APES Review Flashcards
| 13682448429 | altitude | distance above a particular point | 0 | |
| 13682448430 | arid | extremely dry | 1 | |
| 13682450787 | asthenosphere | the upper layer of the earth's mantle, below the lithosphere, in which there is relatively low resistance to plastic flow and convection is thought to occur |  | 2 |
| 13682450788 | atmospheric pressure | the pressure exerted by atoms and molecules in the atmosphere surrounding Earth, resulting from collisions of these particles with objects | 3 | |
| 13682454837 | clay | the finest soil, made up of particles that are less than 0.002 mm in diameter | 4 | |
| 13746536821 | climate | the weather conditions prevailing in an area in general or over a long period | 5 | |
| 13746540402 | cold front | forms when cold air moves under warm air which is less dense and pushes air up (produces thunderstorms heavy rain or snow |  | 6 |
| 13746543510 | condensation | the change of state from a gas to a liquid | 7 | |
| 13746546560 | convection current | a current caused by the rising of heated fluid and sinking of cooled fluid |  | 8 |
| 13746552370 | convection cells | large wind patterns in Earth's atmosphere caused by convection | 9 | |
| 13746554611 | convergent plate boundary | an area where plates move toward one another and collide |  | 10 |
| 13746557395 | core | the central part of the earth below the mantle |  | 11 |
| 13746562261 | Coriolis effect | the effect of Earth's rotation on the direction of winds and currents. |  | 12 |
| 13746593884 | crust | the thin and solid outermost layer of the Earth above the mantle |  | 13 |
| 13746603522 | density | the degree of compactness of a substance | 14 | |
| 13746607951 | divergent plate boundary | boundary between tectonic plates in which the two plates move away from each other, and new crust is created between them |  | 15 |
| 13746611703 | earthquake | a sudden and violent shaking of the ground, sometimes causing great destruction, as a result of movements within the earth's crust or volcanic action |  | 16 |
| 13746619573 | elevation | the height of land above sea level | 17 | |
| 13746638421 | erosion | the process by which wind, water, ice, or gravity transports soil and sediment from one location to another | 18 | |
| 13746647734 | evaporation | the change of a substance from a liquid to a gas | 19 | |
| 13746650637 | front | a boundary between two air masses |  | 20 |
| 13746657631 | greenhouse effect | warming that results when solar radiation is trapped by the atmosphere |  | 21 |
| 13746661740 | greenhouse gases | gases such as carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, water vapor, and ozone in the atmosphere which are involved in the greenhouse effect | 22 | |
| 13746664866 | groundwater | water that fills the cracks and spaces in underground soil and rock layers | 23 | |
| 13746666690 | gully erosion | removal of layers of soil, creating channels or ravines too large to be removed by normal tillage operations | 24 | |
| 13746670115 | hot spots | places where molten material from the mantle reaches the lithosphere |  | 25 |
| 13746676383 | humus | material formed from decaying leaves and other organic matter | 26 | |
| 13746676384 | hydrosphere | all the water at and near the surface of the earth, 97% of which is in oceans | 27 | |
| 13746681451 | igneous rock | a type of rock that forms from the cooling of molten rock at or below the surface | 28 | |
| 13746681452 | infiltration | flow of water from the land surface into the subsurface | 29 | |
| 13746688023 | inorganic compounds | compounds that do not contain carbon | 30 | |
| 13746688024 | jet stream | a high-speed high-altitude airstream blowing from west to east near the top of the troposphere | 31 | |
| 13746690472 | latitude | distance north or south of the Equator, measured in degrees | 32 | |
| 13746693615 | leaching | the transportation of dissolved molecules through the soil via groundwater | 33 | |
| 13746696590 | lithosphere | the rigid outer part of the earth, consisting of the crust and upper mantle |  | 34 |
| 13746698709 | loams | soils containing a mixture of clay, sand, silt, and humus; good for growing most crops | 35 | |
| 13746704805 | mantle | the layer of hot, solid material between Earth's crust and core |  | 36 |
| 13746710284 | metamorphic rock | a type of rock that forms from an existing rock that is changed by heat, pressure, or chemical reactions | 37 | |
| 13746714631 | micronutrients | vitamins and minerals | 38 | |
| 13746717860 | mineral resource | all discovered and undiscovered deposits of a useful mineral that can be extracted now or at some time in the future | 39 | |
| 13746720160 | monsoons | seasonal wind patterns that cause wet and dry seasons | 40 | |
| 13746724235 | natural recharge | process in which aquifers are replenished naturally by precipitation that percolates downward through soil and rock | 41 | |
| 13746728130 | organic compounds | carbon-based molecules | 42 | |
| 13746730380 | ozone layer | a layer in the stratosphere (at approximately 20 miles) that contains a concentration of ozone sufficient to block most ultraviolet radiation from the sun |  | 43 |
| 13746735487 | parent material | the rock material from which the inorganic components of a soil are derived | 44 | |
| 13746735488 | permeability | ability of rock or soil to allow water to flow through it | 45 | |
| 13746741035 | porosity | the volume of open spaces in rock or soil | 46 | |
| 13746744362 | precipitation | any form of water that falls from clouds and reaches Earth's surface | 47 | |
| 13746754054 | rain shadow effect | low precipitation on the far side (leeward side) of a mountain when prevailing winds flow up and over a high mountain or range of high mountains, creates semiarid and arid conditions on the leeward side of a high mountain range |  | 48 |
| 13746758447 | rift | a split, break, breach |  | 49 |
| 13746764025 | rill | a tiny groove in soil made by flowing water | 50 | |
| 13746767398 | ring of fire | a major belt of volcanoes that rims the Pacific Ocean |  | 51 |
| 13746772876 | runoff | water that flows over the ground surface rather than soaking into the ground | 52 | |
| 13746772877 | sand | the coarsest soil, with particles 0.05,2.0 mm in diameter. | 53 | |
| 13746775812 | sedimentary rock | a type of rock that forms when particles from other rocks or the remains of plants and animals are pressed and cemented together | 54 | |
| 13746779566 | sheet | a type of erosion in which surface water or wind peels off thin layers of soil | 55 | |
| 13746799481 | silt | a mixture of rich soil and tiny rocks | 56 | |
| 13746806713 | soil erosion | wearing away of surface soil by water and wind | 57 | |
| 13746806714 | soil horizons | horizontal layers that reveal a soil's history, characteristics, and usefulness |  | 58 |
| 13746811947 | soil permeability | rate at which water and air move from upper to lower soil layers | 59 | |
| 13746811948 | soil porosity | a measure of the volume of pores or spaces per volume of soil and the average distances between those spaces | 60 | |
| 13746814474 | soil profile | a vertical section through a soil showing its succession of horizons and the underlying parent material | 61 | |
| 13746819126 | soil structure | how the particles that make up a soil are organized and clumped together | 62 | |
| 13746822294 | soil texture | the soil quality that is based on the proportions of soil particles | 63 | |
| 13746822295 | stratosphere | the second-lowest layer of Earth's atmosphere |  | 64 |
| 13746832215 | subduction | the process by which oceanic crust sinks beneath a deep-ocean trench and back into the mantle at a convergent plate boundary |  | 65 |
| 13746838165 | surface runoff | water that flows over land until it reaches lakes, rivers, or other areas | 66 | |
| 13746838166 | surface water | water that collects on the surface of the ground | 67 | |
| 13746844980 | tectonic plates | sections of the Earth's crust that move due to convection currents |  | 68 |
| 13746854030 | temperature inversion | atmospheric condition in which warm air traps cooler air near the earth's surface |  | 69 |
| 13746859610 | terrestrial | relating to the land | 70 | |
| 13746859611 | thermal inversion | A situation in which a relatively warm layer of air at mid-altitude covers a layer of cold, dense air below | 71 | |
| 13746865861 | trade winds | prevailing winds that blow northeast from 30 degrees north latitude to the equator and that blow southeast from 30 degrees south latitude to the equator |  | 72 |
| 13746869792 | transform fault | area where the earth's lithospheric plates move in opposite but parallel directions along a fracture (fault) in the lithosphere |  | 73 |
| 13746874617 | transpiration | evaporation of water from the leaves of a plant | 74 | |
| 13746877117 | troposphere | the lowest layer of Earth's atmosphere |  | 75 |
| 13746883120 | upwelling | the movement of deep, cold, and nutrient-rich water to the surface |  | 76 |
| 13746885891 | warm front | a front where warm air moves over cold air and brings drizzly rain and then are followed by warm and clear weather |  | 77 |
