116497 | What countries establish absolute monarchies? | France Spain Prussia Russia Austria | 83 | |
| 8258126550 | The English Civil War begins with opposition to _____ | new taxes | 84 | |
| 8258147045 | ____ and _____ clash in the English Civil War. Who loses? | King Charles I parliamentary armies King Charles I | 85 | |
| 8258173854 | Who takes over England and restores the monarchy to create a dictatorship? | Puritans | 86 | |
| 8258202564 | Who takes the throne after King James II? | daughter Mary and husband William of Orange | 87 | |
| 8275582051 | Who controls the low countries? | King Philip II of Spain | 88 | |
| 8275594435 | King Philip II of Spain attempts to control _______ in Netherlands | Calvinists | 89 | |
| 8275605567 | The Netherlands declares independence based on a ______ system | representative parliamentary | 90 | |
| 8275614545 | What is the Theory of Divine Rights? | kings are lieutenants of god | 91 | |
| 8275628367 | Who designed French absolutism? | Cardinal Richelieu | 92 | |
| 8275641929 | Who came up with the phrase "The State- that's me"? | Louis XI | 93 | |
| 8275648398 | Where does Louis XI build his castle at? | Versailles | 94 | |
| 8275662582 | Who modernized Russia on western European model? | Peter I | 95 | |
| 8275684352 | Where does Peter I build the new capital of Russia at? | St. Petersburg | 96 | |
| 8275691302 | Who divides Russia into 50 administrative districts? | Catherine II | 97 | |
| 8275698016 | What ended the Thirty Years' War? | Treaty of Westphalia | 98 | |
| 8275708566 | Within the Treaty of Westphalia, European states had to be recognized as ______ and _____ | sovereign equal | 99 | |
| 8275719419 | What replaces bread as a staple of diet? | potato | 100 | |
| 8275724016 | Within capitalism, _____ offer goods and services on a free market | private parties | 101 | |
| 8275744893 | Within capitalism, ____ and ____ control prices | supply demand | 102 | |
| 8275754590 | Serfdom was abandoned in _______ | western Europe | 103 | |
| 8275761518 | ______ families replace extended families | nuclear | 104 | |
| 8275778238 | Who theorized that there's a motionless earth inside nine spheres | Claudius Ptolemy | 105 | |
| 8275789934 | Who developed the idea that the planets rotate around the sun? | Nicholas Copernicus | 106 | |
| 8279767011 | What two scientists reinforce the Copernican model? | Johannes Kepler and Galileo Galilei | 107 | |
| 8279767012 | Who advances the study of physics with the concept of universal gravitational force? | Issac Newton | 108 | |
| 8279767013 | The Enlightenment was the movement away from church doctrine in favor of ____ and _____ | rational thought scientific analysis | 109 | |
| 8279767014 | What two people discovered the natural laws of politics and government? | John Locke Baron de Montesquieu | 110 | |
| 8279767015 | John Locke and Baron de Montesquieu argues against divine right _______ and believed sovereignty should rest in the ______ | absolute monarchies people | 111 | |
| 8279832464 | Who were philosophes? | public intellectuals | 112 | |
| 8279832465 | Who was the center of enlightenment? | France philosophes | 113 | |
| 8279832466 | Who places bitter attacks on the Roman Catholic Church through letters and beloved in individual freedom? | Voltaire | 114 | |
| 8279832467 | What is the belief in the existence of a god, but denied the divine teachings of Christianity and believed that God does not intervene in world affairs? | Deism | 115 | |
| 8279832468 | Columbus uses _______ as a base for trading and recruits locals to mine gold | Hispaniola | 116 | |
| 8280016619 | The Encomienda system gave Spanish encomenderos the right to force ____ to work in mines | Taino | 117 | |
| 8280016620 | What causes a new interest in exploiting the Caribbean for sugarcane production? | limited gold | 118 | |
| 8280016621 | Who brings down the Aztec Empire? | Hernán Cortès | 119 | |
| 8280016622 | What destroys Tenochtitlan? | smallpox | 120 | |
| 8280016623 | Who brings down the Inca Empire in Peru? | Franscisco Pizzaro | 121 | |
| 8280016624 | Where was Mexico City built? | atop Tenochtitlan | 122 | |
| 8280016625 | Who ruled the Spanish colonies? Who were they supervised by? | viceroys audiencias | 123 | |
| 8280016626 | What divides the entire Christian world between Spain and Portugal? Who claims Brazil? | Treaty of Tordesillas Portugal | 124 | |