| 13746888367 | water cycle | the continuous process by which water moves from Earth's surface to the atmosphere and back |  | 78 |
| 13746891783 | waterlogging | saturation of soil with irrigation water or excessive precipitation so that the water table rises close to the surface | 79 | |
| 13746896491 | water table | the upper level of the saturated zone of groundwater | 80 | |
| 13746903410 | watershed | the land area that supplies water to a river system |  | 81 |
| 13746907664 | weather | the condition of Earth's atmosphere at a particular time and place. | 82 | |
| 13746910476 | weathering | the chemical and physical processes that break down rock at Earth's surface | 83 | |
| 13746914079 | zone of aeration | the upper zone which usually isn't completely filled with water, but with rocks and soil too | 84 | |
| 13746925681 | zone of illuviation | movement of dissolved material from higher soil layers to lower with the downward movement of water | 85 | |
| 13746938462 | zone of saturation | the lower zone where water accumulates between small rock particles | 86 | |
| 13748793241 | abiotic | non-living things | 87 | |
| 13748795854 | adaptation | inherited characteristic that increases an organism's chance of survival | 88 | |
| 13748798264 | aerobic respiration | respiration that requires oxygen | 89 | |
| 13748801180 | ammonification | the formation of ammonia compounds in the soil by the action of bacteria on decaying matter | 90 | |
| 13748803208 | assimilation | the process of incorporating a nutrient into an organism's cells | 91 | |
| 13748811699 | autotroph | an organism that is able to form nutritional organic substances from simple inorganic substances such as carbon dioxide | 92 | |
| 13748822135 | background extinction | extinction caused by slow and steady process of natural selection | 93 | |
| 13748825066 | bacteria | single-celled organisms that lack a nucleus; prokaryotes | 94 | |
| 13748827648 | benthos | organisms that live attached to or near the ocean floor | 95 | |
| 13748831503 | biodiversity | the variety of life in the world or in a particular habitat or ecosystem | 96 | |
| 13748834364 | biogeochemical cycle | process in which elements, chemical compounds, and other forms of matter are passed from one organism to another and from one part of the biosphere to another | 97 | |
| 13748836574 | biological diversity | the presence of many different types of organisms in an ecosystem | 98 | |
| 13748836575 | biome | group of ecosystems that have the same climate and dominant communities | 99 | |
| 13748840484 | biosphere | part of Earth in which life exists including land, water, and air or atmosphere | 100 | |
| 13748843087 | biotic | living things | 101 | |
| 13748844925 | deciduous plants | plants that lose all of their leaves for part of the year | 102 | |
| 13748848103 | carbon cycle | the movement of carbon from the nonliving environment into living things and back | 103 | |
| 13748911451 | carbon sink | a forest, ocean, or other natural environment viewed in terms of its ability to absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere | 104 | |
| 13748915920 | carnivore | organism that obtains energy by eating animals | 105 | |
| 13748918379 | climax community | a stable community that no longer goes through major ecological changes | 106 | |
| 13748921480 | coastal wetland | coastal land areas covered with water all or part of the year | 107 | |
| 13748921481 | commensalism | an association between two organisms in which one benefits and the other derives neither benefit nor harm | 108 | |
| 13748925867 | community | all the different populations that live together in an area | 109 | |
| 13748928674 | competitive exclusion | strong competition can lead to local elimination of one of the species | 110 | |
| 13748932840 | coniferous trees | trees that produce their seeds in cones and have leaves shaped like needles | 111 | |
| 13748932842 | coral reef | a structure of calcite skeletons built up by coral animals in warm, shallow ocean water | 112 | |
| 13748936299 | decomposer | organism that breaks down and obtains energy from dead organic matter | 113 | |
| 13748942841 | denitrification | process by which bacteria convert nitrates into nitrogen gas | 114 | |
| 13748947295 | detritivore | organism that feeds on plant and animal remains and other dead matter | 115 | |
| 13748962353 | detritus | dead organic matter | 116 | |
| 13748965104 | detritus feeder | organism that extracts nutrients from fragments of dead organisms and their cast-off parts and organic wastes; examples are earthworms, termites, and crabs | 117 | |
| 13748970375 | diffusion | movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. | 118 | |
| 13748973760 | ecological diversity | the variety of terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems found in an area or on the earth | 119 | |
| 13748984895 | ecological niche | the sum of a species' use of the biotic and abiotic resources in its environment | 120 | |
| 13748984896 | ecology | scientific study of interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment | 121 | |
| 13748986814 | ecosystem | a biological community of interacting organisms and their physical environment | 122 | |
| 13748991321 | endangered species | a species whose numbers are so small that the species is at risk of extinction | 123 | |
| 13748994409 | endemic species | species that are native to and found only within a limited area | 124 | |
| 13748997406 | energy productivity | a measure of how much useful work is accomplished by a particular input of energy into a system | 125 | |
| 13748999962 | estuary | a habitat in which the freshwater of a river meets the salt water of the ocean. | 126 | |
| 13749004615 | evolution | change in a kind of organism over time; process by which modern organisms have descended from ancient organisms | 127 | |
| 13749007455 | extinction | a term that typically describes a species that no longer has any known living individuals | 128 | |
| 13749013197 | fundamental niche | the niche species could potentially occupy | 129 | |
| 13769337304 | first law of thermodynamics | energy cannot be created or destroyed | 130 | |
| 13769337305 | food chain | series of steps in an ecosystem in which organisms transfer energy by eating and being eaten | 131 | |
| 13769341037 | food web | a system of interlocking and interdependent food chains | 132 | |
| 13769344856 | freshwater life zones | aquatic systems where water with a dissolved salt concentration of less than 1% by volume accumulates on or flows through the surfaces of terrestrial biomes; examples are standing (lentic) bodies of fresh water such as lakes, ponds, and inland wetlands and flowing (lotic) systems such as streams and rivers | 133 | |
| 13769621832 | generalist species | species with a broad ecological niche; they can live in many different places, eat a variety of foods, and tolerate a wide range of environmental conditions; examples are flies, cockroaches, mice, rats, and human beings | 134 | |
| 13769648052 | genetic diversity | the range of genetic material present in a gene pool or population of a species | 135 | |
| 13769652128 | geographic isolation | form of reproductive isolation in which two populations are separated physically by geographic barriers such as rivers, mountains, or stretches of water | 136 | |
| 13769661059 | gross primary productivity | the total amount of solar energy that producers in an ecosystem capture via photosynthesis over a given amount of time | 137 | |
| 13769667222 | habitat | the natural home or environment of an animal, plant, or other organism | 138 | |
| 13769675099 | herbivore | organism that obtains energy by eating only plants | 139 | |
| 13769678638 | heterotroph | an organism that cannot make its own food | 140 | |
| 13769682325 | host | an organism on which a parasite lives | 141 | |
| 13769684444 | hydrologic cycle | the movement of water through the biosphere |  | 142 |
| 13769690703 | indicator species | species that serve as early warnings that an ecosystem is being damaged | 143 | |
| 13769693747 | interspecific competition | competition between members of different species | 144 | |
| 13769696727 | intraspecific competition | competition between members of the same species | 145 | |
| 13769699668 | keystone species | a species that influences the survival of many other species in an ecosystem | 146 | |
| 13769704537 | kilocalorie | a unit of energy equal to 1,000 calories | 147 | |
| 13769710464 | law of conservation of energy | the law that states that energy cannot be created or destroyed but can be changed from one form to another | 148 | |
| 13769712724 | law of conservation of matter | matter is neither created nor destroyed in any chemical or physical change | 149 | |
| 13769716005 | limiting factor | any biotic or abiotic factor that restricts the existence, numbers, reproduction, or distribution of organisms | 150 | |
| 13769729755 | mass extinction | event in which many types of living things become extinct at the same time | 151 | |
| 13769775811 | mutualism | a relationship between two species in which both species benefit | 152 | |
| 13769775812 | natural selection | a process in which individuals that have certain inherited traits tend to survive and reproduce at higher rates than other individuals because of those traits | 153 | |