| 8280016627 | What are the permanent colonies of France in North America? England? Netherlands? | Quebec Jamestown, Massachusetts Bay Colony New Amsterdam | 125 | |
| 8280016628 | What countries had greater levels of self- government in the North American colonies compared to France and England? | Spain Portuguese | 126 | |
| 8280016629 | Were North American people loosely organized? | yes | 127 | |
| 8280016630 | Was there conflict between colonists and indigenous people? | yes | 128 | |
| 8280016631 | Were European migrants primarily men or women? | men | 129 | |
| 8280016632 | What are descendants of Spaniards and African slaves called? | mulattoes | 130 | |
| 8280016633 | What are descendants of African slaves and natives called? | zambos | 131 | |
| 8280016634 | In the North American colonies, there was a _____ hierarchy | race-based | 132 | |
| 8280016635 | Who was at the top of the social hierarchy in the North American colonies? | peninsulares | 133 | |
| 8280158630 | Who was in the middle of the social hierarchy in the North American colonies? | criollos mestizos mulattoes zambos other combinations of parentage | 134 | |
| 8280158631 | Who was at the bottom of the social hierarchy in the North American colonies? | slaves conquered people | 135 | |
| 8296777686 | Were there more women in the French and English colonies? | yes | 136 | |
| 8296777687 | Did the English colonies experience inter marriages? | not really | 137 | |
| 8296777688 | What are the children from French fur traders who have relations with North American native women? | métis | 138 | |
| 8296777689 | Within the Spanish empire, there was a hunt for ______ and _____ | gold silver | 139 | |
| 8296777690 | Within the mita system, _____ of the males of each village most work for four months | 1/7 | 140 | |
| 8296777691 | What was a major resource of income for the Spanish crown? | silver | 141 | |
| 8296777692 | Who takes silver into the Pacific Rim for trading? | Manila Galleons | 142 | |
| 8296777693 | What are large estates that produce products of European origin? | haciendas | 143 | |
| 8296777694 | What labor system did the haciendas use? | encomienda system | 144 | |
| 8296777695 | What is the name of all productions related to sugar? | Enhenho | 145 | |
| 8296777696 | Portuguese rely on imported ______ slaves | African | 146 | |
| 8296777697 | What products were developed for European markets? | tobacco rice indigo cotton | 147 | |
| 8296777698 | ______ increase demand for imported labor | cash crops | 148 | |
| 8296777699 | Where did workers in North America or finally come from? | Europe | 149 | |
| 8296777700 | Slavery was less prominent in the north due to lack of _____ | cash crops | 150 | |
| 8296777701 | The middle colonies built _____ | slave ships | 151 | |
| 8296777702 | Northern merchants traded in ____ | slaves | 152 | |
| 8296841239 | What type of missionaries were in the Americas? | Franciscan Dominican Jesuit | 153 | |
| 8296841240 | The Virgin of Guadalupe was a _____ symbol of Christianity and a Mexican symbol of ______ | mestizo nationalism | 154 | |
| 8296841241 | Were French and English missions as effective as Spanish missions? | no | 155 | |
| 8296841242 | Who lands on Botany Bay and decides it is suitable for settlement? | Capitan Cook | 156 |
AP Human Geography Agriculture Flashcards
| 9551917766 | Agribusiness | System of food production involving everything from the development of the seeds to the marketing and sale of food products at the market. | 0 | |
| 9551917767 | Cash Crops | Planting large amounts of profitable crops for mass production and sell. | 1 | |
| 9551917768 | Commercial Agriculture | Agriculture undertaken primarily to generate products for sale off the farm. | 2 | |
| 9551917769 | GMOs | Foods that\have their genes altered in a laboratory for specific purposes, such as disease resistant, increased productivity, or nutrients value | 3 | |
| 9551917770 | Intensive Subsistence Farming | A form of subsistence agriculture in which farmers must expend a relatively large amount of effort to produce the maximum feasible yield from a parcel of land. | 4 | |
| 9551917771 | Monoculture | Dependence on a single agricultural commodity. | 5 | |
| 9551917772 | Mechanization | In agriculture, the replacement of human labor with technology or machines. | 6 | |
| 9551917773 | Primary Economy | Any economic activity pertaining to the collecting, harvesting, and obtaining of raw materials. | 7 | |
| 9551917774 | Plantation Agriculture | Raising a large amount of a 'cash crop' for local sale or export. | 8 | |