| 13769778689 | net energy | total amount of useful energy available from an energy resource or energy system over its lifetime, minus the amount of energy used (the first energy law), automatically wasted (the second energy law), and unnecessarily wasted in finding, processing, concentrating, and transporting it to users | 154 | |
| 13769784895 | net primary productivity | the energy captured by producers in an ecosystem minus the energy producers respire | 155 | |
| 13769789310 | niche | an organism's particular role in an ecosystem, or how it makes its living | 156 | |
| 13769793781 | nitrogen cycle | the transfer of nitrogen from the atmosphere to the soil, to living organisms, and back to the atmosphere |  | 157 |
| 13769810060 | nitrogen fixation | process of converting nitrogen gas into ammonia | 158 | |
| 13769814427 | nitrification | ammonia is converted to nitrate ions (NO3-) | 159 | |
| 13769814428 | omnivore | a consumer that eats both plants and animals | 160 | |
| 13769822569 | parasitism | a relationship between two organisms of different species where one benefits and the other is harmed | 161 | |
| 13769822570 | phosphorus cycle | the movement of phosphorus atoms from rocks through the biosphere and hydrosphere and back to rocks |  | 162 |
| 13769909705 | photosynthesis | conversion of light energy from the sun into chemical energy | 163 | |
| 13769912879 | phytoplankton | photosynthetic algae found near the surface of the ocean | 164 | |
| 13769912880 | plankton | tiny organisms that float in the water | 165 | |
| 13769916914 | pioneer species | the first species to populate an area | 166 | |
| 13769931633 | population | group of individuals of the same species that live in the same area | 167 | |
| 13769935511 | predation | an interaction in which one organism kills another for food. | 168 | |
| 13769943610 | primary consumer | an organism that eats producers | 169 | |
| 13769943611 | primary pollutant | a pollutant that is put directly into the atmosphere by human or natural activity | 170 | |
| 13769947788 | primary productivity | the rate at which energy is converted by photosynthetic and chemosynthetic autotrophs to organic substances | 171 | |
| 13769950629 | primary succession | succession that occurs on surfaces where no soil exists | 172 | |
| 13769953196 | producer | an organism that makes its own food | 173 | |
| 13769957106 | pyramid of energy flow | diagram representing the flow of energy through each trophic level in a food chain or food web; with each energy transfer, only a small part (typically 10%) of the usable energy entering one trophic level is transferred to the organisms at the next trophic level | 174 | |
| 13769966815 | range of tolerance | the limits to the abiotic conditions that a species can tolerate | 175 | |
| 13769977574 | realized niche | the range of abiotic and biotic conditions under which a species actually lives | 176 | |
| 13769981345 | reproductive isolation | separation of species or populations so that they cannot interbreed and produce fertile offspring | 177 | |
| 13769981401 | respiration | the process by which cells break down simple food molecules to release the energy they contain | 178 | |
| 13769987471 | resource partitioning | the differentiation of niches that enables similar species to coexist in a community | 179 | |
| 13769993179 | riparian zones | lush vegetation along streams or rivers | 180 | |
| 13769993180 | scavenger | a carnivore that feeds on the bodies of dead organisms | 181 | |
| 13770000709 | second law of energy | energy cannot be changed from one form to another without a loss of usable energy | 182 | |
| 13770004886 | second law of thermodynamics | when energy is changed from one form to another, some useful energy is always degraded into lower quality energy (usually heat) | 183 | |
| 13770009278 | secondary consumer | an organism that eats primary consumers | 184 | |
| 13770012827 | secondary succession | succession following a disturbance that destroys a community without destroying the soil | 185 | |
| 13770020197 | specialist species | species with a narrow ecological niche; they may be able to live in only one type of habitat, tolerate only a narrow range of climatic and other environmental conditions, or use only one type or a few types of food | 186 | |
| 13770025544 | speciation | the formation of new and distinct species in the course of evolution | 187 | |
| 13770029438 | species | a group of living organisms consisting of similar individuals capable of exchanging genes or interbreeding | 188 | |
| 13770034207 | species evenness | the relative proportion of different species in a given area | 189 | |
| 13770034208 | species diversity | variety of different kinds of organisms that make up a community | 190 | |
| 13770041647 | species richness | the number of different species in a community | 191 | |
| 13770047895 | sulfur cycle | the movement of sulfur around the biosphere |  | 192 |
| 13770662415 | sulfur dioxide | a colorless, corrosive gas directly damaging to both plants and animals | 193 | |
| 13770666919 | sulfuric acid | H2SO4 (Strong Acid) | 194 | |
| 13770671980 | tertiary consumers | carnivores that eat secondary consumers | 195 | |
| 13770681609 | theory of evolution | states that organisms change and develop over time to adapt an increase rate of survival | 196 | |
| 13770681610 | trophic level | step in a food chain or food web | 197 | |
| 13770685602 | age structure | number of males and females of each age in a population | 198 | |
| 13807622462 | agricultural revolution | a time when new inventions such as the seed drill and the steel plow made farming easier and faster; the production of food rose dramatically | 199 | |
| 13807626448 | baby bust | a temporary marked decrease in the birth rate | 200 | |
| 13807629796 | baby boom | the larger than expected generation in United States born shortly after World War II | 201 | |
| 13807632256 | biotic potential | the maximum rate at which a population could increase under ideal conditions | 202 | |
| 13807635098 | birth rate | the number of births in a population in a certain amount of time | 203 | |
| 13807635099 | carrying capacity | largest number of individuals of a population that an ecosystem can support | 204 | |
| 13807639247 | competitors | organisms that have the same food source and live in the same habitat | 205 | |
| 13807644991 | cost-benefit analysis | a study that compares the costs and benefits to society of providing a public good | 206 | |
| 13807644992 | crude birth rate | the number of live births yearly per thousand people in a population | 207 | |
| 13807648189 | crude death rate | the number of deaths per year per 1,000 people | 208 | |
| 13807651099 | death rate | the number of deaths in a population in a certain amount of time | 209 | |
| 13807658314 | debt-for-nature swap | forgiveness of international debt in exchange for nature protection in developing countries | 210 | |
| 13807662125 | demographic transition | change in a population from high birth and death rates to low birth and death rates |  | 211 |
| 13807662126 | demography | the scientific study of population characteristics | 212 | |
| 13807668207 | density dependent factors | limiting factor that depends on population size | 213 | |
| 13807670036 | density independent factors | limiting factor that affects all populations in similar ways, regardless of population size | 214 | |
| 13807682587 | developed country | a modern, industrialized country in which people are generally better educated and healthier and live longer than people in developing countries do | 215 | |
| 13807685622 | developing country | a country that has low industrial production and little modern technology | 216 | |
| 13807689539 | doubling time | the time required for a population to double in size | 217 | |
| 13807693100 | ecological footprint | the impact of a person or community on the environment, expressed as the amount of land required to sustain their use of natural resources | 218 | |
| 13807695715 | economy | the wealth and resources of a country or region, especially in terms of the production and consumption of goods and services | 219 | |
| 13807695716 | emigration | movement of individuals out of an area | 220 | |
| 13807698054 | environmental degradation | damage to or destruction of the natural environment | 221 | |
| 13807701015 | environmental ethics | the application of ethical standards to relationships between humans and their environment | 222 | |
| 13807705111 | environmental resistance | all the limiting factors that act together to limit the growth of a population | 223 | |
| 13807709575 | environmentally sustainable economic development | using political and economic systems to discourage environmentally harmful and unsustainable forms of economic growth that degrade natural capital, and to encourage environmentally beneficial and sustainable forms of economic development that help sustain natural capital | 224 | |
| 13807713318 | exponential growth | growth whose rate becomes ever more rapid in proportion to the growing total number or size |  | 225 |