| 9551917775 | Transhumance | Movement of animal herd to cooler highland areas in the summer to warmer lowland areas in the winter. | 9 | |
| 9551917776 | Von Thunen Model | Theory that a commercial farmer wull decide which crops to grow and which livestock to raise depending on the proximity to market. |  | 10 |
| 9551917777 | Green Revolution | An outgrowth of the 3rd agricultural revolution, this effort began in the 1940s and developed new strains of hybrid seeds and fertilizers that dramatically increased the crop output possible from each farm. | 11 | |
| 9551917781 | Nomadism | Dry Areas Same climate as livestock ranching(commercial farms in MDCs) Marginalized land | 12 | |
| 9551917782 | Mixed livestock and grain | Raise domesticated animals and growing feed | 13 | |
| 9551917783 | Commercial Grain Farming | Wheat belt Bread-basket US Corn belt | 14 | |
| 9551917784 | Mediterranean Agriculture | An agricultural system practiced in the Mediterranean-style climates of Western Europe, California, and portions of Chile and Australia, in which diverse specialty crops such as grapes, avocados, | 15 | |
| 9551917785 | Agrarian | relating to land; relating to the management or farming of land | 16 | |
| 9551917786 | Agricultural Industrialization | The use of machinery in agriculture, like tractors etc. - makes it easier for farmers to have higher crop yields. | 17 | |
| 9551917787 | Agricultural Landscape | The land that we farm on and what we choose to put were on our fields. | 18 | |
| 9551917788 | Agricultural Location Model | An attempt to explain the pattern of agricultural land use in terms of accessibility, costs, distance, and prices. | 19 | |
| 9551917789 | Cultivation Regions | Regions were there is agricultural activity. Know these specifically! (ie. Southwestern US is cattle ranching, Mediterranean is crop trees). | 20 | |
| 9551917790 | Dairy Farms | specialized in dairy products, N. America, Europe, NOT Africa, South America, Asia | 21 | |
| 9551917791 | Desertification | Degradation of land, especially in semiarid areas, primarily because of human actions like excessive crop planting, animal grazing, and tree cutting. | 22 | |
| 9551917792 | Extensive Commercial Agriculture | A crop or livestock system in which land quality or extent is more important than capital or labor inputs in determining output | 23 | |
| 9551917793 | Feedlot | a plot of land on which livestock are fattened for market | 24 | |
| 9551917794 | Food Desert | An area in a developed country where healthy food is difficult to obtain | 25 | |
| 9551917795 | Food Manufacturing | The processes that are used to convert raw materials into finished food products | 26 | |
| 9551917796 | Hunting and Gathering | the killing of wild animals and fish as well as the gathering of fruits, roots, nuts, and other plants for sustenance | 27 | |
| 9551917797 | Intensive Commercial Agriculture | Intensive farming in a commercial economy, crops have high yields and market value | 28 | |
| 9551917798 | Livestock Ranching | an extensive commercial agricultural activity that involves the raising of livestock over vast geographic spaces typically located in semi-arid climates like the American West | 29 | |
| 9551917799 | Long-Lot Survey System | A distinct regional approach to land surveying whereby land is divided into narrow parcels stretching back from rivers, roads, or canals | 30 | |
| 9551917800 | Luxury Crops | Non-subsistence crops such as tea, cacao, coffee, and tobacco | 31 | |
| 9551917802 | Pastoralism | A type of agricultural activity based on nomadic animal husbandry or the raising of livestock to provide food, clothing, and shelter. | 32 | |
| 9551917803 | Organic Agriculture | Approach to farming and ranching that avoids the use of herbicides, pesticides, growth hormones, and other similar synthetic inputs. | 33 | |
| 9551917804 | Pesticides | Chemicals used on plants that do not harm the plants, but kill pests and have negative repercussions on other species who ingest the chemicals. | 34 | |
| 9551917805 | Plant Domestication | genetic modification of a plant such that its reproductive success depends on human intervention | 35 | |
| 9551917810 | Carl Sauer | Defined the concept of cultural landscape as the fundamental unit of geographical analysis. | 36 | |
| 9551917811 | 2nd Agriculture Revolution | Innovations led to agricultural surpluses, food surpluses, let people move from farms to factories, growth of cities increased. | 37 | |