| 13807713319 | external cost | an uncompensated cost that an individual or firm imposes on others | 226 | |
| 13807717863 | family planning | the practice of regulating the number or spacing of offspring through the use of birth control | 227 | |
| 13807720461 | famine | a severe shortage of food (as through crop failure) resulting in violent hunger and starvation and death | 228 | |
| 13807722635 | fertility | a measure of how well soil supports plant growth | 229 | |
| 13807726717 | globalization | growth to a global or worldwide scale | 230 | |
| 13807731287 | green revolution | rapid diffusion of new agricultural technology, especially new high-yield seeds and fertilizers | 231 | |
| 13807737091 | gross domestic product | the total value of goods produced and services provided in a country during one year | 232 | |
| 13807739621 | immigration | movement of individuals into a population | 233 | |
| 13807742717 | industrial | of, relating, or characterized by industry | 234 | |
| 13807742718 | infant mortality rate | the percentage of children who die before their first birthday within a particular area or country | 235 | |
| 13807749076 | K-strategists | species where organisms tend to reproduce later in life, have a smaller number of offspring, and are long living | 236 | |
| 13807752152 | J-curve | a growth curve that depicts exponential growth |  | 237 |
| 13807756057 | land degradation | occurs when natural or human-induced processes decrease the future ability of land to support crops, livestock, or wild species | 238 | |
| 13807761323 | land-use planning | determining in advance how land will be used | 239 | |
| 13807764941 | less developed country | a country that is at a relatively early stage in the process of economic development | 240 | |
| 13807802506 | life expectancy | the average number of years an individual can be expected to live, given current social, economic, and medical conditions; life expectancy at birth is the average number of years a newborn infant can expect to live. | 241 | |
| 13807806263 | linear growth | expansion that increases by the same amount during each time interval |  | 242 |
| 13807814276 | logistic growth | growth pattern in which a population's growth rate slows or stops following a period of exponential growt |  | 243 |
| 13807817548 | malnutrition | lack of proper nutrition | 244 | |
| 13807819841 | mass transit | public transportation systems that carry large numbers of people | 245 | |
| 13807819842 | more developed countries | countries with greater overall wealth; these countries tend to be more industrialized, bringing in money from manufacturing more goods | 246 | |
| 13807827803 | natural capital | natural resources and natural services that keep us and other species alive and support our economies | 247 | |
| 13807831202 | opportunist | an organism that exists as part of the normal flora but may become pathogenic under certain conditions | 248 | |
| 13807837651 | overnutrition | excess energy or nutrients | 249 | |
| 13807843175 | overshoot | when a population becomes larger than the environment's carrying capacity | 250 | |
| 13807843176 | per capita GDP | Gross Domestic Product per person | 251 | |
| 13807846884 | population density | a measurement of the number of people per given unit of land | 252 | |
| 13807853067 | population dispersion | way in which individuals of a population are spread out over an area or volume | 253 | |
| 13807853068 | population distribution | a description of how individuals are distributed with respect to one another | 254 | |
| 13807855531 | population dynamics | the study of short‐ and long‐term changes in the number of individuals for a given population, as affected by birth, death, immigration, and emigration | 255 | |
| 13807859117 | population momentum | continued population growth that does not slow in response to growth reduction measures | 256 | |
| 13807863499 | population size | the number of individuals in a population | 257 | |
| 13807863500 | post-industrial | an economy with less emphasis on heavy industry and manufacturing and more emphasis on services and technology | 258 | |
| 13807869825 | post-reproductive age | those too old to reproduce | 259 | |
| 13807869826 | poverty | inability to meet basic needs for food, clothing, and shelter | 260 | |
| 13807875328 | pre-industrial | that period in development of a society when manufacturing industry has yet to develop | 261 | |
| 13807877703 | pre-reproductive age | not mature enough to reproduce | 262 | |
| 13807881103 | replacement-level fertility | the total fertility rate required to offset the average number of deaths in a population in order to maintain the current population size | 263 | |
| 13807883561 | r-strategists | a species that grow exponentially when environmental conditions allow them to reproduce | 264 | |
| 13807892784 | rule of 70 | doubling time (in years) = 70/(percentage growth rate). | 265 | |
| 13807898985 | S-curve | a curve that depicts logistic growth; shape of an "S;" the leveling off of a J-Curve exponential growth |  | 266 |
| 13807905950 | surplus | a situation in which quantity supplied is greater than quantity demanded | 267 | |
| 13807908943 | survivorship curve | graph showing the number of survivors in different age groups for a particular species | 268 | |
| 13807912766 | total fertility rate | the average number of children born to a woman during her childbearing years | 269 | |
| 13807915385 | transitional | population grows rapidly because birth rates are high and death rates drop because of improved food production and health | 270 | |
| 13807919174 | tragedy of the commons | situation in which people acting individually and in their own interest use up commonly available but limited resources, creating disaster for the entire community | 271 | |
| 13807919175 | undernutrition | the condition in which not enough calories are ingested to maintain health | 272 | |
| 13807922859 | urban area | an area that contains more than 385 people per square kilometer (1,000 people per square mile) | 273 | |
| 13807925954 | urban growth | the rate of increase of urban populations | 274 | |
| 13807929562 | urban sprawl | the process of urban areas expanding outwards, usually in the form of suburbs, and developing over fertile agricultural land | 275 | |
| 13807932021 | urbanization | an increase in the percentage and in the number of people living in urban settlements. | 276 |
AP Review Flashcards
| 13959974926 | isotope | different number of neutrons ex. carbon-12 and carbon-13 | 0 | |
| 13959974927 | ionic bond | atoms exchange electrons to create ions (charged molecule) | 1 | |
| 13959974928 | covalent bond | atoms share electrons | 2 | |
| 13959974929 | bicarbonate | H2CO3 = HCO3- + H+ carbonic acid = bicarbonate ion+hydrogen ion | 3 | |
| 13959974930 | isomers | molecules with same molecular formula but different structures | 4 | |
| 13959974931 | hydroxyl group |  | 5 | |
| 13960074147 | carbonyl group |  | 6 | |
| 13960074148 | carboxyl group |  | 7 | |
| 13960074149 | amino group |  | 8 | |
| 13960074150 | phosphate group |  | 9 | |
| 13960074151 | methyl group |  | 10 |
AP Psychology AP Review Flashcards
| 13918191216 | psychology | the study of behavior and mental processes | 0 | |
| 13918191217 | psychology's biggest question | Which is more important in determining behavior, nature or nurture? | 1 | |
| 13918191218 | psychology's three levels of analysis | biopsychosocial approach (looks at the biological, psychological, and social-cultural approaches together) | 2 | |
| 13918191219 | biological approach | genetics, close-relatives, body functions | 3 | |
| 13918191220 | evolutionary approach | species - helped with survival (ancestors) | 4 | |
| 13918191221 | psychodynamic approach | (Freud) subconscious, repressed feelings, unfulfilled wishes | 5 | |
| 13918191222 | behavioral approach | learning (classical and operant) observed | 6 | |
| 13918191223 | cognitive approach | thinking affects behavior | 7 | |
| 13918191224 | humanistic approach | becoming a better human (behavior, acceptance) | 8 | |
| 13918191225 | social-cultural approach | cultural, family, environment | 9 | |
| 13918191226 | two reasons of why experiments are important | hindsight bias + overconfidence | 10 | |
| 13918191227 | types of research methods | descriptive, correlational, and experimental | 11 | |
| 13918191228 | descriptive methods | case study survey naturalistic observation (DON'T SHOW CAUSE/EFFECT) | 12 | |
| 13918191229 | case study | studies one person in depth may not be typical of population | 13 | |
| 13918191230 | survey | studies lots of people not in depth | 14 | |
| 13918191231 | naturalistic observation | observe + write facts without interference | 15 | |
| 13918191232 | correlational method | shows relation, but not cause/effect scatterplots show research | 16 | |
| 13918191233 | correlation coefficient | + 1.0 (both increase) 0 (no correlation - 1.0 (one increases, other decreases) | 17 | |
| 13918191234 | experimental method | does show cause and effect | 18 | |
| 13918191235 | population | type of people who are going to be used in experiment | 19 | |