| 9551917813 | Seed Crops | crop that is reproduced by cultivating the seeds of the plants. crop that is reproduced by cultivating the seeds of the plants. | 38 | |
| 9551917815 | Slash and Burn Agriculture | a farming technique in which trees are cut down and burned to clear and fertilize the land | 39 | |
| 9551917818 | Third Agriculture Revolution | 'green revolution' rapid diffusion of new ag techniques between 1970's and 1980's, especially new high-yield seeds and fertilizers | 40 | |
| 9551917819 | Soil Erosion | the wearing away and removal of rock and soil particles from exposed surfaces by agents such as moving water, wind, or ice | 41 |
AP Unit 3.Thermochemistry Flashcards
| 5264027383 | Energy | the ability to do work | 0 | |
| 5264028071 | Potential energy | The energy stored in chemical bonds | 1 | |
| 5264030310 | Kinetic energy | energy of motion, proportional to Kelvin temperature |  | 2 |
| 5264034942 | Law of conservation of energy | energy is neither created nor destroyed in a chemical change, but is simply changed from one form to another | 3 | |
| 5264037187 | First law of thermodynamics | the energy of the universe is constant | 4 | |
| 5264037690 | Heat (q) | an exchange of thermal energy when two systems are at different temperatures | 5 | |
| 5264039333 | Temperature | A measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in a sample of matter. |  | 6 |
| 5264040353 | Enthalpy (ΔH) | change in energy of a system. Variable = H | 7 | |
| 5264042816 | Enthalpy of a reaction (ΔHrxn) | The quantity of energy released or absorbed as heat during a chemical reaction at constant pressure | 8 | |
| 5264043953 | Enthalpy of combustion (ΔHcomb) | enthalpy change for the complete burning of one mole of a substance | 9 | |
| 5264044604 | Enthalpy of formation (ΔHf) | enthalpy change when one mole of a compound is formed from its elements in their standard states | 10 | |
| 5264045980 | Enthalpy of fusion (ΔHfus) | change in enthalpy resulting from heating one mole of a substance to change its state from a solid to a liquid. | 11 | |
| 5264049943 | Enthalpy of vaporization (ΔHvap) | The enthalpy change that occurs when one mole of a pure liquid is vaporised at its boiling point | 12 | |
| 5264050443 | System | area of the universe we are focusing on (ie. the experiment) | 13 | |
| 5264051127 | Surroundings | anything and everything outside the system | 14 | |
| 5264051557 | Endothermic | +∆H (energy flows in, energy is a reactant) | 15 | |
| 5264053445 | Exothermic | -∆H (energy flows out, energy is a product) | 16 | |
| 5264054456 | Entropy (S) | measure of the disorder (dispersal) or matter in a system | 17 | |
| 5264055629 | Gibbs Free energy | amount of energy available to do work, determines if a reaction is thermodynamically favored | 18 | |
| 5264058536 | Thermodynamics | the study of energy and its interconversions | 19 | |
| 5264059763 | Work | w = PΔV | 20 | |
| 5264060186 | Standard conditions | 1 atm, 298 K | 21 |
AP Psych Unit 9 Flashcards
| 12291925290 | Develpmental Psychology | a branch of psychology that studies physical, cognitive, and social change throughout the life span | 0 | |
| 12292006410 | Zygote | the fertilized egg; it enters a 2-week period of rapid cell division and develops into an embryo | 1 | |
| 12292014659 | embryo | the developing human organism from about 2 weeks after fertilization through the second month | 2 | |
| 12292017963 | fetus | the developing human organism from 9 weeks after conception to birth | 3 | |
| 12292020549 | teratogens | agents, such as chemicals and viruses, that can reach the embryo or fetus during prenatal development and cause harm | 4 | |
| 12292030143 | fetal alcohol syndrome | physical and cognitive abnormalities in children caused by a pregnant woman's heavy drinking | 5 | |
| 12292181982 | habituation | decreasing responsiveness with repeated stimulation. As infants gain familiarity with repeated exposure to a visual stimulus, their interest wanes and they look away sooner. | 6 | |
| 12292193563 | Maturation | biological growth processes that enable orderly changes in behavior, relatively uninfluenced by experience | 7 | |
| 6545439509 | Cognition | All the mental activities associated with thinking, knowing, remembering, and communicating | 8 | |
| 6545442101 | Schema | A concept or framework that organizes and interprets information | 9 | |
| 6545445215 | Assimilation | Interpreting our new experiences in terms of our existing schema | 10 | |
| 6545450611 | Accommodation | Adapting our current understandings (schemas) to incorporate new information | 11 | |
| 6545452929 | Sensorimotor Stage | In Piaget's theory, the stage (from birth to about 2 years of age) during which infants know the world mostly in terms of their sensory impressions and motor activities | 12 | |
| 6545470270 | Object Permanence | The awareness that things continue to exist even when not perceived | 13 | |
| 6545472223 | Preoperational stage | In Piaget's theory, the stage (from 2 to about 6 or 7 years of age) during which a child learns to use language but does not yet comprehend the mental operations of concrete logic | 14 | |
| 6545478093 | Conservation | The principle (which Piaget believed to be a part of concrete operational reasoning) that properties such as mass, volume, and number remain the same despite changes in the forms of objects | 15 | |
| 6545492904 | Egocentrism | In Piaget's theory, the preoperational child's difficulty taking another's point of view | 16 | |
| 6545494934 | Theory of mind | People's ideas about their own and others' mental states-about their feelings, perceptions, and thoughts, and the behaviors these might predict | 17 | |
| 6545498523 | Concrete Operational stage | In Piaget's theory, the stage of cognnitive development (from about 6 or 7 to 11 years of age) during which children gain the mental operations that enable them to think logically about concrete events | 18 | |
| 6545505622 | Formal Operational Stage | In Piaget's theory, the stage of cognitive development (normally beginning about age 12) during which people begin to think logically about abstract concepts | 19 | |
| 6545507877 | Autism | A disorder that appears in childhood and is marked by deficient communication, social interaction, and understanding of others' states of mind | 20 | |
| 6545522744 | stranger anxiety | The fear of strangers that infants commonly display, beginning by about 8 months of age | 21 | |
| 6545525004 | attachment | An emotional tie with another person; shown in young children by their seeking closeness to the caregiver and showing distress on separation | 22 | |
| 6545527394 | critical period | An optimal period shortly after birth when an organism's exposure to certain stimuli or experiences produces proper development | 23 | |
| 6545530861 | imprinting | the process by which certain animals form attachments during a critical period very early in life | 24 | |
| 6545532508 | temperament | A person's characteristic emotional reactivity and intensity | 25 | |
| 6545535121 | basic trust | According to Erik Erikson, a sense that the world is predictable and trustworthy; said to be formed during infancy by appropriate experiences with responsive caregivers | 26 | |
| 8560505477 | gender | in psychology, the biologically and socially influenced characteristics by which people define male and female | 27 | |
| 8560510089 | aggression | physical or verbal behavior intended to hurt someone | 28 | |
| 8560516687 | x-chromosom | the sex chromosome found in both men and women. | 29 | |
| 8560518987 | y chromosome | the sex chromosome found only in males. When paired with an X chromosome from the mother, it produces a male child. | 30 | |
| 8560522638 | testosterone | The most important of the male sex hormones. Both males and females have it | 31 | |
| 8560525889 | role | a set of expectations (norms) about a social position, defining how those in the position ought to behave | 32 | |
| 8560529945 | gender role | a set of expected behaviors for males or for female | 33 | |
| 8560535473 | gender identity | our sense of being male or female | 34 | |
| 8560539609 | gender typing | the acquisition of a traditional masculine or feminine role | 35 | |
| 8560542182 | social learning theory | the theory that we learn social behavior by observing and imitating and by being rewarded or punished | 36 | |
| 6545543412 | adolescence | the transition period from childhood to adulthood, extending from puberty to independence | 37 | |
| 6545548089 | puberty | the period of sexual maturation, during which a person becomes capable of reproducing | 38 | |
| 6545551643 | primary sex characteristics | the body structures (ovaries, testes, and external genitalia) that make sexual reproduction possible {E}the first menstrual period | 39 | |