| 13918191236 | sample | actual people who will be used (randomness reduces bias) | 20 | |
| 13918191237 | random assignment | chance selection between experimental and control groups | 21 | |
| 13918191238 | control group | not receiving experimental treatment receives placebo | 22 | |
| 13918191239 | experimental group | receiving treatment/drug | 23 | |
| 13918191240 | independent variable | drug/procedure/treatment | 24 | |
| 13918191241 | dependent variable | outcome of using the drug/treatment | 25 | |
| 13918191242 | confounding variable | can affect dependent variable beyond experiment's control ex: genetics, age | 26 | |
| 13918191243 | scientific method | theory hypothesis operational definition revision | 27 | |
| 13918191244 | theory | general idea being tested | 28 | |
| 13918191245 | hypothesis | measurable/specific | 29 | |
| 13918191246 | operational definition | procedures that explain components survey to measure happiness - happiness is measured by what score they receive on survey | 30 | |
| 13918191247 | mode | appears the most | 31 | |
| 13918191248 | mean | average | 32 | |
| 13918191249 | median | middle | 33 | |
| 13918191250 | range | highest - lowest | 34 | |
| 13918191251 | standard deviation | how scores vary around the mean | 35 | |
| 13918191252 | central tendency | single score that represents the whole | 36 | |
| 13918191253 | bell curve | (natural curve) |  | 37 |
| 13918191254 | ethics of testing on animals | need to be treated humanly basically similar to humans | 38 | |
| 13918191255 | ethics of testing on humans | consent debriefing no unnecessary discomfort/pain confidentiality | 39 | |
| 13918191256 | sensory neurons | travel from sensory receptors to brain | 40 | |
| 13918191257 | motor neurons | travel from brain to "motor" workings -- muscles/glands | 41 | |
| 13918191258 | interneurons | (in brain and spinal cord) connecting motor and sensory neurons | 42 | |
| 13918191454 | neuron |  | 43 | |
| 13918191259 | dendrites | receive messages from other neurons | 44 | |
| 13918191260 | myelin sheath | protects the axon - insulates axon to increase speed of messages | 45 | |
| 13918191261 | axon | where charges travel from cell body to axon terminal | 46 | |
| 13918191262 | neurotransmitters | chemical messengers | 47 | |
| 13918191263 | reuptake | extra neurotransmitters are taken back | 48 | |
| 13918191264 | excitatory charge | "Let's do it!" | 49 | |
| 13918191265 | inhibitory charge | "Let's not do it!" | 50 | |
| 13918191266 | central nervous system | brain and spinal cord | 51 | |
| 13918191267 | peripheral nervous system | somatic nervous system autonomic nervous system | 52 | |
| 13918191268 | somatic nervous system | voluntary movements | 53 | |
| 13918191269 | autonomic nervous system | involuntary movements (sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems) | 54 | |
| 13918191270 | sympathetic nervous system | arousing | 55 | |
| 13918191271 | parasympathetic nervous system | calming | 56 | |
| 13918191272 | neural pathways | more connections form with greater use others fall away if not used | 57 | |
| 13918191273 | spinal cord | expressway of information bypasses brain when reflexes involved | 58 | |
| 13918191274 | endocrine system | slow uses hormones in the blood system | 59 | |
| 13918191275 | master gland | pituitary gland | 60 | |
| 13918191276 | brainstem | extension of the spinal cord responsible for automatic survival | 61 | |
| 13918191277 | reticular formation (if stimulated) | sleeping subject wakes up | 62 | |
| 13918191278 | reticular formation (if damaged) | coma | 63 | |
| 13918191279 | brainstem (if severed) | still move (without purpose) | 64 | |
| 13918191280 | thalamus | sensory switchboard (does not process smell) | 65 | |
| 13918191281 | hypothalamus | basic behaviors (hunger, thirst, sex, blood chemistry) | 66 | |
| 13918191282 | cerebellum | nonverbal memory, judge time, balance emotions, coordinate movements | 67 | |
| 13918191283 | cerebellum (if damaged) | difficulty walking and coordinating | 68 | |
| 13918191284 | amygdala | aggression, fear, and memory associated with these emotions | 69 | |
| 13918191285 | amygdala (if lesioned) | subject is mellow | 70 | |
| 13918191286 | amygdala (if stimulated) | aggressive | 71 | |
| 13918191287 | hippocampus | process new memory | 72 | |
| 13918191288 | cerebrum | two large hemispheres perceiving, thinking, and processing | 73 | |
| 13918191289 | cerebral cortex | only in higher life forms | 74 | |
| 13918191290 | association areas | integrate and interpret information | 75 | |
| 13918191291 | glial cells | provide nutrients to myelin sheath marks intelligence higher proportion of glial cells to neurons | 76 | |
| 13918191292 | frontal lobe | judgement, personality, processing (Phineas Gage accident) | 77 | |
| 13918191293 | parietal lobe | math and spatial reasoning | 78 | |
| 13918191294 | temporal lobe | audition and recognizing faces | 79 | |
| 13918191295 | occipital lobe | vision | 80 | |
| 13918191296 | corpus callosum | split in the brain to stop hyper-communication (eliminate epileptic seizures) | 81 | |
| 13918191297 | Wernicke's area | interprets auditory and hearing | 82 | |
| 13918191298 | Broca's area | speaking words | 83 | |
| 13918191299 | plasticity | ability to adapt if damaged | 84 | |
| 13918191300 | sensation | what our senses tell us | 85 | |
| 13918191301 | bottom-up processing | senses to brain | 86 | |
| 13918191302 | perception | what our brain tells us to do with that information | 87 | |
| 13918191303 | top-down processing | brain to senses | 88 | |
| 13918191304 | inattentional blindness | failure to notice "gorilla" because attention is elsewhere | 89 | |
| 13918191305 | cocktail party effect | even with tons of stimuli, we are able to pick out our name, etc. | 90 | |
| 13918191306 | change blindness | giving directions and person is changed and we don't notice | 91 | |
| 13918191307 | choice blindness | when defending the choice we make, we fail to notice choice was changed | 92 | |
| 13918191308 | absolute threshold | is the smallest level of stimulus that can be detected, usually defined as at least half the time | 93 | |
| 13918191309 | signal detection theory | we notice what is more important to us (rather hear a baby crying) | 94 | |
| 13918191310 | JND (just noticeable difference) | (Weber's law) difference between different stimuli noticed in proportion | 95 | |
| 13918191311 | sensory adaptation | tired of noticing (Brain says, "Been there, done that. Next?" | 96 | |
| 13918191312 | rods | more in periphery - less color detection; better for night vision | 97 | |
| 13918191313 | cones | color; fovea is only cones; not in periphery | 98 | |
| 13918191314 | parallel processing | notice color, form, depth, movement, etc. at same time | 99 | |
| 13918191315 | Young-Helmholtz trichromatic theory | 3 corresponding color receptors (RGB) | 100 | |
| 13918191316 | Hering's opponent-process theory | after image in opposite colors (RG, YB, WB) | 101 | |
| 13918191317 | trichromatic + opponent-process | Young-Helmholtz -> color stimuli Hering -> en route to cortex | 102 | |
| 13918191318 | frequency we hear most | human voice | 103 | |
| 13918191319 | Helmoltz (hearing) | we hear different pitches in different places in basilar membrane (high pitches) | 104 | |
| 13918191320 | frequency theory | impulse frequency (low pitches) | 105 | |
| 13918191321 | Helmholtz + frequency theory | middle pitches | 106 | |
| 13918191322 | Skin feels what? | warmth, cold, pressure, pain | 107 | |
| 13918191323 | gate-control theory | feel pain and if you put a lot of pressure you'll feel less pain | 108 | |
| 13918191324 | memory of pain | peaks and ends | 109 | |
| 13918191325 | smell | close to memory section (not in thalamus) | 110 | |
| 13918191326 | grouping | Gestalt make sense of pieces create a whole whole is the sum of its parts | 111 | |
| 13918191327 | grouping groups | proximity similarity continuity connectedness closure | 112 | |
| 13918191328 | make assumptions of placement | higher - farther smaller - farther blocking - closer, in front | 113 | |
| 13918191329 | perception = | mood + motivation | 114 | |
| 13918191330 | consciousness | awareness of ourselves and the environment | 115 | |
| 13918191331 | circadian rhythm | daily biological clock and regular cycle (sleep and awake) | 116 | |
| 13918191332 | circadian rhythm pattern | - activated by light - light sensitive retinal proteins signal brains SCN (suprachiasmatic nucleus) - pineal gland decreases melatonin | 117 | |
| 13918191333 | What messes with circadian rhythm? | artificial light | 118 | |
| 13918191334 | The whole sleep cycle lasts how long? | 90 minutes | 119 | |
| 13918191335 | sleep stages | relaxed stage (alpha waves) stage 1 (early sleep) (hallucinations) stage 2 (sleep spindles - bursts of activity) (sleep talk) stage 3 (transition phase) (delta waves) stage 4 (delta waves) (sleepwalk/talk + wet the bed) stage 5 (REM) (sensory-rich dreams) (paradoxical sleep) | 120 | |
| 13918191336 | purpose of sleep | 1. recuperation - repair neurons and allow unused neural connections to wither 2. making memories 3. body growth (children sleep more) | 121 | |
| 13918191337 | insomnia | can't sleep | 122 | |