| 6545553991 | secondary sex characteristics | nonreproductive sexual characteristics, such as female breasts and hips, male voice quality, and body hair | 40 | |
| 6545561343 | menarche | the first menstrual period | 41 | |
| 6545563845 | preconventional morality | morality focuses on self-interest: They obey rules either to avoid punishment or to gain concrete rewards | 42 | |
| 6545571357 | conventional morality | Morality focuses on caring for others and on upholding laws and social rules, simply because they are the laws and rules | 43 | |
| 6545574845 | postconventional morality | Actions are judged "right" because they flow from people's rights or from self-defined, basic ethical principles | 44 | |
| 6545637404 | identity | our sense of self; according to Erikson, the adolescent's task is to solidify a sense of self by testing and integrating various roles. | 45 | |
| 6545649903 | social identity | the "we" aspect of our self-concept; the part of our answer to "Who am I?" that comes from our group memberships | 46 | |
| 6545652520 | intimacy | In Erikson's theory, the ability to form close, loving relationships; a primary developmental tasks in late adolescence and early adulthood | 47 | |
| 6545655852 | emerging adulthood | for some people in modern cultures, a period from the late teens to mid-twenties, bridging the gap between adolescent dependence and full independence and responsible adulthood. | 48 | |
| 6545658280 | trust vs. mistrust | If needs are dependably met, they develop a sense of basic trust | 49 | |
| 6545667507 | autonomy vs shame and doubt | learn to exercise their will and do things for themselves, or they doubt their abilities | 50 | |
| 6545671559 | integrity vs despair | Reflecting on his or her life, an older adult may feel a sense of satisfaction or failure | 51 | |
| 6545677730 | identity vs. role confusion | work at refining a sense of self by testing roles and then integrating them to form a single identity, or they become confused about who they are | 52 | |
| 6545680516 | initiative vs guilt | learn to initiate tasks and carry out plans, or they feel guilty about their efforts to be independent | 53 | |
| 6545683882 | generativity vs stagnation | people discover a sense of contributing to the world, usually through family and work, or they may feel a lack of purpose | 54 | |
| 6545687015 | industry vs inferiority | learn the pleasure of applying themselves to tasks, or they feel inferior | 55 | |
| 6545689701 | intimacy vs isolation | struggle to form close relationships and to gain the capacity for intimate love, or they feel socially isolated | 56 | |
| 8587725125 | menopause | The time of natural cessation of menstruation; also refers to the biological changes a woman experiences as her ability to reproduce declines | 57 | |
| 8587727172 | cross-sectional study | A study in which people of different ages are compared with one another. | 58 | |
| 8587731062 | longitudinal stud | research in which the same people are restudied and retested over a long period | 59 | |
| 8587732647 | crystallized intelligence | Our accumulated knowledge and verbal skills; tends to increase with age | 60 | |
| 8587734591 | fluid intelligence | Our ability to reason speedily and abstractly; tends to decrease during late adulthood | 61 | |
| 8587737280 | social clock | the culturally preferred timing of social events such as marriage, parenthood, and retirement | 62 | |
| 8587745353 | Erik Erikson | Contended that each stage of life has its own psychosocial task, a task that needs resolution. | 63 | |
| 8587749621 | Mary Ainsworth | Performed a study on attachment and infants. Found that sensitive mothers and fathers tend to have securely attached infants. | 64 | |
| 8587754347 | Lev Vygotsky | Studied how child's mind grows, but looked more at the growth due to interactions with the social environment rather than the physical environment. | 65 | |
| 8587756369 | Jean Piaget | Proposed that children progress through four stages of cognitive development, each with distinctive characteristics that permit specific kinds of thinking. | 66 | |
| 8587760873 | Lawrence Kohlberg | Sought to describe the development of moral reasoning, the thinking that occurs as we consider right and wrong. | 67 | |
| 8587765039 | Carol Gilligan | Studied gender differences. Believed females tend to differ from males both in being less concerned with viewing themselves as separate individuals and in being more concerned with "making connections" | 68 | |
| 8587792093 | G. Stanely Hall | One of the first psychologists to describe adolescence, believed that this tension between biological maturity and social dependence creates a period of "storm and stress" | 69 | |
| 8587795929 | Harry Harlow | He raised monkeys with two artificial mothers. He found that the infants much preferred contact with the comfortable cloth mother. | 70 |
AP French Vocabulary Beauty Flashcards
| 6634372167 | la beauté | the beauty | 0 | |
| 6634372168 | le beau | the concept of beauty | 1 | |
| 6634372169 | l'idéal de la beauté | the ideals of beauty | 2 | |
| 6634372170 | les canons de la beauté | the standards of beauty | 3 | |
| 6634372171 | un critère | the criteria of beauty | 4 | |
| 6634372172 | un idéal | an ideal | 5 | |
| 6634372173 | l'art | the art | 6 | |
| 6634372174 | les beaux-arts | the architecture, painting, sculpting, engravings | 7 | |
| 6634372175 | les arts visuels | the visual art | 8 | |
| 6634372176 | les arts plastiques | the sculpture, painting, textiles, design | 9 | |
| 6634372177 | un(e) artiste | an artist | 10 | |
| 6634372178 | un objet d'art | a piece of art | 11 | |
| 6634372179 | un œuvre d'art | a work of art | 12 | |
| 6634372180 | une peinture | a painting | 13 | |
| 6634372181 | peindre | to paint | 14 | |
| 6634372182 | un peintre | a painter | 15 | |
| 6634372183 | un dessin | a drawing | 16 | |
| 6634372184 | dessiner | to draw | 17 | |
| 6634372185 | le style | the style | 18 | |
| 6634372186 | le genre | the genre | 19 | |
| 6634372187 | la littérature | the literature | 20 | |
| 6634372188 | la poésie | the poetry | 21 | |
| 6634372189 | un poète | a poet | 22 | |
| 6634372190 | un écrivain (e) | a writer | 23 | |
| 6634372191 | un(e) auteur | an author | 24 | |
| 6634372192 | le théâtre | the theater | 25 | |
| 6634372193 | un spectacle | a show | 26 | |
| 6634372194 | la musique | the music | 27 | |
| 6634372195 | une chanson | a song | 28 | |
| 6634372196 | un chanteur (une chanteuse) | a singer | 29 | |
| 6634372197 | le cinéma | the movies | 30 | |
| 6634372198 | un film | a movie | 31 | |
| 6634372199 | le goût | the taste | 32 | |
| 6634372200 | admirer | to admire | 33 | |
| 6634372201 | apprécier | to appreciate | 34 | |
| 6634372202 | juger | to judge | 35 | |
| 6634372203 | percevoir | to perceive | 36 | |
| 6634372204 | agréable à voir | nice to look at | 37 | |
| 6634372205 | agréable à entendre | nice to listen to | 38 | |
| 6634372206 | désagréable | unpleasant | 39 | |
| 6634372207 | un réalisateur | director (m) | 40 | |
| 6634372208 | une réalisation | production | 41 | |
| 6634372209 | une intrigue | plot | 42 | |
| 6634372210 | les personnages principaux | main characters | 43 | |
| 6634372211 | un personnage principal | main character | 44 | |
| 6634372212 | se dérouler | to happen / take place | 45 | |
| 6634372213 | un rappel / un flashback | flashback | 46 | |
| 6634372214 | complet / complète | complete / full | 47 | |
| 6634372215 | un débutant | beginner | 48 | |
| 6634372216 | un spectacle | show / spectacle | 49 | |
| 6634372217 | un spectateur | watcher / audience member | 50 | |
| 6634372218 | une exposition (d'art) | exhibit | 51 | |
| 6634372219 | une peinture, un tableau, une toile | painting | 52 | |
| 6634372220 | la danse | dance | 53 | |
| 6634372221 | le ballet | ballet | 54 | |
| 6634372222 | un danseur / une danseuse | dancer / ballerina | 55 | |
| 6634372223 | une sculpture | sculpture | 56 | |
| 6634372224 | un sculpteur | sculptor (male or female) | 57 | |
| 6634372225 | un groupe | (musical) group | 58 | |
| 6669984115 | l'estime de soi | confidence | 59 | |
| 6669984116 | avoir honte | to be ashamed | 60 | |
| 6669987624 | paraître | to seem | 61 | |
| 6669993594 | être bien dans sa peau | To feel good about yourself |  | 62 |
APES Chemistry Review Flashcards
| 7282693331 | Energy | The capacity to do work or transfer heat | 0 | |
| 7282697294 | Physical change | An event which may alter the appearance but not the chemical composition of a sample of matter | 1 | |
| 7283347324 | Proton | Positive particle within an atom | 2 | |
| 7283348591 | Element | Fundamental substance that can't be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means | 3 | |
| 7283349825 | Scientific law | A well-tested pattern observed in data | 4 | |
| 7283351404 | Hypothesis | A testable explanation for observations in nature | 5 | |
| 7283352916 | Scientific theory | A well-tested & widely accepted scientific hypothesis | 6 | |