| 13918191338 | narcolepsy | fall asleep anywhere at anytime | 123 | |
| 13918191339 | sleep apnea | stop breathing in sleep | 124 | |
| 13918191340 | night terrors | prevalent in children | 125 | |
| 13918191341 | sleepwalking/sleeptalking | hereditary - prevalent in children | 126 | |
| 13918191342 | dreaming (3) | 1. vivid bizarre intense sensory experiences 2. carry fear/survival issues - vestiges of ancestors' survival ideas 2. replay previous day's experiences/worries | 127 | |
| 13918191343 | purpose of dreaming (5 THEORIES) | 1. physiological function - develop/preserve neural pathways 2. Freud's wish-fulfillment (manifest/latent content) 3. activation synthesis - make sense of stimulation originating in brain 4. information processing 5. cognitive development - reflective of intelligence | 128 | |
| 13918191344 | 1. Can hypnosis bring you back in time? 2. Can hypnosis make you do things you wouldn't normally do? 3. Can it alleviate pain? 4. What state are you in during hypnosis? 5. Who is more susceptible? | 1. cannot take you back in time 2. cannot make you do things you won't do 3. can alleviate pain 4. fully conscious ((IMAGINATIVE PEOPLE MORE SUSCEPTIBLE)) | 129 | |
| 13918191345 | depressants | slows neural pathways | 130 | |
| 13918191346 | alcohol | ((depressant)) disrupts memory formation (REM) lowers inhibition expectancy effect | 131 | |
| 13918191347 | barbituates (tranquilizers) | ((depressant)) reduce anxiety | 132 | |
| 13918191348 | opiates | ((depressant)) pleasure reduce anxiety/pain | 133 | |
| 13918191349 | stimulants | hypes neural processing | 134 | |
| 13918191350 | methamphetamine | ((stimulant)) heightens energy euphoria affects dopamine | 135 | |
| 13918191351 | caffeine | ((stimulant)) | 136 | |
| 13918191352 | nicotine | ((stimulant)) CNS releases neurotransmitters calm anxiety reduce pain affects (nor)epinephrine and dopamine | 137 | |
| 13918191353 | cocaine | ((stimulant)) euphoria affects dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine | 138 | |
| 13918191354 | hallucinogen | excites neural activity | 139 | |
| 13918191355 | ecstasy | ((hallucinogen)) reuptake is blocked affects dopamine and serotonin | 140 | |
| 13918191356 | LSD | ((hallucinogen)) affects sensory/emotional "trip" (+/-) affects serotonin | 141 | |
| 13918191357 | marijuana | ((hallucinogen)) amplify sensory experience disrupts memory formation | 142 | |
| 13918191358 | learning | organism changing behavior due to experience (association of events) | 143 | |
| 13918191359 | types of learning | classical operant observational | 144 | |
| 13918191360 | famous classical psychologists | Pavlov and Watson | 145 | |
| 13918191361 | famous operant psychologist | Skinner | 146 | |
| 13918191362 | famous observational psychologists | Bandura | 147 | |
| 13918191363 | classical conditioning | outside stimulus | 148 | |
| 13918191364 | Pavlov's experiment | Step 1: US (food) -> UR (salivation) Step 2: NS (bell) -> US (food) -> UR (salivation) Later... CS (bell) -> CR (salivation) | 149 | |
| 13918191365 | Watson's experiment | white rat was given to Little Albert Step 1: US (noise) -> UR (cry) Step 2: NS (rat) -> US (noise) -> UR (cry) Later... CS (rat) -> CR (cry) | 150 | |
| 13918191366 | generalization | any small, white fluffy creature will make Albert cry now | 151 | |
| 13918191367 | discriminate | any large, white fluffy creature won't make Albert cry | 152 | |
| 13918191368 | extinction | stop "treating" with conditioned response | 153 | |
| 13918191369 | spontaneous recovery | bring stimulus back after a while | 154 | |
| 13918191370 | operant conditioning | control by organism | 155 | |
| 13918191371 | Skinner's experiment | operant chamber / Skinner box (lead to shaping) | 156 | |
| 13918191372 | shaping | get animal closer to doing what you want them to do | 157 | |
| 13918191373 | reinforcers | want to continue behavior (positive reinforcement: give money to do laundry) (negative reinforcement: do to avoid nagging) | 158 | |
| 13918191374 | punishments | want to stop behavior (positive reinforcement: smack) (negative reinforcement: take away phone) | 159 | |
| 13918191375 | fixed ratio | happens a certain number of times (Starbucks punch card) | 160 | |
| 13918191376 | variable ratio | happens an unpredictable number of times (winning the lottery) | 161 | |
| 13918191377 | organism must do these (2 times) | fixed ratio and variable ratio | 162 | |
| 13918191378 | fixed interval | happens at a certain time (mailman comes to the house at 10:00 AM) | 163 | |
| 13918191379 | variable interval | happens at any time (receive texts from friends) | 164 | |
| 13918191380 | these things happen regardless (2 times) | fixed interval and variable interval | 165 | |
| 13918191381 | Which (fixed/variable) conditions better? | variable | 166 | |
| 13918191382 | criticisms of Skinner | doesn't take into account intrinsic motivation | 167 | |
| 13918191383 | intrinsic motivation | doing something for yourself, not the reward | 168 | |
| 13918191384 | extrinsic motivation | doing something for reward | 169 | |
| 13918191385 | Skinner's legacy | use it personally, at school, and at work | 170 | |
| 13918191386 | famous observational experiment | Bandura's Bobo doll | 171 | |
| 13918191387 | famous observational psychologist | Bandura | 172 | |
| 13918191388 | mirror neurons | "feel" what is observed happens in higher order animals | 173 | |
| 13918191389 | Bobo doll experiment legacy | violent video games/movies desensitize us see good: do good see evil: do evil | 174 | |
| 13918191390 | observational learning | biological behaviors work best | 175 | |
| 13918191391 | habituation | get used to it -> stop reacting | 176 | |
| 13918191392 | examples for observational learning | lectures and reading | 177 | |
| 13918191393 | serotonin involved with memory | speeds the connection between neurons | 178 | |
| 13918191394 | LTP | ((long-term potentiation)) strengthens potential neural forming (associated with speed) | 179 | |
| 13918191395 | CREB | protein that can switch genes on/off with memory and connection of memories | 180 | |
| 13918191396 | glutamate involved with memory | neurotransmitter that enhances LTP | 181 | |
| 13918191397 | glucose involved with memory | released during strong emotions ((signaling important event to be remembered)) | 182 | |
| 13918191398 | flashbulb memory | type of memory remembered because it was an important/quick moment | 183 | |
| 13918191399 | amygdala (memory) | boosts activity of proteins in memory-forming areas to fight/flight | 184 | |
| 13918191400 | cerebellum (memory) | forms and stores implicit memories ((classical conditioning)) | 185 | |
| 13918191401 | hippocampus (memory) | active during sleep (forming memories) ((information "moves" after 48 hours)) | 186 | |
| 13918191402 | memory | learning over time contains information that can be retrieved | 187 | |
| 13918191403 | processing stages | encoding -> storage -> retrieval | 188 | |
| 13918191404 | encoding | information going in | 189 | |
| 13918191405 | storage | keeping information in | 190 | |
| 13918191406 | retrieval | taking information out | 191 | |
| 13918191407 | How long is sensory memory stored? | seconds | 192 | |
| 13918191408 | How long is short-term memory stored? | less than a minute | 193 | |
| 13918191409 | How many bits of information is stored in short-term memory? | 7 | 194 | |
| 13918191410 | How many chunks of information is stored in short-term memory? | 4 | 195 | |
| 13918191411 | How many seconds of words is stored in short-term memory? | 2 | 196 | |
| 13918191412 | short term memory goes to ______________ | working memory | 197 | |
| 13918191413 | working memory | make a connection and process information to mean something | 198 | |
| 13918191414 | working memory goes to _________________ | long-term memory | 199 | |
| 13918191415 | How much is stored in long-term memory? | LIMITLESS | 200 | |
| 13918191416 | implicit memory | naturally do | 201 | |
| 13918191417 | explicit memory | need to explain | 202 | |
| 13918191418 | automatic processing | space, time, frequency, well-learned information | 203 | |
| 13918191419 | effortful processing | processing that requires effort | 204 | |
| 13918191420 | spacing effect | spread out learning over time | 205 | |
| 13918191421 | serial position effect | primary/recency effect | 206 | |
| 13918191422 | primary effect | remember the first things in a list | 207 | |
| 13918191423 | recency effect | remember the last things in a list | 208 | |
| 13918191424 | effortful processing (4 things) | 1. recency effect 2. spacing effect 3. testing effect 4. serial position effect | 209 | |
| 13918191425 | semantic encoding (1) meaning (2) how to | make meaning out of something --- chunk, hierarchy, or connect to you | 210 | |
| 13918191426 | if we can't remember a memory... | 1. change memory to suit us 2. fill in the blanks with logical story | 211 | |
| 13918191427 | misinformation effect | not correct information | 212 | |
| 13918191428 | imagination inflation | imagine or visualize something that isn't real | 213 | |
| 13918191429 | source amnesia | what is the truth? (is it a dream, story, memory, etc.?) | 214 | |