| 7283357668 | Chemical change | An event which alters the arrangement of atoms or ions within molecules of the substances involved | 7 | |
| 7283360503 | Electromagnetic radiation | A form of kinetic energy that travels in waves, for example X-rays or ultraviolet waves | 8 | |
| 7283365203 | First law of thermodynamics | The law that states energy input must equal energy output | 9 | |
| 7283366702 | Organic compounds | The group of compounds which contain at least 2 carbon atoms combined with other elements (often H & O) | 10 | |
| 7283370419 | Amino acids | The monomer of proteins | 11 | |
| 7283372128 | Mass number | The number of protons & neutrons in the nucleus of an atom | 12 | |
| 7283375412 | pH | The measure of hydrogen ions contained in a particular solution | 13 | |
| 7283376747 | Nucleotides | The monomer for nucleic acids | 14 | |
| 7283379709 | Second law of thermodynamics | The law stating that when energy is changed from one form to another, it is always changed to a less useful or lower-quality form of energy | 15 | |
| 7283381532 | Atomic number | The number of protons in an atom | 16 | |
| 7283383086 | Carbohydrates | The polymer made of simple sugars such as glucose | 17 | |
| 7283386006 | Coal | An example of high-quality energy | 18 | |
| 7283387761 | Heat stored in the Atlantic Ocean | An example of low-quality energy | 19 | |
| 7283387762 | Energy efficiency | The measure of how much useful work is actually produced from a given unit of energy | 20 | |
| 7283389941 | Isotope | The variations of an element which have the same atomic number but different mass numbers | 21 | |
| 7283394206 | Ion | A charged atom or group of atoms | 22 | |
| 7283396811 | Electron | Negative particle of an atom | 23 | |
| 7283405286 | Fission | The nuclear change in which large, unstable atoms split into lighter nuclei | 24 | |
| 7283408406 | Law of conservation of matter | The law which explains why all waste products must be dealt with in nature | 25 | |
| 7283409542 | Fusion | A change in which 2 small nuclei are forced together at very high temperatures, form a heavier nucleus | 26 | |
| 7313172213 | Positive feedback loop | Causes a system to change further in the same direction. | 27 | |
| 7313172936 | Negative feedback loop | Causes a system to change in the opposite direction from which it is moving | 28 | |
| 7283434075 | Nitrate ion |  | 29 | |
| 7283435897 | Sulfate ion |  | 30 | |
| 7283437177 | Phosphate ion |  | 31 | |
| 7283438883 | Ammonium ion |  | 32 | |
| 7283441009 | Methane |  | 33 | |
| 7283444883 | Ammonia |  | 34 | |
| 7283450305 | Sulfur dioxide |  | 35 |
AP world history period review Flashcards
| 9785218620 | Period 1 8000- c. 600 BCE | technological & environmental transformation. nomadic lifestyle- hunting gathering, pastoralist - followed animals , Agricultureal Revolution (AR) to sedentary life- Farmers, resaltent b/c the preserve of food - surplus, class structures, political structures, specialization of jobs. domestication of plants & animals early River-valley civilizations Egypt, Nubia, Mesopotamia, Indus valley, - expanded trade - unifying force (laws-- code, language, religion--vedic). | 0 | |
| 9785218621 | Period 3 c. 600 CE - c. 1450 CE | Vikings | 1 | |
| 9785218622 | period 4 c. 1450 C.E. - c. 1750 C.E | rise of eourpe - crusades, plauge - Renaissance - sailing thecnology advancement - scientific revolution - enlightenment motivation - acess to trade - econimics - Columbia exchange - labor - servents, slavery, - silver - ottomans | 2 | |
| 9785218623 | period 5 c. 1750 CE - c. 1900 CE | 3 | ||
| 9785218624 | Period 6 c. 1900 CE - Present Day | 4 | ||
| 9801711852 | Period 2. c. 600 BCE - c. 600 CE | emergence and spread of religion (codified - stabilized or more defined) | 5 |
Pages
Need Help?
We hope your visit has been a productive one. If you're having any problems, or would like to give some feedback, we'd love to hear from you.
For general help, questions, and suggestions, try our dedicated support forums.
If you need to contact the Course-Notes.Org web experience team, please use our contact form.
Need Notes?
While we strive to provide the most comprehensive notes for as many high school textbooks as possible, there are certainly going to be some that we miss. Drop us a note and let us know which textbooks you need. Be sure to include which edition of the textbook you are using! If we see enough demand, we'll do whatever we can to get those notes up on the site for you!