| 13918191430 | priming | association (setting you up) | 215 | |
| 13918191431 | context | environment helps with memory | 216 | |
| 13918191432 | state-dependency | you may remember something if you go back to the state you were in (go back to high) | 217 | |
| 13918191433 | mood-congruency | emotion will bring back similar emotional memories | 218 | |
| 13918191434 | forgetting curve | forget after 5 days forget after 5 years | 219 | |
| 13918191435 | the forgetting curve was created by | Ebbinghaus | 220 | |
| 13918191436 | proactive interference | old information interferes with the new | 221 | |
| 13918191437 | retroactive interference | new information interferes with the old | 222 | |
| 13918191438 | children can't remember before age __ | 3 | 223 | |
| 13918191439 | Loftus | connected to abuse cases/childhood | 224 | |
| 13918191440 | prototypes | generalize | 225 | |
| 13918191441 | problem-solving (4) | trial + error algorithms heuristic (representative + availability) insight - "AHA!" | 226 | |
| 13918191442 | against problem-solving | fixation | 227 | |
| 13918191443 | mental set | what has worked in the past | 228 | |
| 13918191444 | functional fixedness | only way to do this is with this | 229 | |
| 13918191445 | Chomsky (nature or nurture?) | "born with language" (nature) | 230 | |
| 13918191446 | Skinner (nature or nurture?) | language is learned (nurture) | 231 | |
| 13918191447 | grammar is _________ | universal | 232 | |
| 13918191448 | phonemes | smallest sound unit | 233 | |
| 13918191449 | morphemes | smallest meaning unit | 234 |
AP Macro Section 6 Flashcards
| 9596328838 | cyclically adjusted budget balance | An estimate of what the budget ballence would really be if real GDP were exactly equal to potential output | 0 | |
| 9596328839 | Government Debt | Is the accumulations of past budget deficits, minus past budget surpluses | 1 | |
| 9596328840 | Fiscal year | Runs from October 1 to September 30 and is labeled according to the calendar year in which it ends | 2 | |
| 9596328841 | Public debt | Is government debt held by individuals and institutions outside the government | 3 | |
| 9596328842 | Debt GDP Ratio | Is the government's debt as a percentage of GDP | 4 | |
| 9596328843 | Implicit liabilities | Spending promises made by the government that are effectively a debt despite the fact that they are not included in the usual debt statistics. | 5 | |
| 9596328844 | Target Federal funds | A desired level for federal funds rates. The Fed will use open market operations to achieve that target. | 6 | |
| 9596328845 | Expansionary monetary policy | Is monetary policy that increases aggregate demand | 7 | |
| 9596328846 | Contractionary Monetary policy | Policy that reduces aggregate demand |  | 8 |
| 9596368730 | Taylor rule for monetary policy | a rule for setting the federal funds rate that takes in account both the inflation rate and the output gap. | 9 | |
| 9596328847 | Inflationary targeting | occurs when the central bank sets an explicit target for the inflation rate and sets monetary policy in order to hit that target | 10 | |
| 9596328848 | Monetary neutrality | changes in the money supply have no real effects on the economy | 11 | |
| 9596328849 | Classical model of the price level | according to this model the quantity of money is always at its long-run equilibrium level | 12 | |
| 9596328850 | Inflation tax | Is the reduction in the value of money held by the public caused by inflation | 13 | |
| 9596328851 | cost-push inflation | is inflation that is caused by a significant increase in the price of an input with an economy-wide importance | 14 | |
| 9596328852 | Demand pull inflation | Is inflation that is caused by an increase in aggregate demand | 15 | |
| 9596328853 | nonaccelerating inflation rate of unemployment (NAIRU) | the unployment rate at which inflation does not chnage over time. |  | 16 |
| 9596328854 | Long run Philips curve | shows the relationship between unemployment and inflation after expectations of inflation have had time to adjust to experience | 17 | |
| 9596328855 | Debt deflation | Is the reduction in aggregate demand arising from the increase in the real burden of outstanding debt caused by deflation | 18 | |
| 9596328856 | Zero bound | when the nominal interest rate cannot go below zero | 19 | |
| 9596328859 | Monetarism | asserts that GDP will grow steadily if the money supply grows steadily | 20 | |
| 9596328860 | discretionary monetary policy | is the use of changes in rate or money supply to stabilize the economy | 21 | |
| 9596328861 | Monetary policy rule | Is a formula that determines the central bank's actions. | 22 | |
| 9596328862 | Quantity theory of money | Emphasizes the positive relationship between the price level and the money supply M x V = P x Y | 23 | |
| 9596328863 | velocity of money | is the ratio of nominal GDP to the money supply. it is a measure of the average number of times the average dollar bill is spent per year. | 24 | |
| 9596328864 | Natural rate hypothesis | to avoid accelerating inflation over time, the unemployment rate must be high enough that actual inflation rate equals the expected rate of inflation | 25 | |
| 9596328865 | Political business cycle | results when politicians use macroeconomic policy to serve political ends | 26 | |
| 9596328866 | New classical macroeconomics | is an approach to the business cycle that returns to the classical view that shifts in the aggregate demand curve affect only the aggregate price level, not aggregate output | 27 | |
| 9596328867 | Rational expectations | is the view that individuals and firms make decisions optimally, using all available information | 28 | |
| 9596328868 | new Keynesian economics | market imperfections can lead to price stickiness for the economy as a whole | 29 | |
| 9596328869 | real businiess cycle theory | claims that fluctuations in the rate of growth of total factor productivity cause the business cycle | 30 |
Flashcards
AP Calculus AB Review* Flashcards
| 13755973600 | Limit Definition of Derivative | limit (as h approaches 0)= F(x+h)-F(x)/h ; means take derivative of f(x) |  | 0 |
| 13755973601 | Alternate Definition of Derivative | limit (as x approaches a number c)= f(x)-f(c)/x-c x≠c ; means take derivative of f(x) and plug in a |  | 1 |
| 13755973602 | limit as x approaches 0: sinx/x | 1 | 2 | |
| 13755973603 | limit as x approaches 0: 1-cosx/x | 0 | 3 | |
| 13755973604 | Continuity Rule | If the limit exists (aka left limit and right limit are equal), and the limit equals the function at that point. | 4 | |
| 13755973605 | Basic Derivative | f(x^n)= nX^(n-1) | 5 | |
| 13755973606 | d/dx(sinx) | cosx | 6 | |
| 13755973607 | d/dx(cosx) | -sinx | 7 | |
| 13755973608 | d/dx(tanx) | sec²x | 8 | |
| 13755973609 | d/dx(cotx) | -csc²x | 9 | |
| 13755973610 | d/dx(secx) | secxtanx | 10 | |
| 13755973611 | d/dx(cscx) | -cscxcotx | 11 | |
| 13755973612 | d/dx(lnu) | u'/u | 12 | |
| 13755973613 | d/dx(e^u) | e^u(u') | 13 | |
| 13755973614 | d/dx(a^u) | a^u(lna)(u') | 14 | |
| 13755973615 | Chain rule of f(x)^n | nf(x)f'(x) | 15 | |
| 13755973616 | Product rule of f(x)g(x) | f'(x)g(x)+g'(x)f(x) OR first(d last)+(last)(d First) | 16 | |
| 13755973617 | Quotient rule of f(x)/g(x) | g(x)f'(x)-f(x)g'(x)/g(x)² OR lo(d hi)-hi(d lo) all divided by (lo)^2 | 17 | |
| 13755973618 | Intermediate Value Theorem | if f(x) is continuous on [a,b], then there will be a point x=c that lies in between [a,b] | 18 | |
| 13755973619 | Extreme Value Theorem | if f(x) is continuous on [a,b], then f(x) has an absolute max or min on the interval | 19 | |
| 13755973620 | Rolle's Theorem | if f(x) is continuous on [a,b] and differentiable on (a,b), and if f(a)=f(b), then there is at least one point (x=c) on (a,b) [DON'T INCLUDE END POINTS] where f'(c)=0 | 20 | |
| 13755973621 | Mean Value Theorem | if f(x) is continuous on [a,b] and differentiable on (a,b), there is at least one point (x=c) where f'(c)= F(b)-F(a)/b-a | 21 | |
| 13755973622 | If f'(x)=0 | there is a max or min on f(x) [number line test] | 22 | |
| 13755973623 | If f'(x)>0 | f(x) is increasing | 23 | |
| 13755973624 | If f'(x)<0 | f(x) is decreasing | 24 | |
| 13755973625 | If f''(x)=0 | f(x) has a point of inflection & f'(x) has a max or min | 25 | |
| 13755973626 | If f''(x)>0 | f(x) is concave up & f'(x) is increasing | 26 | |
| 13755973627 | If f''(x)<0 | f(x) is concave down & f'(x) is decreasing | 27 | |
| 13755973628 | p(t), x(t), s(t) | means position function | 28 | |
| 13755973629 | p'(t) or x'(t) or s'(t) | v(t)= velocity | 29 | |
| 13755973630 | p''(t) or v'(t) | a(t)= acceleration | 30 | |
| 13755973631 | v(t)=0 | p(t) is at rest or changing direction | 31 | |
| 13755973632 | v(t)>0 | p(t) is moving right | 32 | |
| 13755973633 | v(t)<0 | p(t) is moving left | 33 | |
| 13755973634 | a(t)=0 | v(t) not changing | 34 | |
| 13755973635 | a(t)>0 | v(t) increasing | 35 | |
| 13755973636 | a(t)<0 | v(t) decreasing | 36 | |
| 13755973637 | v(t) and a(t) has same signs | speed of particle increasing | 37 | |
| 13755973638 | v(t) and a(t) has different signs | speed of particle decreasing | 38 | |
| 13755973639 | ∫(x^n)dx | x^(n+1)∕(n+1) +C | 39 | |
| 13755973640 | ∫(1/x)dx | ln|x|+C | 40 | |
| 13755973641 | ∫(e^kx)dx | ekx/k +C | 41 | |
| 13755973642 | ∫sinx dx | -cosx+C | 42 | |
| 13755973643 | ∫cosx dx | sinx+C | 43 | |
| 13755973644 | ∫sec²x dx | tanx+C | 44 | |
| 13755973645 | ∫csc²x dx | -cotx+C | 45 | |
| 13755973646 | ∫secxtanx dx | secx+C | 46 | |
| 13755973647 | ∫cscxcotx | -cscx+C | 47 | |
| 13755973648 | ∫k dx [k IS A CONSTANT] | kx+C | 48 | |
| 13755973649 | 1st fundamental theorem of calculus | (bounded by a to b) ∫f(x)dx= F(b)-F(a) | 49 | |
| 13755973650 | 2nd fundamental theorem | (bounded by 1 to x) d/dx[∫f(t)dt]= f(x)(x') | 50 | |
| 13755973651 | average value | (1/(b-a))[∫f(x)dx] [BOUNDED BY A TO B] | 51 | |
| 13755973652 | Area between curves | A=∫f(x)-g(x) dx = integral of top - bottom dx OR integral of right- left dy | 52 | |
| 13755973653 | Volume (DISK, no hole) | V=π∫f(x)²dx | 53 | |
| 13755973654 | Volume (WASHER, hole) | V=π∫f(x)²-g(x)²dx, where f(x)=farther equation from axis rotating & g(x)= closer equation from axis rotating | 54 | |
| 13755973655 | ∫f(x)dx [BOUNDS ARE SAME] | 0 | 55 | |
| 13755973656 | Displacement of particle | ∫v(t)dt | 56 | |
| 13755973657 | total distance of particle | ∫|v(t)|dt | 57 | |
| 13755973658 | position of particle at specific point | p(x)= initial condition + ∫v(t)dt (bounds are initial condition and p(x)) | 58 | |
| 13755973659 | derivative of exponential growth equation: P(t)=Pe^kt | dP/dt=kP | 59 | |
| 13755973660 | Cross section for volume: square [A=s²] | v=∫[f(x)-g(x)]²dx | 60 | |
| 13755973661 | Cross section for volume: isosceles triangle [A=1/2s²] | v= 1/2∫[f(x)-g(x)]²dx | 61 | |
| 13755973662 | Cross section for volume: equilateral triangle [A=√3/4s²] | v= √3/4∫[f(x)-g(x)]²dx | 62 | |
| 13755973663 | Cross section for volume: semicircle [A=1/2πs²] | v= 1/2π∫[f(x)-g(x)]²dx | 63 | |
| 13755973664 | d/dx(sin⁻¹u) | u'/√(1-u²) | 64 | |
| 13755973666 | d/dx(tan⁻¹u) | u'/(1+u²) | 65 | |
| 13755973670 | ∫du/√(a²-u²) | (sin⁻¹u/a)+C | 66 | |
| 13755973671 | ∫du/(a²+u²) | (1/a)(tan⁻¹u/a)+C | 67 |
Flashcards
Flashcards
AP World Period 3 Flashcards
| 14035054660 | Trans -Saharan Trade | Trade of goods through the Sahara dessert Goods: Salt, gold, animal hides, slaves Important points: Timbuktu, Goa,Djenne |  | 0 |
| 14035054661 | Islam | Monotheistic religion created in the 7th century by Arabic merchant, Muhammed |  | 1 |
| 14035054662 | Caliphate | A regional state unified by Islam |  | 2 |
| 14035054663 | Crusades | A series of Christian vs Muslim military campaigns for the "holy land" |  | 3 |
| 14035054664 | Dar-al-Islam | territory of Islam |  | 4 |
| 14035054665 | Byzantine Empire | Eastern Roman empire extending to the Eastern Mediterranean and Southwest Asia |  | 5 |
| 14035054666 | Sinification | Chinese-ification of Japan, Korea, and Southeast Asia |  | 6 |
| 14035054667 | Mongols | nomadic invaders that conquered Eurasia with force and diplomacy |  | 7 |
| 14035054668 | Black Death | Plague that killed 1/3 of European population |  | 8 |
| 14035054669 | Maya | MesoAmerican civilization that had pyramids, large cities, a written system, and complex society |  | 9 |
| 14035054670 | Coerced labor | slavery, serfdom, corvee (government-recquired labor on public works projects), and indentured servitude |  | 10 |
| 14035054671 | Feudalism | Agricultural workers serving landowners or lords (knights and samurai) |  | 11 |
| 14035054672 | Zheng He | Ming explorer that crossed the Indian Ocean |  | 12 |
| 14035054673 | Silk | highly-priced luxury commodity mainly exported from China |  | 13 |
| 14035054674 | Chinese Inventions | gunpowder, compass, paper, astrolabe |  | 14 |
| 14035054675 | Tang Dynasty | (618-907 CE) The Chinese dynasty that was much like the Han, who used Confucianism. This dynasty had the equal-field system, a bureaucracy based on merit, and a Confucian education system. | 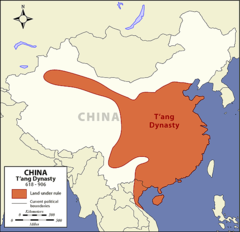 | 15 |
| 14035054676 | Song Dynasty | (960 - 1279 AD); started by Tai Zu; by 1000, a million people were living there; started feet binding; had a magnetic compass, navy, traded with india and persia (brought pepper and cotton), first to have paper money, explosive gun powder |  | 16 |
| 14035054677 | Central Asia | A region that includes the republics of Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan |  | 17 |
| 14035054678 | Indian Ocean trade | trade between Arab, Persian, Turkish, Indian, African, Chinese, and Europe merchants |  | 18 |
| 14035054679 | Ming Dynasty | Succeeded Mongol Yuan dynasty in China in 1368; lasted until 1644; initially mounted huge trade expeditions to southern Asia and elsewhere, but later concentrated efforts on internal development within China. |  | 19 |
| 14035054680 | Grand Canal | an inland waterway 1000 miles long in eastern China |  | 20 |
| 14035054681 | Pax Mongolica | Mongol peace from mid-1200's through mid-1300's imposed stability and law and order across Eurasia. Guaranteed safe passage for trade caravans, travelers, and missionaries from one end of empire to other. |  | 21 |
| 14035054682 | Vikings | A nomadic group that conquered ex: Normans |  | 22 |
| 14035054683 | Syncretism | A blending of two or more religious traditions |  | 23 |
| 14035054684 | Marco Polo | Italian explorer and author who made numerous trips to China and returned to Europe to write of his journeys, responsible for much of the knowledge exchanged between Europe and China during this time period. |  | 24 |
| 14035054685 | Ibn Battuta | (1304-1369) Morrocan Muslim scholar, the most widely traveled individual of his time. He wrote a detailed account of his visits to Islamic lands from China to Spain and the western Sudan. His writings gave a glimpse into the world of that time period. |  | 25 |
| 14035054686 | Mansa Musa | Emperor of the kingdom of Mali in Africa. He made a famous pilgrimage to Mecca and established trade routes to the Middle East. |  | 26 |
| 14035054687 | The Renaissance | (1350-1600) bagan in Italy. Rebirth of learning, science, art, music, literature, and culture. Rediscovery of Ancient Greece and Rome |  | 27 |
| 14035054688 | Secular | Non-religious |  | 28 |
| 14035054689 | Missionary | A person who spreads his or her religious beliefs to others |  | 29 |
| 14035054690 | Charlemagne | 768-843; reunited western Europe for the first time since the Roman Empire. |  | 30 |
| 14035054691 | Justinian | 6th century Byzantine emperor; failed to reconquer the western portions of the empire; rebuilt Constatinople; codified Roman law |  | 31 |
| 14035054692 | hajj | A pilgrimage to Mecca, performed as a duty by Muslims |  | 32 |
| 14035054693 | Zakat | part of 4th Pillar, charitable giving of 2.5% of your net worth to community treasury |  | 33 |
| 14035054694 | jihad | A holy struggle or striving by a Muslim for a moral or spiritual or political goal |  | 34 |
| 14035054695 | Umayyad Caliphate | First hereditary dynasty of Muslim caliphs (661 to 750). From their capital at Damascus, the Umayyads ruled one of the largest empires in history that extended from Spain to India. Overthrown by the Abbasid Caliphate. |  | 35 |
| 14035054696 | Abbasid Caliphate | (750-1258 CE) The caliphate, after the Umayyads, who focused more on administration than conquering. Had a bureaucracy that any Mulim could be a part of |  | 36 |
| 14035054697 | Baghdad | Abbasid capital |  | 37 |
| 14035054698 | Sudanic States | Songhay Ghana and Mali. often led by patriarch or council of elders from a family or lineage |  | 38 |
| 14035054699 | Chinampas | Aztec floating gardens |  | 39 |
| 14035054700 | Champa Rice | a quick-maturing, drought resistant rice that can allow two harvests, of sixty days each in one growing season. | 40 | |
| 14035054701 | Hijrah | Muhammad's migration from Mecca to (Yathrib) Medina | 41 | |
| 14035054702 | Khanates | Four regional Mongol kingdoms that arose following the death of Chinggis Khan. | 42 | |
| 14035054703 | Ghengis Khan | Mongol leader who led their conquest westward and who is renowned for his ability and his ruthlessness. | 43 | |
| 14035054704 | Kublai Khan | (1215-1294) Grandson of Genghis Khan and founder of the Mongol Yuan Dynasty in China. | 44 | |
| 14035054705 | Post Classical Period | 600 CE - 1450 CE | 45 | |
| 14035054706 | Golden Horde | a Mongolian army that swept over eastern Europe in the 13th century | 46 | |
| 14035054707 | Caesaropapism | the dual role of the state and leader of the church in which a state ruler extends his own powers to be the leader in theological and ecclesiastical matters | 47 |
Pages
Need Help?
We hope your visit has been a productive one. If you're having any problems, or would like to give some feedback, we'd love to hear from you.
For general help, questions, and suggestions, try our dedicated support forums.
If you need to contact the Course-Notes.Org web experience team, please use our contact form.
Need Notes?
While we strive to provide the most comprehensive notes for as many high school textbooks as possible, there are certainly going to be some that we miss. Drop us a note and let us know which textbooks you need. Be sure to include which edition of the textbook you are using! If we see enough demand, we'll do whatever we can to get those notes up on the site for you!

